Study on numerical simulation of rock breaking by PDC wear teeth cutting
-
摘要: 现有文献针对切削齿的数值模拟研究较少考虑磨损高度对切削齿温度、切削载荷的影响,然而聚晶金刚石复合片(PDC)切削齿磨损后受力恶化、热磨损加剧会导致其快速失效。为探讨这一问题,基于弹塑性力学和岩石力学,以Drucker-Prager准则为岩石的本构模型建立磨损齿的三维动态旋切仿真模型,运用数值模拟的方法分析在不同磨损高度、切削深度、前倾角的条件下切削齿的受力状态以及温升幅度。结果表明:与未磨损齿相比,磨损齿的切削载荷随磨损高度的增加而变大,且切削齿(直径13.4 mm、总高8 mm)磨损高度为1.5 mm时达到最大;切削齿磨损越严重,吃入到同一深度所需的力越大;前倾角增加,导致切削载荷也会变大。因此磨损齿在切削钻进过程中,磨损高度越高、前倾角越大,切削齿的失效风险越高;随着切削齿磨损高度增加,切削齿温升显著增加,在模拟条件下可提高54%~103%。
-
关键词:
- PDC切削齿 /
- Drucker-Prager准则 /
- 单齿切削 /
- 切削载荷 /
- 切削热
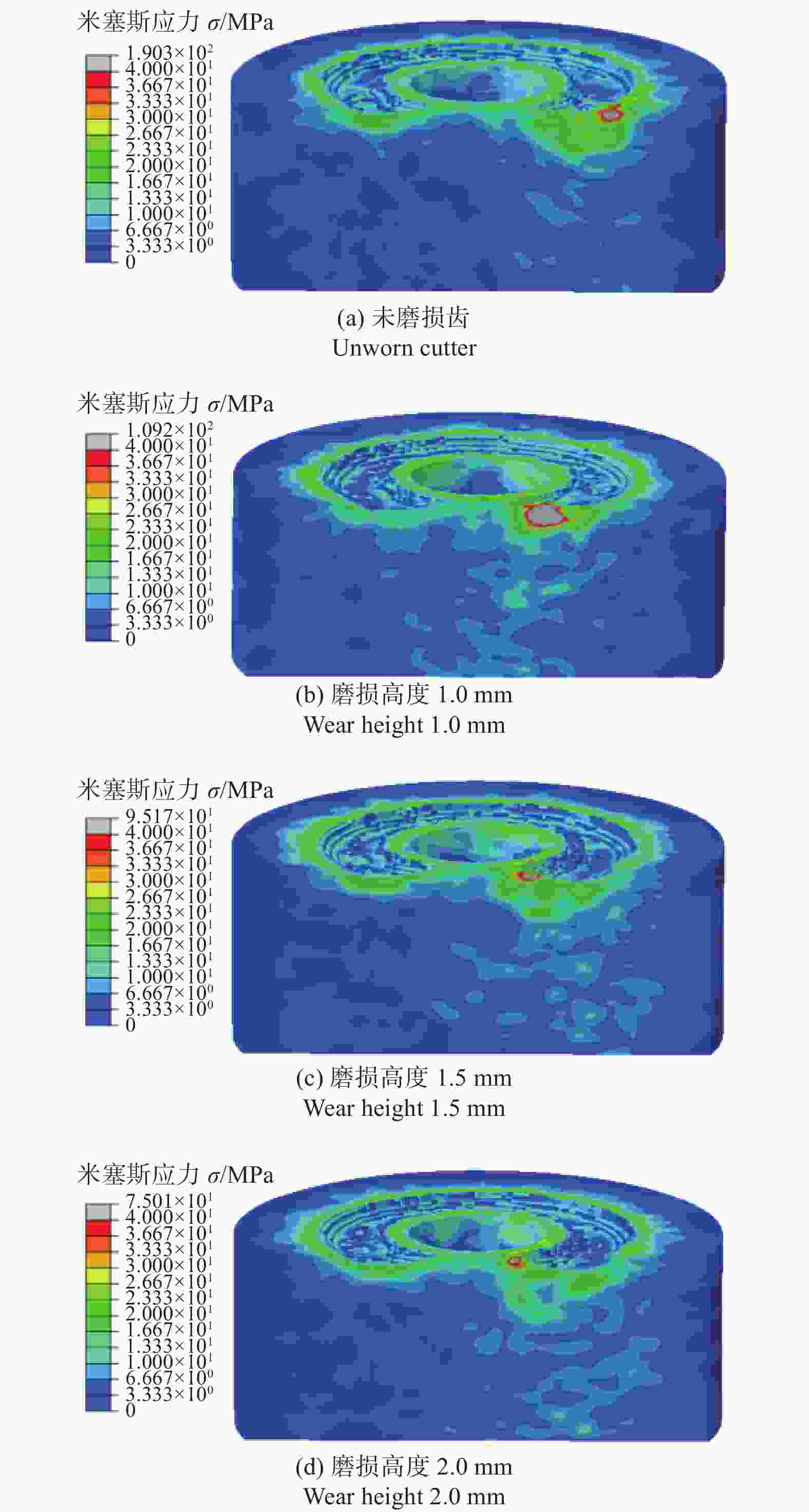
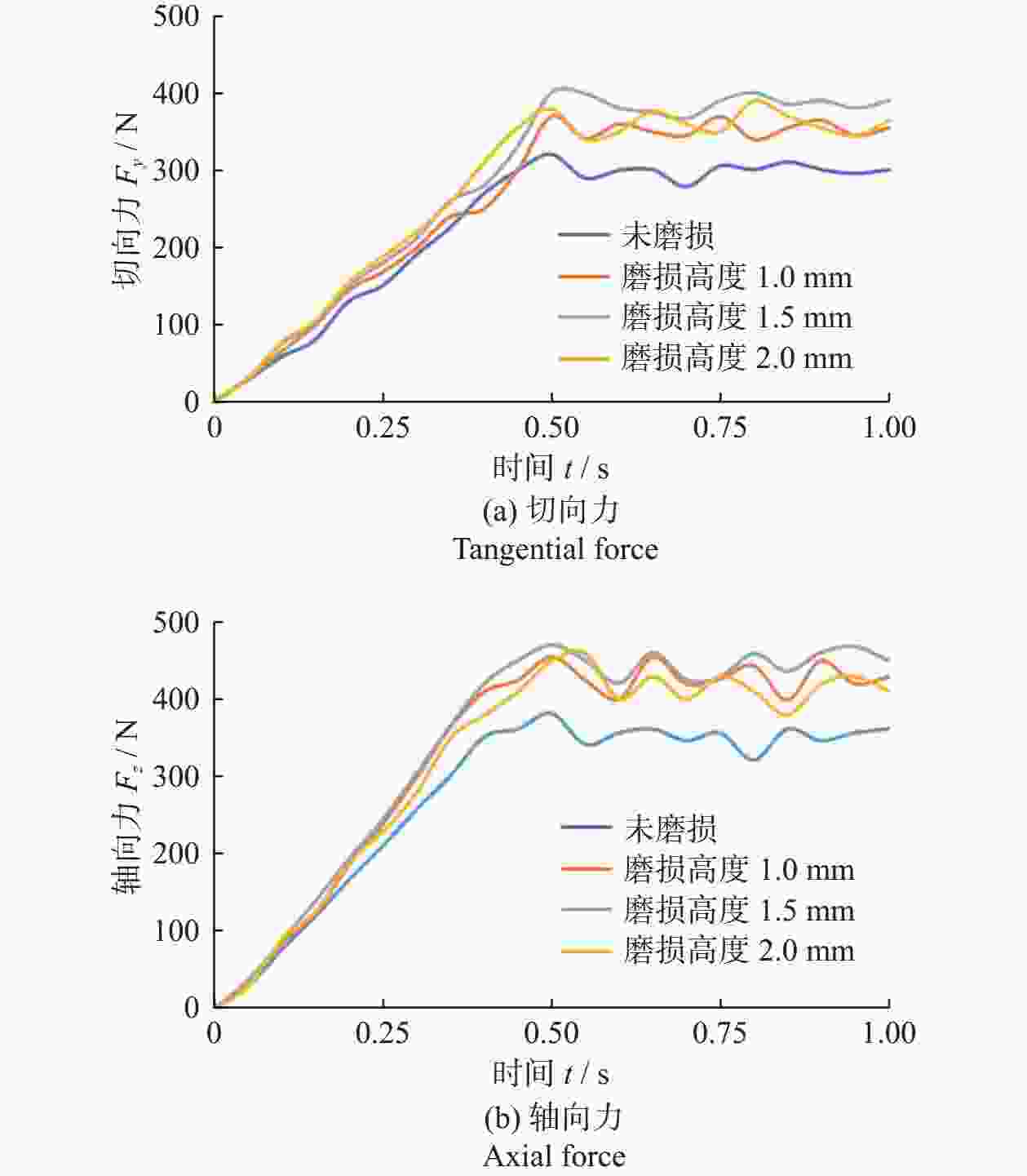
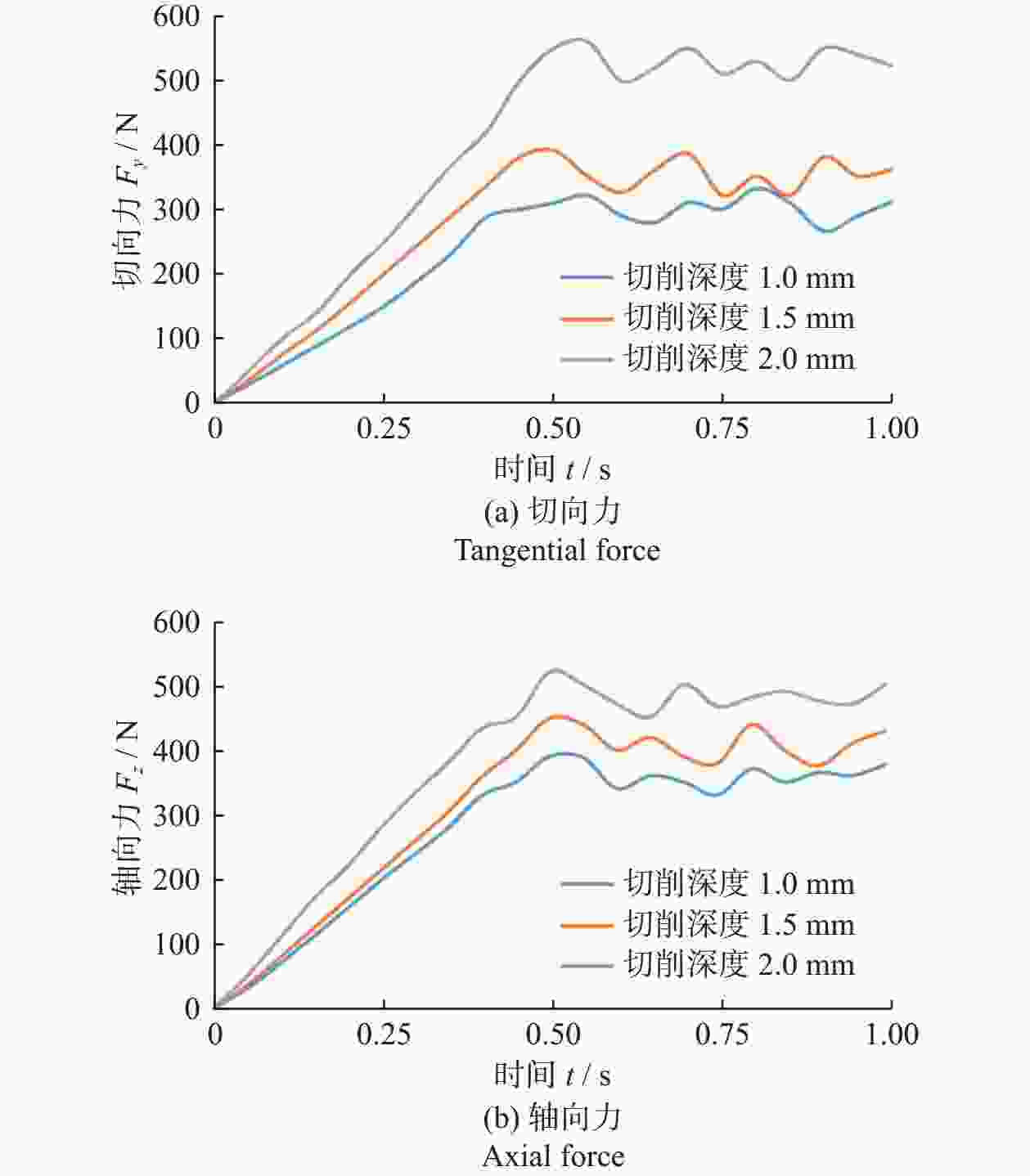
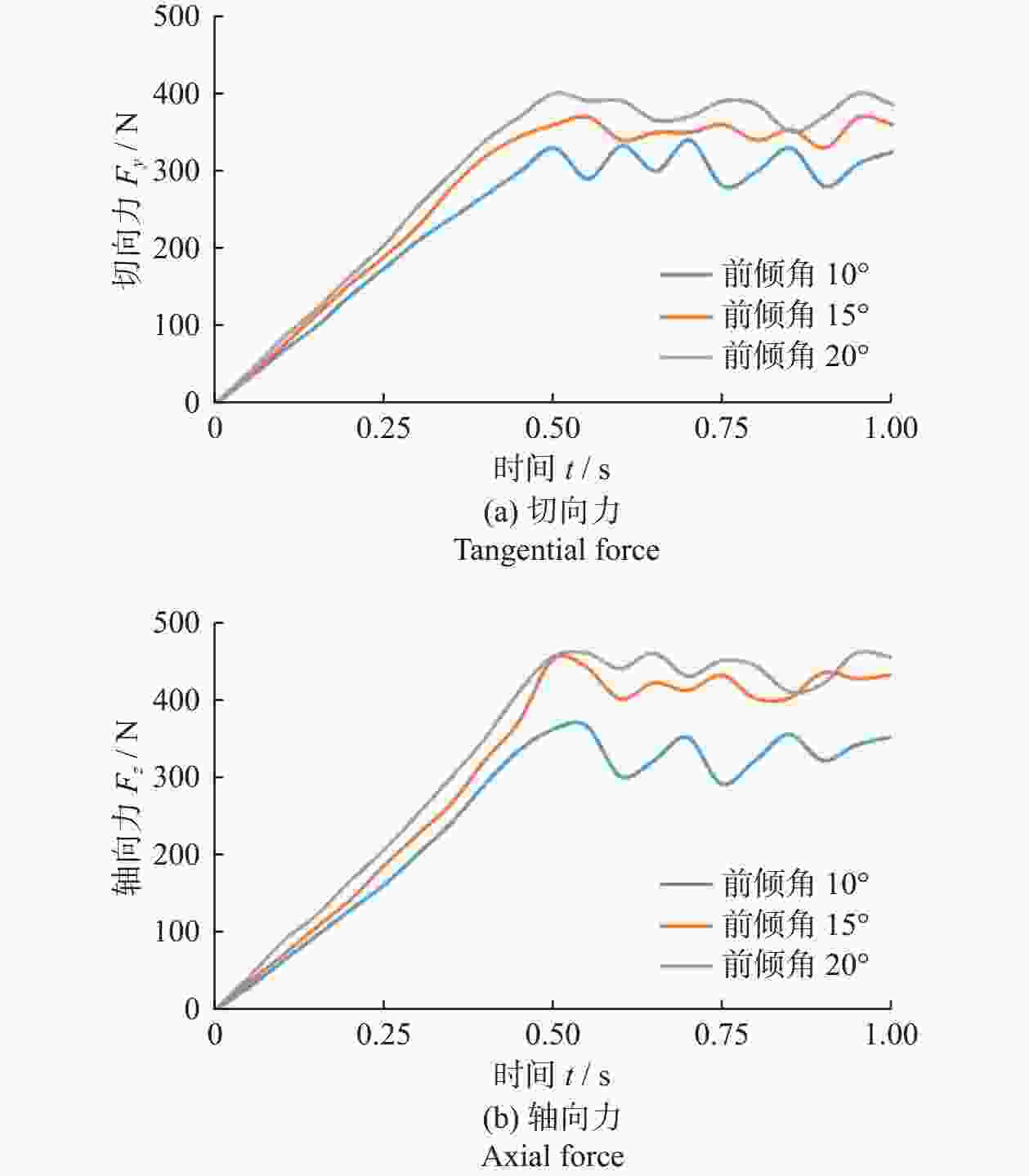
Abstract: Objectives: The existing literature on numerical simulation of cutters rarely considers the effect of wear height on the temperature and cutting load of cutters. However, the deterioration of force and the aggravation of thermal wear after the wear of polycrystalline diamond composite (PDC) cutters lead to their rapid failure. Therefore, it is particularly necessary to study the change of cutting load and the law of heat generation of worn cutters to extend their service life. Methods: Based on elastoplastic mechanics and rock mechanics, a 3D dynamic rotational simulation model of worn teeth is established with the Drucker-Prager criterion as the rock constitutive model. The stress state and temperature rise amplitude of cutting teeth under different wear heights, cutting depths, and front inclination angles are analyzed by numerical simulation. Results: (1) Influence of wear height on cutting load: Under simulated conditions (front inclination 15°, cutting depth 1.5 mm), the size and the fluctuation