Recent advances in ultra-precision machining of lithium niobate crystals
-
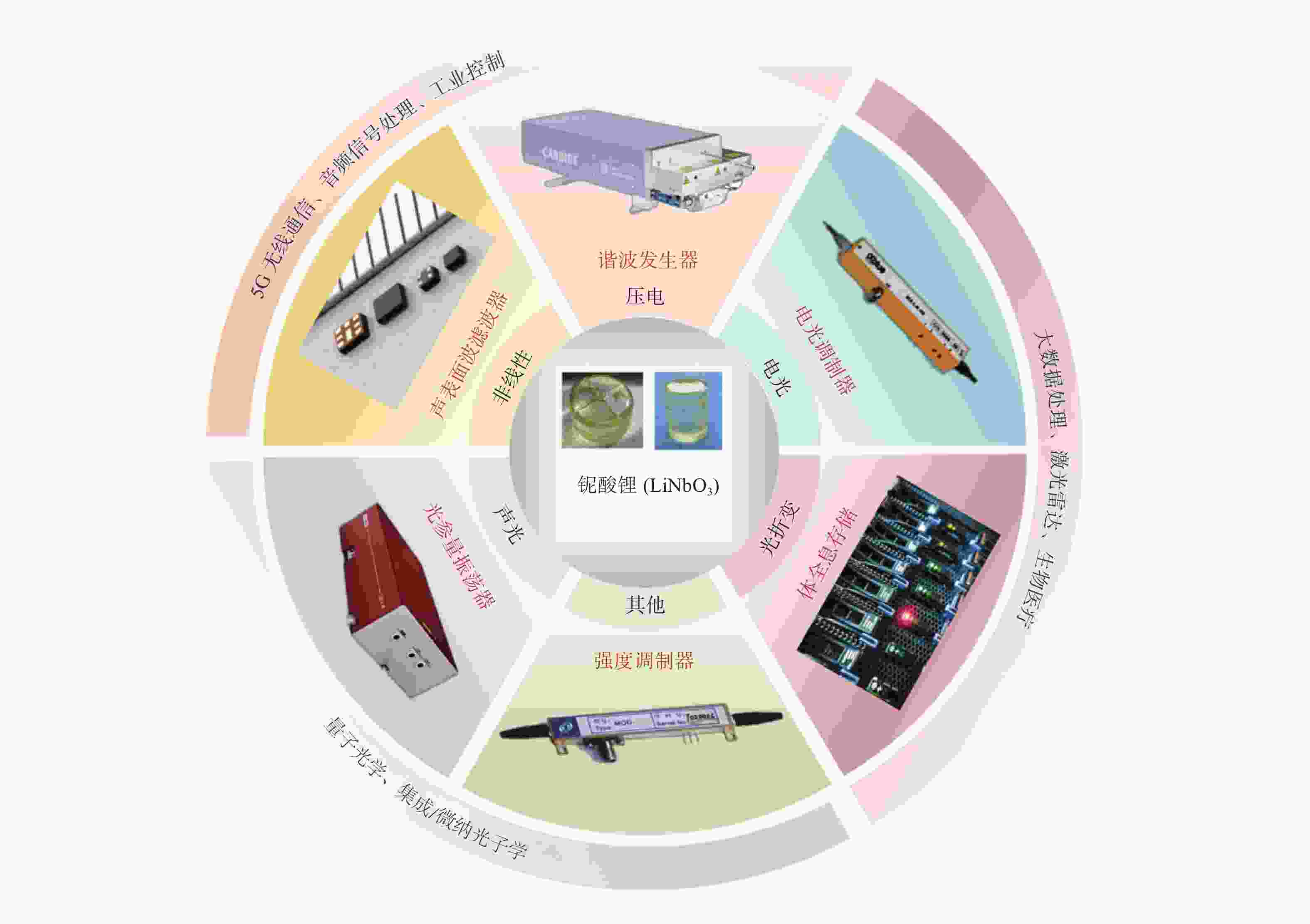
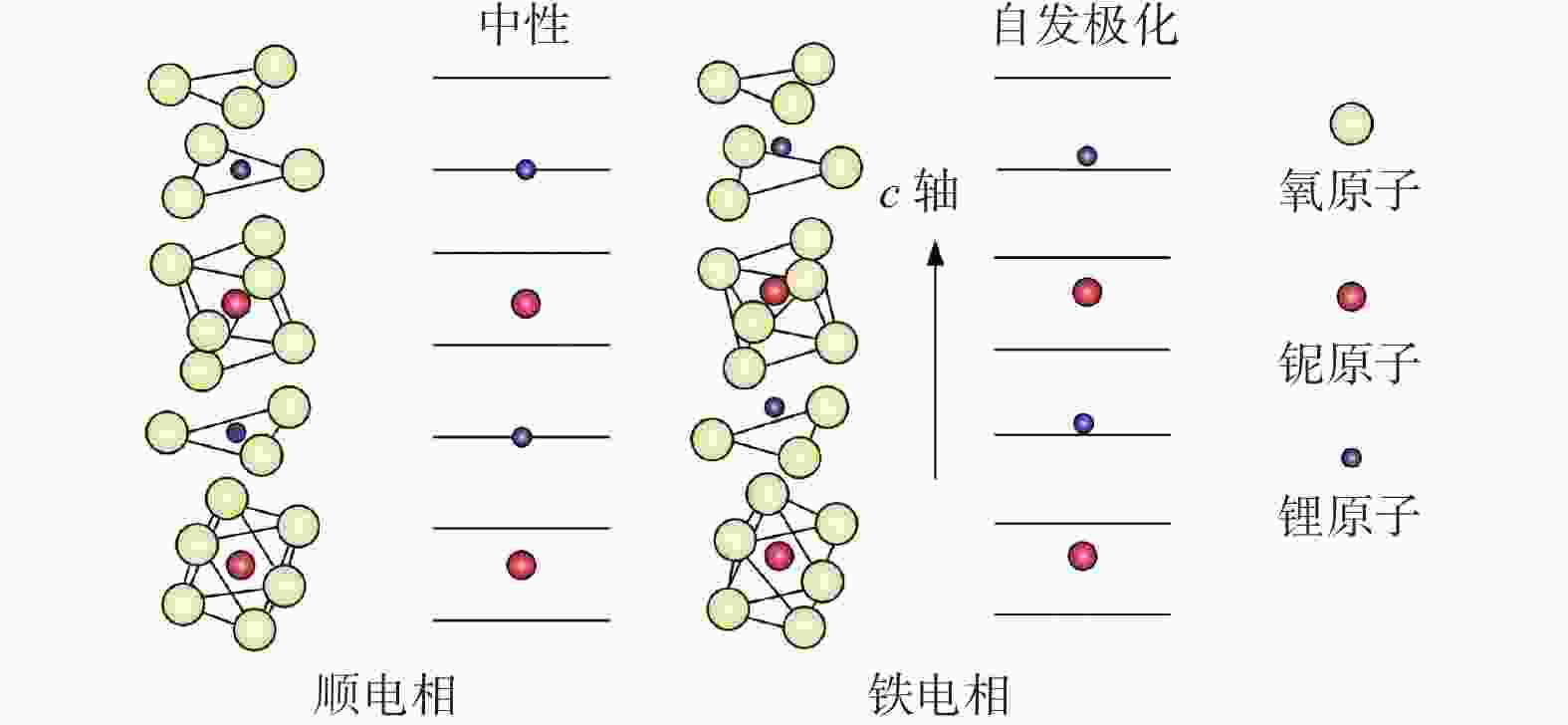
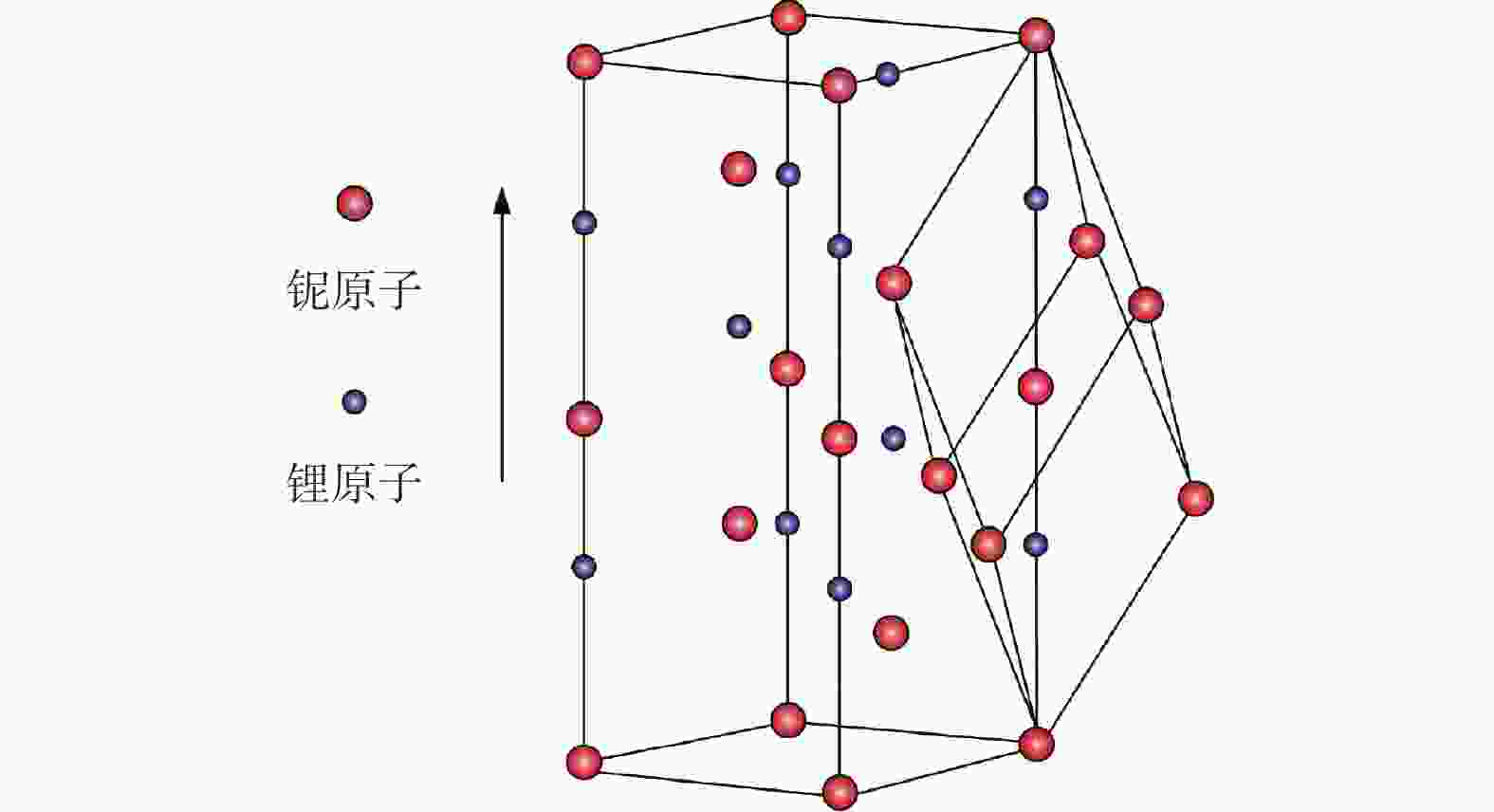
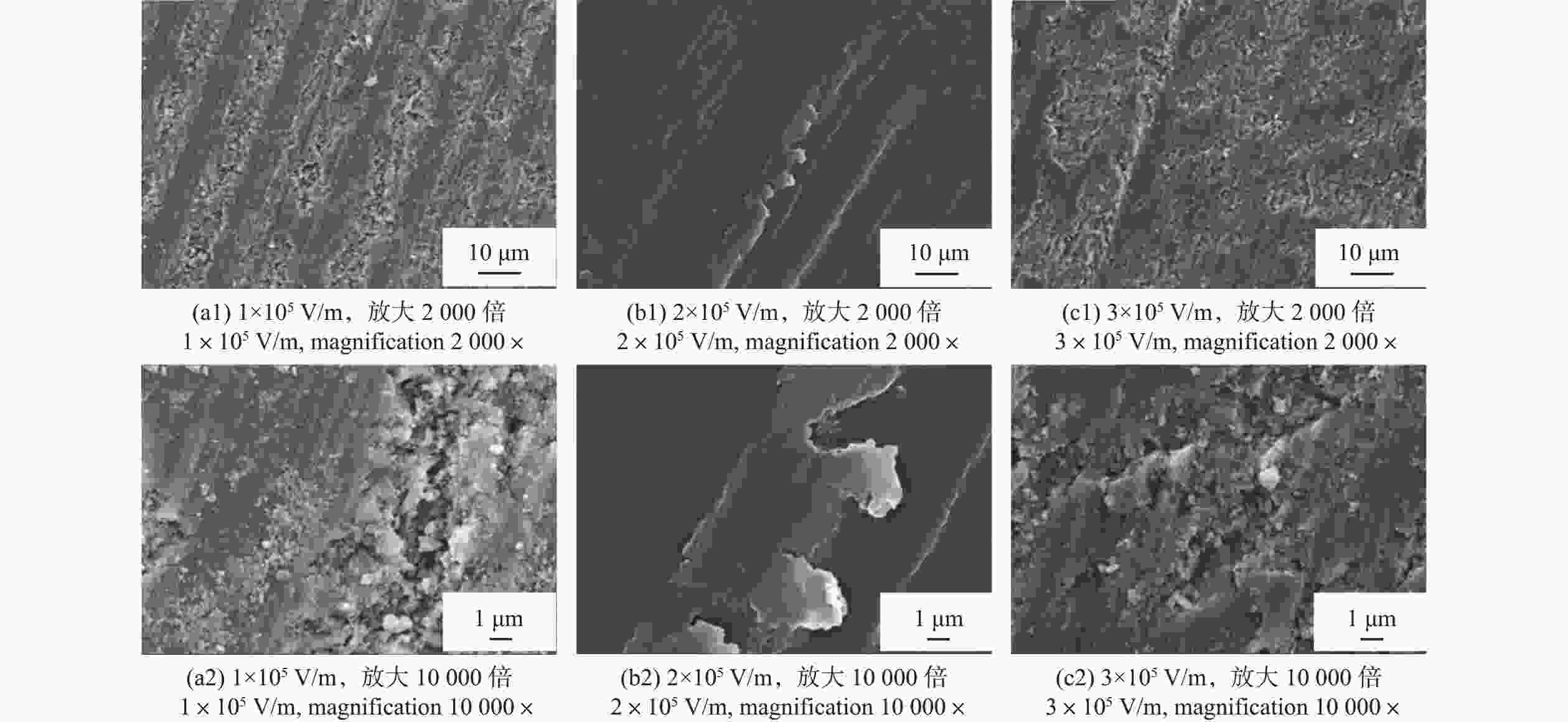
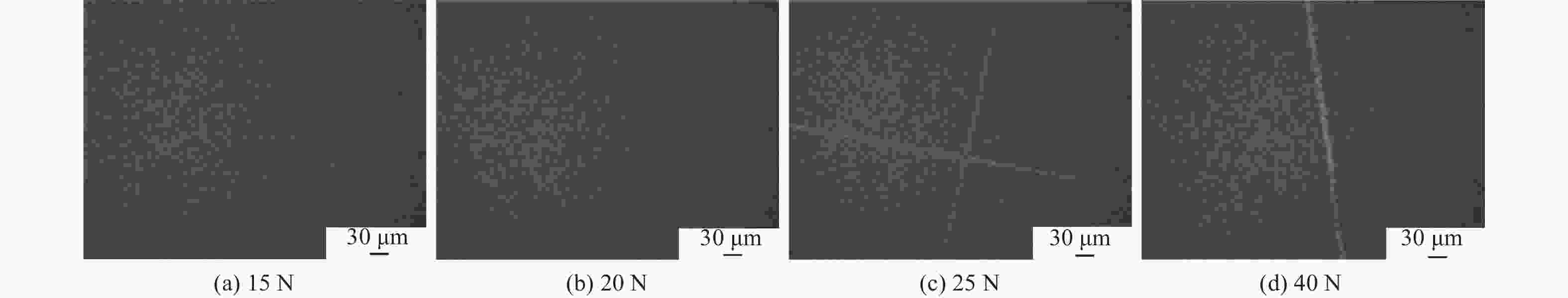
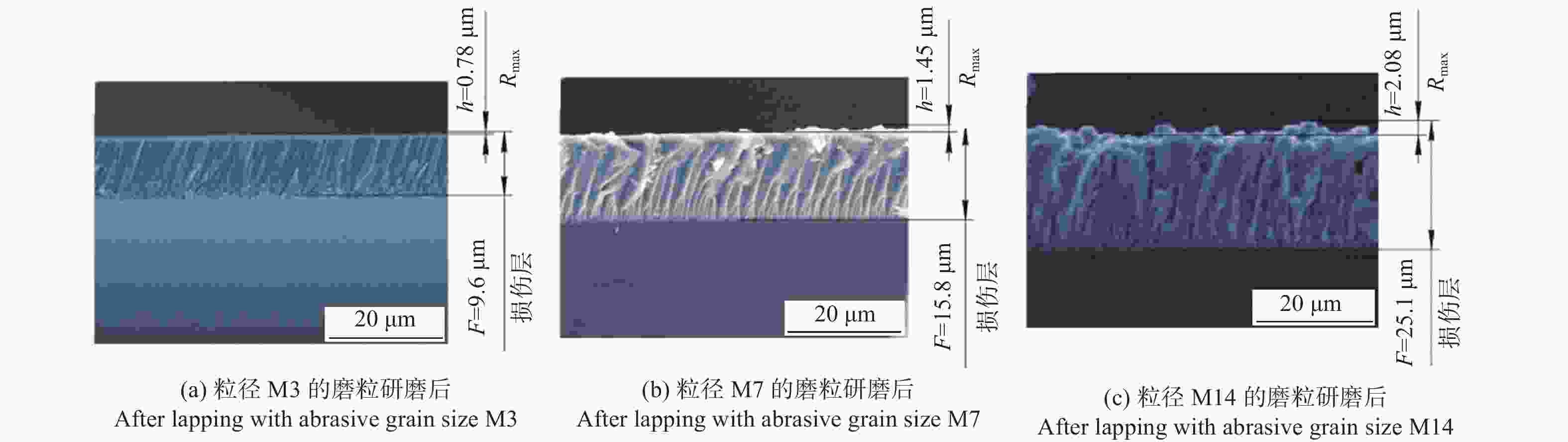
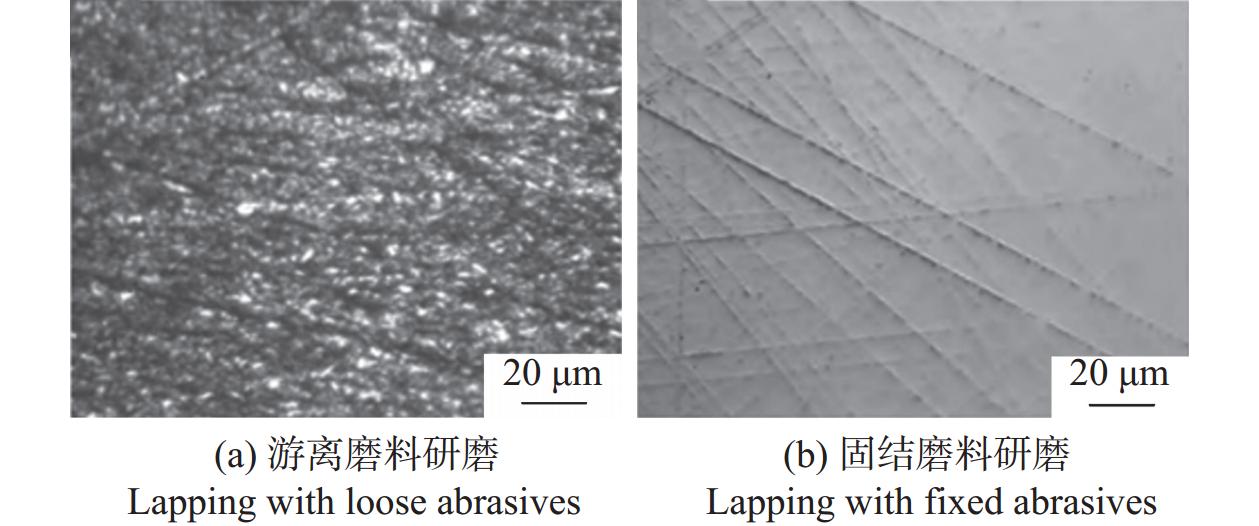
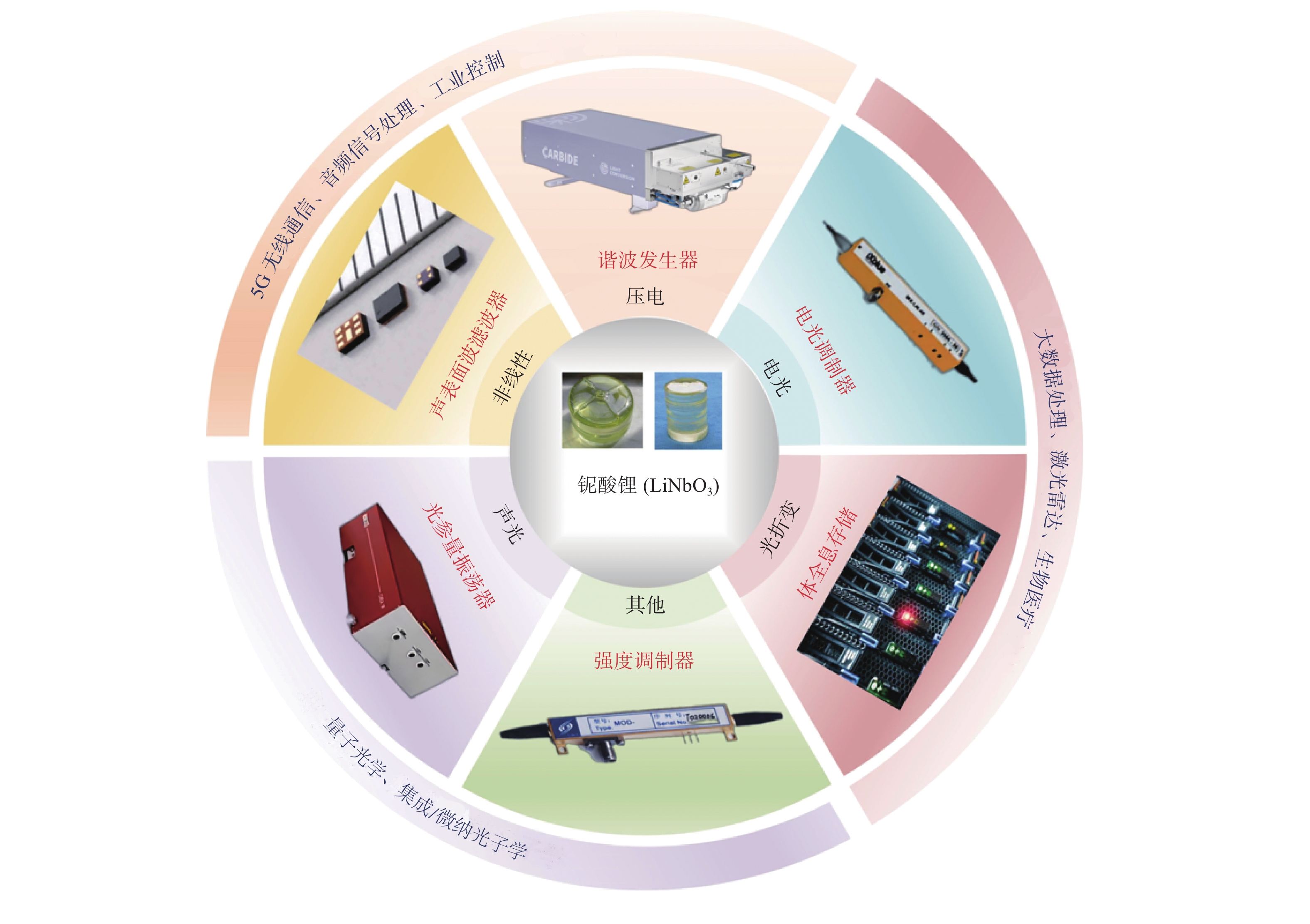
摘要: 铌酸锂(LiNbO3)晶体光电特性优异,是制造光学调制器、频率倍增器、滤波器等光电子器件的首选材料,在5G无线通信、微纳/集成光子学和人工智能等前沿领域具有巨大应用价值。然而,铌酸锂晶体硬度低、脆性大、各向异性强,大尺寸高品质晶体的制备方法及其高效高质低/无损伤的超精密加工技术是实现铌酸锂晶体器件广泛应用的重要瓶颈。本文主要介绍超精密加工铌酸锂晶体过程中表面/亚表面损伤的产生机理与演变规律,以及减薄、研磨、抛光、超构表面制备等方面的研究进展。分析铌酸锂加工过程中易出现划痕、裂纹和磨料嵌入的原因,以及目前常用铌酸锂晶体超精密加工方法的特点及局限性,提出未来实现大尺寸铌酸锂高效率高表面质量加工的新技术。研究表明:离子切片和磨削能有效实现铌酸锂晶体减薄,研磨和化学机械抛光是常用的铌酸锂晶体表面超精密加工技术,刻蚀、激光烧蚀、聚焦离子束等技术是制备高质量铌酸锂超构表面的微纳加工技术。同时,高剪低压磨削、磁性剪切增稠抛光等新技术在实现铌酸锂晶体表面高效高质加工方面具有极大潜力,但铌酸锂晶体材料去除机理、弹-塑-脆加工临界条件和表面质量控制等问题还亟待系统研究。Abstract: Significance: The fabrication of high-performance optoelectronic devices requires substrate materials with exceptional optoelectronic properties, robust mechanical stability, and broad application versatility. These substrates are crucial for advancing the information technology sector and driving economic growth. Lithium niobate (LiNbO3) crystal has the advantages in piezoelectric, electro-optic, nonlinear optical, and photorefractive effects, and exhibits superior thermal stability, chemical resilience, and tenability, making it an ideal substrate for the development of optoelectronic components such as optical modulators, frequency doublers, and optical filters. The LiNbO3 crystal is quite promising for application in cutting-edge technologies, such as 5G communication systems, micro/nano-integrated photonics, and artificial intelligence. Achieving an ultra-smooth, low/no-damage crystal surface is paramount for LiNbO3-based optoelectronic devices. Any imperfections, such as scratches, cracks, or embedded abrasives, can lead to scattering, absorption, or diffraction of optical signals, adversely affecting device performance. However, the challenges posed by LiNbO3’s intrinsic properties—namely, its relatively low hardness, high brittleness, and significant anisotropy—complicate the precise surface processing. High-efficiency, high-quality, and low/no-damage ultra-precision machining technology for large-sized high-quality crystals is a critical bottleneck in enabling the widespread application of LiNbO3 crystal devices. Progress: Thinning, lapping, and polishing are essential for LiNbO3 crystals to meet industrial application requirements for high-performance optoelectronic devices. The stability and reliability of optoelectronic devices are significantly influenced by the generation and evolution of surface and subsurface damages. The hardness, fracture toughness, Young's modulus, and other material properties of LiNbO3 along different crystallographic orientations are investigated using methods such as nanoindentation and scratch tests. The surface damage patterns of various planes are analyzed. The material removal behaviors under different parameters are revealed. Ion slicing and grinding are two critical processes for thinning LiNbO3 crystals. Ion slicing, which relies on ion implantation and wafer bonding, enables the precise thinning of crystals. Currently, it is possible to produce high-quality LiNbO3 films with thicknesses varying from several hundred nanometers to a few micrometers. Grinding utilizes the mechanical