Experimental study on creep-feed grinding burn of DD9 Nickel-based single crystal superalloy
-
摘要:
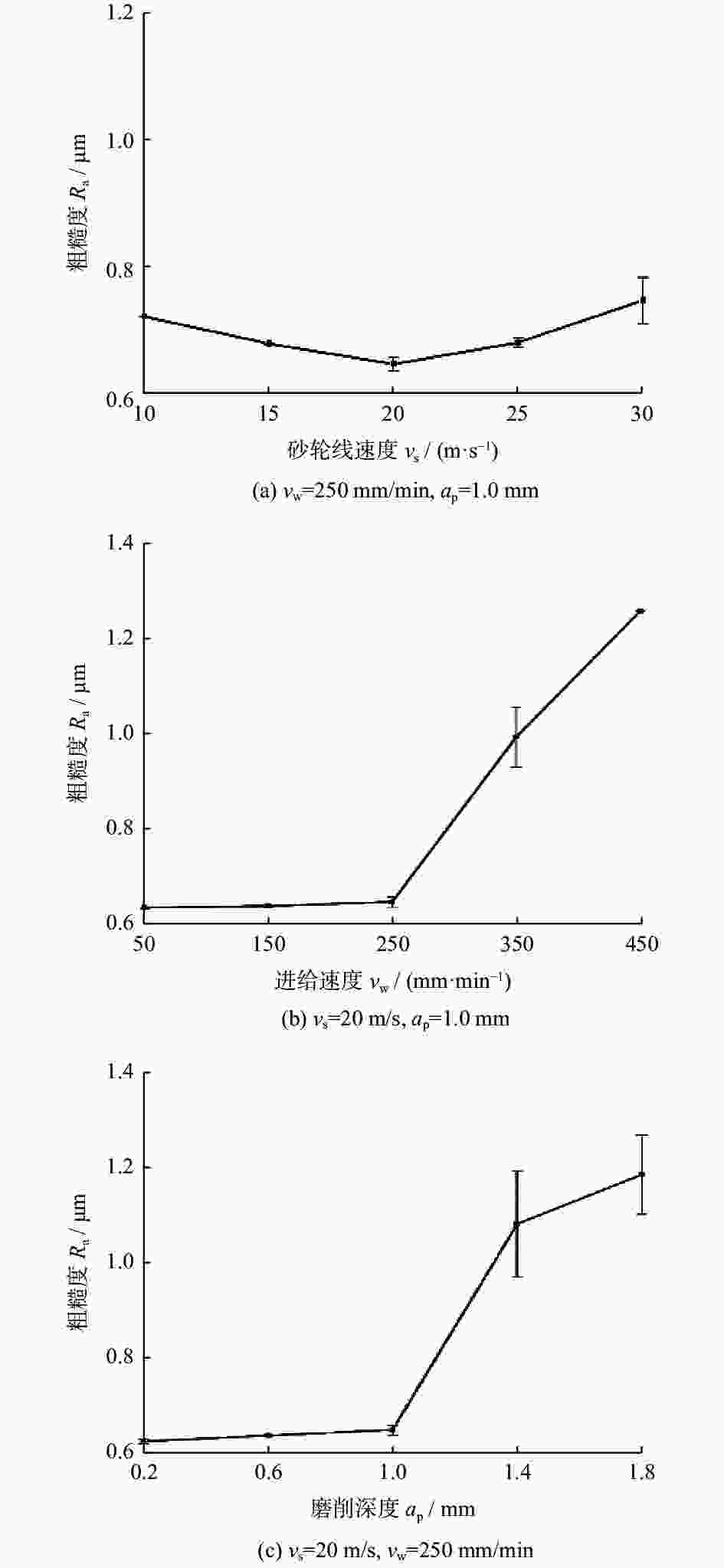
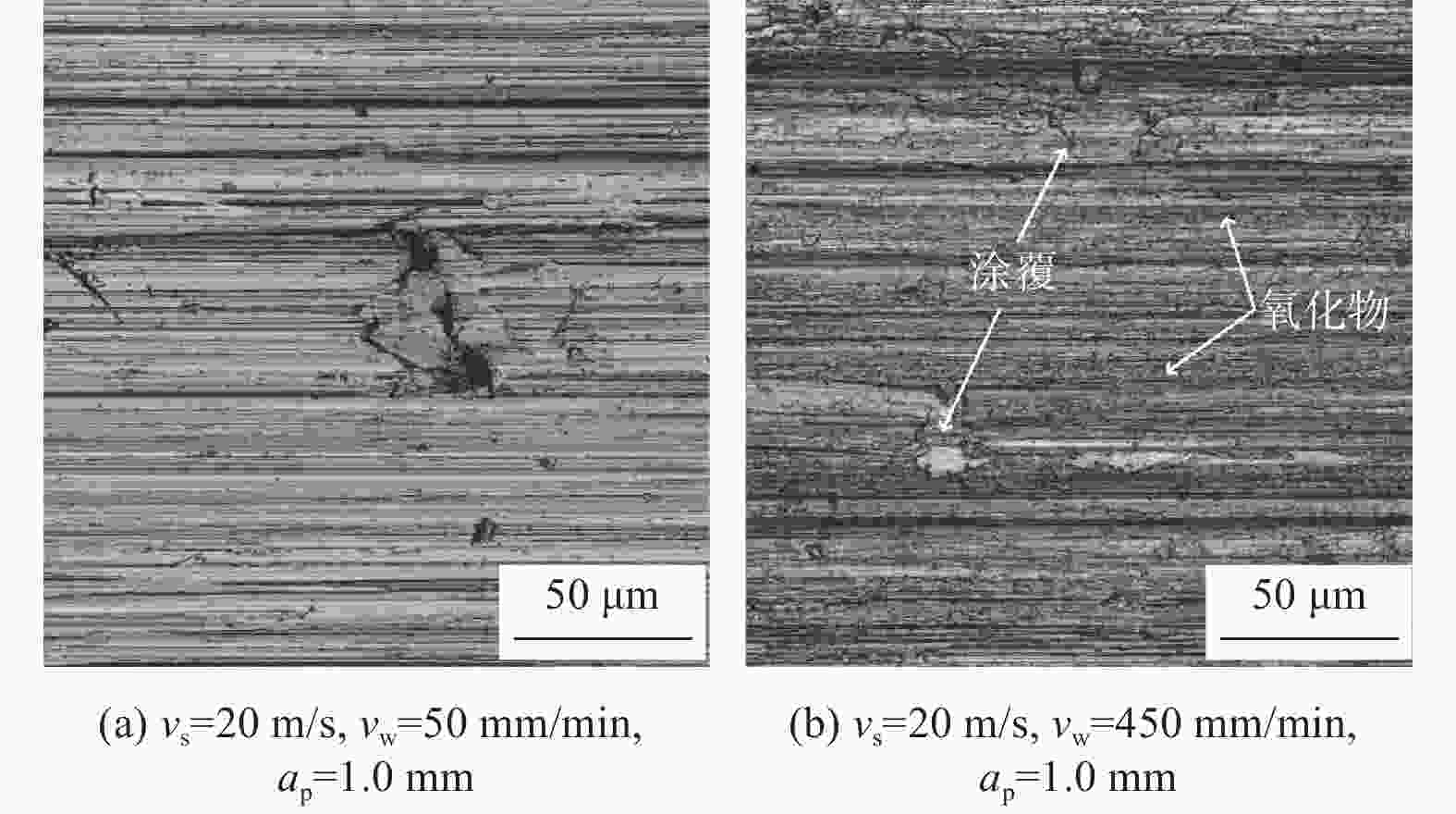
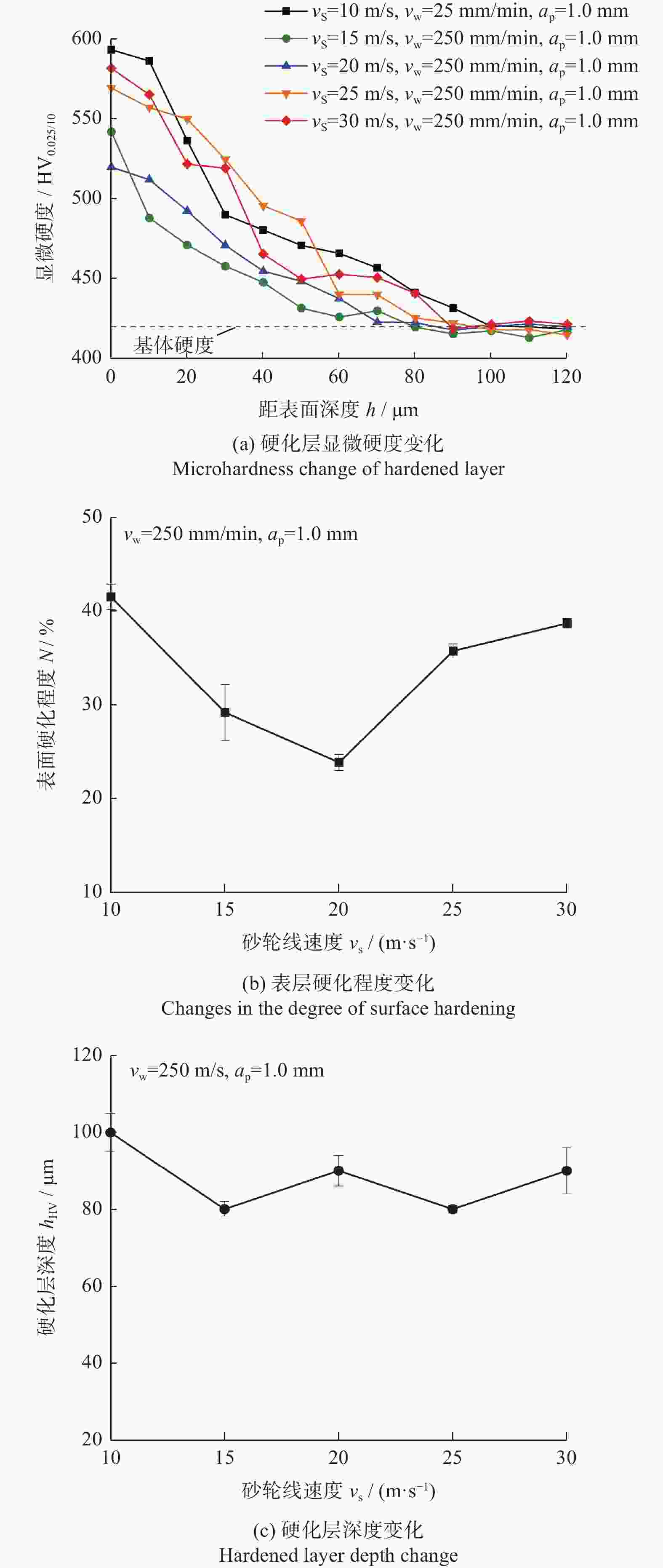
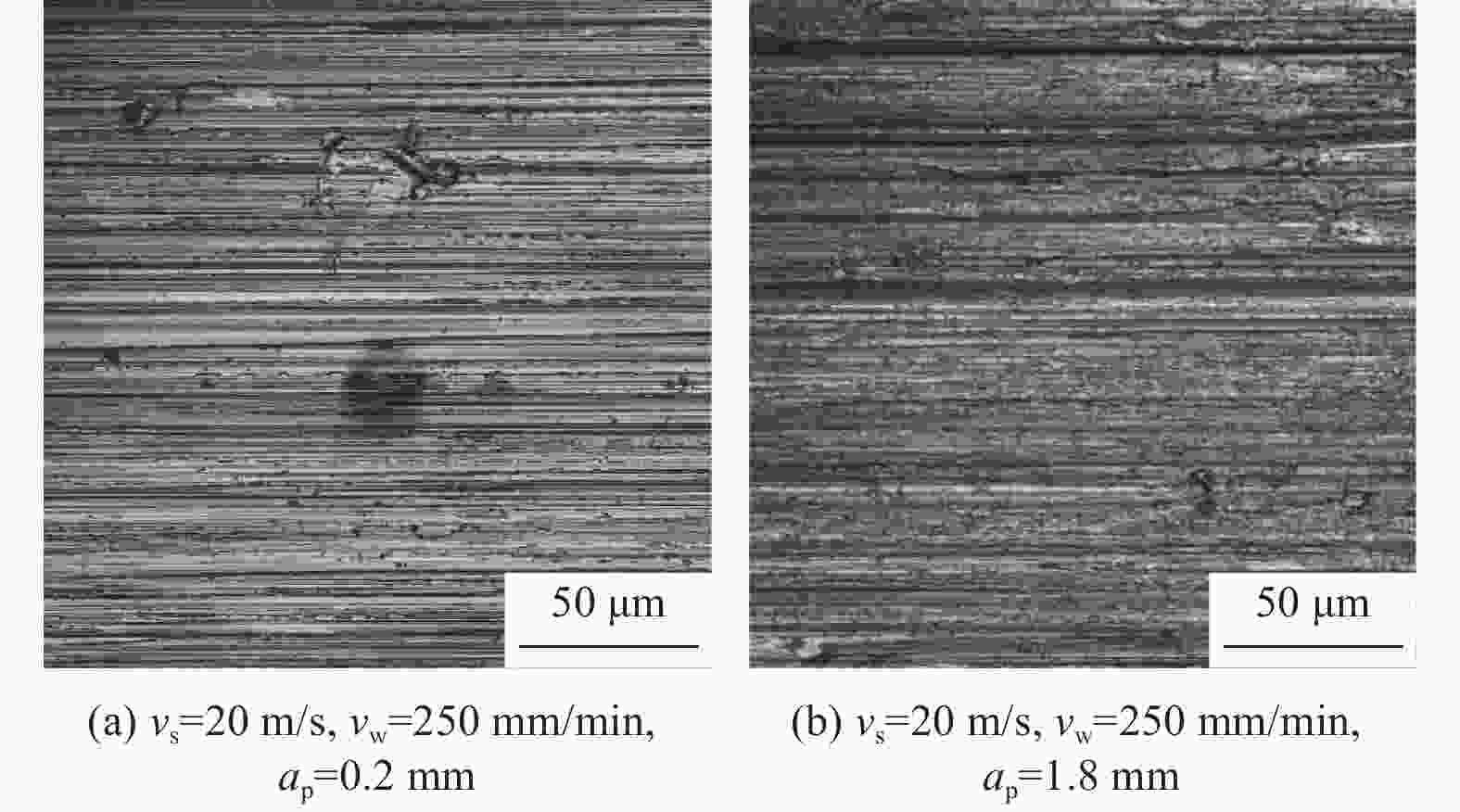
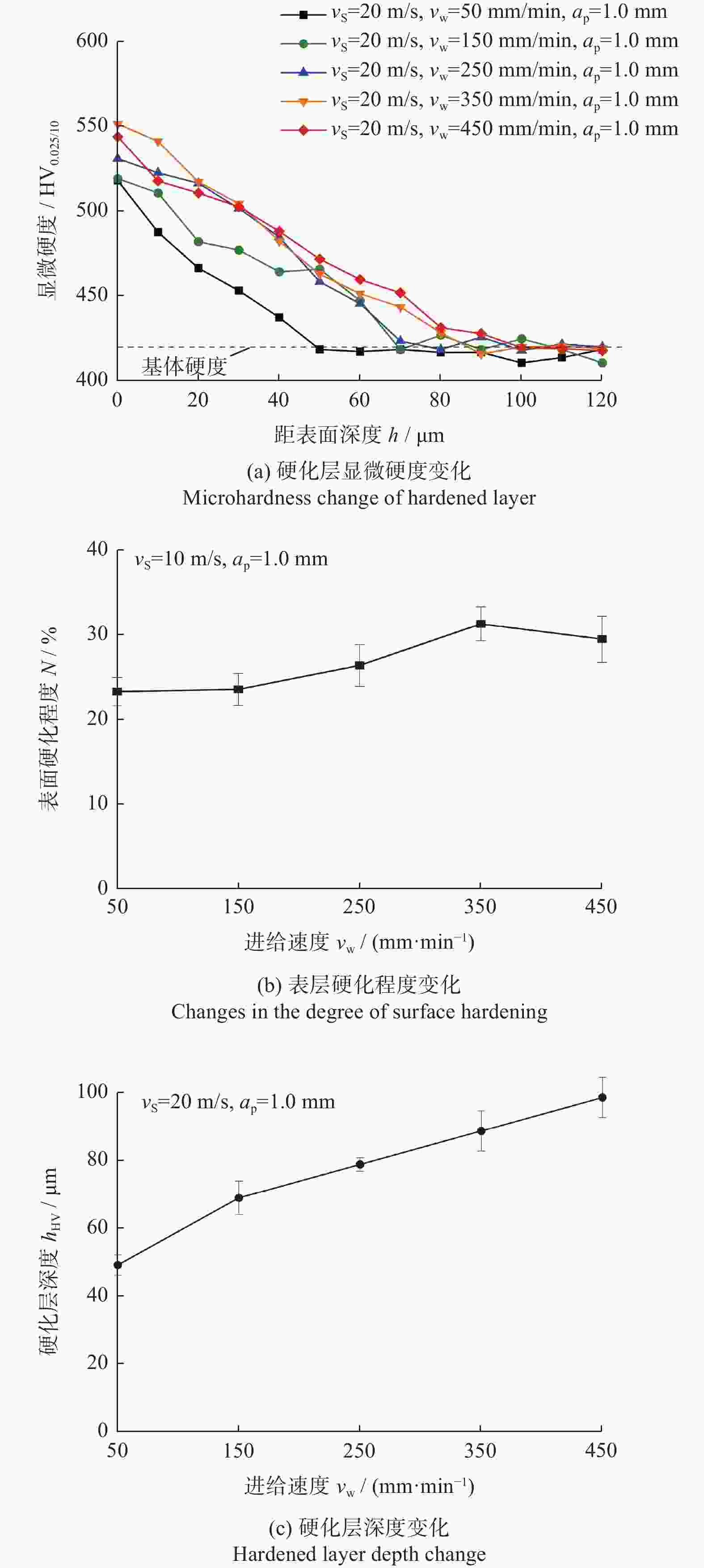
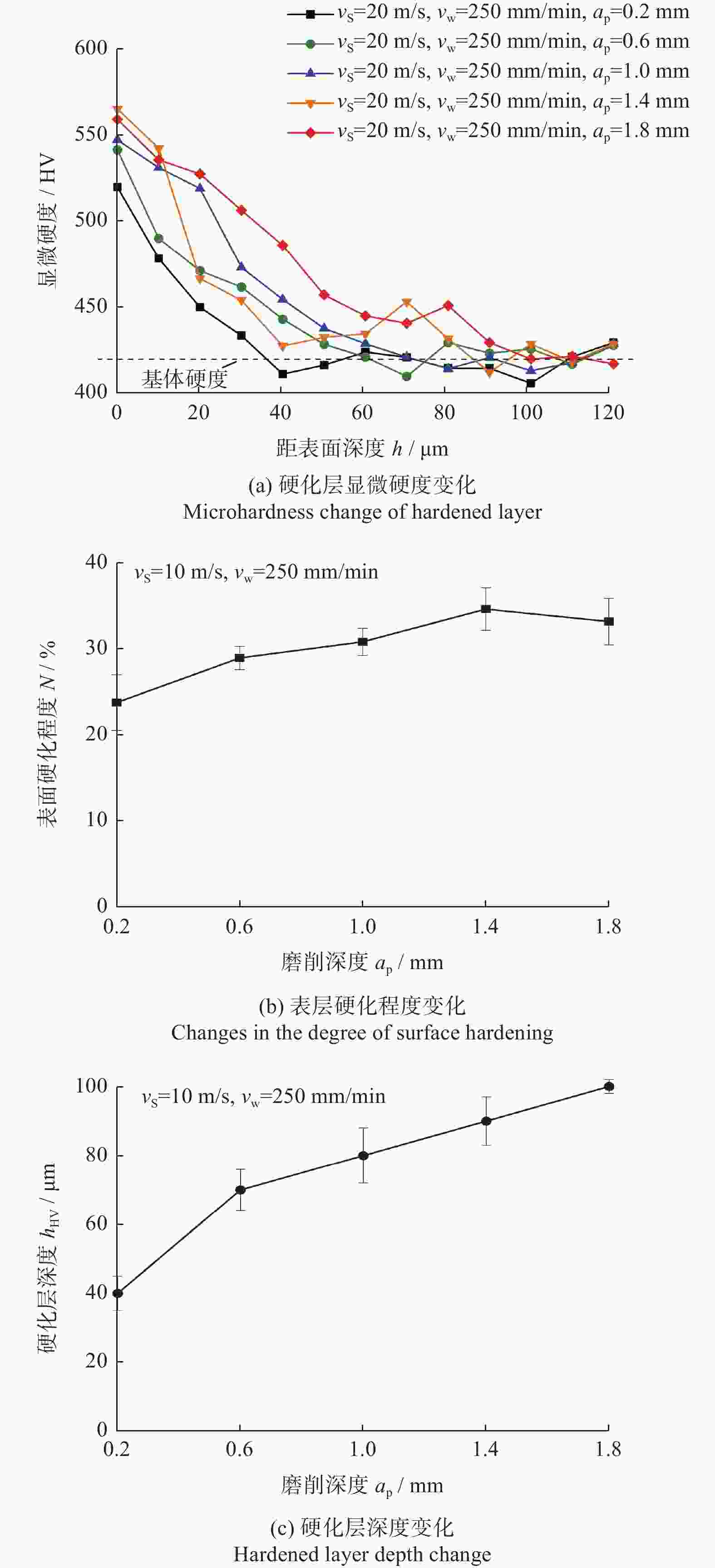
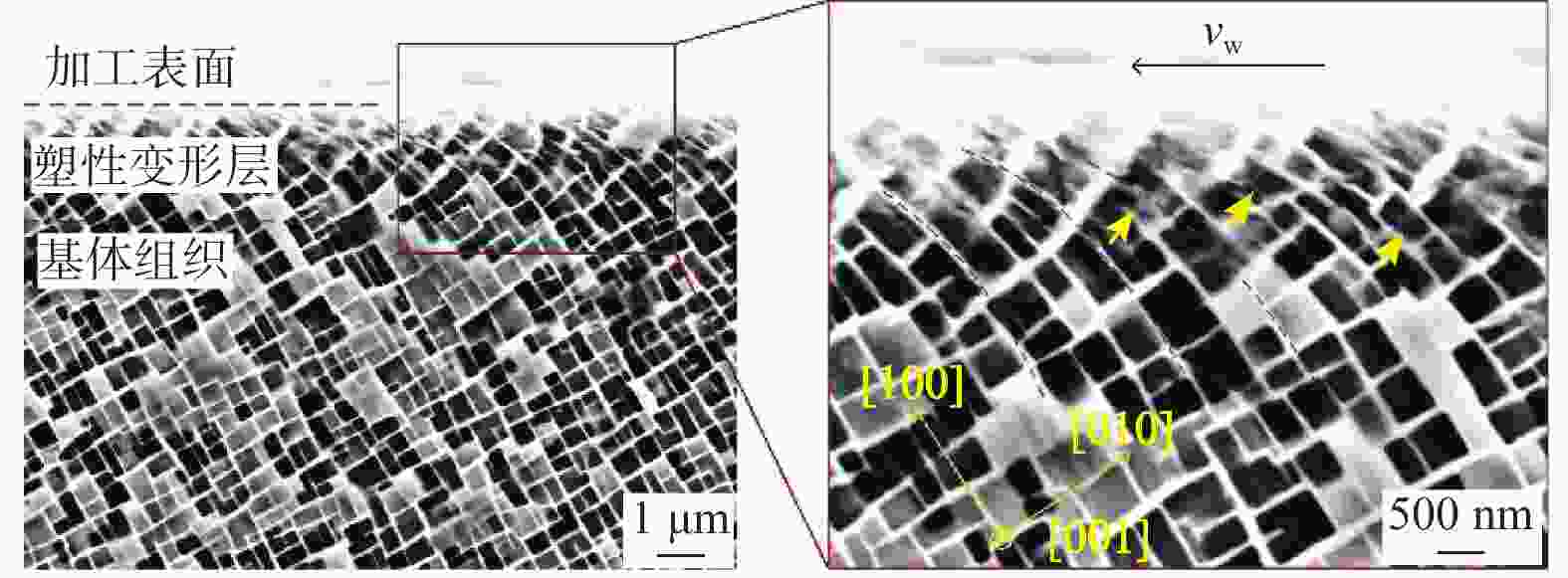
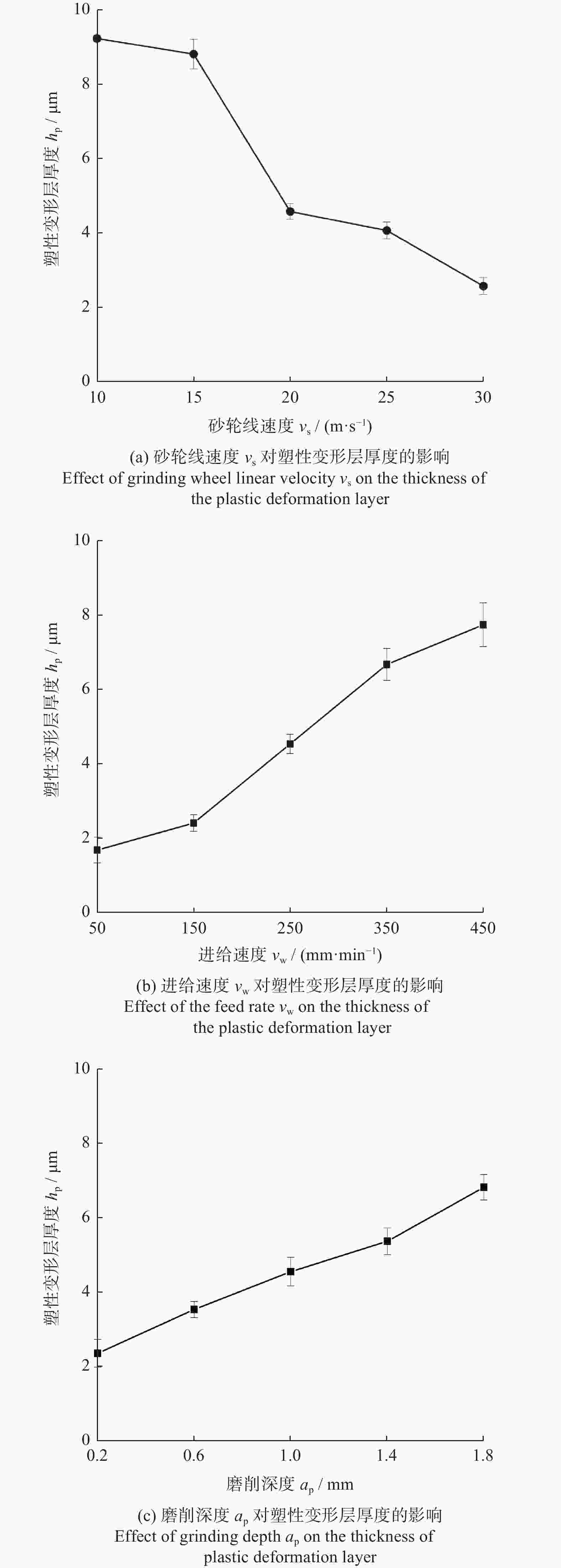
针对第三代单晶高温合金DD9磨削烧伤问题,设计三因素五水平实验,从表面形貌、显微硬度和显微组织等角度出发,研究磨削工艺参数对烧伤的影响规律。结果表明:当工件进给速度小于等于250 mm/min时,磨削表面粗糙度Ra在0.8 μm左右小幅度变化,表面质量较好;当工件进给速度大于250 mm/min,磨削深度超过1.0 mm后,磨削区域温度急剧上升,磨削纹路被破坏,出现涂覆、凹坑等磨削缺陷,工件表面发生烧伤;DD9合金缓进给磨削工件表面及表层均表现为加工硬化,显微硬度为400~600 HV,硬化层深度在50~110 μm,塑性变形层厚度为1~10 μm。推荐的DD9磨削工艺参数组合为:砂轮线速度vs=20 m/s,进给速度vw=250 mm/min,磨削深度ap=0.6 mm。