Model and experimental verification of grinding surface roughness based on acoustic emission
-
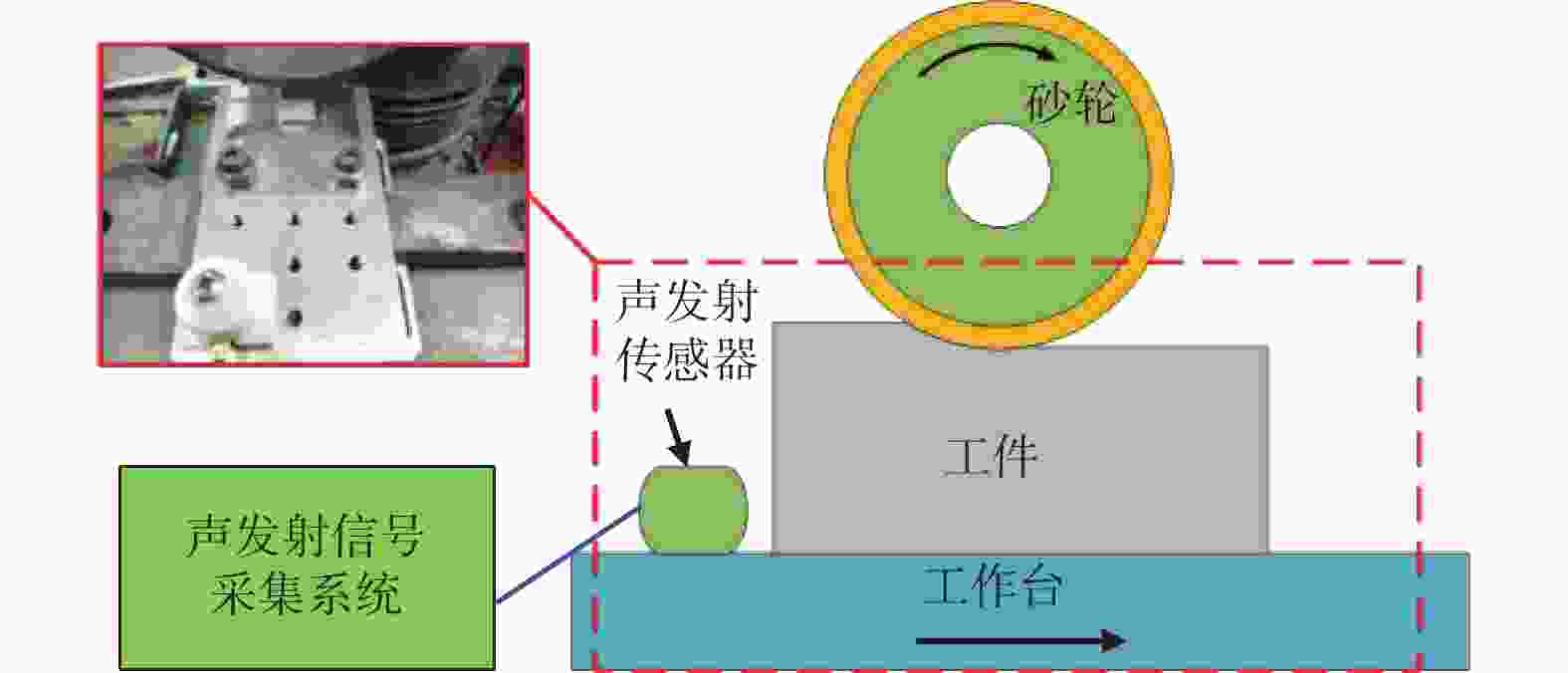
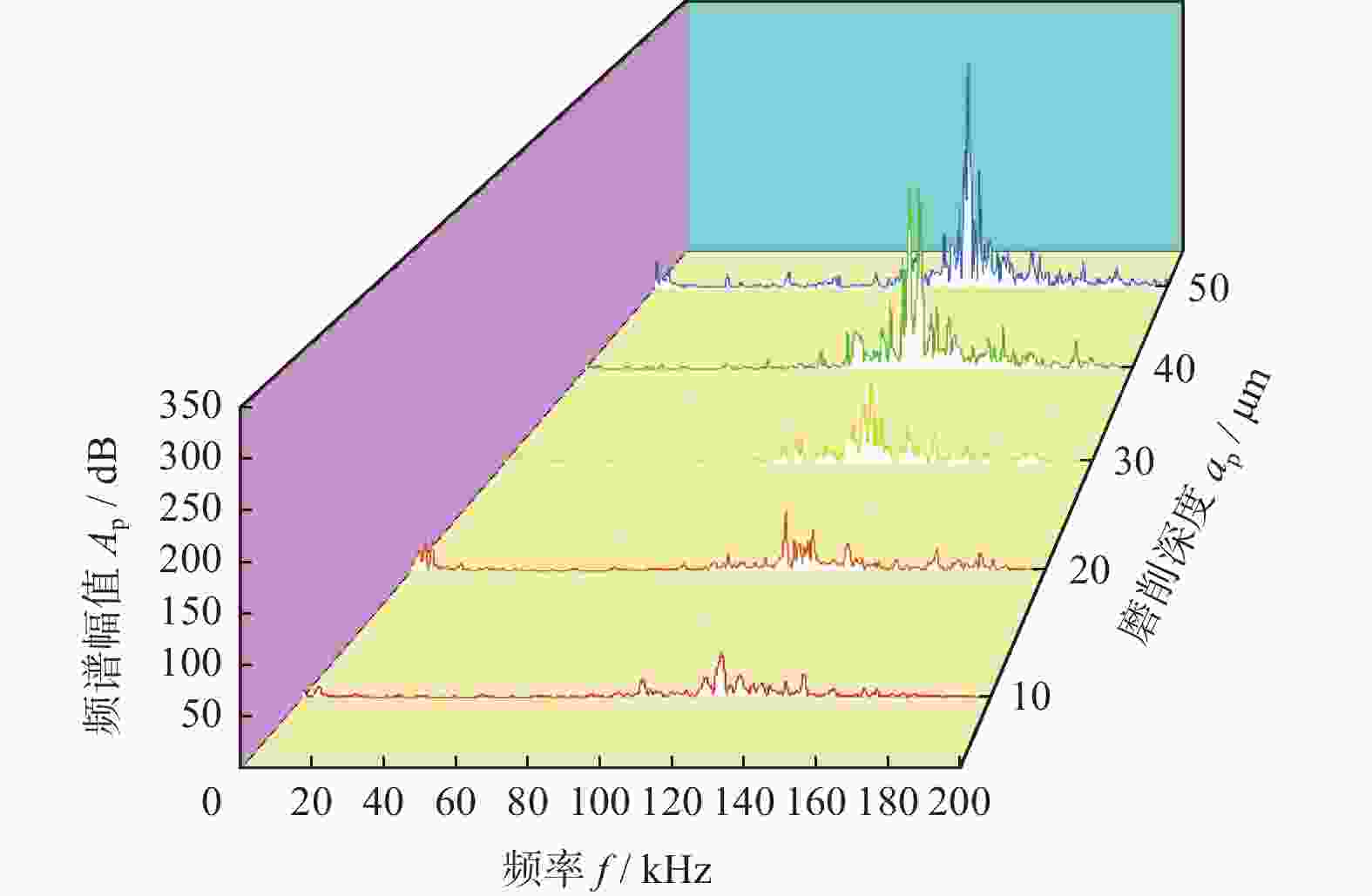
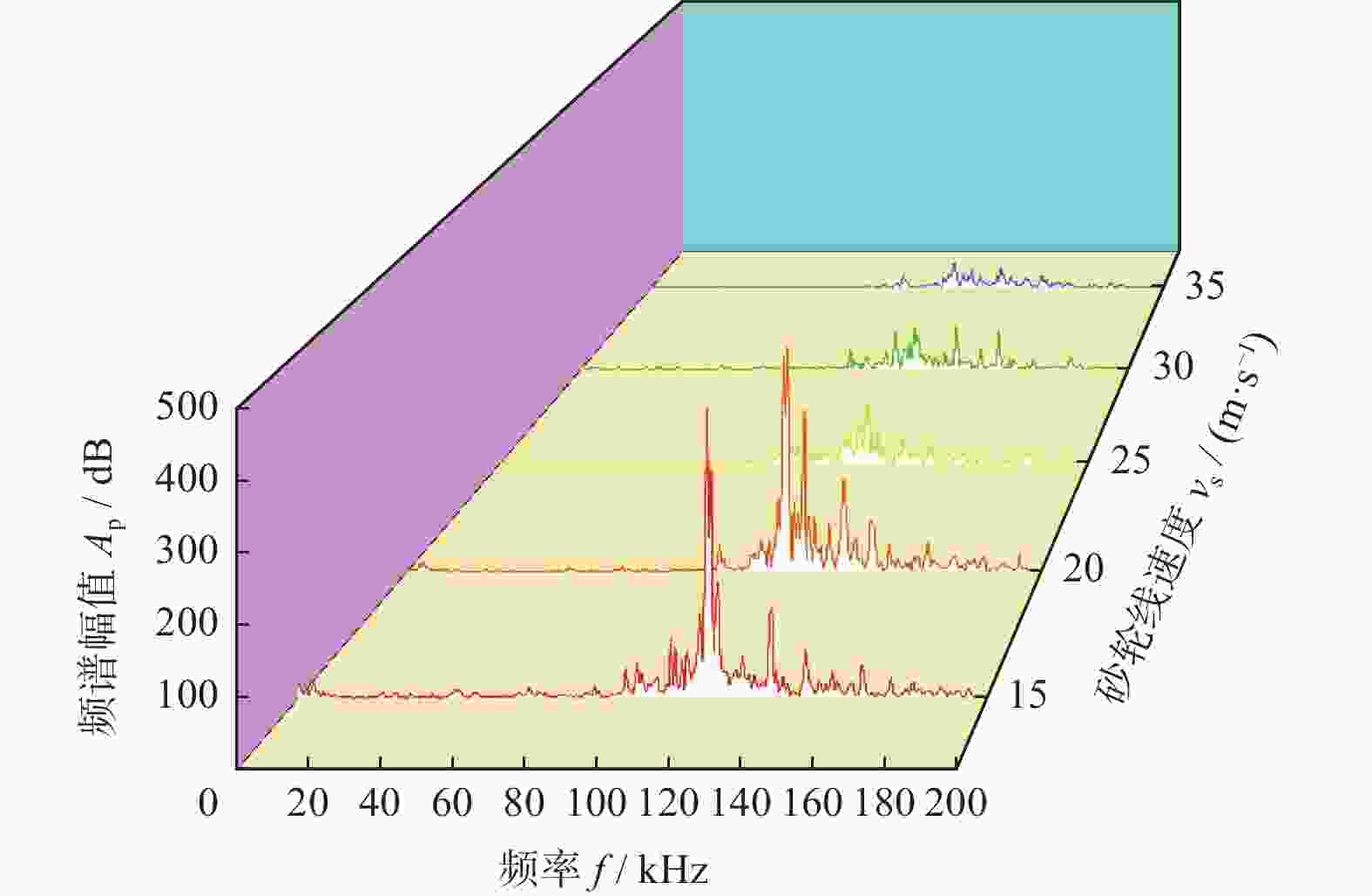
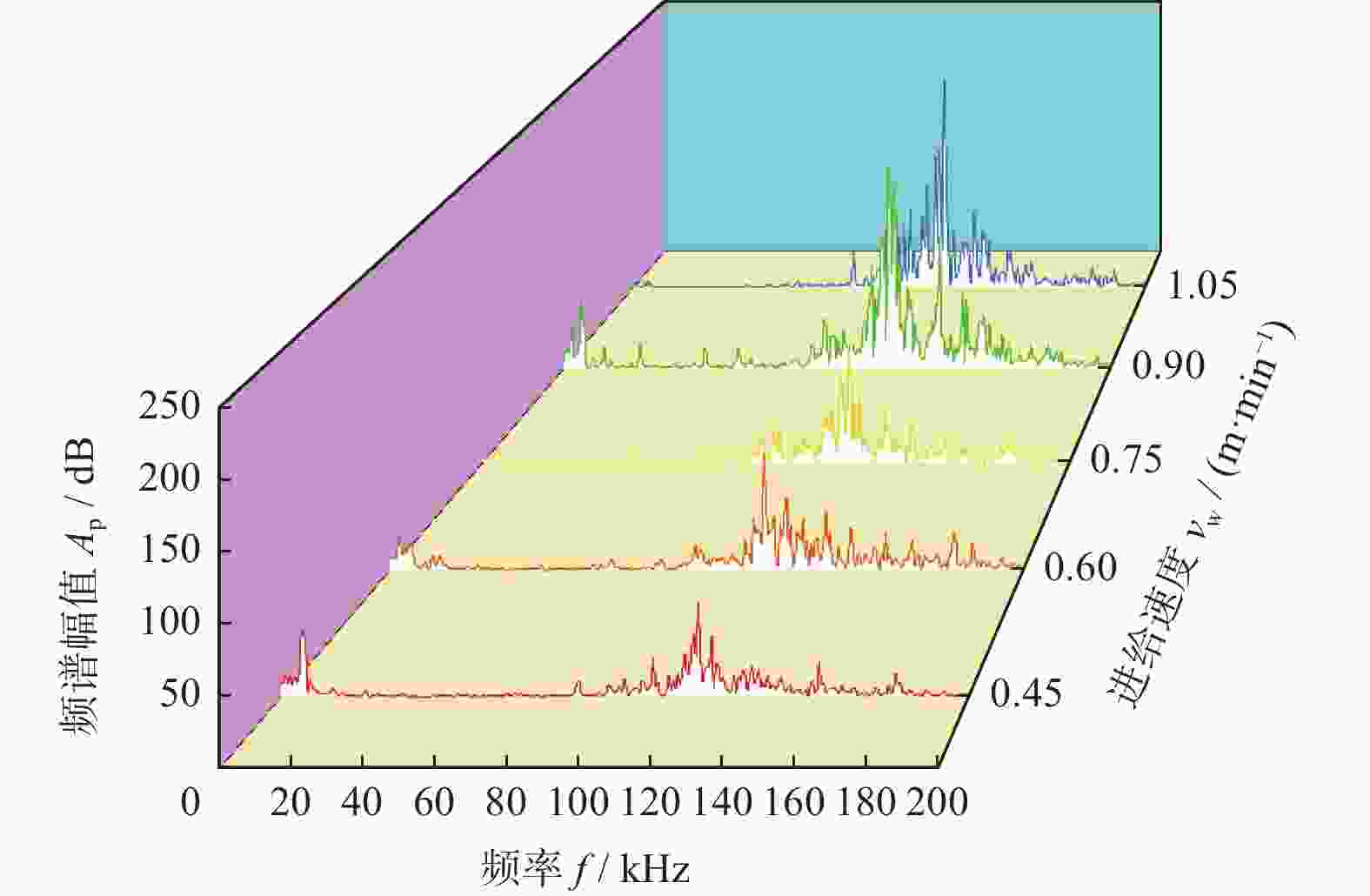
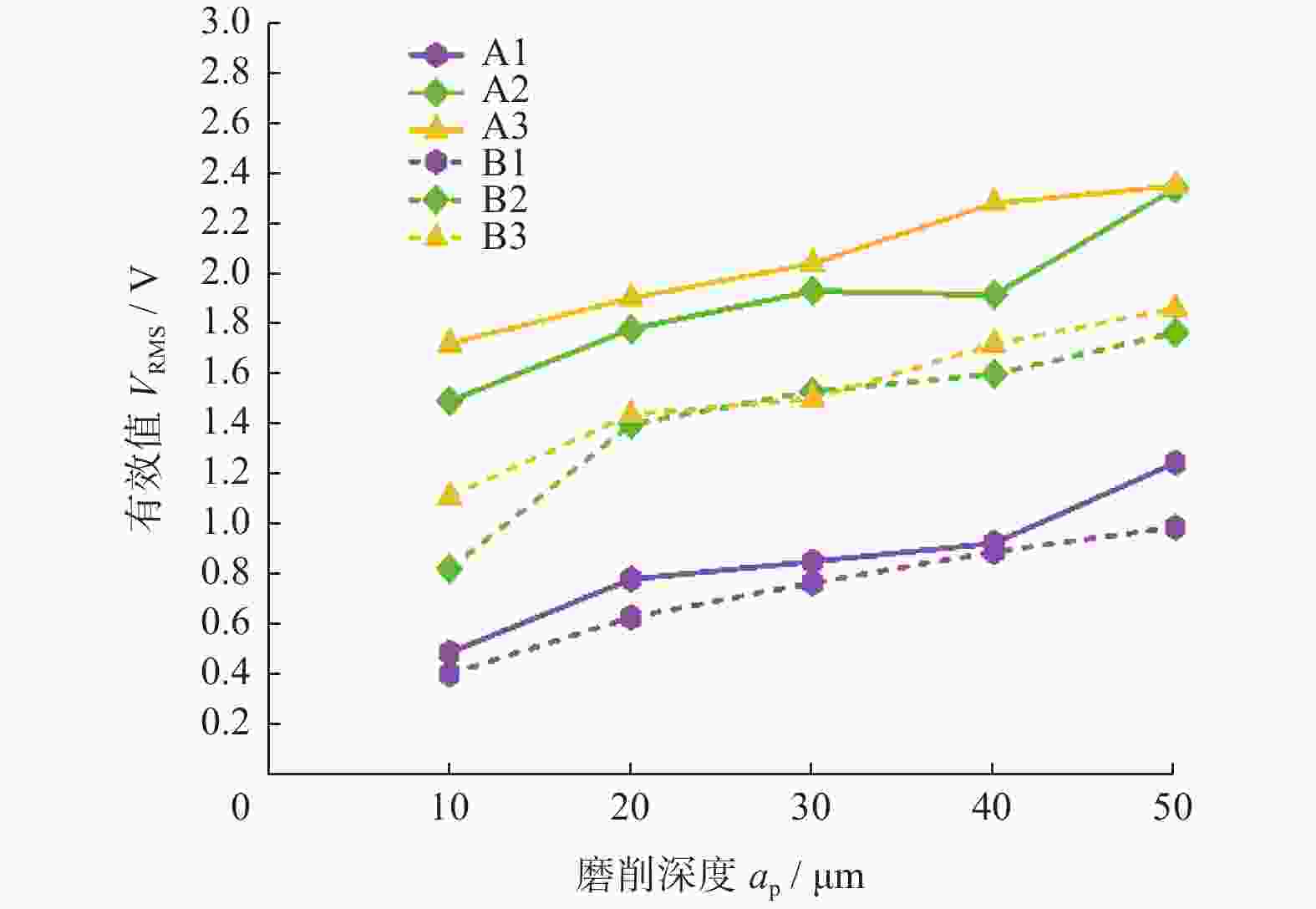
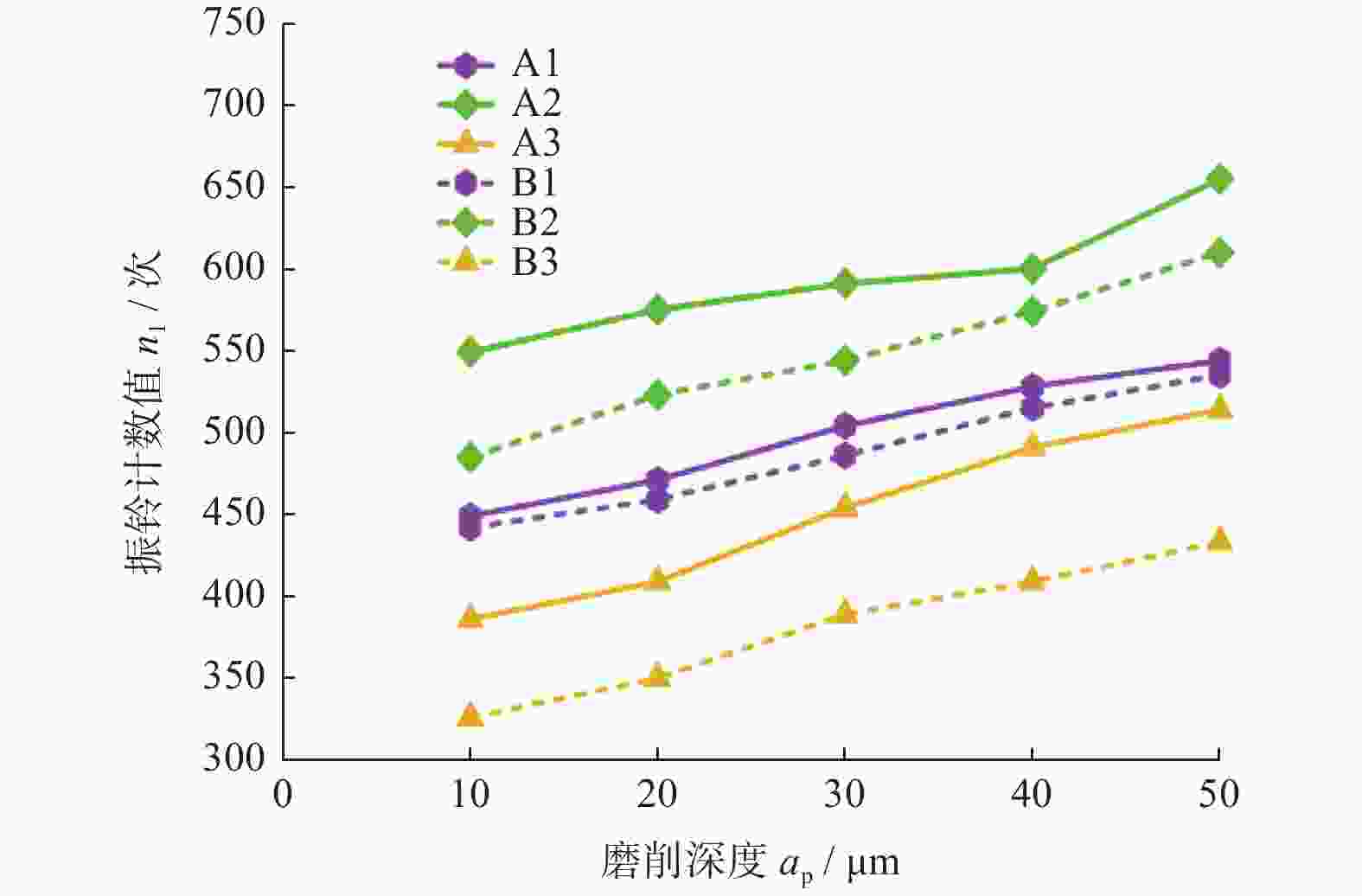
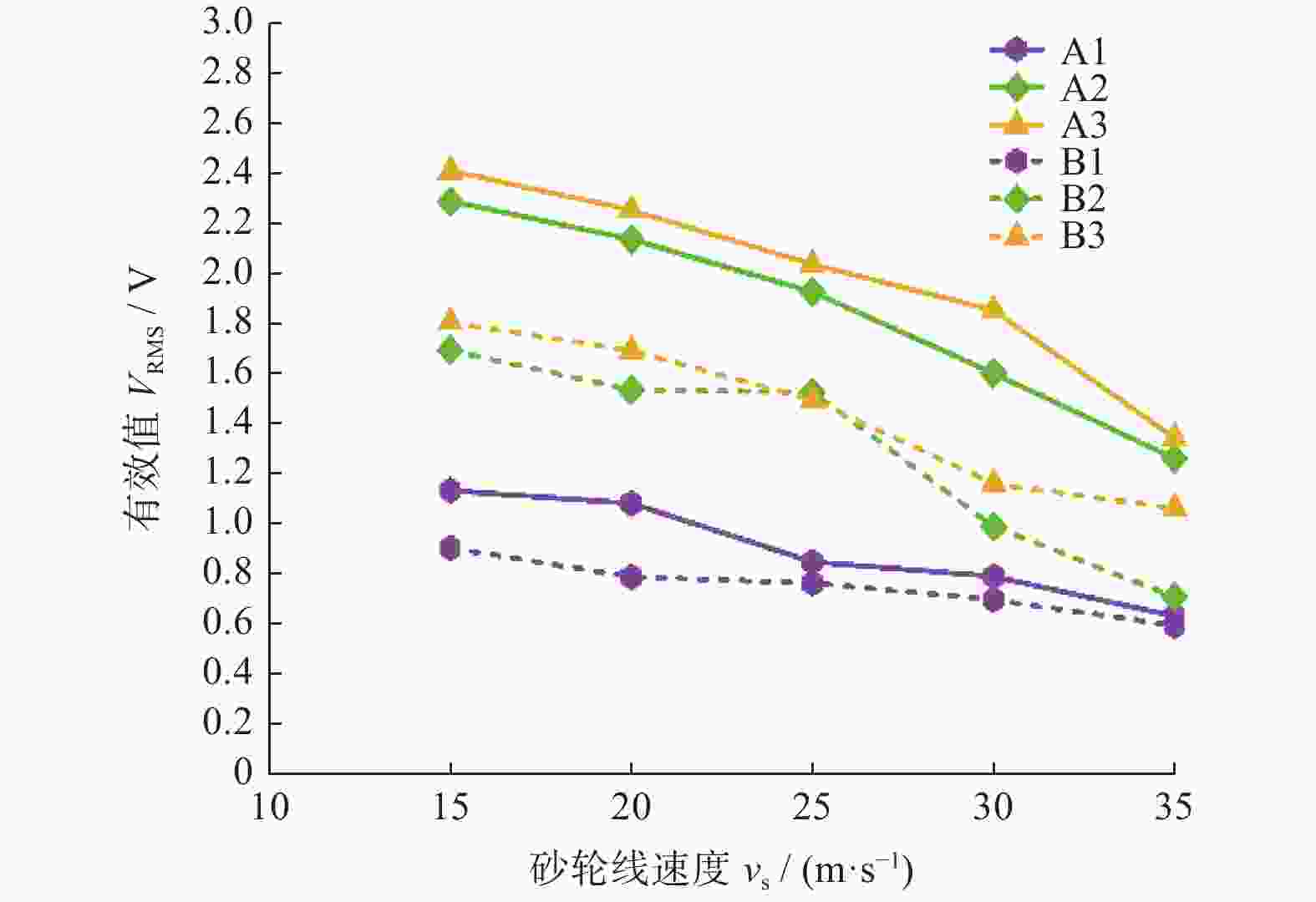
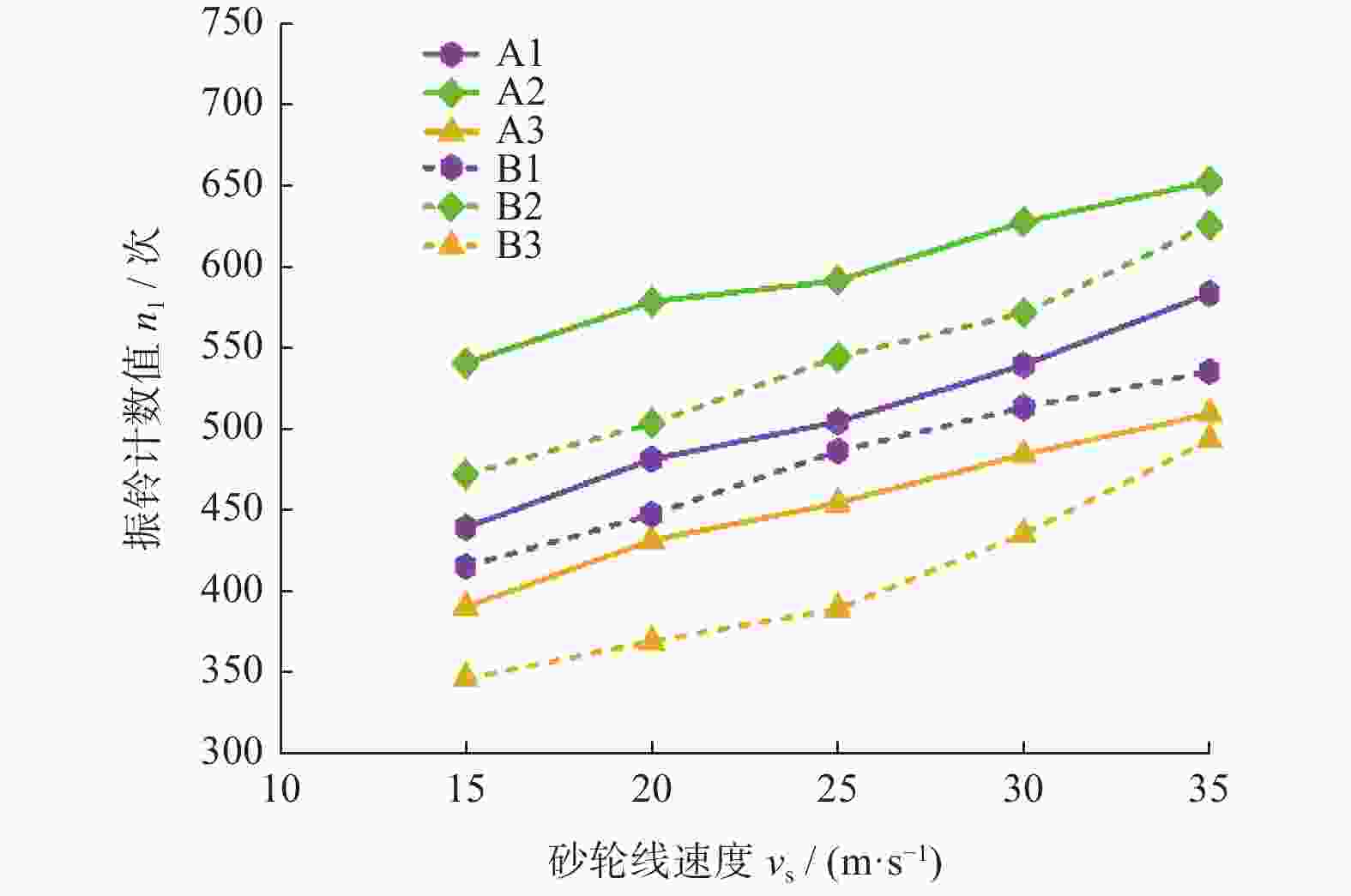
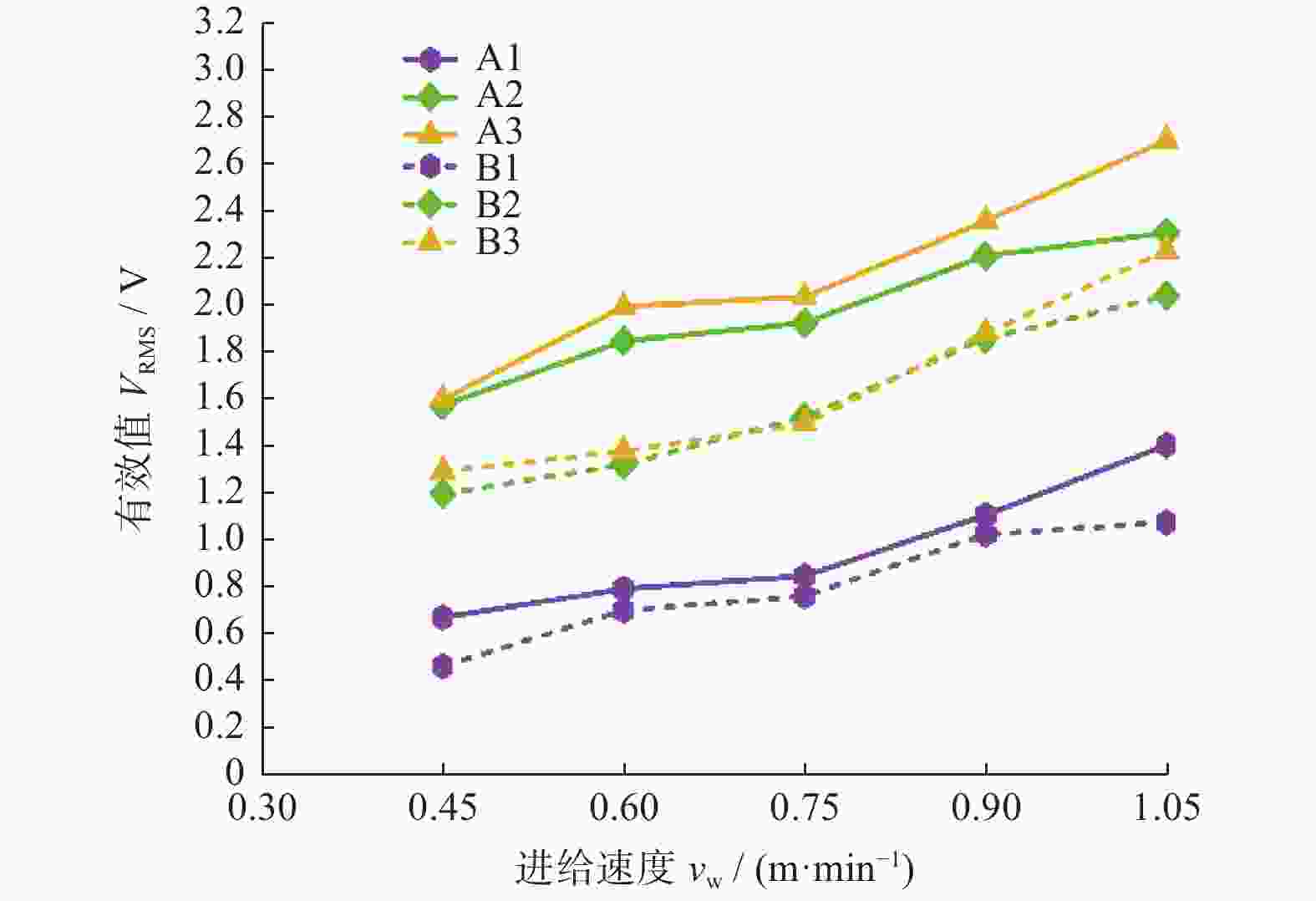
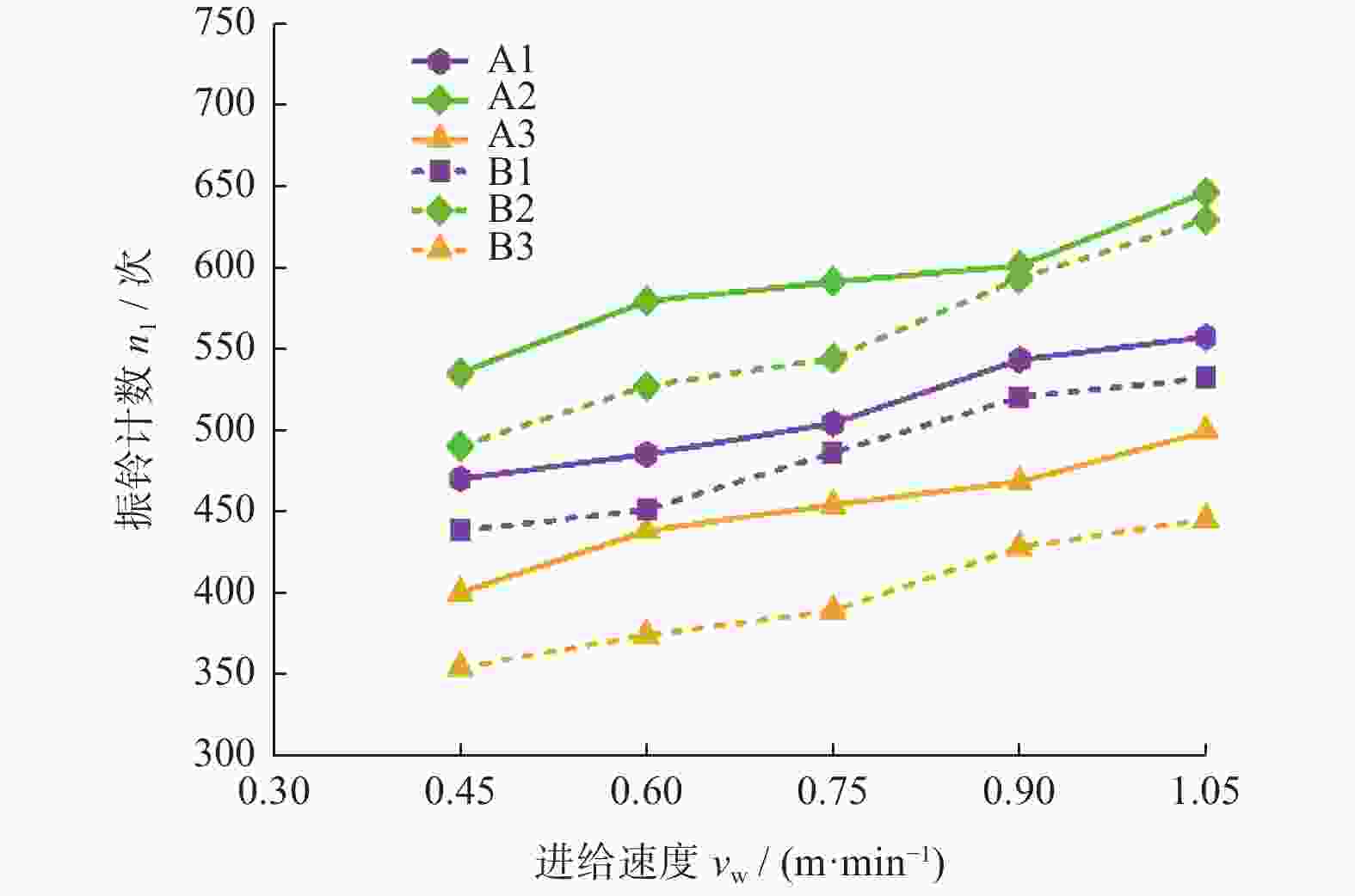
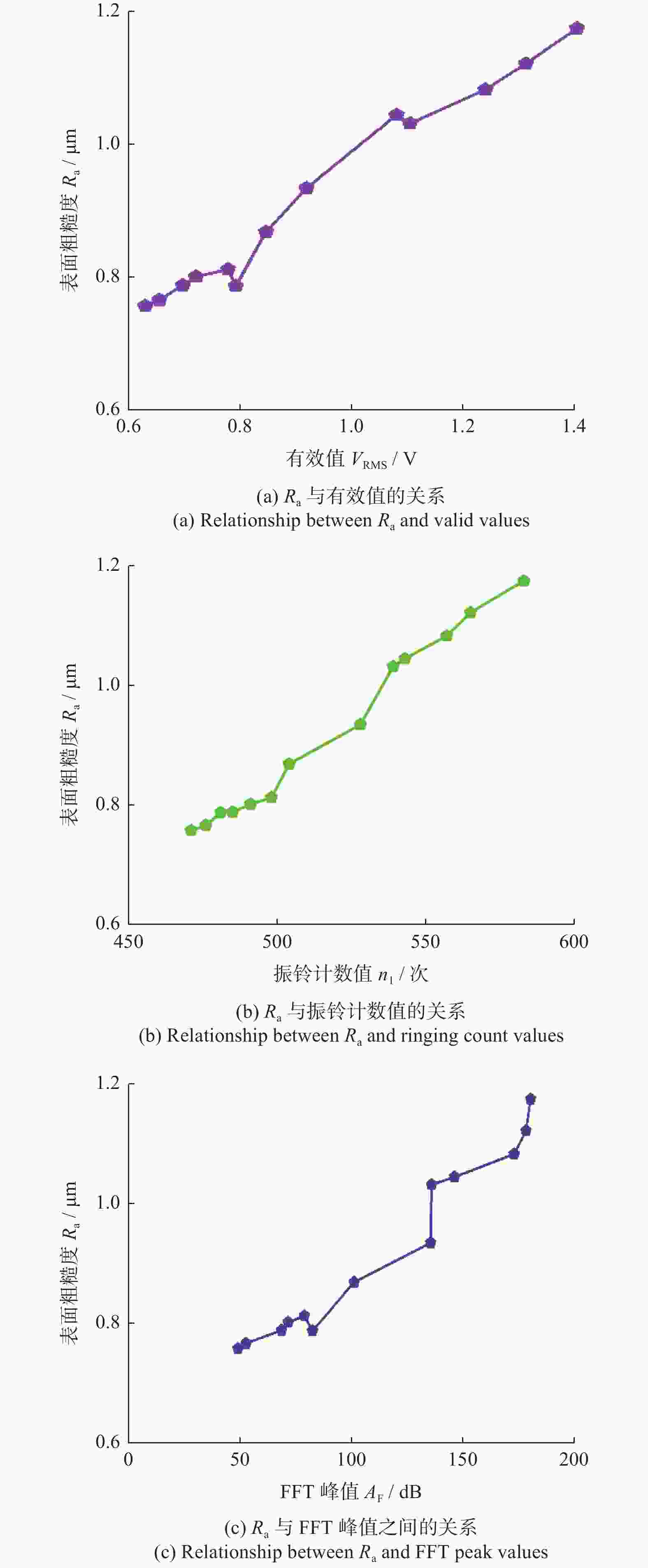
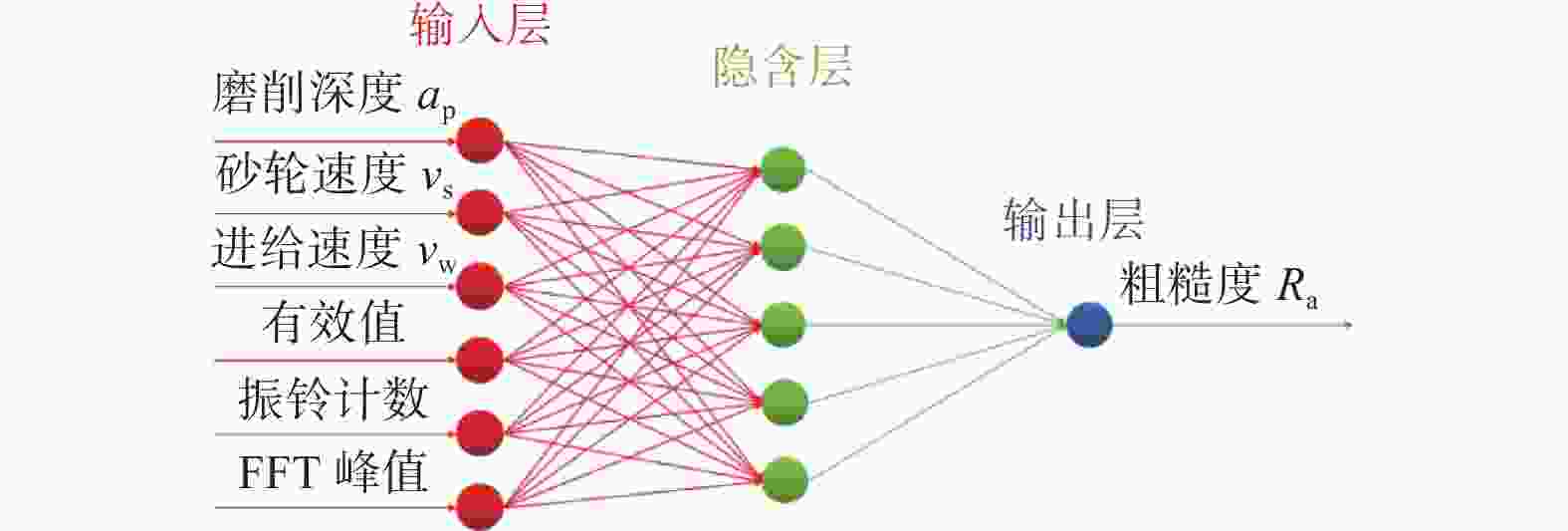
摘要: 为实现对磨削过程中表面粗糙度的预测,在磨削过程中增加声发射装置,采用AE信号监测磨削状态,分析AE信号特征参量和频谱随磨削深度ap、砂轮速度vs和进给速度vw等磨削参数变化的规律。结果表明:随着ap和vw的增大,AE信号特征参量的有效值和振铃计数值都增大,AE信号的主要能量集中频谱在90~140 kHz,对应的频谱幅值呈逐渐增大趋势;而随着vs逐渐增大,AE信号特征参量的有效值逐渐减小,振铃计数值逐渐增大,频段对应的频谱幅值呈逐渐减小的趋势。对数据进一步分析,得出AE信号特征参量与加工表面粗糙度的对应关系,为表面粗糙度预测模型建立提供样本。利用基于BP神经网络的多信息融合算法对AE信号的多种特征参量信息进行合理融合,建立基于AE信号的磨削加工表面粗糙度多信息融合预测模型,该模型可在实际生产中预测磨削表面粗糙度。Abstract: To predict the surface roughness in the grinding process, an acoustic emission device (AE) was incorporated into the grinding process to monitor the grinding state using