Grinding of TiC particle-reinforced steel-matrix composite GT35 with small diameter grinding rods
-
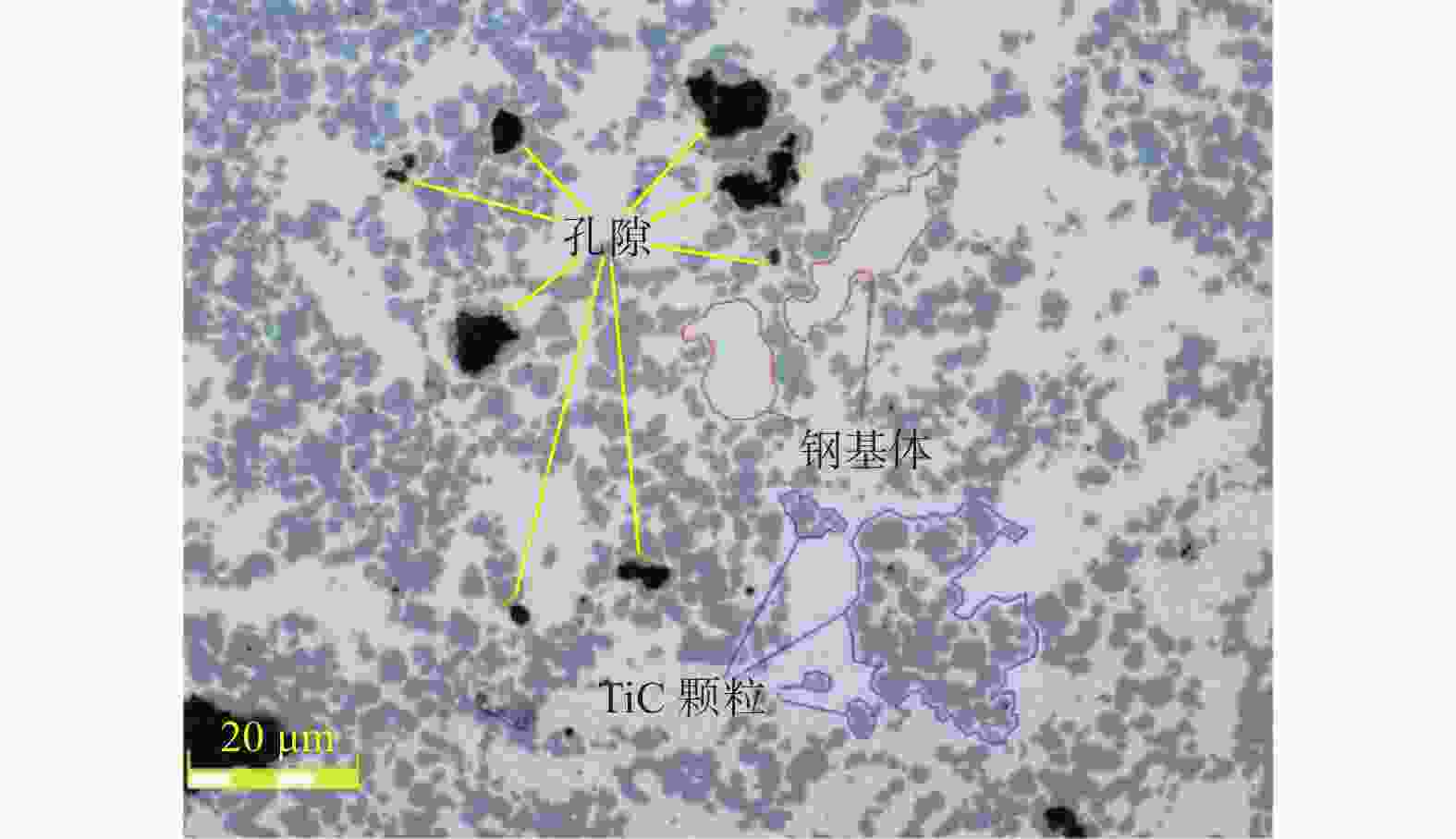
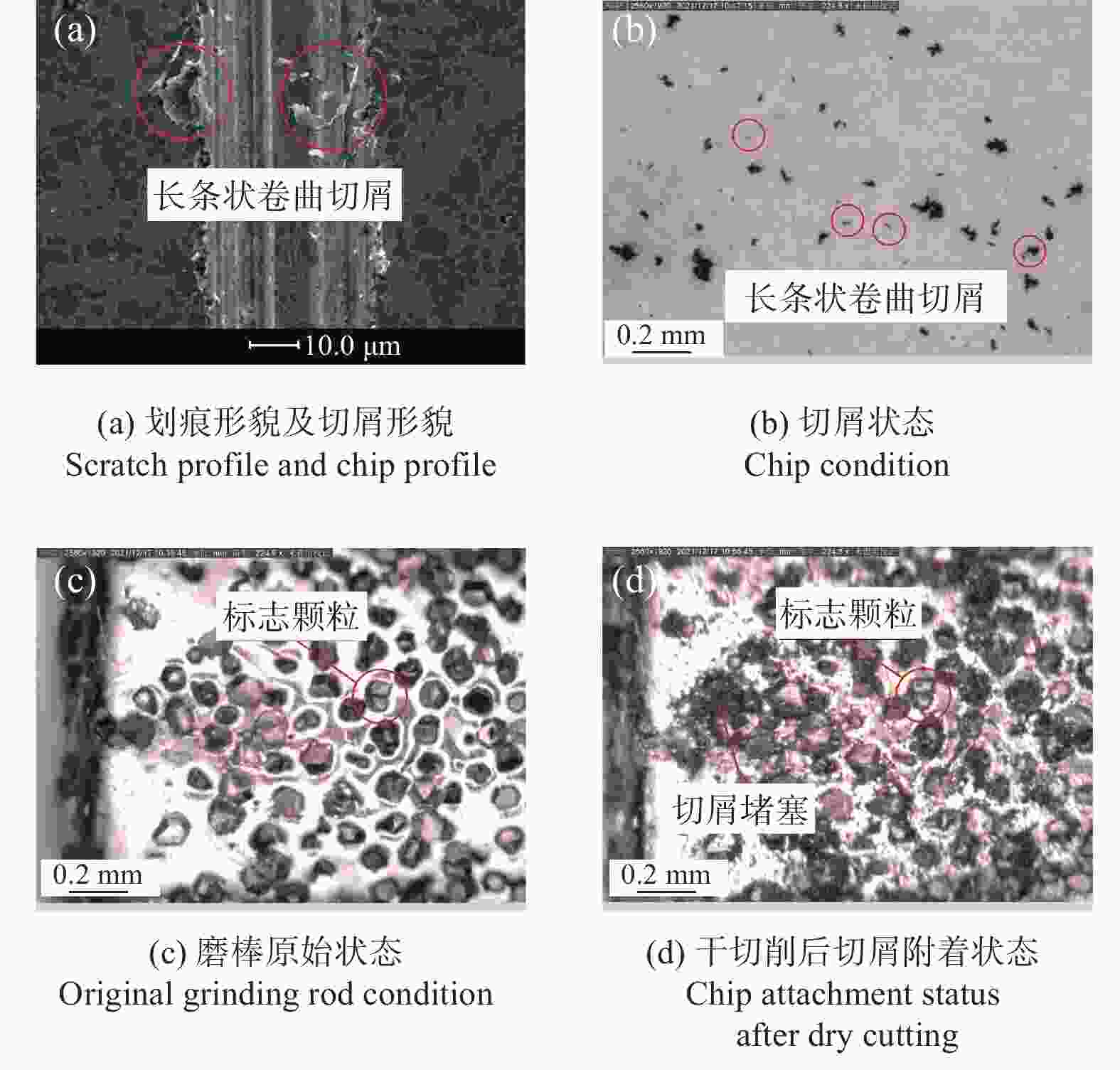
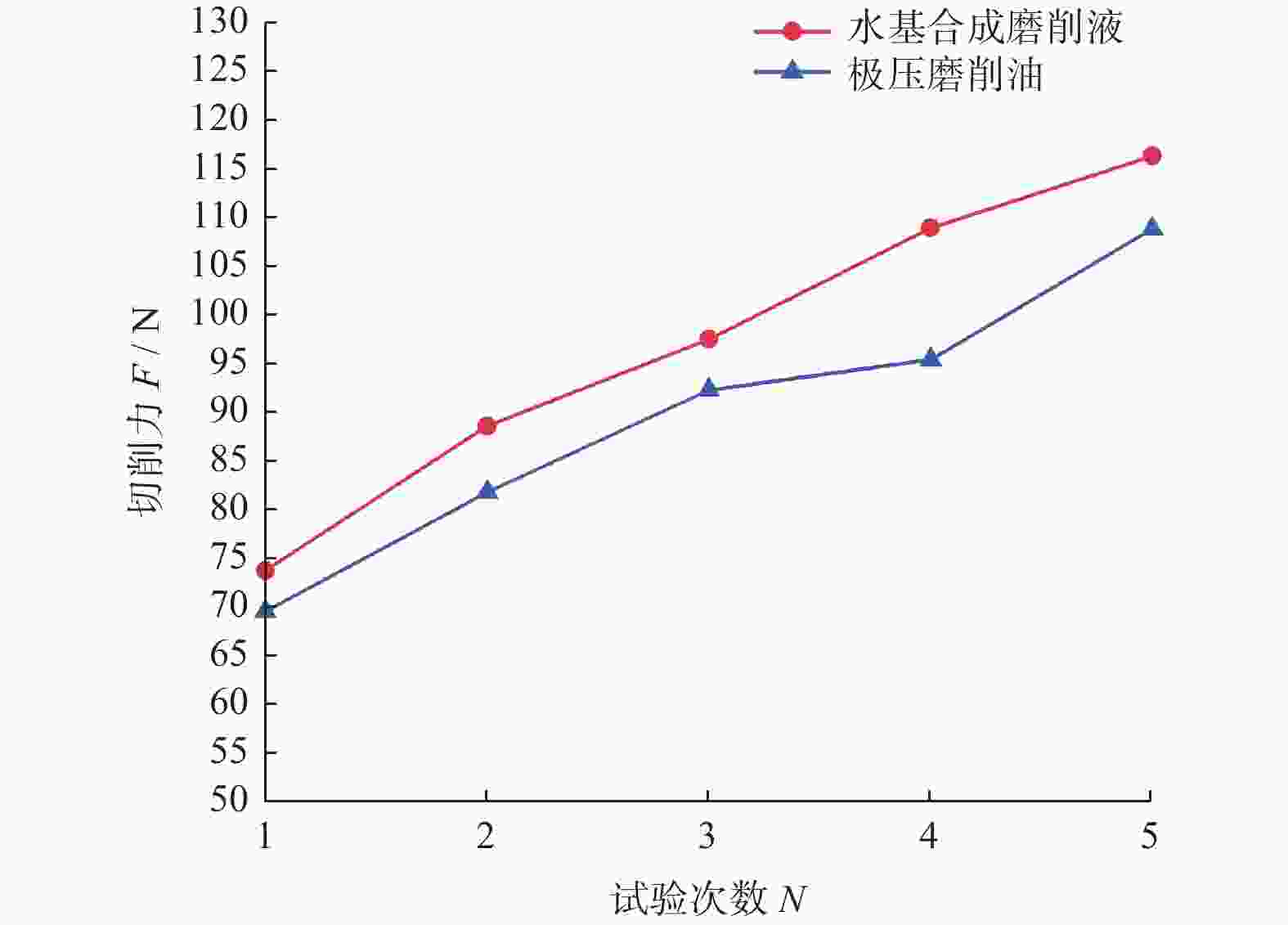
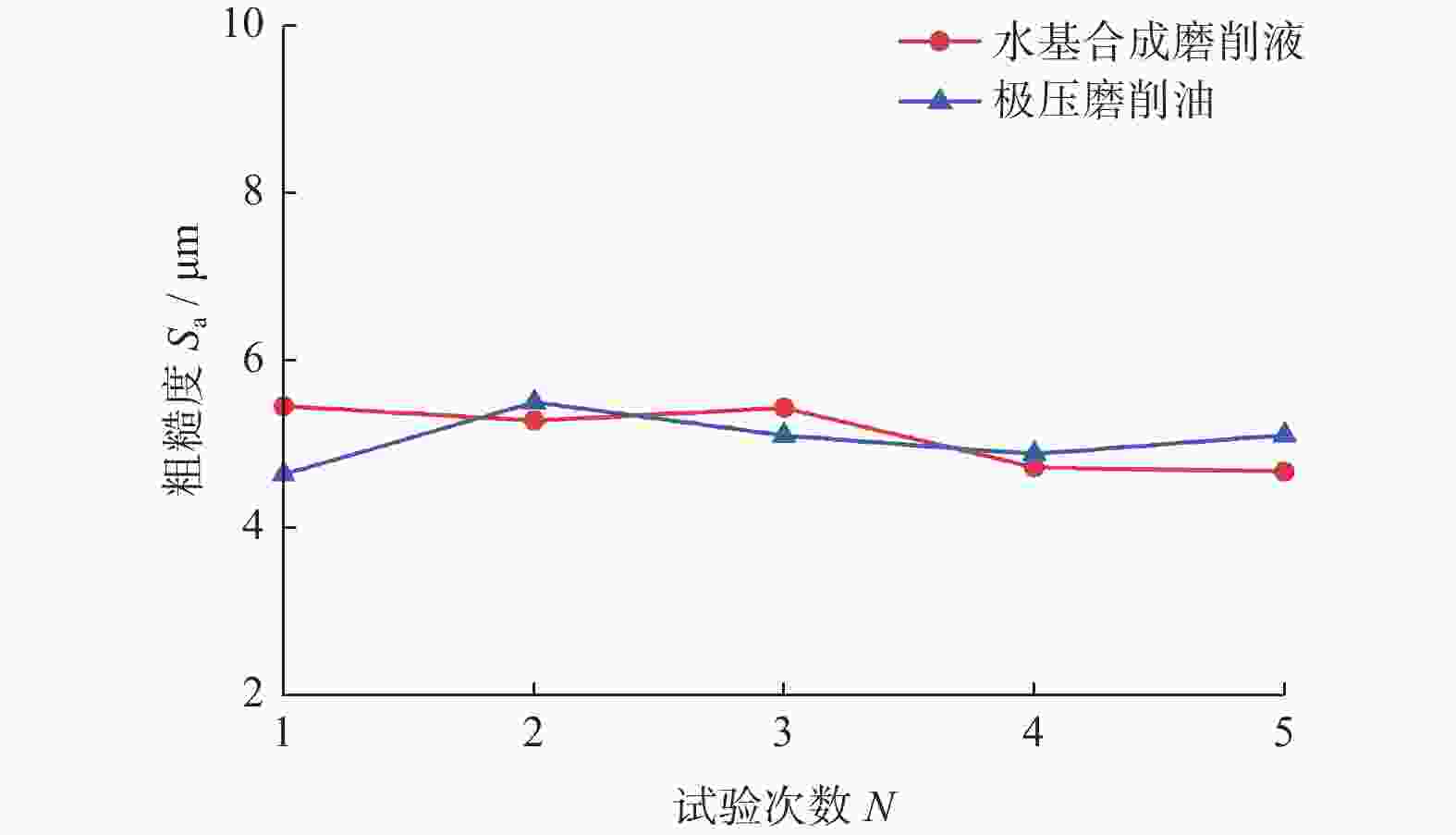
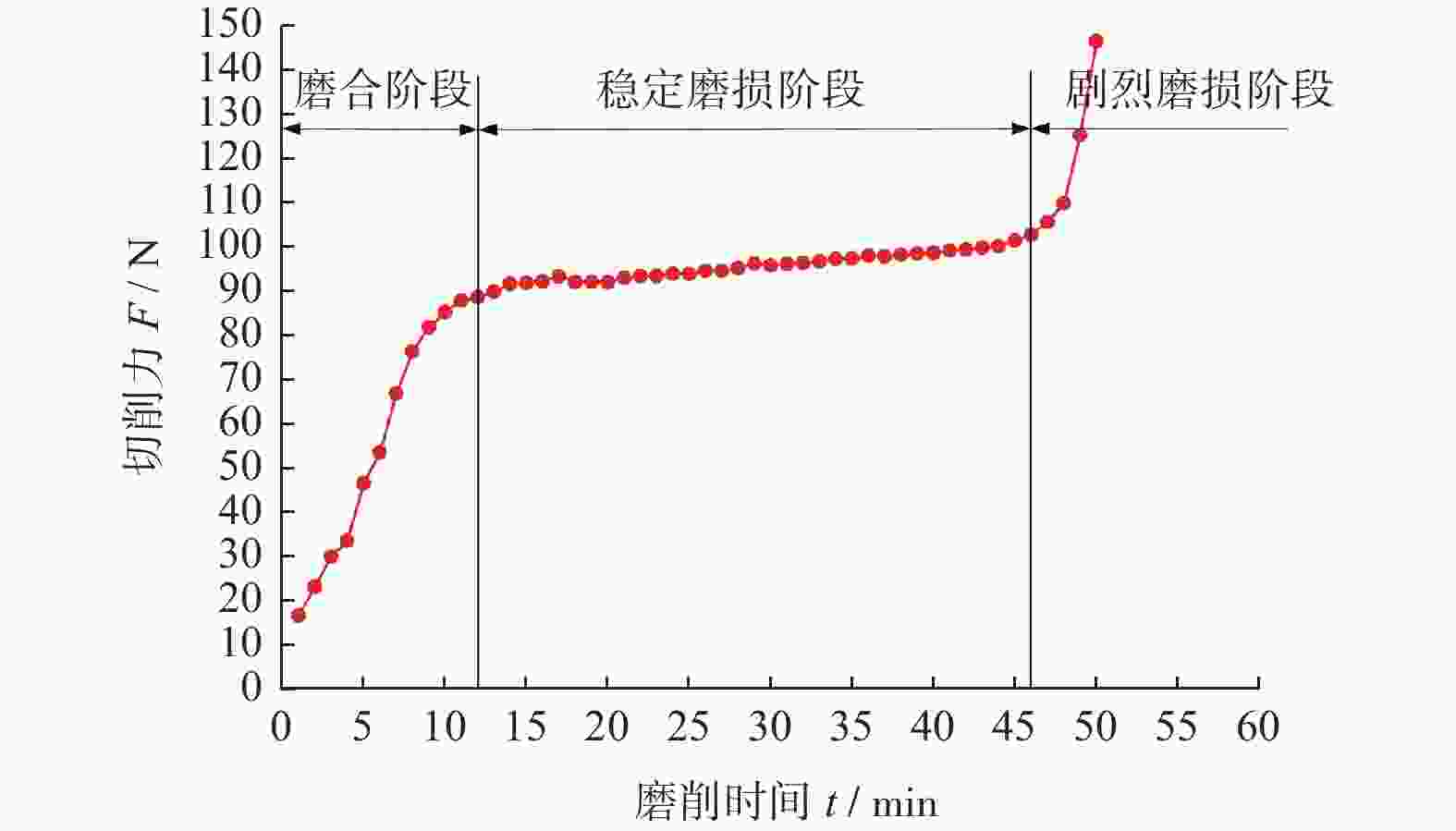