behavior of abrasives to rapidly remove material from the LiNbO3 crystal. A crystal substrate with a thickness of 80 μm is prepared effectively by optimizing the grinding parameters. Free-abrasive lapping has a wide range of applicability. However, lapping for LiNbO3can easily lead to surface damage and abrasive embedding. During fixed abrasive lapping, abrasive embedding is effectively prevented, and surface and subsurface damage are reduced. It also exhibits notable advantages for continuous batch grinding. Chemical mechanical polishing is a widely adopted final polishing method that effectively reduces damage from previous processes, achieving a surface roughness (Ra) of less than 1 nm. With advancements in grinding and chemical mechanical polishing, techniques such as photolithography, etching, and femtosecond laser ablation have been employed to fabricate LiNbO3 crystal metasurfaces, facilitating the development and application of multifunctional and ultra-compact integrated optoelectronic devices. Additionally, innovative methods, such as optimizing polishing slurry compositions with nanomaterial additives and adaptive shearing-gradient thickening polishing, have enabled ultra-precision processing, achieving ultra-smooth and low/no-damage results. High-shear and low-pressure grinding and magnetorheological shear thickening polishing under the coupling of magnetic, stress, and flow fields hold significant promise for the ultra-precision polishing of LiNbO3 crystals. Conclusions and Prospects: As critical functional materials in advanced applications, such as 5G wireless communication, integrated/micro-nanophotonics, and big-data processing, LiNbO3 crystals have garnered significant attention for their potential in ultra-precision machining technologies. Research shows that the development and evolution of surface/subsurface damage have been examined using methods such as nano-indentation and scratch testing. Ion slicing and grinding are effective techniques for thinning lithium niobate crystals. Lapping and chemical mechanical polishing are commonly used techniques to achieve ultra-precision machining. Furthermore, high-quality LiNbO3 metasurfaces can be generated using micro-nano manufacturing methods such as femtosecond laser ablation, etching, and photolithography. New technologies, such as high-shear and low-pressure grinding and magnetorheological shear thickening polishing, are the most promising methods for achieving ultra-precision machining of LiNbO3 crystals. Considering the complex interplay between material properties, processing parameters, and underlying mechanisms, the ongoing exploration of new ultra-precision machining techniques and process optimizations for LiNbO3 crystals is critical. Such advancements are essential for enhancing machining efficiency, improving surface quality, and minimizing damage. However, future work, including the material removal mechanism of LiNbO3 crystals, the critical machining conditions of elastic-plastic-brittle transition, and surface/subsurface quality control, needs to be systematically studied to provide theoretical and technical guidance for the ultra-precision machining of LiNbO3 crystals. Given the fundamental challenges and technological implications, the ultra-precision machining of LiNbO3 crystals is expected to remain a focal point of research for the foreseeable future, warranting continued investigation and development in this field.