AE signals. The variations in AE signal characteristic parameters and frequency spectrum with respect to grinding parameters, such as grinding depth ap, grinding wheel speed vs and feed speed vw were analyzed. The results show that as ap and vw increase, the effective values and ringing count values of the AE signal's characteristic parameters both increase. The main energy concentration spectrum of the AE signal is between 90 and 140 kHz, and the corresponding spectrum amplitude shows a gradual increasing trend. With the gradual increase of vs, the effective value of AE signal characteristic parameters gradually decreases, the ringing count value gradually increases, and the spectral amplitude corresponding to the frequency band shows a gradual decreasing trend. Further data analysis reveals the corresponding relationship between AE signal characteristic parameters and machining surface roughness, providing a sample for establishing a surface roughness prediction model. The multi-information fusion algorithm, based on a BP neural network, is used to reasonably fuse various characteristic parameters of the AE signal. And the multi-information fusion prediction model for grinding surface roughness based on AE signal was established. After experimental verification, this model can predict the roughness of the ground surface in actual production.
-
Key words:
- grinding process /
- acoustic emission(AE) /
- surface roughness /
- multi-information fusion
-
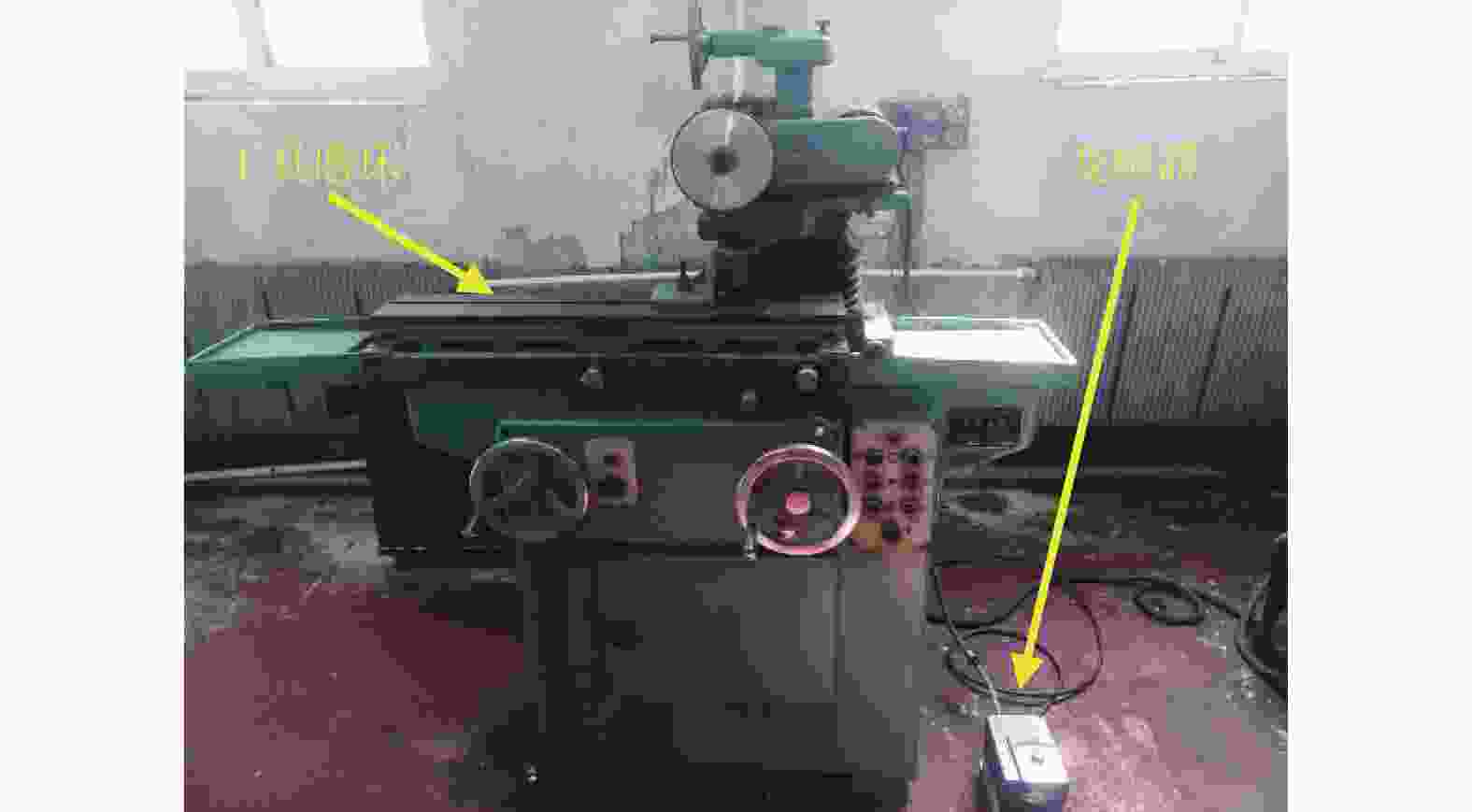
表 1 单因素实验参数
Table 1. Single factor experimental parameters
编号 磨削深度
ap / μm砂轮线速度
vs / (m·s−1)工件进给速度
vw / (m·min−1)1 10,20,30,40,50 25 0.75 2 30 15,20,25,30,35 0.75 3 30 25 0.45,0.60,0.75,0.90,1.05 表 2 表面粗糙度预测模型的测试样本数据
Table 2. Test sample data of surface roughness prediction model
样本号 ap
/ μmvs
/ (m·s−1)vw
/ (m·min−1)有效值 VRMS / V 振铃
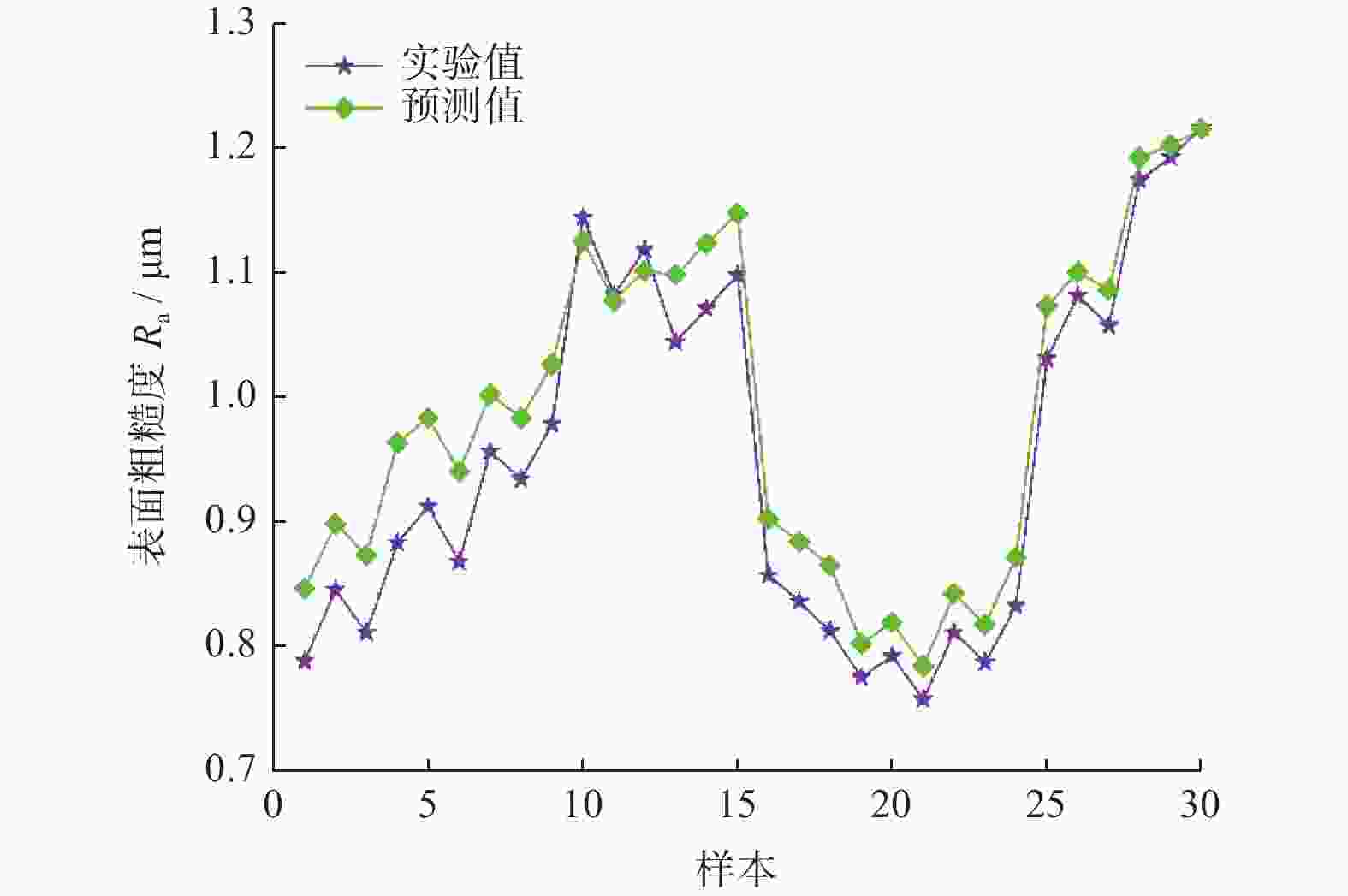
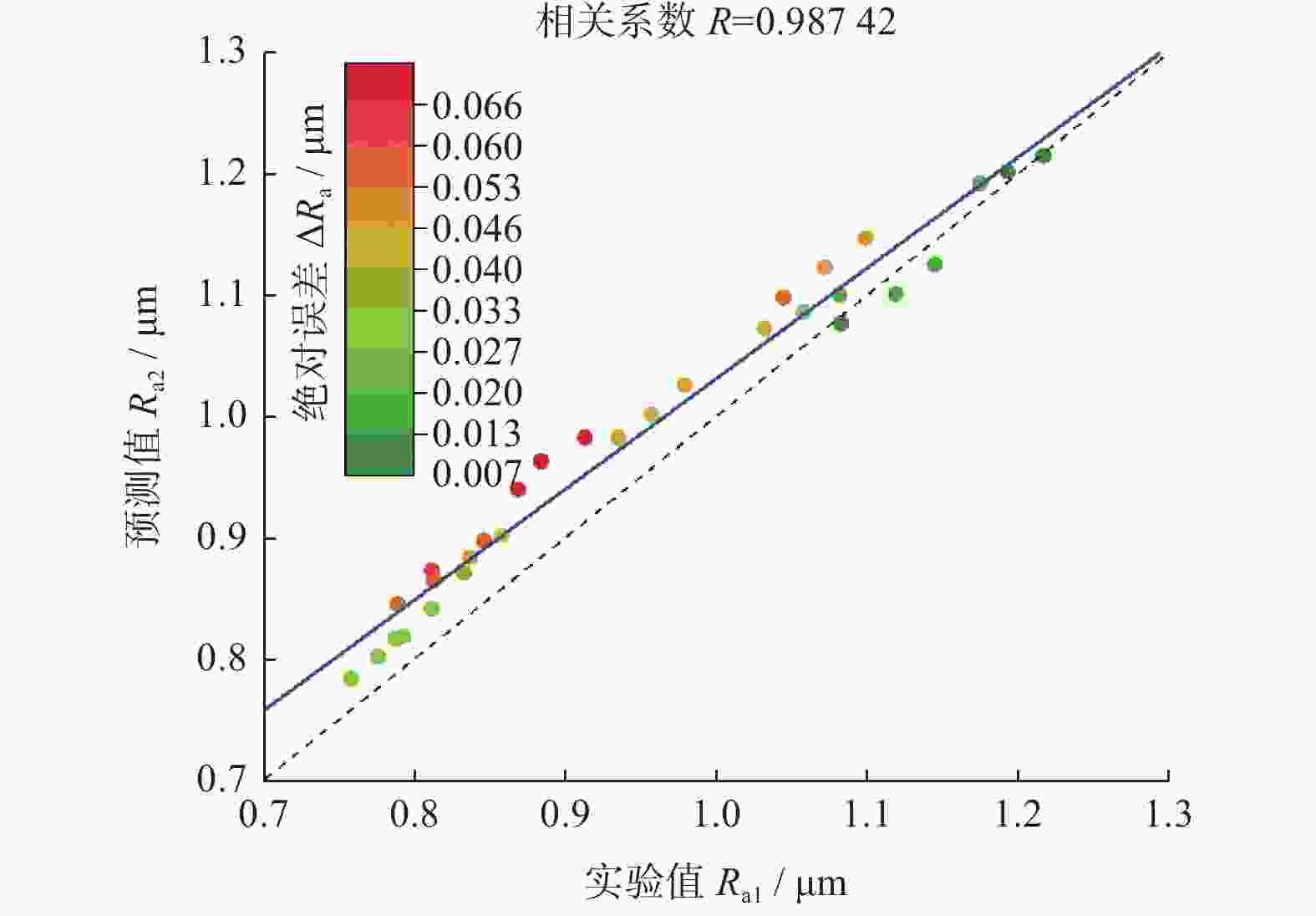
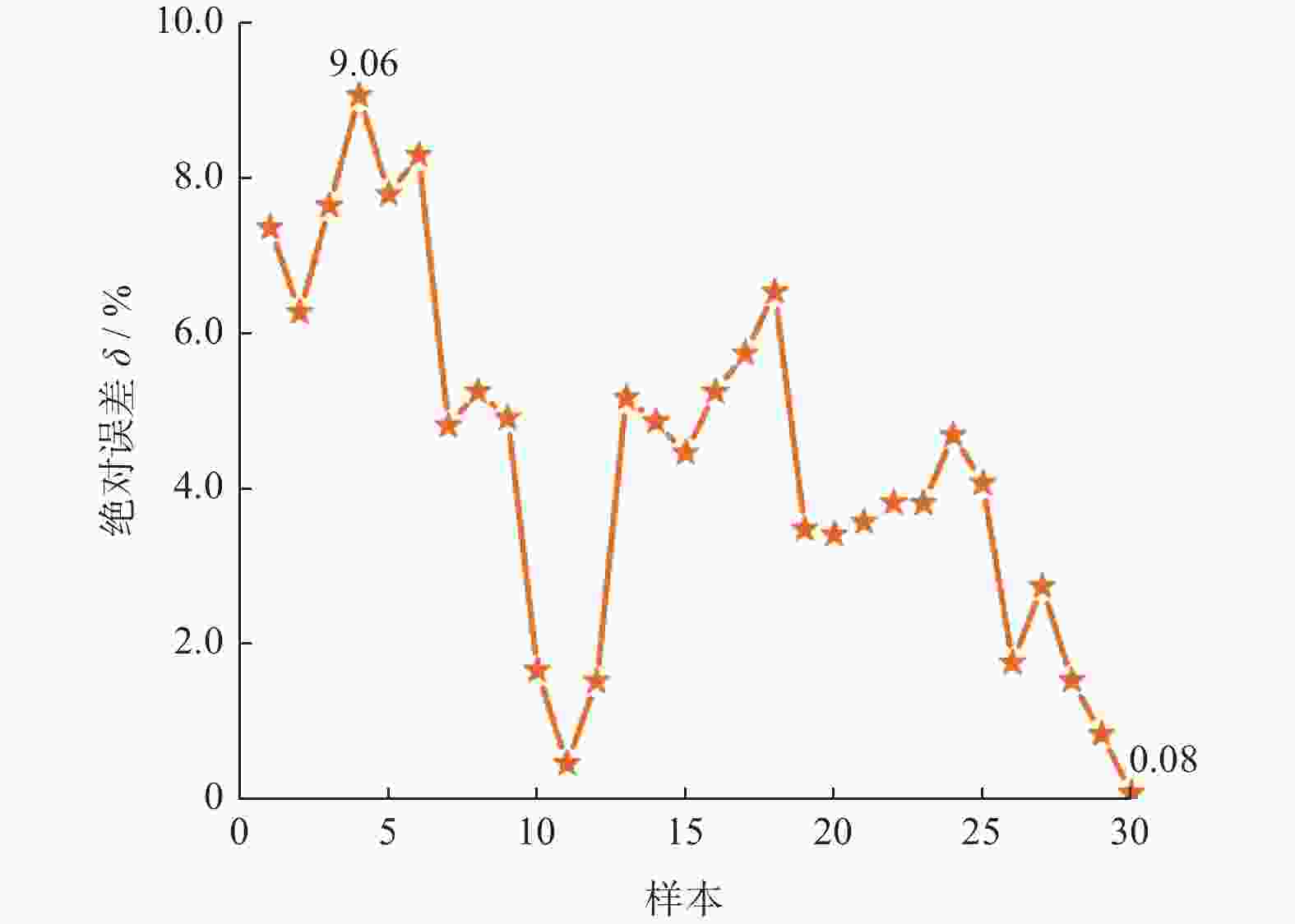
计数值 n1 / 次FFT峰值 AF / dB 实验值 Ra1 / μm 预测值 Ra2 / μm 1 20 25 0.75 7.765 471 68.329 0.788 0.831 2 20 25 0.75 9.212 496 94.135 0.845 0.884 3 20 25 0.75 8.499 483 81.574 0.811 0.858 4 30 25 0.75 9.145 514 115.232 0.883 0.949 5 30 25 0.75 9.838 525 127.084 0.912 0.971 6 30 25 0.75 8.458 504 