degree of cutting load increase with the increase of wear height when the wear height is 0−1.5 mm, and decrease slightly when the wear height is larger than 1.5 mm. In terms of tangential force, the cutter with a wear height of 1.5 mm is subjected to the largest tangential force, but when the wear height is 2.0 mm, the tangential force is reduced. In terms of axial force, the axial force of worn teeth is higher than that of unworn teeth. When the wear height is 0−1.5 mm, the axial force gradually increases with the increase of wear height. When the wear height is 1.5 mm, the axial force reaches its maximum, and when the wear height is larger than 1.5 mm, the axial force decreases. The axial force of the cutter with a wear height of 1.0 mm and wear height of 2.0 mm is exactly 1.2 times that of the unworn tooth, and the axial force of the cutter with a wear height of 1.5 mm is 1.3 times that of the unworn tooth. (2) Influence of cutting depth on cutting load: Under simulated conditions (wear height 1.0 mm, front inclination angle 15°), tangential force and axial force gradually increase with the increase of cutting depth, and the degree of fluctuation is more intense. In terms of tangential force, the tangential force of the worn tooth with the cutting depth of 2.0 mm is 1.9 times that of the worn tooth with the cutting depth of 1.0 mm, and the increase is larger. The tangential force of the worn tooth with the cutting depth of 1.5 mm is only 25% higher than that of the worn tooth with the cutting depth of 1.0 mm, and the increase is small. In terms of axial force, with the increase of cutting depth, the increase in axial force is relatively balanced. (3) Influence of front inclination