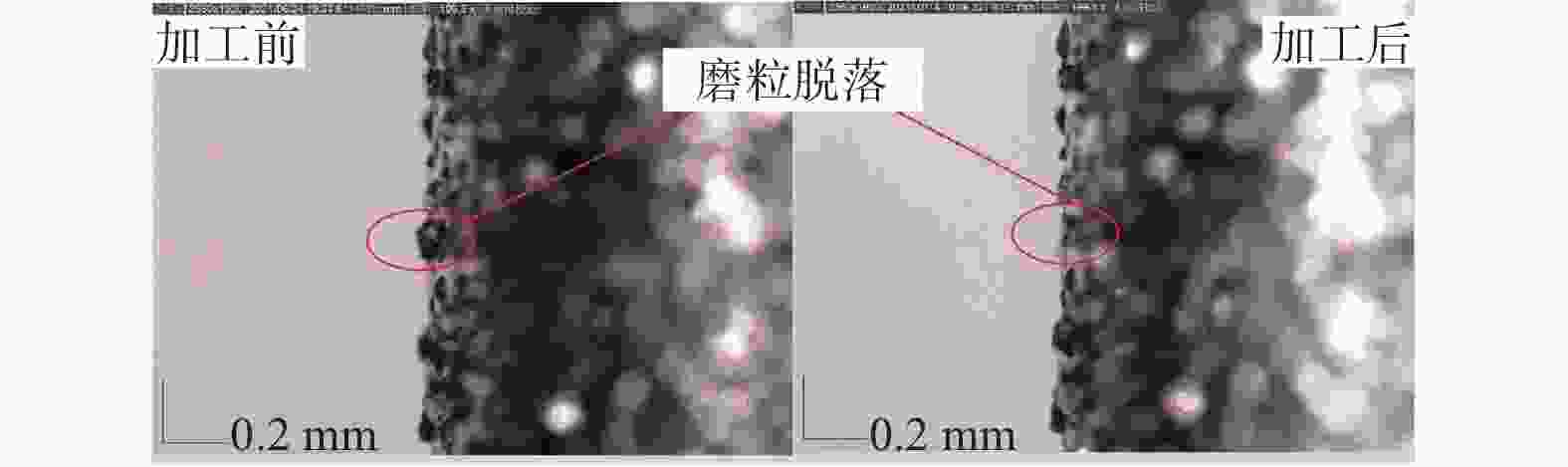
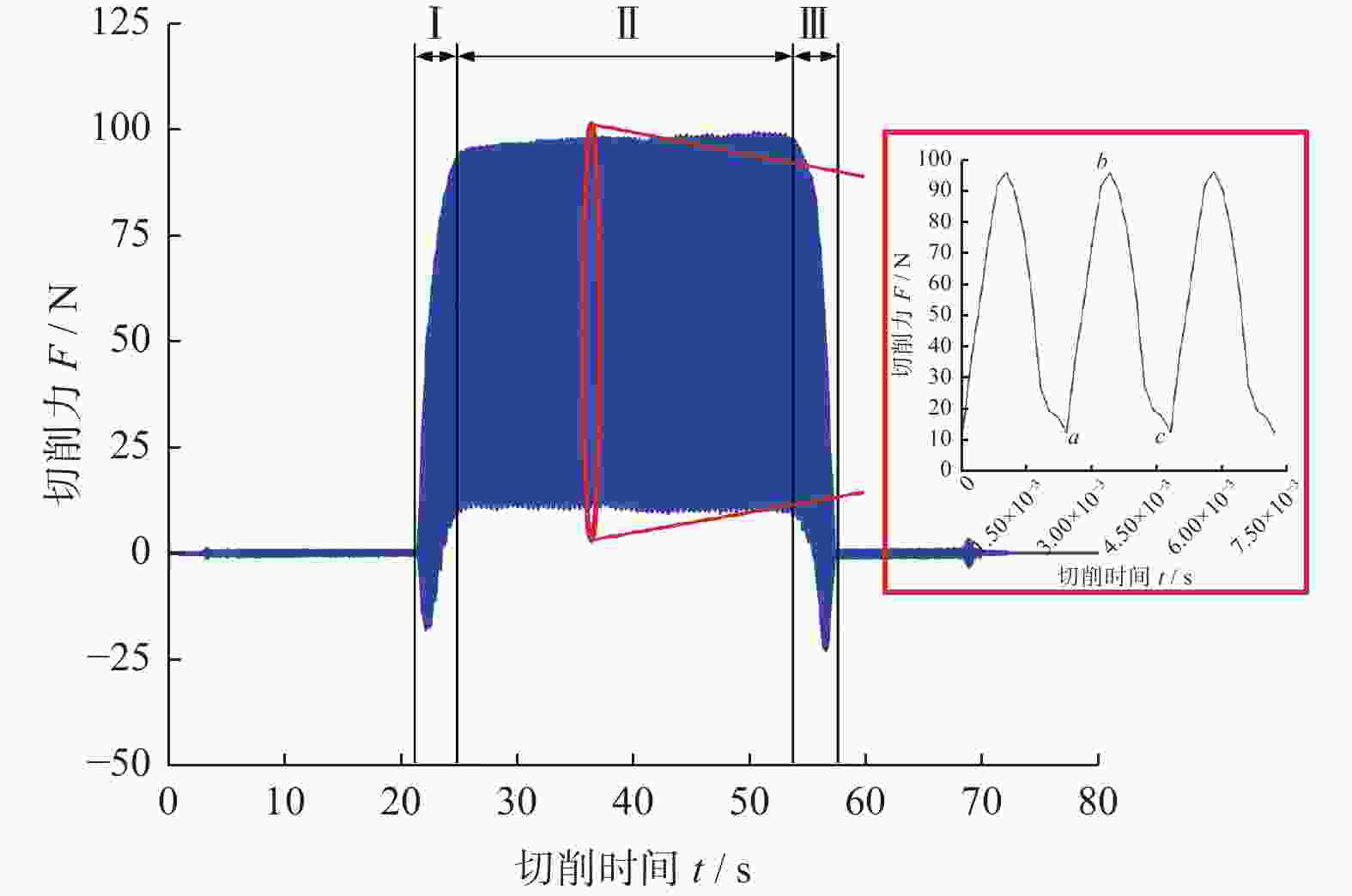
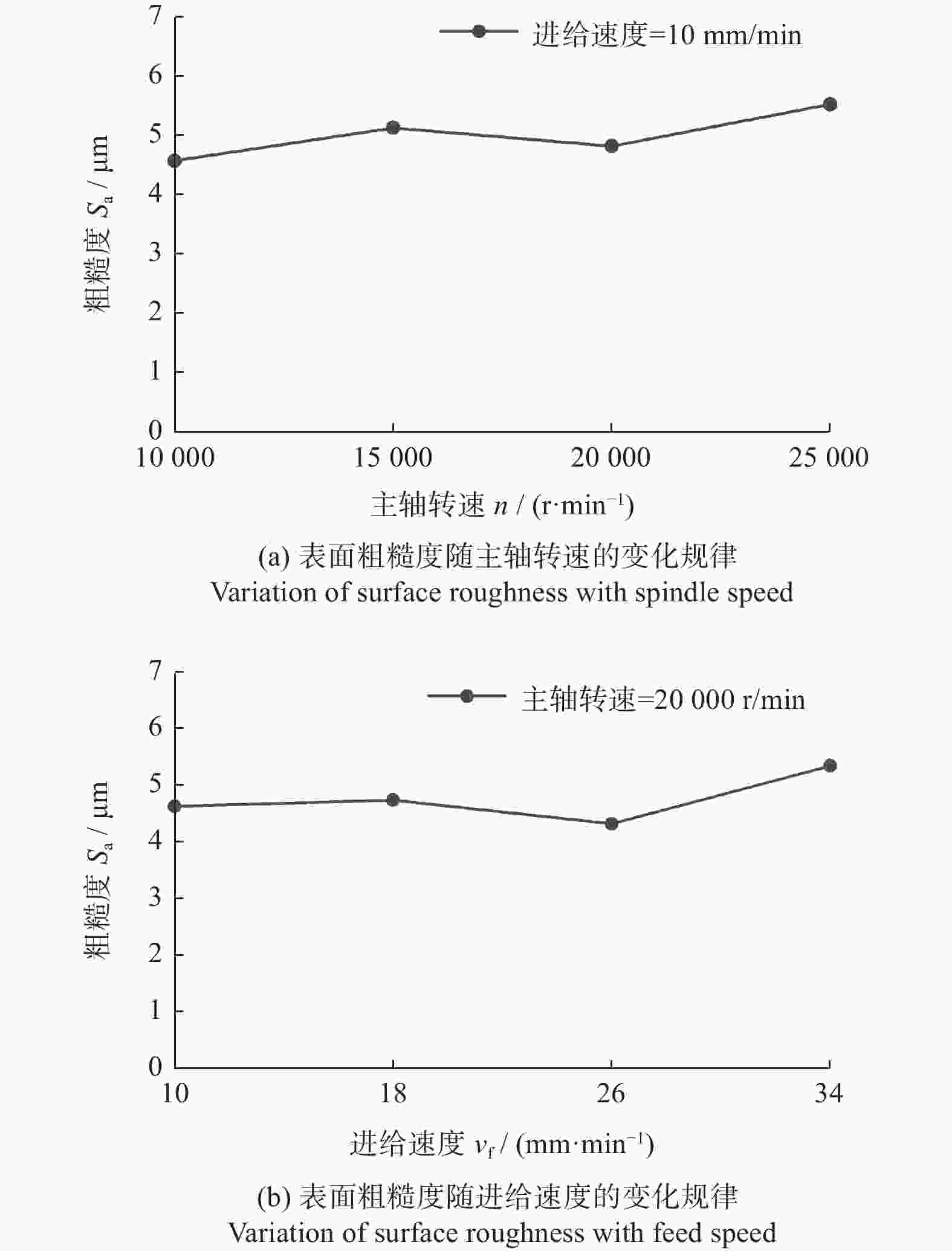
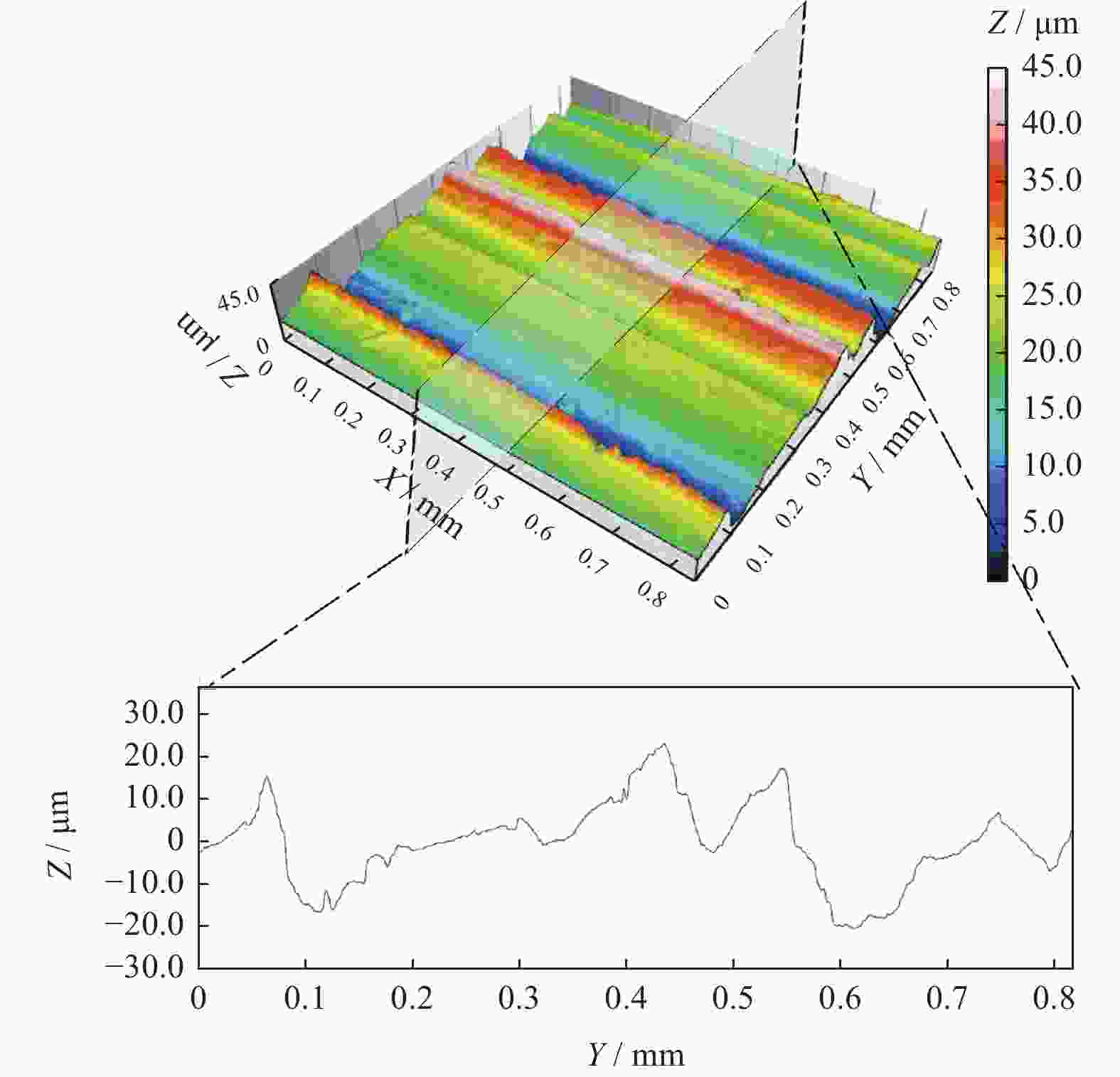
摘要: 为探究TiC颗粒增强钢基复合材料GT35合理的加工参数和冷却润滑条件,研究其对切削力、表面质量及刀具磨损的影响规律,采用小直径磨棒以侧面磨削方式开展试验。