100.918 0.868 0.926 7 40 25 0.75 9.862 540 147.075 0.956 0.986 8 40 25 0.75 9.183 528 135.207 0.934 0.967 9 40 25 0.75 10.605 554 161.422 0.978 1.009 10 50 25 0.75 13.821 570 206.153 1.144 1.116 11 50 25 0.75 12.394 544 180.042 1.082 1.068 12 50 25 0.75 13.157 558 193.296 1.118 1.092 13 30 20 0.75 10.802 481 145.916 1.044 1.076 14 30 20 0.75 11.477 495 160.353 1.071 1.101 15 30 20 0.75 12.212 506 172.231 1.098 1.124 16 30 30 0.75 9.231 563 104.284 0.857 0.905 17 30 30 0.75 8.572 550 91.832 0.836 0.885 18 30 30 0.75 7.878 539 78.545 0.812 0.864 19 30 35 0.75 7.027 595 61.518 0.775 0.807 20 30 35 0.75 7.709 609 74.732 0.792 0.827 21 30 35 0.75 6.292 583 48.757 0.757 0.785 22 30 25 0.6 8.591 495 96.334 0.811 0.851 23 30 25 0.6 7.917 485 82.196 0.787 0.823 24 30 25 0.6 9.352 506 110.598 0.832 0.881 25 30 25 0.9 11.043 543 135.637 1.031 1.068 26 30 25 0.9 12.408 570 159.955 1.081 1.103 27 30 25 0.9 11.711 558 148.391 1.057 1.086 28 30 25 1.05 14.037 557 172.682 1.174 1.198 29 30 25 1.05 14.786 570 184.636 1.192 1.214 30 30 25 1.05 15.501 584 197.579 1.216 1.229 -