angle on cutting load: Under simulated conditions (wear height 1.0 mm, cutting depth 1.5 mm), the cutting load of worn teeth gradually increases with the increase of front inclination angle, with the tangential force increasing by 28% and the axial force increasing by 32%. When the front angle is 10°, the fluctuation of the cutting load is more severe than at other time with 15° and 20°. (4) Influence of wear height on cutting heat: according to the temperature cloud map of the cutter, because the cutter rotates around the central axis to break rock, the linear speed of the cutting edge differs, and the temperature on the side away from the central axis will be higher than that on the side near the central axis. With the increase of wear degree, the temperature rise of the cutter becomes more significant, and the high-temperature area is concentrated in the cutting-cutter contact area, where plastic deformation and frictional heat generation are concentrated. The temperature change curve can be divided into three stages: rising period, transitional period, and stable period. With the passage of time, the temperature of the cutter continues to rise, and the temperature rise rate in the rising period is greater than in the transitional period, tending to flatten after entering the stable period. In the process of rock breaking, the temperature rise of worn teeth is much higher than that of unworn teeth, with a temperature increase of 54%−103%. Conclusions: The force on a cutter with excessive wear is more complex and variable, increasing the risk of fatigue failure. In terms of tooth layout, it can be considered to place the auxiliary cutting unit behind the main cutting unit composite