结果表明:干磨削会引起磨棒烧伤,极压磨削油的润滑效果优于水基合成磨削液的;磨棒在极压磨削油润滑下,磨削工件12 min后进入稳定磨损状态,其主要磨损形式为磨粒破碎、磨粒磨耗和磨粒脱落;主轴转速对切削力的影响大于进给速度的,且转速越高,切削力越小;工件表面粗糙度主要与磨棒磨粒出露高度的平整度有关,受加工参数的影响较小。用小直径磨棒磨削加工GT35材料时,应选择极压磨削油润滑,高主轴转速、中速进给的加工方式,以获得良好的刀具寿命、工件加工表面质量及适当的加工效率。
-
关键词:
- 碳化钛颗粒增强钢基复合材料 /
- 磨削 /
- 冷却润滑 /
- 刀具磨损 /
- 工艺特征
Abstract: Side milling experiments with small diameter grinding rods were carried out on TiC particle-reinforced steel-matrix composite to investigate the reasonable machining parameters and the cooling and lubrication conditions for this material, and to understand the influence of machining parameters on cutting forces, surface quality and tool wear. The results show that dry cutting and water-based synthetic grinding fluids lubrication are not as effective as extreme pressure grinding oil lubrication, especially that dry cutting causes tool burn. With extreme pressure grinding oil lubrication, the tool