[1] ZHENG X H, LIU Z Q, GUO G Q, et al. Experimental research of grinding TC4 titanium alloy using green silicon carbide wheel [J]. Key Engineering Materials,2011,487:121-125. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.487.121 [2] HUANG S T, YU X L. A study of grinding forces of SiCp/Al composites [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2018,94(9/10/11/12):3633-3639. doi: 10.1007/s00170-017-1115-2 [3] PAN Y, WANG Y, ZHOU P, et al. Activation functions selection for BP neural network model of ground surface roughness [J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,2020,31:1825-1836. doi: 10.1007/s10845-020-01538-5 [4] 陈明, 朱明武. 声发射在磨削难加工材料中的应用 [J]. 南京理工大学学报,1995(3):193-197. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.1995.03.001CHEM Ming, ZHU Mingwu. Application of acoustic emission signal in grinding difficult-to-machine materials [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,1995(3):193-197. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.1995.03.001 [5] 刘贵杰, 巩亚东, 王宛山. 声发射技术在磨削加工监测中的应用 [J]. 机械工程师,2001(12):4-6.LIU Guijie, GONG Yadong, WANG Wanshan. Applications of acoustic emission technology in monitoring of grinding processes [J]. Mechanical Engineer,2001(12):4-6. [6] DING N, ZHAO C L, LUO X C, et al. An intelligent prediction of surface roughness on precision grinding [J]. Solid State Phenomena, 2017, 261: 221-225. [7] ARUN A, RAMESHKUMER K, UNNIKRISHNAN D, et al. Tool condition monitoring of cylindrical grinding process using acoustic emission sensor [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2018,5(5):11888-11899. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.02.162 [8] LIU H, XU S H, GE X M, et al. Automatic sedimentary microfacies identification from logging curves based on deep process neural network [J]. Cluster Computing,2019,22:12451-12457. doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-1656-z [9] HWEJU Z, ABOU-El-HOSSEIN K. Surface roughness prediction based on acoustic emission signals in high-precision diamond turning of rapidly solidified optical aluminum grade (RSA443) [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2020, 841: 363-368. [10] 郭力, 杜厚斌, 邓喻. 硬质合金PA30高速深磨过程中声发射信号特征的变化研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2017,37(3):35-39. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2017.3.0008GUO Li, DU Houbin, DENG Yu. Characteristic changes of acoustic emission(AE) signal during high speed deep grinding of cemented carbide PA30 [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2017,37(3):35-39. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2017.3.0008 [11] PANDIYAN V, CAESARENDRA W, TJAHJOWIDODO T, et al. In-process tool condition monitoring in compliant abrasive belt grinding process using support vector machine and genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2018,31:199-213. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.11.014 [12] MAHATA S, SHAKYA P, BABU N R. A robust condition monitoring methodology for grinding wheel wear identification using Hilbert Huang transform [J]. Precision Engineering,2021,70:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.01.009 [13] QI J, CHEN B, ZHANG D. Multi-information fusion-based belt condition monitoring in grinding process using the improved-Mahalanobis distance and convolutional neural networks [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2020,59:302-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.09.061 [14] WANG N, ZHANG G, REN L, et al. Vision and sound fusion-based material removal rate monitoring for abrasive belt grinding using improved LightGBM algorithm [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,66:281-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.04.014 [15] LIU C W, CHEN H C, LIN S C. Acoustic emission monitoring system for hard polishing of sapphire wafer [J]. Sensors and Materials,2019,31(9):2681-2689. doi: 10.18494/SAM.2019.2369 [16] WANG R, JIANG J C, PAN Y, et al. Prediction of impact sensitivity of nitro energetic compounds by neural network based on electrotopological-state indices [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,166(1):155-186. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.005 [17] GAO L, LI F, HUO P D, et al. Accurate prediction of the extrusion forming bonding reliability for heterogeneous welded sheets based on GA-BP neural network [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2021,117:765-774. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07797-7 -



 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