sheet and make its exposure height lower than the composite sheet, which can effectively reduce the load on the main cutting gear and reduce the probability of overload damage to the cutting gear. The cutting load of the worn teeth increases with the increase of the front angle. Considering the fluctuation of cutting efficiency and load, the front angle should be controlled at 15°−20° as far as possible, which is beneficial to prolong the service life of the cutting teeth. After cutter wear, its ability to break rock is weakened, the rock pre-crushing area is reduced, and the way of cutting the rock gradually transitions from shear failure to extrusion failure, greatly reducing the rock-breaking efficiency of the cutter. In the process of cutting rock breaking, the temperature rise of the worn teeth is much higher than that of the unworn teeth, and the temperature rise increases with the increase of wear degree. Thus, the thermal wear of the cutting teeth will continue to intensify after wear, accelerating the wear and failure of the cutting teeth. In the subsequent cutting process, cutter of wear-resistant and high-temperature-resistant materials can be selected to reduce the weight on the bit and the speed of drilling while increasing the water power of the pump, effectively inhibiting thermal wear.-
Key words:
- PDC cutter /
- Drucker-Prager criterion /
- single tooth cutting /
- cutting load /
- cutting heat
-
表 1 PDC切削齿和岩石的参数
Table 1. Parameters of PDC cutters and rocks
材 料 PDC 岩石 密度ρ / (kg·m−3) 3 510 2 580 弹性模量 E / GPa 890 25 泊松比 ν 0.077 0.150 热传导率 λ /(W·m−1·℃−1) 543.0 3.5 比热容 c /(J·kg−1·℃−1) 790 800 热膨胀系数 α / ℃−1 2.5 × 10−6 12.0 × 10−6 内摩擦角 φ / (°) — 42 抗压强度 σ bc/ MPa — 40 表 2 切削齿破岩仿真方案