-
表 1 铌酸锂晶体的基本物理化学参数(20 ℃)[11]
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of lithium niobate crystals (20 °C) [11]
基本性质 实验数值 晶体密度 ρ / (g·cm−3) 4.612 莫氏硬度 Hm 5 熔点 Tm / ℃ 1260 居里温度 Tc / ℃ 1210 菱形晶胞参数 al / Å 5.4920 菱形晶胞参数 α1 55°53′ 六角晶胞参数 a2 / Å 5.14829 ±0.00002 六角晶胞参数 c2 / Å 13.86310 ±0.00004 菱形晶胞分子数 Nl 2 六角晶胞分子数 N2 6 a轴热膨胀系数 λa / ℃-1 16.7 × 10−6 c轴热膨胀系数 λc / ℃-1 2.0 × 10−6 介电常数 εs11=44, εt11=84, εs33=29, εt33=30 折射率 n ( 632.8 nm)no=2.286, ne=2.202 25 ℃水溶解度 S / (mol·L−1) 2.8 × 10−4 分解热 ΔH / ( J·mol−1) 25941.42 表 2 铌酸锂晶体的系列化学机械抛光实验
Table 2. A series of chemical mechanical polishing experiments on lithium niobate crystals
序号 磨料 粒径
d / nmpH 载荷
F / kPa转速
v / (r·min−1)流量
q / (mL·min−1)时间
t / min效果 1[46] SiO2 25 9.5 6.5 100 200 — 无划痕和缺陷 2[47] SiO2 20~40 9.5~10 — 15 10 360 Ra 0.387 nm
面型误差<4 μm3[48] SiO2 50 9.5~10 170 40 3 60 Ra 0.32 nm,表面平整光滑 4[49] SiO2 — 11.26 140 60 120 — Ra 0.21 nm 5[50] SiO2 — — 140 60 120 — 300 nm/min
Ra 0.21 nm6[51] SiO2 50 9.5~10 17 40 3 60 Ra 0.20 nm 7[52] — — 10.8 90 50 — 180 Ra 1.0 nm 8[53] SiO2 20 11 140 60 180 — 350 nm/min 9[54] SiO2 40 9.0~11.5 60 60 50 5 Ra 0.38 nm 10[55] — — 10 160 60 3000 — Ra 0.196 nm -
[1] YAN C L, ZHAO S, WANG S Q, et al. Proton exchange thin film lithium niobate semi-nonlinear waveguides for highly efficient tunable second harmonic generation [J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2024,170:110274. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2023.110274 [2] MANDAL S, ARTS K, MORGAN D J, et al. Zeta potential and nanodiamond self assembly assisted diamond growth on lithium niobate and lithium tantalate single crystal [J]. Carbon,2023,212:118160. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118160 [3] ZHANG L Y, GENG W P, CHEN X, et al. Enhancing the thermal stability of switched domains in lithium niobate single-crystal thin films [J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(7):9192-9197. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.171 [4] 黄水泉, 高尚, 黄传真, 等. 脆性材料磨粒加工的纳米尺度去除机理 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2022,42(3):257-267, 384. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.3009HUANG Shuiquan, GAO Shang, HUANG Chuanzhen, et al. Nanoscale removal mechanisms in abrasive machining of brittle solids [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2022,42(3):257-267, 384. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.3009 [5] 高尚, 李洪钢, 康仁科, 等. 新一代半导体材料氧化镓单晶的制备方法及其超精密加工技术研究进展 [J]. 机械工程学报,2021,57(9):213-232. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.09.213GAO Shang, LI Honggang, KANG Renke, et al. Recent advance in preparation and ultra-precision machining of new generation semiconductor material of β-Ga2O3 single crystals [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,57(9):213-232. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.09.213 [6] LIN S P, XIONG C W, MA D C, et al. Persistent luminescence found in Mg2 + and Pr3 + Co-doped LiNbO3 single crystal [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2018,6(37):10067-10072. doi: 10.1039/C8TC03783C [7] VOSKRESENSKII V M, STARODUB O R, SIDOROV N V, et al. Investigation of the cluster formation in lithium niobate crystals by computer modeling method [J]. Crystallography Reports,2017,62(2):205-209. doi: 10.1134/S1063774517020316 [8] KONG Y F, BO F, WANG W W, et al. Recent progress in lithium niobate: Optical damage, defect simulation, and on‐chip devices [J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(3):e1806452. doi: 10.1002/adma.201806452 [9] SCHMIDT F, KOZUB A L, BIKTAGIROV T, et al. Free and defect-bound (bi) polarons in LiNbO3: Atomic structure and spectroscopic signatures from ab initio calculations [J]. Physical Review Research,2020,2(4):043002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.2.043002 [10] SÁNCHEZ-DENA O, FIERRO-RUIZ C D, VILLALOBOS-MENDOZA S D, et al. Lithium niobate single crystals and powders reviewed: Part I [J]. Crystals,2020,10(11):973. doi: 10.3390/cryst10110973 [11] PROKHOROV A M, KUZʹMINOV I, PYANKOVA T M, et al. Physics and chemistry of crystalline lithium niobate [M]. Bristol: IOP Publishing Ltd., Adam Hilger, 1990. [12] BHAGAVAT S, KAO I. Nanoindentation of lithium niobate: Hardness anisotropy and pop-in phenomenon [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2005,393(1/2):327-331. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.11.027 [13] ZHANG Z Y, YANG S, XU C G, et al. Deformation and stress at pop-in of lithium niobate induced by nanoindentation [J]. Scripta Materialia,2014,77:56-59. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.01.018 [14] WANG H C, ZHANG Y, XIANG D, et al. Growth and mechanical properties of near-stoichiometric LiNbO3 crystal [J]. Optik,2018,164:385-389. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.03.011 [15] GRUBER M, LEITNER A, KIENER D, et al. Incipient plasticity and surface damage in LiTaO3 and LiNbO3 single crystals [J]. Materials & Design,2018,153(5):221-231. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.04.082 [16] GRUBER M, LEITNER A, KIENER D, et al. Effect of crystal orientation on the hardness and strength of piezoelectric LiNbO3 substrates for microelectronic applications [J]. Materials & Design,2022,213:110306. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110306 [17] ZHENG H, WEN D H, KONG F Z, et al. Research on critical load of lithium niobate crystal lapping [J]. Processes,2022,10(5):912. doi: 10.3390/pr10050912 [18] ZHU N N, CHEN J P, ZHOU P, et al. Effect of the anisotropy mechanical properties on LN crystals fixed-abrasive lapping [J]. Materials,2020,13(19):4455. doi: 10.3390/ma13194455 [19] SOSUNOV A V, VOLYNTSEV A B, TSIBERKIN K B, et al. Features of structure and mechanical properties LiNbO3 [J]. Ferroelectrics,2017,506(1):24-31. doi: 10.1080/00150193.2017.1281686 [20] SCHMIDT E, STEINBACH T, WESCH W. Ion-beam-induced thin film stress in lithium niobate [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,2014,47(26):265302. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/47/26/265302 [21] ZVEREV G M, LEVCHUK E A, PASHKOV V A, et al. Laser-radiation-induced damage to the surface of lithium niobate and tantalate single crystals [J]. Soviet Journal of Quantum Electronics,1972,2(2):167-169. doi: 10.1070/QE1972v002n02ABEH004409 [22] CHONG H W, MITCHELL A, HAYES J P, et al. Investigation of KrF excimer laser ablation and induced surface damage on lithium niobate [J]. Applied Surface Science,2002,201(1/2/3/4):196-203. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(02)00904-2 [23] LIU P, ZHANG Y, XUE H, et al. A coupled effect of nuclear and electronic energy loss on ion irradiation damage in lithium niobate [J]. Acta Materialia,2016,105:429-437. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.12.048 [24] HAN X Q, LIU C, ZHANG M, et al. Thermal spike responses and structure evolutions in lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) under swift ion irradiation [J]. Crystals,2022,12(7):943. doi: 10.3390/cryst12070943 [25] HUO D H, CHOONG Z J, SHI Y L, et al. Diamond micro-milling of lithium niobate for sensing applications [J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering,2016,26(9):095005. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/26/9/095005 [26] SHIZUKA H, OKUDA K, NUNOBIKI M, et al. A study on the ductile mode cutting of lithium niobate [J]. Advanced Materials Research,2010(126/127/128):246-251. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.126-128.246 [27] JIA Y C, WANG L, CHEN F. Ion-cut lithium niobate on insulator technology: Recent advances and perspectives [J]. Applied Physics Reviews,2021,8(1):011307. doi: 10.1063/5.0037771 [28] POBERAJ G, HU H, SOHLER W, et al. Lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) for micro‐photonic devices [J]. Laser &Photonics Reviews,2012,6(4):488-503. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201100035 [29] LI Q Y, ZHANG H H, ZHU H B, et al. Characterizations of single-crystal lithium niobate thin films [J]. Crystals,2022,12(5):667. doi: 10.3390/cryst12050667 [30] WU C C, HORNG R H, WUU D S, et al. Thinning technology for lithium niobate wafer by surface activated bonding and chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics,2006,45(4):3822-3827. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.45.3822 [31] XUE G, GENG W P, FU W X, et al. Integrated fabrication and ferroelectric domain adjustment of lithium niobate single crystal films based on silicon substrate [J]. Materials & Design,2022,215:110447. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110447 [32] BAI X Y, SHUAI Y, GONG C G, et al. Surface modifications of crystal-ion-sliced LiNbO3 thin films by low energy ion irradiations [J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,434:669-673. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.184 [33] GENG W P, YANG X Y, XUE G, et al. Integration technology for wafer-level LiNbO3 single-crystal thin film on silicon by polyimide adhesive bonding and chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Nanomaterials,2021,11(10):2554. doi: 10.3390/nano11102554 [34] 胡天明, 孔凡志, 贡燕, 等. 软脆铌酸锂晶体磨削的实验仿真研究 [J]. 机电工程,2016,33(9):1071-1075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2016.09.007HU Tianming, KONG Fanzhi, GONG Yan, et al. Simulation and experimental of grinding soft-brittle lithium niobate crystals [J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Magazine,2016,33(9):1071-1075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2016.09.007 [35] 贡燕. 外场对铌酸锂磨削加工的作用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2017.GONG Yan. The effects of multiphysics fields on grindingprocess of soft-brittle lithium niobate crystals [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2017. [36] 贡燕, 胡天明, 张丽慧, 等. 温度对铌酸锂晶片磨削减薄的影响 [J]. 表面技术,2017,46(7):233-239. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2017.07.038GONG Yan, HU Tianming, ZHANG Lihui, et al. Effects of temperature on grinding and thinning of soft-brittle lithium niobate crystals [J]. Surface Technology,2017,46(7):233-239. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2017.07.038 [37] 王晓娟. 外场作用下铌酸锂晶体Y-Cut表面的多晶化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2019.WANG Xiaojuan. Study on the polycrystallization of Y-Cut surface of lithium niobate crystal under external field [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019. [38] 李清连, 孙军, 吴婧, 等. 铌酸锂晶体的研磨损伤层研究 [J]. 人工晶体学报,2019,48(5):883-888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.05.019LI Qinglian, SUN Jun, WU Jing, et al. Damage layer of lithium niobate crystals after grinding [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2019,48(5):883-888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.05.019 [39] MURATOV K R, ABLYAZ T R, GASHEV E A, et al. Study of lapping and polishing performance on lithium niobate single crystals [J]. Materials,2021,14(17):4968. doi: 10.3390/ma14174968 [40] 朱楠楠, 朱永伟, 李军, 等. 铌酸锂晶体的研磨亚表面损伤深度 [J]. 光学精密工程,2015,23(12):3387-3394. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152312.3387ZHU Nannan, ZHU Yongwei, LI Jun, et al. Subsurface damage depth of lithium niobate crystal in lapping [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering,2015,23(12):3387-3394. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152312.3387 [41] ZHU N N, WANG H J, HU D C, et al. Research of subsurface damage depth of lithium niobate crystal by fixed-abrasive lapping [J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics,2020,209(1):181-187. doi: 10.1080/10584587.2020.1728828 [42] ZHU N N, ZHENG F Z, ZHU Y W, et al. Research of abrasive embedment-free lapping on soft-brittle lithium niobate wafer [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2016,87(5):1951-1956. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-8582-8 [43] ZHU N N, ZHAO S L, ZHANG S B, et al. Machining stability research of soft-brittle crystals lapping by fixed-abrasive pad [J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics,2022,229(1):45-53. doi: 10.1080/10584587.2022.2074222 [44] 李攀, 白满社, 邢云云, 等. LiNbO3芯片的无损边缘抛光实验 [J]. 应用光学,2014,35(6):1069-1074. doi: 10.5768/JAO201435.0605004LI Pan, BAI Manshe, XING Yunyun, et al. Experiment on defect-free edge polishing of LiNbO3 chips [J]. Journal of Applied Optics,2014,35(6):1069-1074. doi: 10.5768/JAO201435.0605004 [45] 徐嘉慧, 康仁科, 董志刚, 等. 硅片化学机械抛光技术的研究进展 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(4):24-33. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.4.0004XU Jiahui, KANG Renke, DONG Zhigang, et al. Review on chemical mechanical polishing of silicon wafers [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(4):24-33. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.4.0004 [46] 邢彤, 袁巨龙, 赵文宏, 等. 铌酸锂晶片的化学机械抛光质量研究 [J]. 机械工程师,2003(7):19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2333.2003.01.007XING Tong, YUAN Julong, ZHAO Wenhong, et al. Study on the chemo-mechanical polishing quality of LiNbO3 cubic flake [J]. Mechanical Engineer,2003(7):19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2333.2003.01.007 [47] 王占银, 孔勇发, 陈绍林, 等. 大直径铌酸锂晶片的化学机械抛光研究 [J]. 人工晶体学报,2006,35(1):99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2006.01.022WANG Zhanyin, KONG Yongfa, CHEN Shaolin, et al. Study on the chemical mechanical polishing of large diameter lithium niobate wafer [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2006,35(1):99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2006.01.022 [48] 吕凯. 铌酸锂晶体的抛光机理及工艺方法研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2007.LÜ Kai. Study on polishing mechanismm & technology method of lithium niobate crystal [D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2007. [49] 武晓玲, 刘玉岭, 王胜利, 等. pH值对铌酸锂晶片抛光速率及抛光表面的影响 [J]. 半导体技术,2007(1):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-353X.2007.01.009WU Xiaoling, LIU Yuling, WANG Shengli, et al. Effect of pH on the polishing velocity and glazed surface of LN wafer [J]. Semiconductor Technology,2007(1):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-353X.2007.01.009 [50] WANG S L, LIU Y L, LI Z X. Study on chemical mechanical polishing process of lithium niobate[C]//3rd International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies. Chengdu, China. SPIE, 2007, 6722: 801-804. [51] 刘立新, 张学建, 张莹, 等. 铌酸锂晶体的抛光机理及精密加工工艺 [J]. 硅酸盐学报,2008,36(11):1609-1614. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2008.11.022LIU Lixin, ZHANG Xuejian, ZHANG Ying, et al. Polishing mechanism and precision machining technology of lithium niobate crystal [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2008,36(11):1609-1614. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2008.11.022 [52] 郁炜, 吕迅. 基于田口方法的铌酸锂基片CMP工艺研究 [J]. 轻工机械,2009,27(1):95-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2895.2009.01.027YU Wei, LV Xun. Study on chemical mechanical polishing of LiNbO3 wafer by taguchi method [J]. Light Industry Machinery,2009,27(1):95-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2895.2009.01.027 [53] WANG S L, LI Z X, LIU Y L, et al. Study on optimization of process parameters for lithium niobate photoelectric material in CMP [C]//5th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies. Dalian, China. SPIE, 2010, 7655: 765532. [54] 徐朝阁. 铌酸锂晶体纳米力学及化学机械抛光研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014.XU Chaoge. Nanomechanies and chemical mechanical polishing of lithiumniobate crystals [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2014. [55] 杨静, 杨洪星, 韩焕鹏, 等. 