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of grinding burns on the third-generation single crystal superalloy DD9, a three-factor and five-level experiment is designed in this paper. From the perspectives of surface morphology, microhardness and microstructure, the effect of grinding process parameters on grinding burns are studied. The experimental results show that: when the workpiece feed speed is less than 250 mm/min, the grinding surface roughness Ra changes slightly around 0.8 μm, and the surface quality is good. When the feed speed is more than 250 mm/min and the grinding depth is more than 1.0 mm, the temperature in the grinding area rises sharply, the grinding lines are destroyed, grinding defects such as coating and pits appear, and the surface of the workpiece burns. The surface and surface of DD9 alloy are work hardened by slow feed grinding. The microhardness range is 400 to 600 HV, the depth of hardened layer is 50 to 110 μm, and the thickness range of plastic deformation layer is 1 to 10 μm. The recommended combination of DD9 grinding process parameters is: grinding wheel linear velocity vs=20 m/s, feed speed vw=250 mm/min, grinding depth ap=0.6 mm.
-
Key words:
- DD9 /
- grinding burn /
- surface roughness /
- microhardness /
- microstructure
-
表 1 三因素五水平实验表
Table 1. Three-factor five-level experiment table
水平 因素 砂轮线速度
vs / (m·s-1)工件进给速度
vw / (mm·min-1)磨削深度
ap / mm−2 10 50 0.2 −1 15 150 0.6 0 20 250 1.0 1 25 350 1.4 2 30 450 1.8 表 2 烧伤与未烧伤DD9合金磨削表面元素含量对比(元素质量分数 ω / %)
Table 2. Comparison of element content on the ground surface of burnt and unburned DD9 alloys (element mass fraction ω / %)
元素 未烧伤表面 轻度烧伤表面 严重烧伤表面 Ni 67.3 59.9 57.6 O 0.1 5.3 5.7 C 1.7 1.6 3.0 Al 4.9 4.6 4.7 Cr 3.4 3.0 2.8 Co 7.2 6.9 7.7 其他 15.4 18.7 18.5 -