Table 2. Simulation scheme of cutter rock breaking
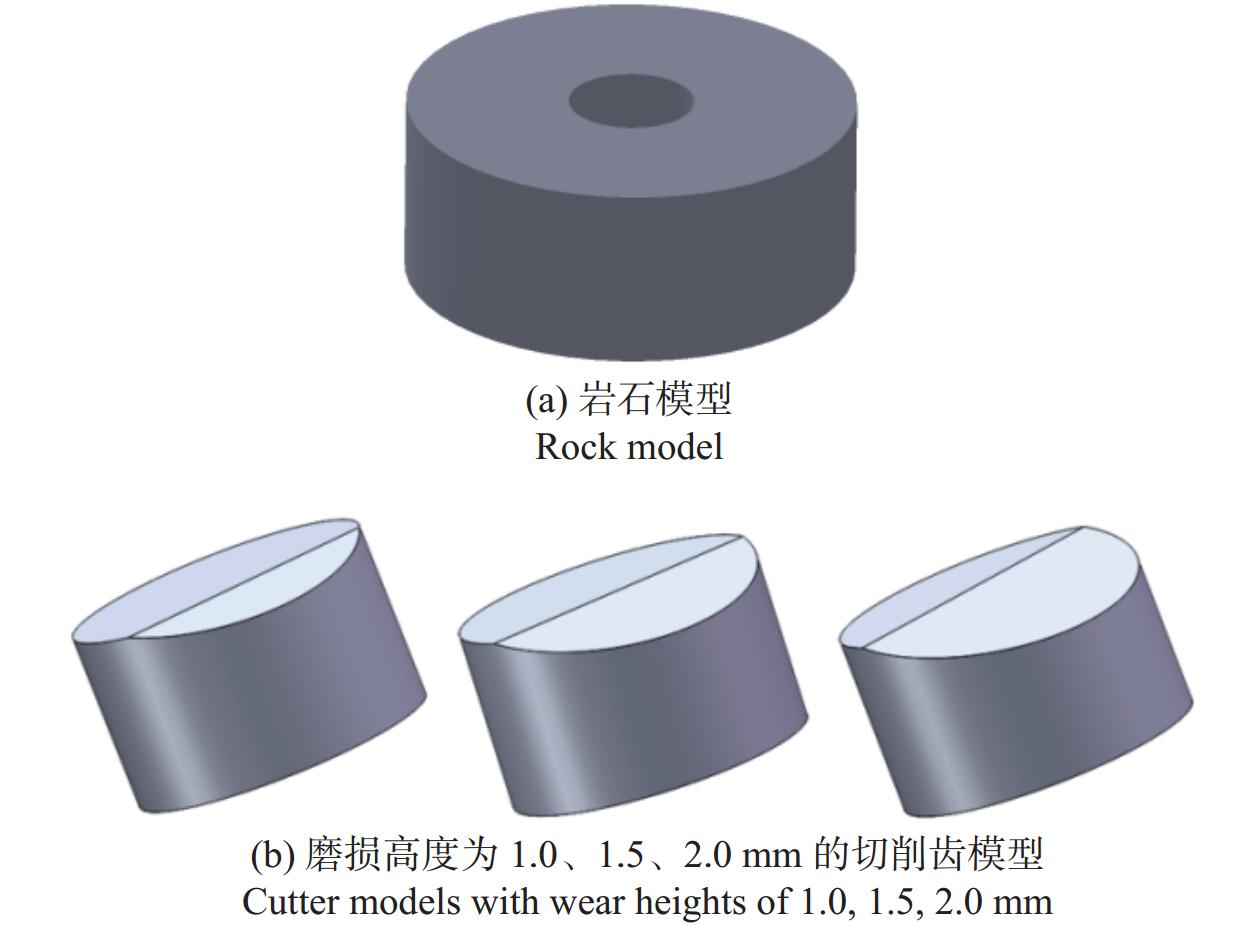
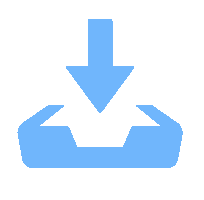
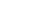
仿真方案 仿真参数 磨损高度 H / mm 前倾角 θ / (°) 切削深度 dDOC / mm 方案一 0、1.0、1.5、2.0 15 1.5 方案二 1.0 10、15、20 1.5 方案三 1.0 15 1.0、1.5、2.0 -
[1] 刘维, 高德利. PDC钻头研究现状与发展趋势 [J]. 前瞻科技,2023,2(2):168-178. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.2097-0781.2023.02.013LIU Wei, GAO Deli. Research status and development trends of polycrystalline diamond compact bits [J]. Prospect Science and Technology,2023,2(2):168-178. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.2097-0781.2023.02.013 [2] 苏义脑, 路保平, 刘岩生, 等. 中国陆上深井超深井钻完井技术现状及攻关建议 [J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):527-542. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.001SU Yinao, LU Baoping, LIU Yansheng, et al. Status and research suggestions on the drilling and completion technologies for onshore deep and ultra deep wells in China [J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology,2020,42(5):527-542. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.001 [3] 张富晓, 黄志强, 周已. PDC钻头切削齿失效分析 [J]. 石油矿场机械,2015,44(9):44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2015.09.011ZHANG Fuxiao, HUANG Zhiqiang, ZHOU Yi. Failure analysis of PDC bit cutter [J]. Oil Field Equipment,2015,44(9):44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2015.09.011 [4] 邓敏凯, 伍开松, 胡伟. PDC钻头切削齿破岩仿真与试验分析 [J]. 石油机械,2014,42(1):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2014.01.003DENG Minkai, WU Kaisong, HU Wei. Rock-breaking simulation and experimental analysis of PDC bit cutter [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2014,42(1):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2014.01.003 [5] 祝效华, 李海. PDC切削齿破岩效率数值模拟研究 [J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2015,23(1):182-191. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2015.01.017ZHU Xiaohua, LI Hai. Numerical simulation on mechanical special energy of PDC cutter rock-cutting [J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2015,23(1):182-191. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2015.01.017 [6] 杨迎新, 谢松, 蔡灿, 等. PDC磨损齿切削破岩过程的实验研究 [J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2023,45(1):180-188. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2020.06.04.03YANG Yingxin, XIE Song, CAI Can, et al. A study on the mechanism and heat generation law of PDC wear tooth cutting [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2023,45(1):180-188. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2020.06.04.03 [7] 赵润琦, 陈振良, 史怀忠, 等. 斧形PDC齿破碎致密硬质砂岩特性数值模拟研究 [J]. 石油机械,2021,49(10):8-16. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.10.002ZHAO Runqi, CHEN Zhenliang, SHI Huaizhong, et al. Numerical simulation study on characteristics of tight hard sand broken by axe-shaped PDC cutter [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2021,49(10):8-16. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.10.002 [8] 张春亮, 王锦成, 柯晓华, 等. 磨损齿PDC钻头的切削性能试验 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2023,43(1):35-42. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2022.0084ZHANG Chunliang, WANG Jincheng, KE Xiaohua, et al. Experimental study on working mechanics of PDC bit with worn teeth [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2023,43(1):35-42. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2022.0084 [9] ROSTAMSOWLAT I, AKBARI B, EVANS B. Analysis of rock cutting process with a blunt PDC cutter under different wear flat inclination angles [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,171:771-783. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.003 [10] 朱光辉, 况雨春, 林伟. PDC磨损齿切削载荷与生热规律研究 [J]. 石油机械,2021,49(5):68-73. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.05.010ZHU Guanghui, KUANG Yuchun, LIN Wei. Research on cutting load and heat generation law of PDC wearing cutter [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2021,49(5):68-73. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.05.010 [11] VORONTSOV A L, SULTAN-ZADE N M, ALBAGACHIEV A Y, et al. Development of a new theory of thermal cutting processes 3. Influence of cutter's front angle on the cutting temperature and influence of preheating of the blank on the cutting force [J]. Russian Engineering Research,2010,30(3):274-275. doi: 10.3103/S1068798X10030159 [12] 邓嵘, 李勇. PDC钻头切削齿破岩温度场有限元仿真分析 [J]. 石油机械,2012,40(12):37-42.DENG Rong, LI Yong. Simulation analysis of temperature field for PDC bit cutter rock breaking [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2012,40(12):37-42. [13] MAMALIS A G, HORVÁTH M, BRANIS A S, et al. Finite element simulation of chip formation in orthogonal metal cutting [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2001,110(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(00)00861-X [14] 张在兴, 周琴, 张凯, 等. 切削角度对切削齿温度分布的影响分析 [J]. 石油机械,2021,49(12):17-26. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.12.003ZHANG Zaixing, ZHOU Qin, ZHANG Kai, et al. Analysis of effect of cutting angle on temperature distribution of cutting gear [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2021,49(12):17-26. doi: 10.16082/j.cnki.issn.1001-4578.2021.12.003 [15] 邓楚键, 何国杰, 郑颖人. 