铌酸锂晶片抛光的主要物理及化学因素分析 [J]. 材料导报,2017,31(S2):273-276.YANG Jing, YANG Hongxing, HAN Huanpeng, et al. Analysis of physical and chemical factors of chemical mechanical polishing about lithium niobate [J]. Materials Reports,2017,31(S2):273-276. [56] JEONG S H, KIM Y J, LEE H S, et al. Study on optical properties of lithium niobate using CMP [J]. Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers A,2009,33(3):196-200. doi: 10.3795/KSME-A.2009.33.3.196 [57] JEONG S, LEE H, CHO H, et al. Effect of additives for higher removal rate in lithium niobate chemical mechanical planarization [J]. Applied Surface Science,2010,256(6):1683-1688. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.09.094 [58] 马驰, 李庆忠, 范晓策. 雾化施液CMP中铌酸锂晶片抛光液优化及抛光效果 [J]. 半导体技术,2020,45(3):213-218. doi: 10.13290/j.cnki.bdtjs.2020.03.007MA Chi, LI Qingzhong, YUAN Xiaoce. Polishing slurry optimization and polishing effect of lithium niobate wafer in atomized slurry applied CMP [J]. Semiconductor Technology,2020,45(3):213-218. doi: 10.13290/j.cnki.bdtjs.2020.03.007 [59] 崔雪晴, 谢冉冉, 刘洪亮, 等. 铌酸锂超构表面: 制备及光子学应用 [J]. 光电工程,2022,49(10):37-52. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220093CUI Xueqing, XIE Ranran, LIU Hongliang, et al. Lithium niobate metasurfaces: Preparation and photonics applications [J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering,2022,49(10):37-52. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220093 [60] GOODBERLET J G, DUNN B L. Deep-ultraviolet contact photolithography [J]. Microelectronic Engineering,2000,53(1/2/3/4):95-99. doi: 10.1016/S0167-9317(00)00272-0 [61] PEASE R F W. Electron beam lithography [J]. Contemporary Physics,2006,22(3):265-290. doi: 10.1080/00107518108231531 [62] VIEU C, CARCENAC F, PÉPIN A, et al. Electron beam lithography: Resolution limits and applications [J]. Applied Surface Science,2000,164(1/2/3/4):111-117. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(00)00352-4 [63] WEIGAND H, VOGLER-NEULING V V, ESCALÉ M R, et al. Enhanced electro-optic modulation in resonant metasurfaces of lithium niobate [J]. ACS Photonics,2021,8(10):3004-3009. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00935 [64] SALGAEVA U O, MUSHINSKY S S, VOLYNCEV A B, et al. Effect of pre-annealing process on the surface roughness of ridge waveguides formed with wet etching of–Z–cut LiNbO3 [J]. Ferroelectrics,2016,496(1):143-148. doi: 10.1080/00150193.2016.1155399 [65] LIN J T, XU Y X, FANG Z W, et al. Second harmonic generation in a high-Q lithium niobate microresonator fabricated by femtosecond laser micromachining [J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy,2015,58(11):114209. doi: 10.1007/s11433-015-5728-x [66] QU M N, SHEN Y L, WU L Y, et al. Homogenous and ultra-shallow lithium niobate etching by focused ion beam [J]. Precision Engineering,2020,62:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.11.001 [67] MALSHE A, DESHPANDE D, STACH E, et al. Investigation of femtosecond laser-assisted micromachining of lithium niobate [J]. CIRP Annals,2004,53(1):187-190. doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60675-1 [68] BUI P V, TOH D, KANAOKA M, et al. Planarization of lithium niobate surface using a thin film catalyst in pure water [J]. EPJ Web of Conferences,2022,266:03006. doi: 10.1051/epjconf/202226603006 [69] GUO J, SHI H H, TONG Z, et al. A new chemo-mechanical slurry for close-to-atomic scale polishing of LiNbO3 crystal [J]. CIRP Annals,2023,72(1):293-296. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2023.04.076 [70] PAN B, HE Z X, GUO J, et al. Modelling and optimization of surface roughness in chemical mechanical polishing based on DNN-GA [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,2023,237(14):3198-3209. doi: 10.1177/09544062221147132 [71] LI M, KARPUSCHEWSKI B, OHMORI H, et al. Adaptive shearing-gradient thickening polishing (AS-GTP) and subsurface damage inhibition [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2021,160:103651. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103651 [72] LI M, LIU M H, RIEMER O, et al. Origin of material removal mechanism in shear thickening-chemical polishing [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2021,170:103800. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2021.103800 [73] TANG C, HUANG Z F, TANG L Y, et al. The effect of pH value on shear thickening and chemical compound effect polishing solution [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2023,2566(1): 012033. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2566/1/012033 [74] TIAN Y B, LI L G, FAN S, et al. A novel high-shear and low-pressure grinding method using specially developed abrasive tools [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture,2021,235(1/2):166-172. doi: 10.1177/0954405420949106 [75] TIAN Y B, LI L G, HAN J G, et al. Development of novel high-shear and low-pressure grinding tool with flexible composite [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2020,36(4):479-487. doi: 10.1080/10426914.2020.1843673 [76] TIAN Y B, LI L G, LIU B, et al. Experimental investigation on high-shear and low-pressure grinding process for Inconel718 superalloy [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2020,107(7/8):3425-3435. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-05284-z [77] WEI C W, TIAN Y B, CHOWDHURY S, et al. Investigation on high-shear and low-pressure grinding characteristics for zirconia ceramics using newly developed flexible abrasive tool [J]. Ceramics International,2023,49(6):8725-8735. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.265 [78] LIU B, TIAN Y B, HAN J G, et al. Development of a new high-shear and low-pressure grinding wheel and its grinding characteristics for Inconel718 alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2022,35(12):278-286. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.08.013 [79] 田业冰, 范增华. 磁性剪切增稠超精密光整加工技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022.TIAN Yebing, FAN Zenghua. Magnetorheological shear thickening ultra-precision finishing technology [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022. [80] SUN Z G, TIAN Y B, FAN Z H, et al. Experimental investigations on enhanced alternating-magnetic field-assisted finishing of stereolithographic 3D printing zirconia ceramics [J]. Ceramics International,2022,48(24):36609-36619. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.08.220 [81] QIAN C, TIAN Y B, FAN Z H, et al. Investigation on rheological characteristics of magnetorheological shear thickening fluids mixed with micro CBN abrasive particles [J]. Smart Material Structures,2022,31(9):095004. doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ac7bbd [82] FAN Z H, TIAN Y B, ZHOU Q, et al. Enhanced magnetic abrasive finishing of Ti–6Al–4V using shear thickening fluids additives [J]. Precision Engineering,2020,64:300-306. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2020.05.001 -



 下载:
下载:


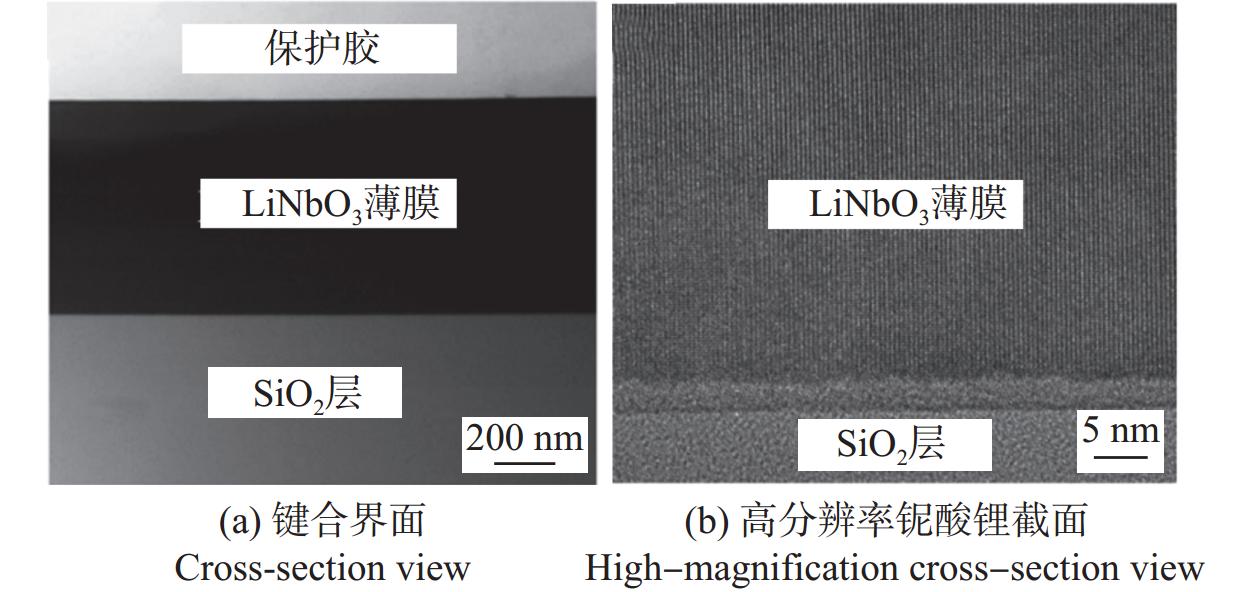
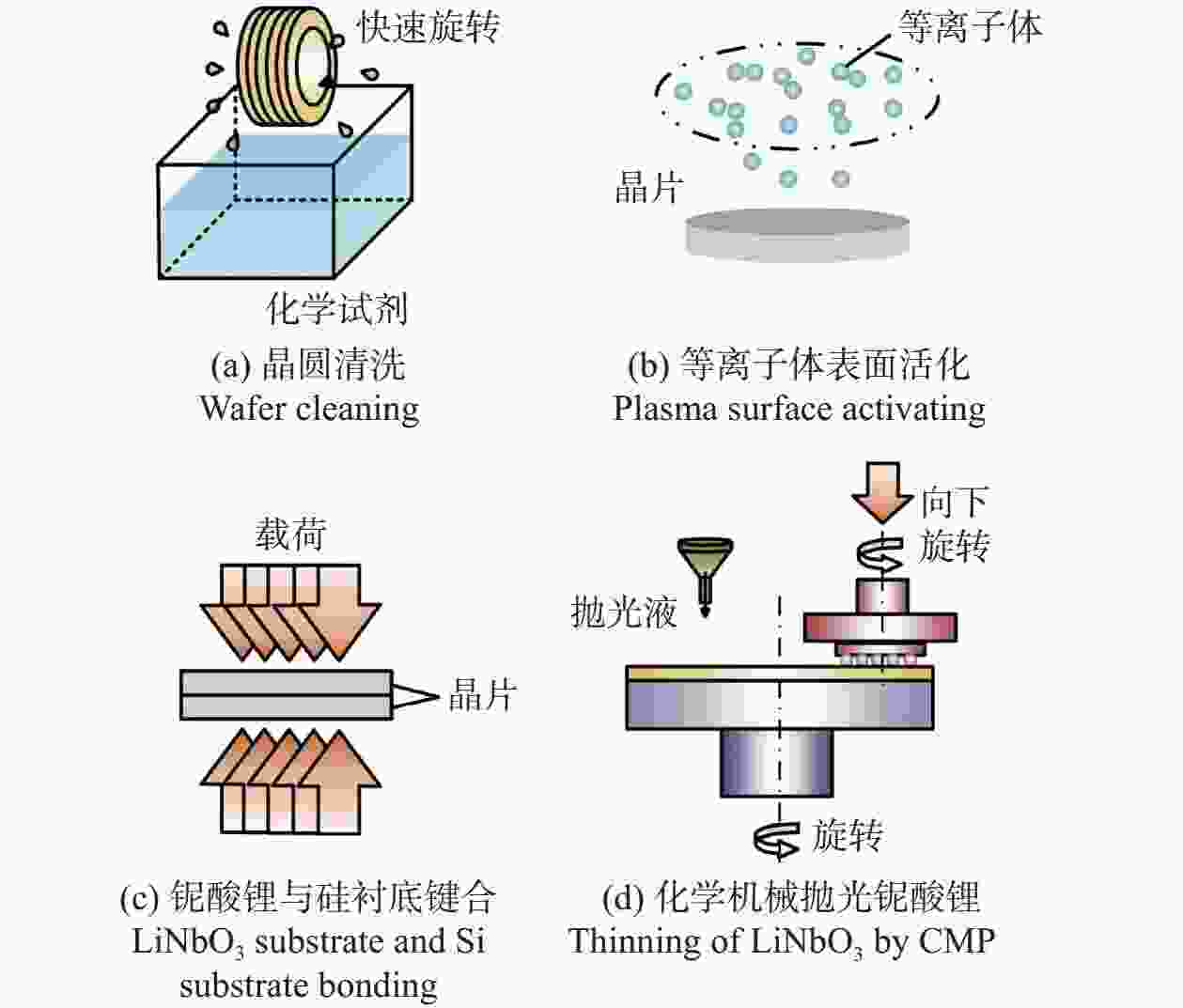
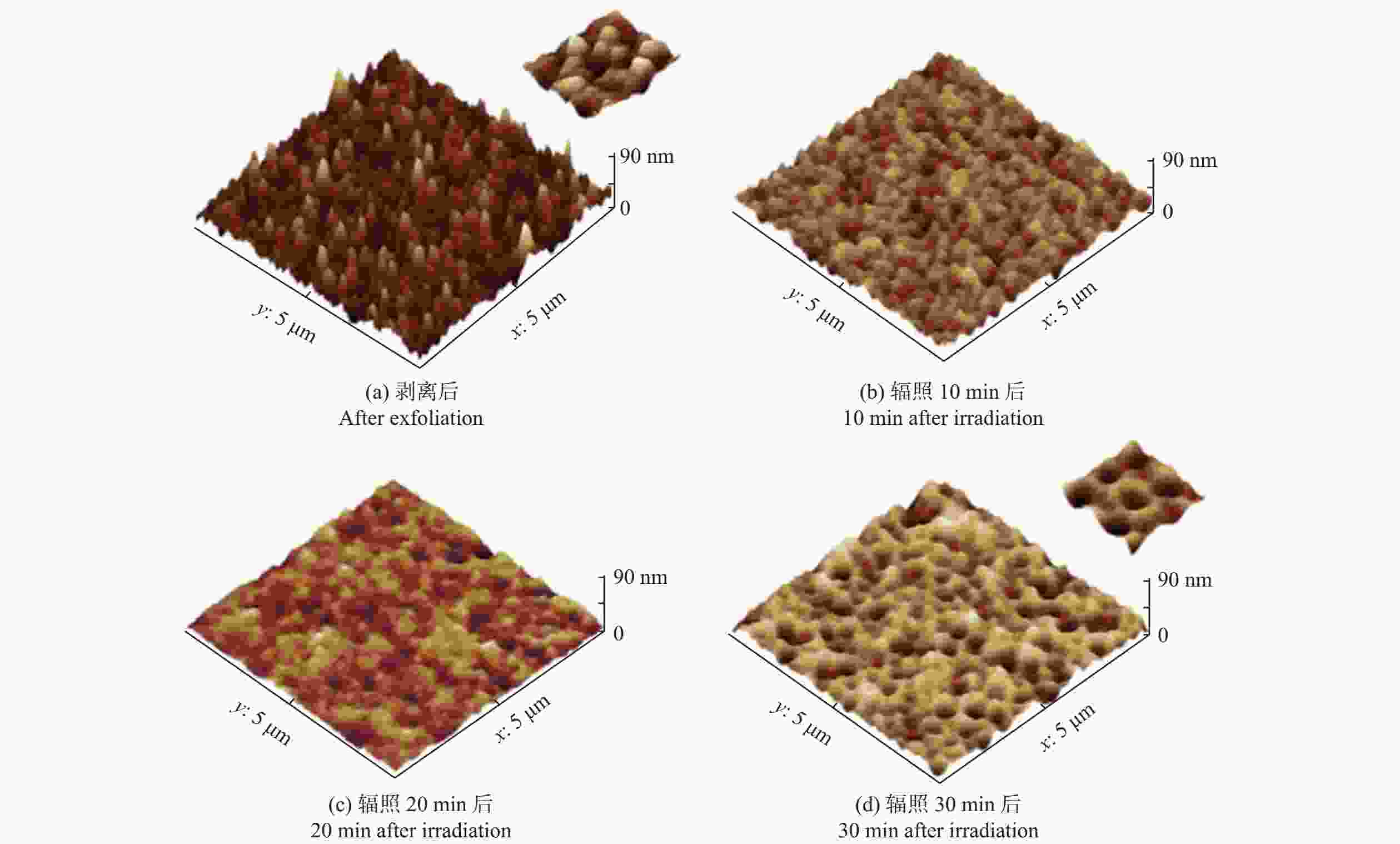

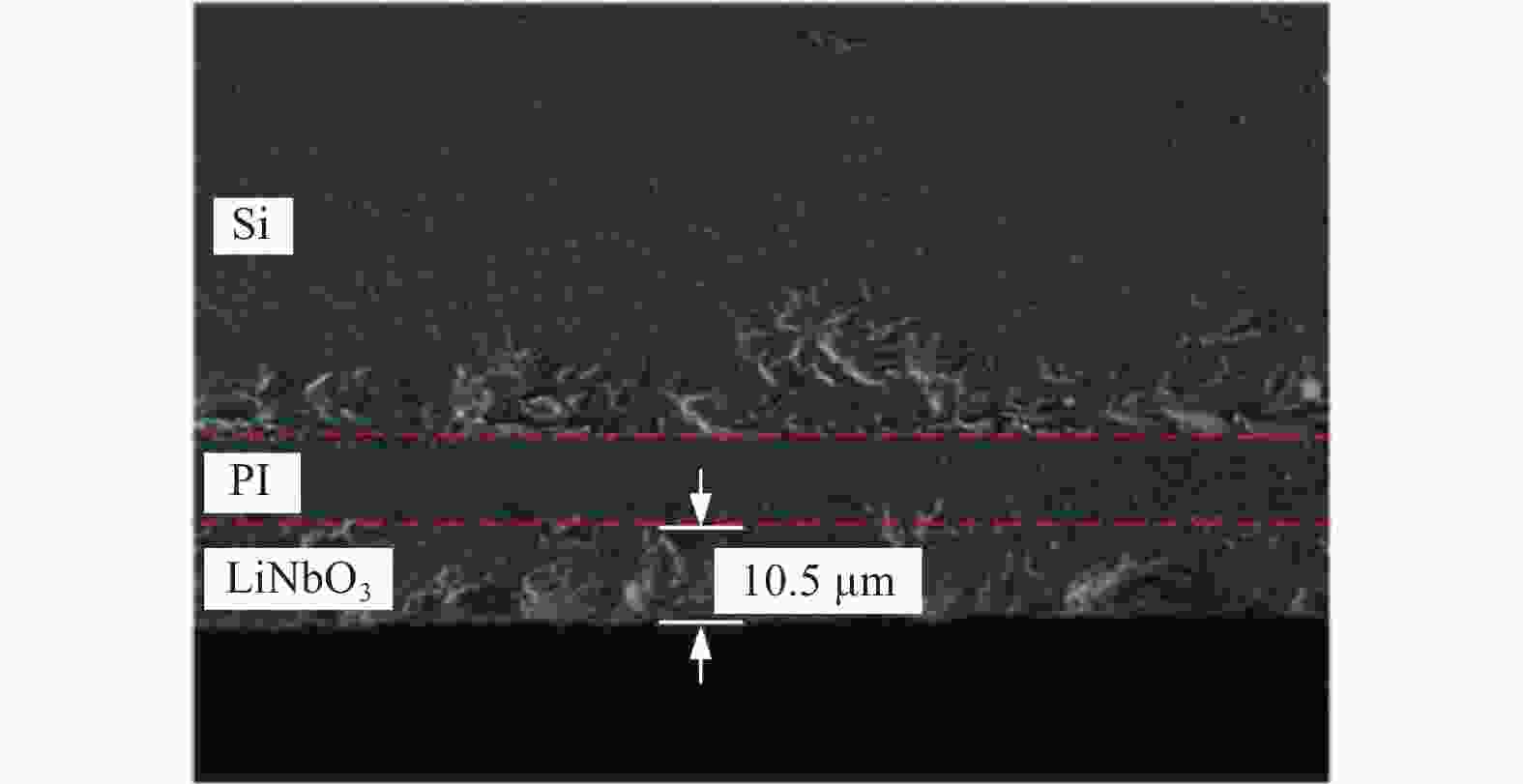

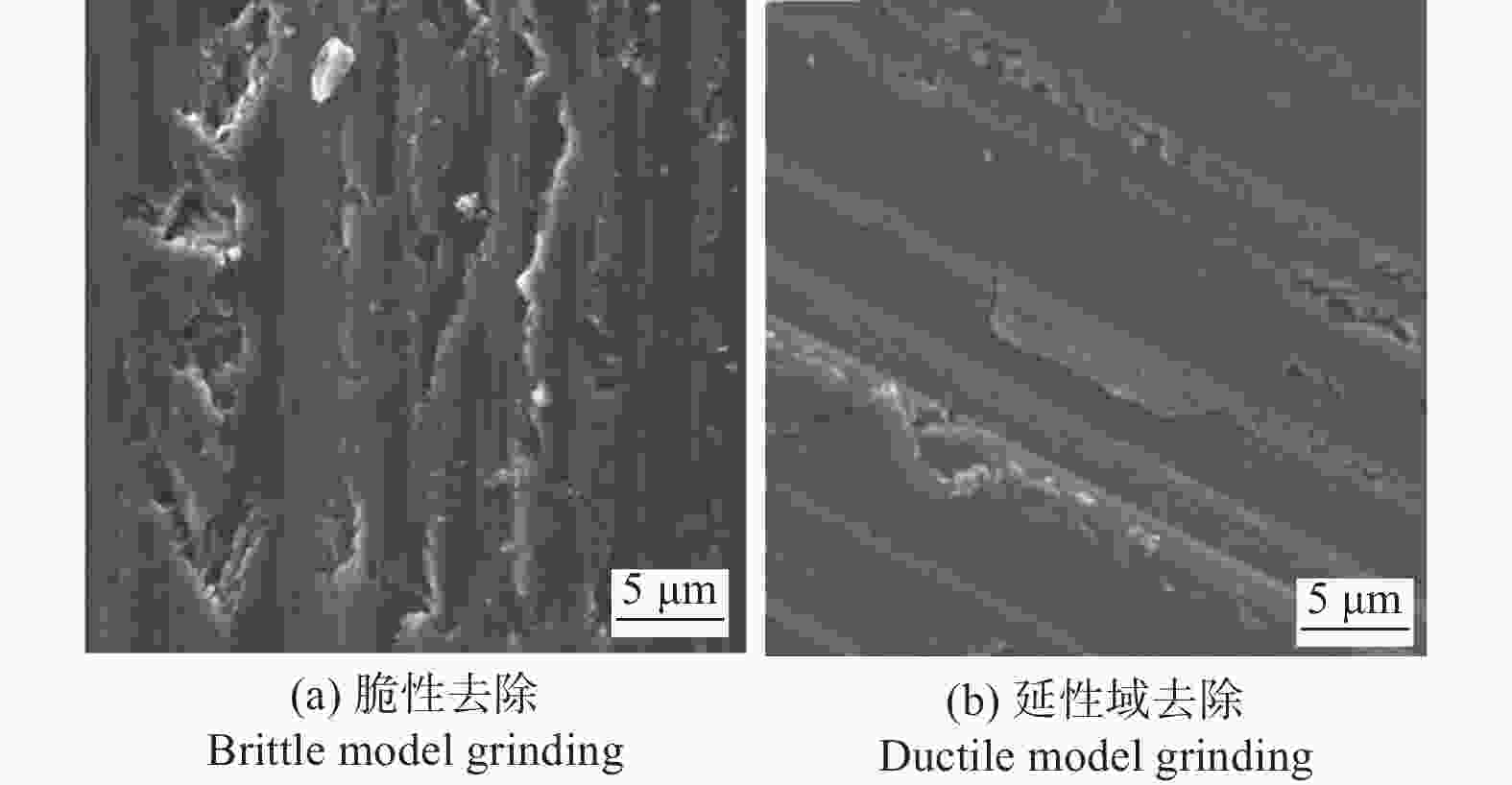
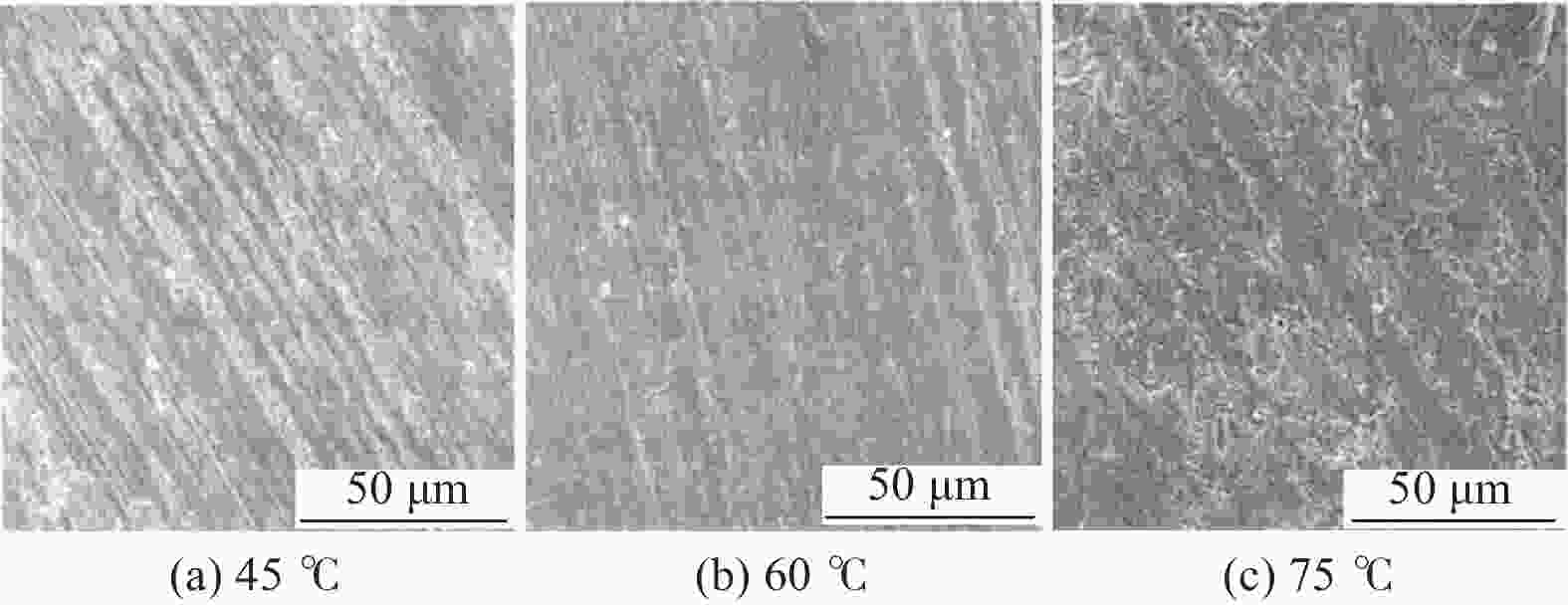

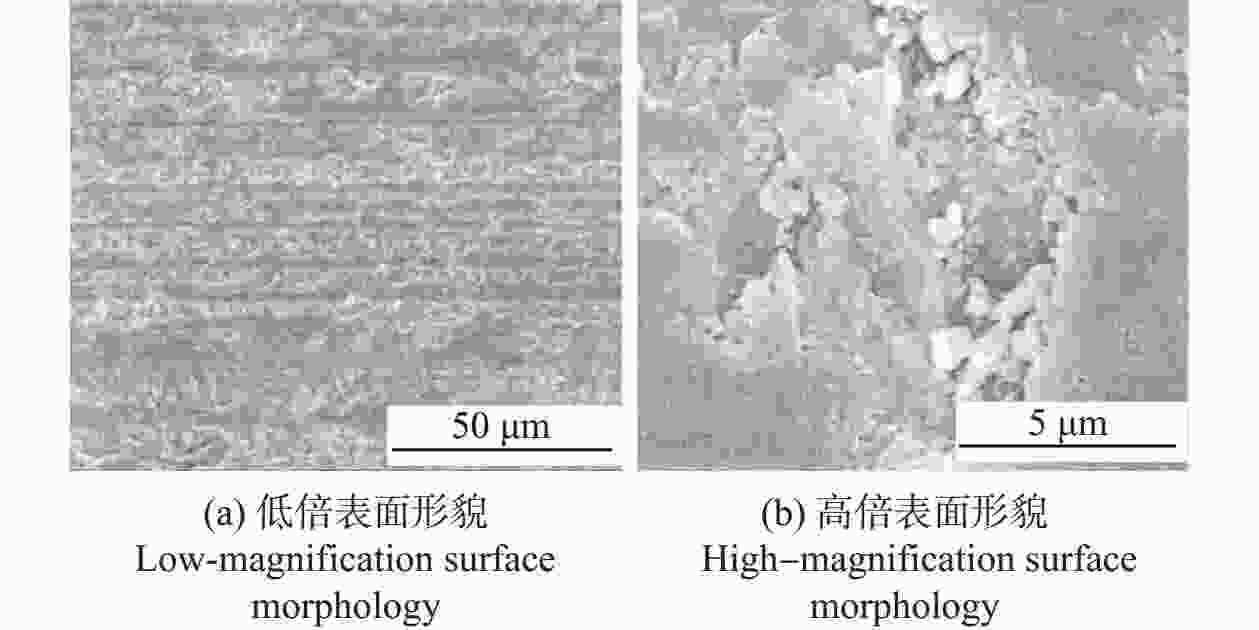
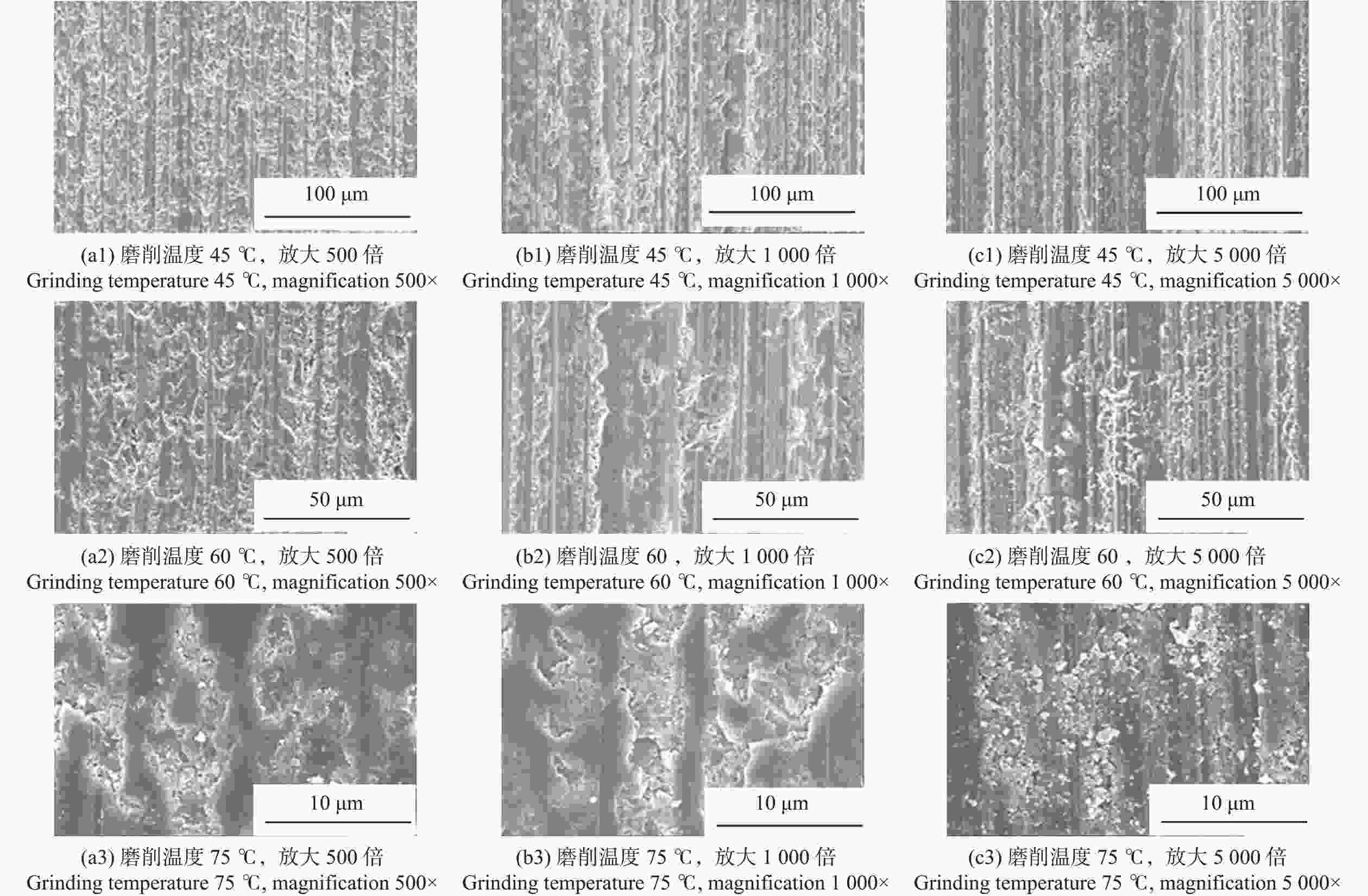
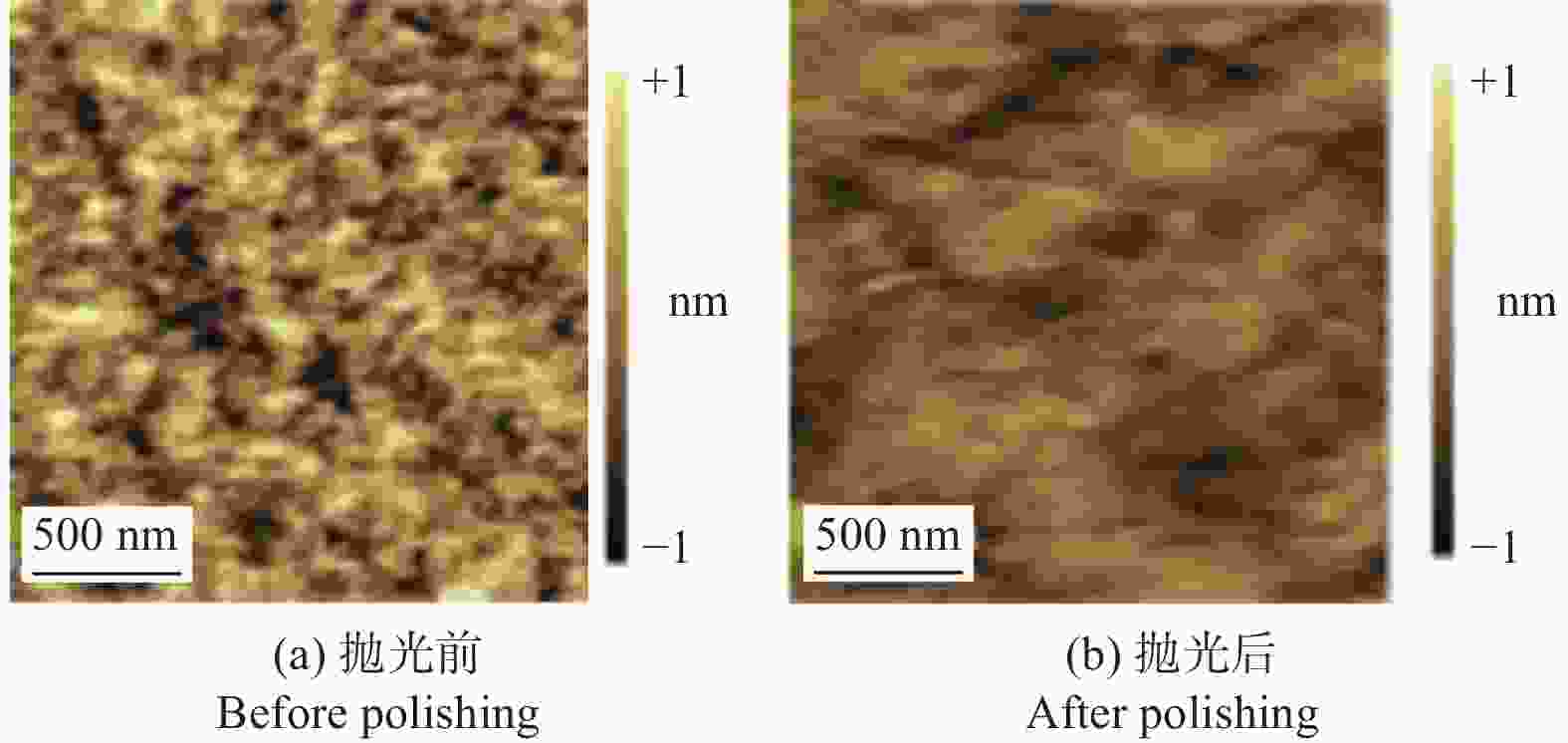
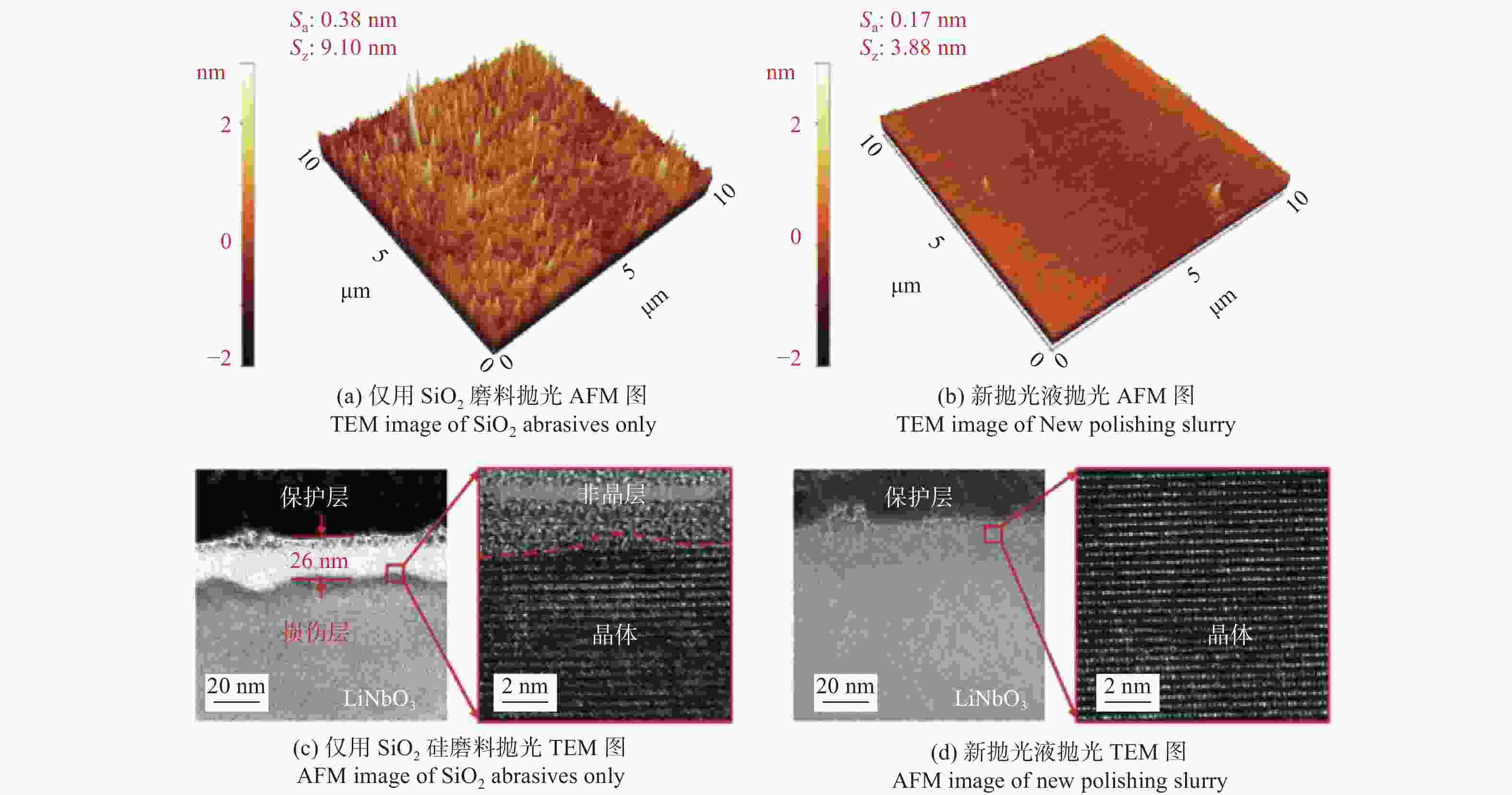
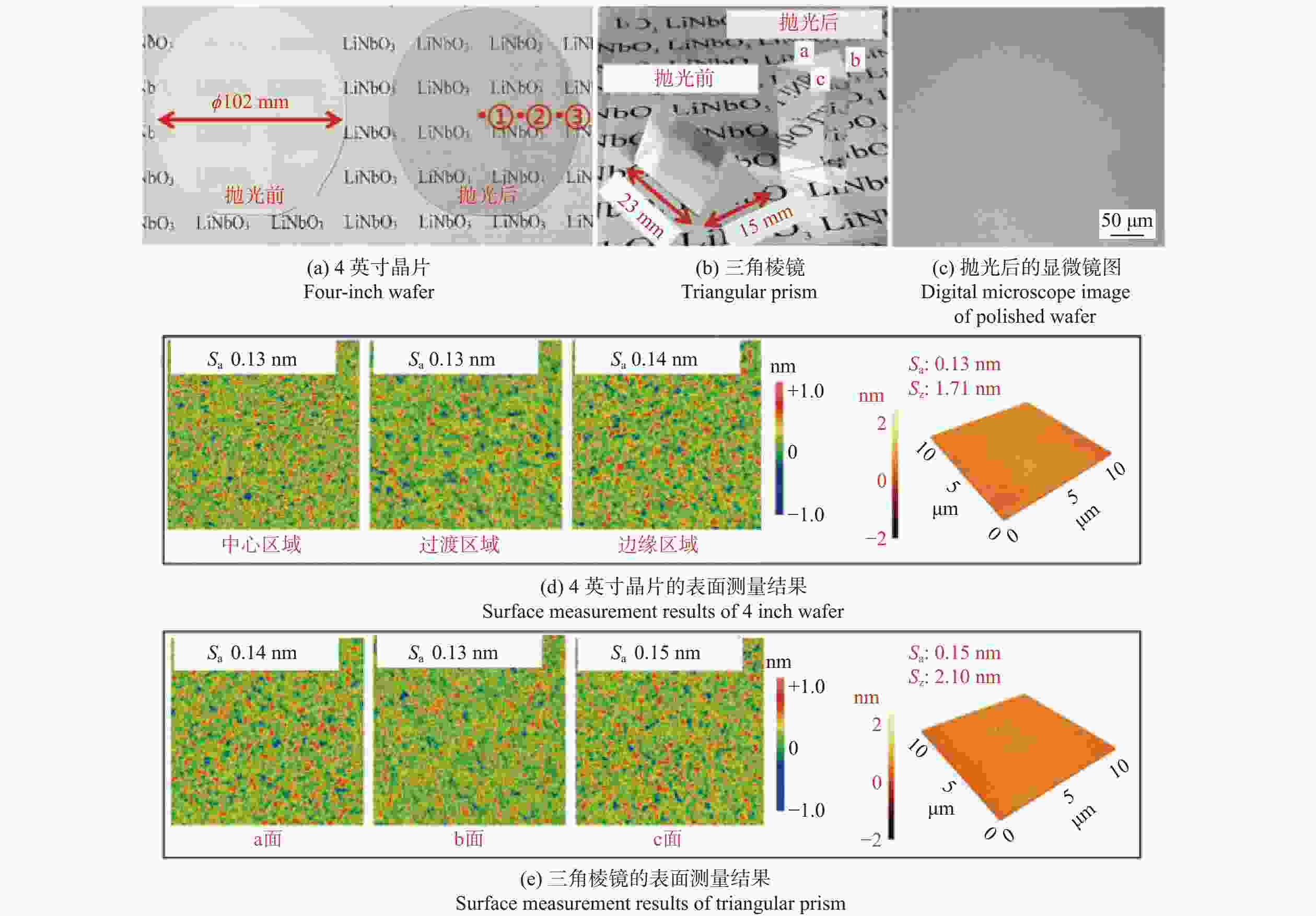
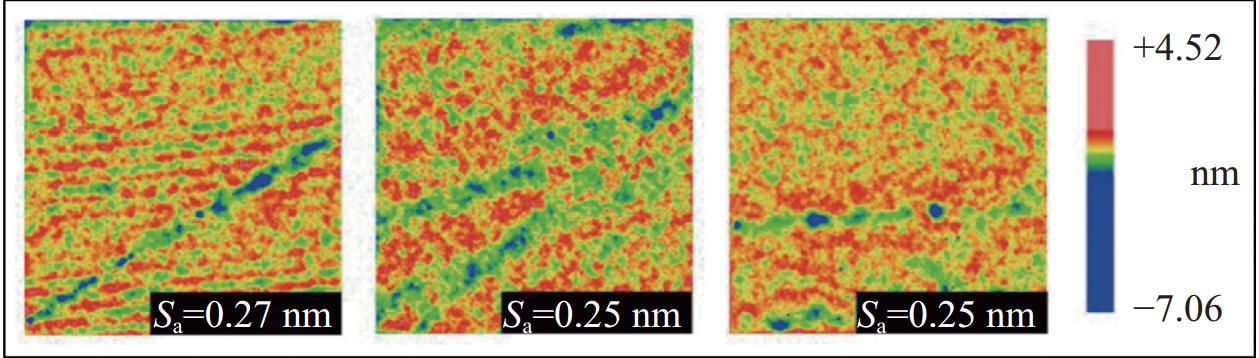
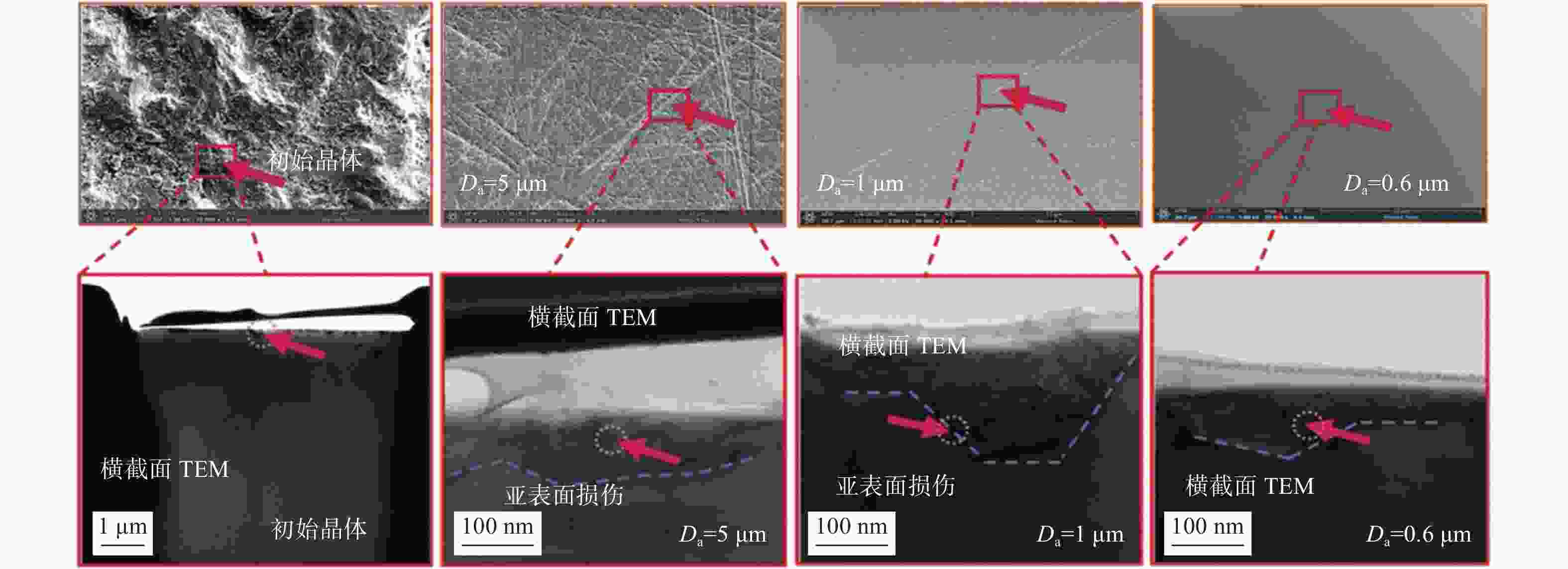
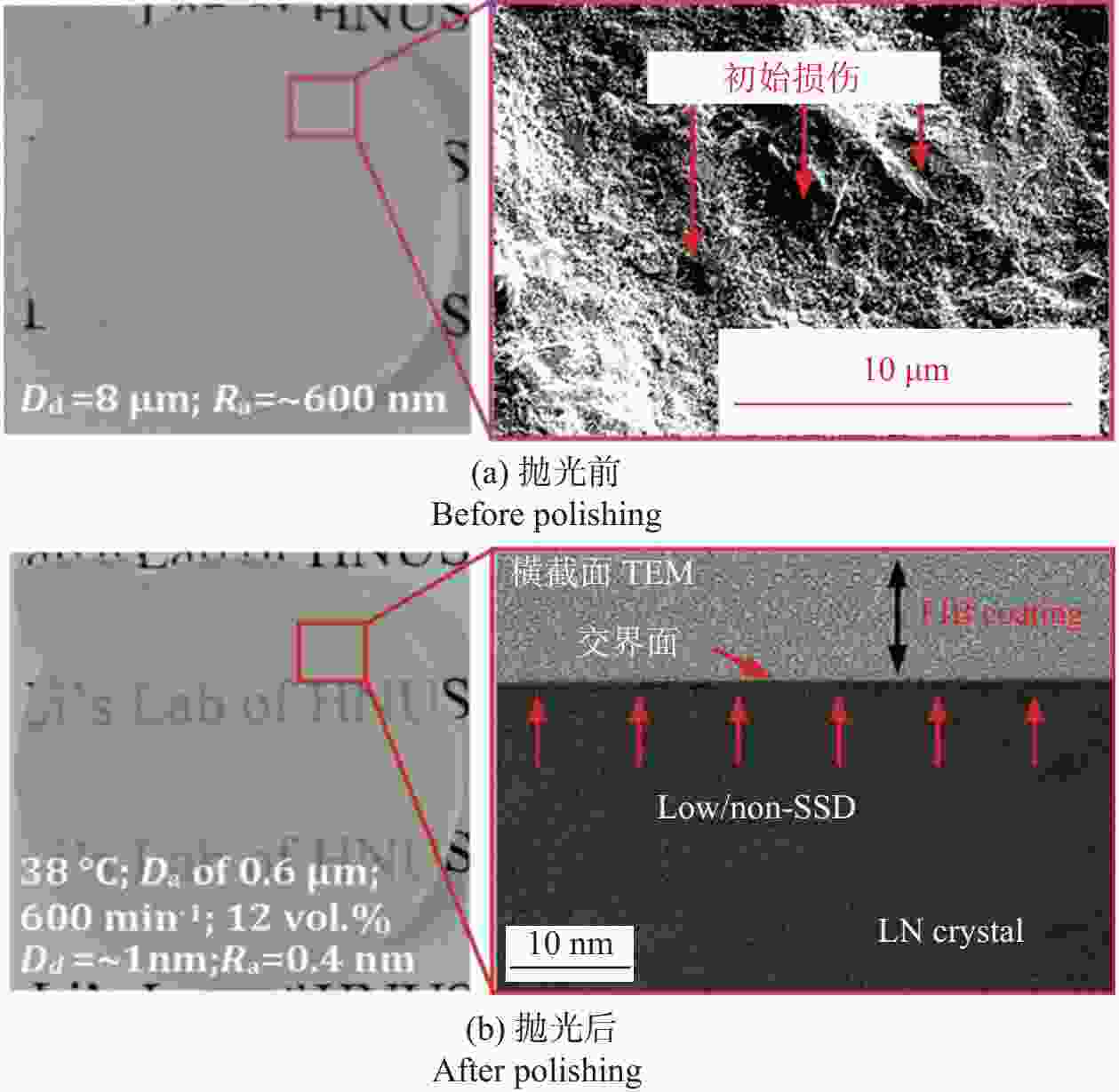
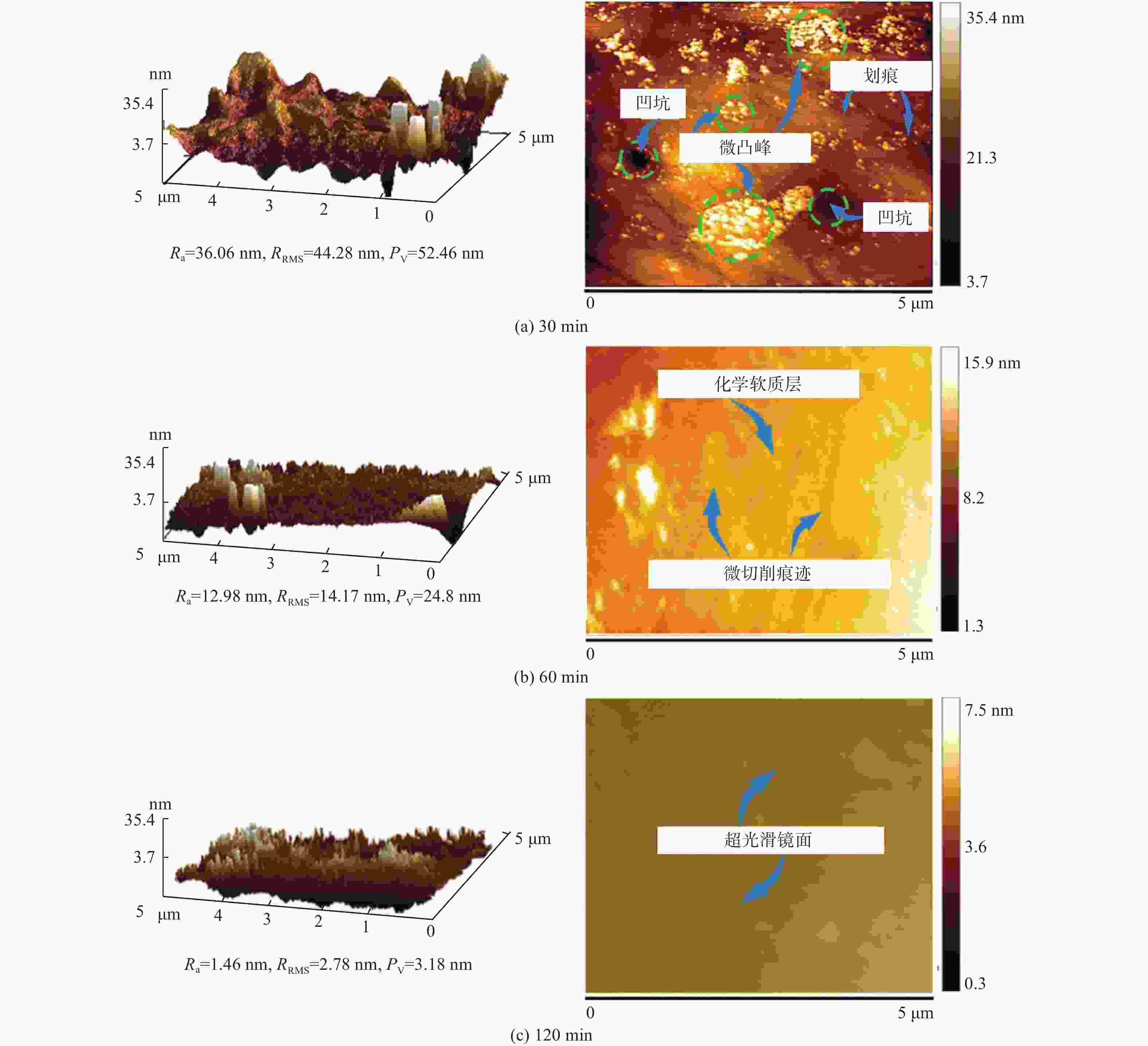
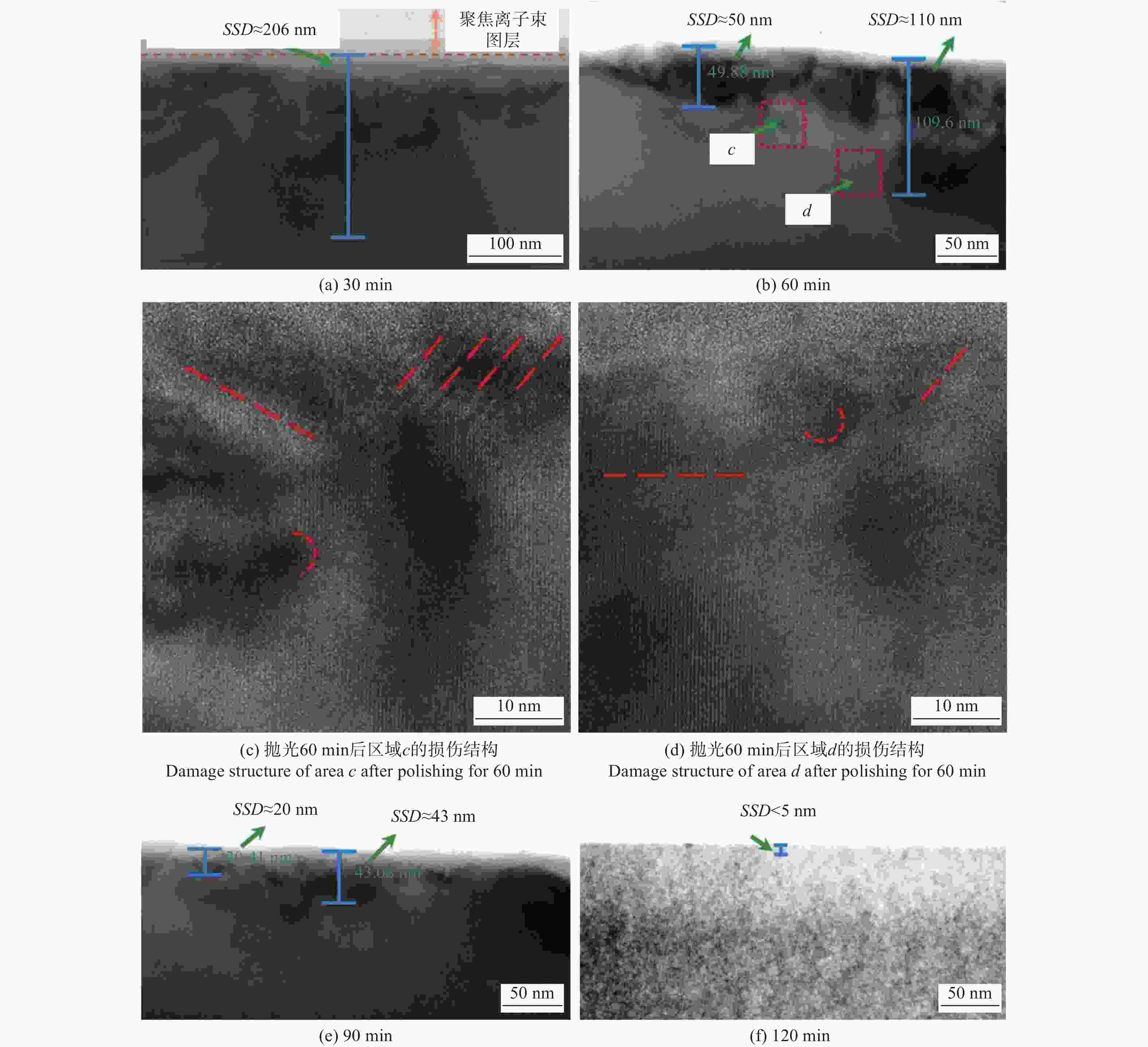


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