[1] LI J R, LIU S Z, WANG X G, et al. Development of a low-cost third generation single crystal superalloy DD9 [A]. Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium of Superalloys [C]. HOBOKEN, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2016: 57-63. [2] 《航空工程制造手册》总编委会. 航空制造工程手册 [M]. 北京: 北京航空工业出版社, 1998.Editor-in-chief of "Aeronautical Engineering Manufacturing Manual" . Aeronautical engineering manufacturing manual [M]. Beijing: Beijing Aviation Industry Press, 1998. [3] 张帅奇, 杨忠学, 张长春, 等. DD5镍基单晶高温合金缓进磨削力和温度实验研究 [J]. 航空工程进展,2021,12(4):80-89. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2021.04.09ZHANG Shuaiqi, YANG Zhongxue, ZHANG Changchun, et al. Experimental study on creep grinding force and temperature of DD5 nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2021,12(4):80-89. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2021.04.09 [4] SUN Y, SU Z P, GONG Y D, et al. Analytical and experimental study on micro-grinding surface-generated mechanism of DD5 single-crystal superalloy using micro-diamond pencil grinding tool [J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,2021,21(1):1-22. doi: 10.1007/s43452-020-00148-5 [5] 靳淇超, 曹帅帅, 汪文虎, 等. DD5镍基单晶高温合金缓进磨削表面完整性研究 [J]. 西北工业大学学报,2022,40(1):189-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.01.024JIN Qichao, CAO Shuaishuai, WANG Wenhu, et al. Research on surface integrity of DD5 nickel-based single crystal superalloy slow-feed grinding [J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University,2022,40(1):189-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.01.024 [6] CAI M, GONG Y D, SUN Y, et al. Experimental study