基于M-C准则的D-P系列准则在岩土工程中的应用研究 [J]. 岩土工程学报,2006,28(6):735-739. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.06.011DENG Chujian, HE Guojie, ZHENG Yingren. Studies on Drucker-Prager yield criterions based on M-C yield criterion and application in geotechnical engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2006,28(6):735-739. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.06.011 [16] 袁小平, 刘红岩, 王志乔. 基于Drucker-Prager准则的岩石弹塑性损伤本构模型研究 [J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(4):1103-1108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.021YUAN Xiaoping, LIU Hongyan, WANG Zhiqiao. Study of elastoplastic damage constitutive model of rocks based on Drucker-Prager criterion [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(4):1103-1108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.021 [17] CHEN S L, KHLEFAT Y, CLEBOSKI C, et al. A new method of backup-cutter layout to extend bit life without sacrificing rate of penetration [J]. SPE Drilling & Completion,2018,33(2):115-129. doi: 10.2118/187644-PAArticlehistory [18] 梁尔国, 李子丰, 邹德永. PDC切削齿受力的试验研究 [J]. 石油机械,2009,37(11):12-15.LIANG Erguo, LI Zifeng, ZOU Deyong. Experimental study on force of PDC cutter [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2009,37(11):12-15. [19] 李勇. PDC钻头切削齿破岩过程热分析与仿真[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2012.LI Yong. Thermal analysis and simulation of rock breaking process of PDC bit cutter [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2012. -



 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