on grinding surface properties of nickel-based single crystal superalloy DD5 [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,101:71-85. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2839-3 [7] 蔡明, 巩亚东, 屈硕硕, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金磨削表面质量及亚表面微观组织试验 [J]. 东北大学学报 (自然科学版),2019,40(3):386-391.CAI Ming, GONG Yadong, QU Shuoshuo, et al. Grinding surface quality and subsurface microstructure test of nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2019,40(3):386-391. [8] GU Y L, LI H N, DU B C, et al. Towards the understanding of creep-feed deep grinding of DD6 nickel-based single-crystal superalloy [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,100:445-455. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2686-2 [9] 顾玉栊. 刚玉砂轮缓进深切磨削加工镍基单晶合金叶片榫头研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019.GU Yulong. Research on the slow-feed and deep-cut grinding of corundum grinding wheel for nickel-based single crystal alloy blade tenon [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019. [10] THANEDAR A, DONGER G G, SINGH R, et al. Surface integrity investigation including grinding burns using barkhausen noise (BNA) [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2017,30:226-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.09.026 [11] 苏旭峰. 高温合金缓进磨削烧伤机理实验研究 [J]. 中国计量学院学报,2009,20(1):46-50.SU Xufeng. Experimental research on burning mechanism of superalloy creep-feed grinding [J]. Journal of China University of Metrology,2009,20(1):46-50. [12] ZHANG S Q, YANG Z X, JIANG R S, et al. Effect of creep feed grinding on surface integrity and fatigue life of Ni3Al based superalloy IC10 [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,34(1):438-448. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.02.025 [13] DING W F, XU J H, CHEN Z Z, et al. Grindability and surface integrity of cast nickel-based superalloy in creep feed grinding with brazed CBN abrasive wheels [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2010,23:501-510. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(09)60247-8 [14] ZHAO Z C, QIAN N, DING W F, et al. Profile grinding of DZ125 nickel-based superalloy: Grinding heat, temperature field, and surface quality [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2020,57:10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.022 -



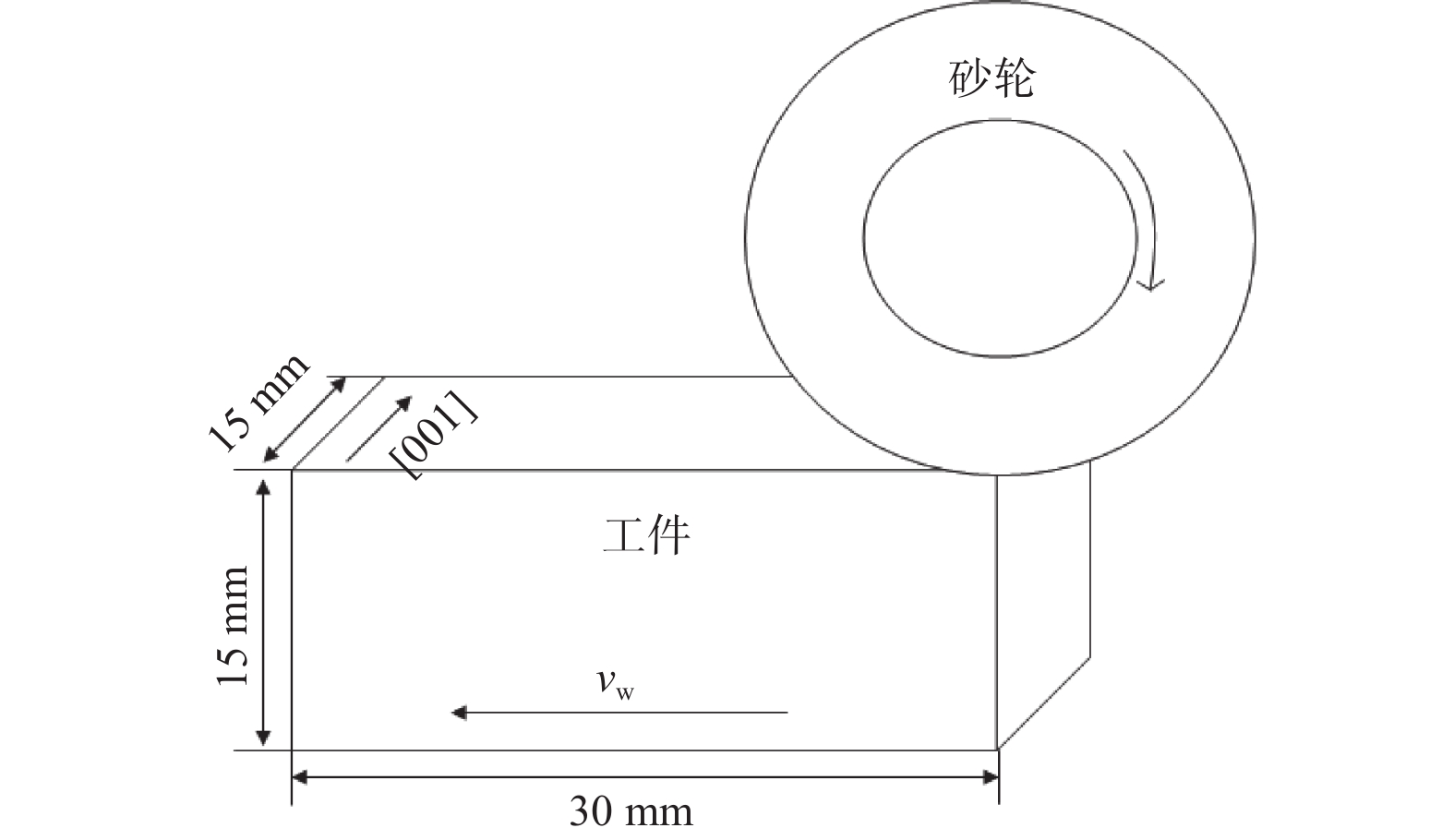
 下载:
下载:
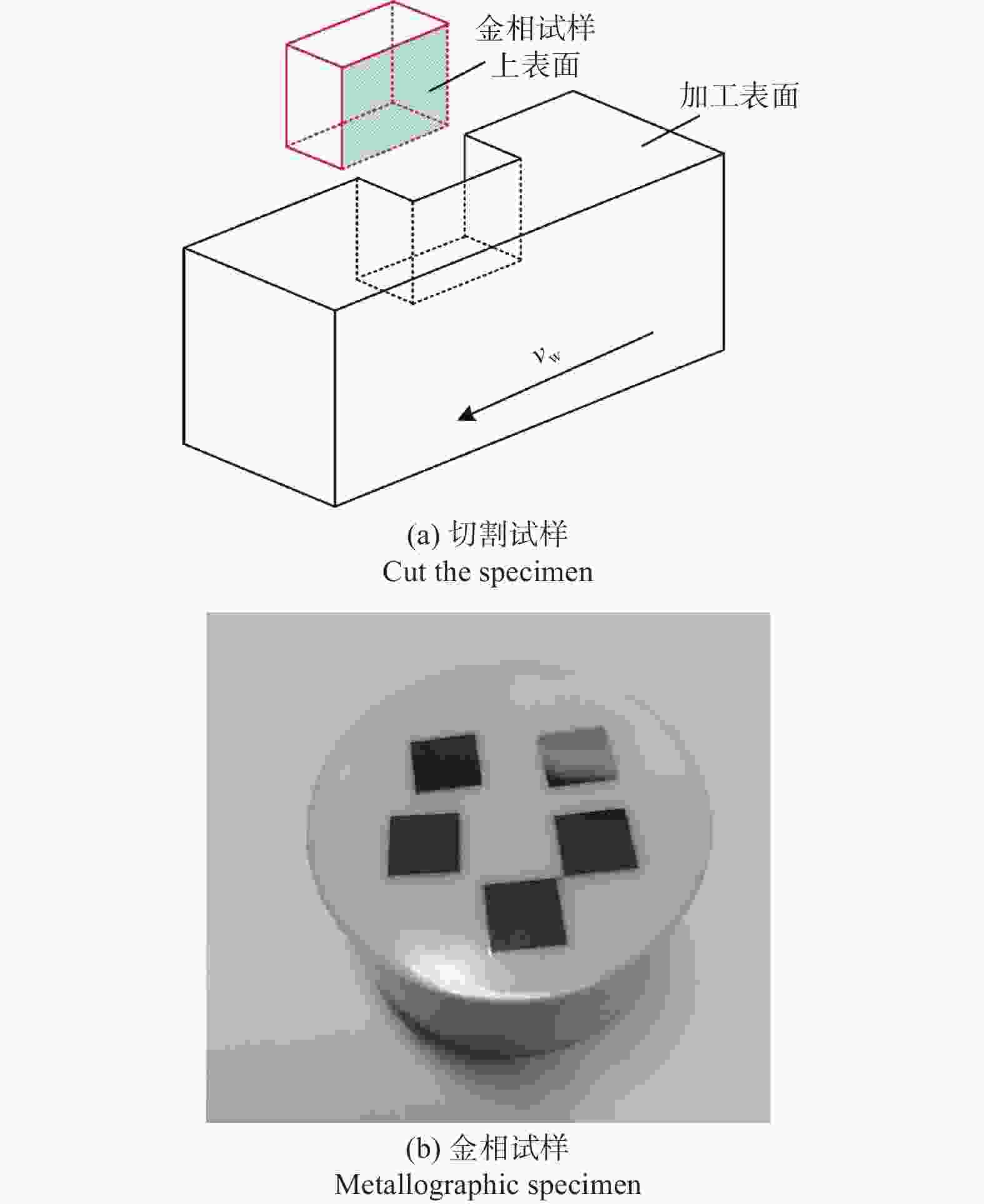




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