wear is stable after 12 minutes of continuous grinding, the main wear forms of which are fracture of abrasive grain wear, abrasive grain breakage and abrasive grain shedding. It is also found that the influence of spindle speed on cutting force is greater than that of feed speed, namely higher spindle speed leading to smaller cutting force, and that the machined surface roughness is mainly related to the level of tool abrasive grain but less affected by spindle speed and feed speed. In conclusion, when grinding TiC particle-reinforced steel-matrix composites, the conditions of extreme pressure grinding oil lubrication, high spindle speed and medium feed rate are recommended to obtain good tool life, surface quality and appropriate processing efficiency. -
表 1 冷却润滑试验参数设置
Table 1. Cooling-lubrication test parameter setting
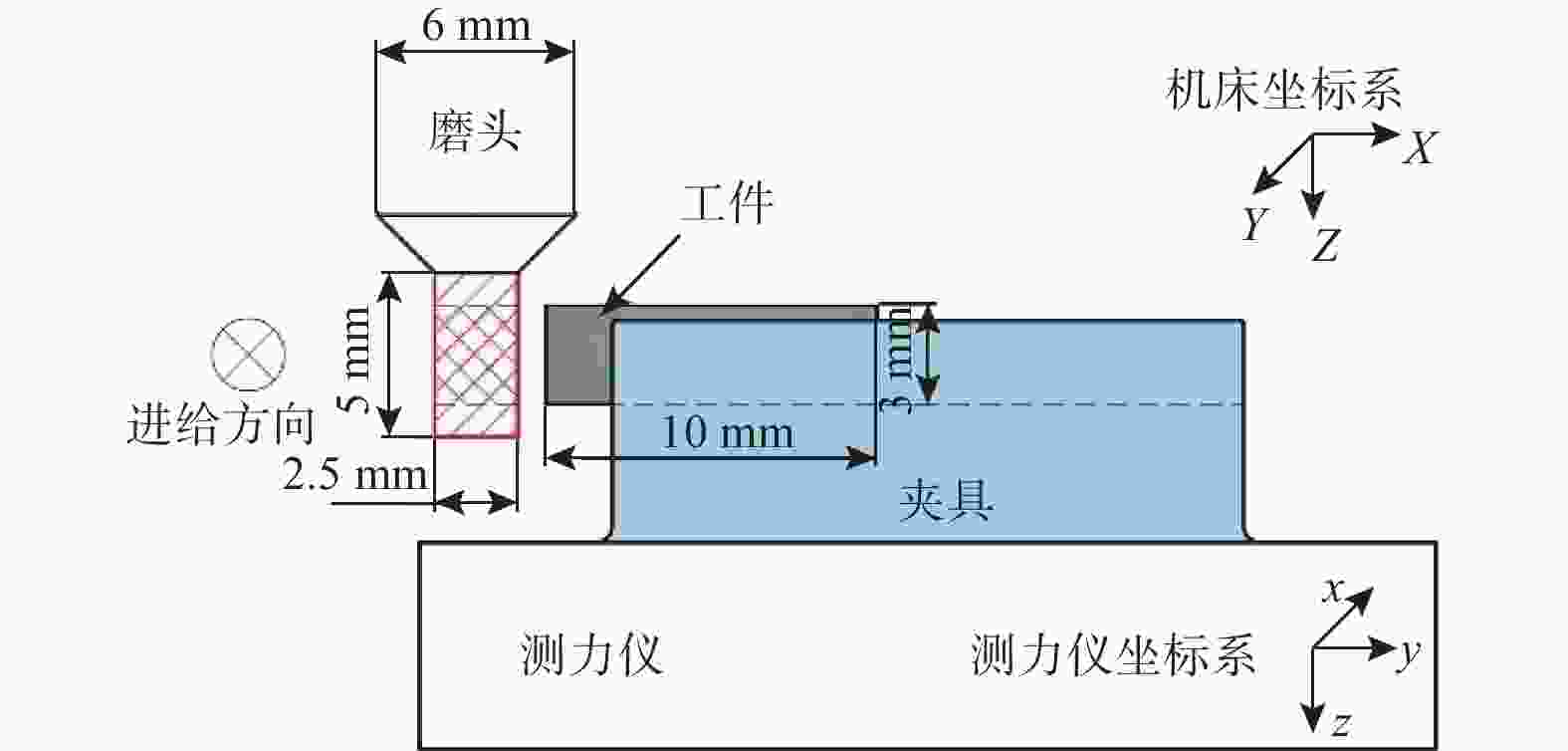
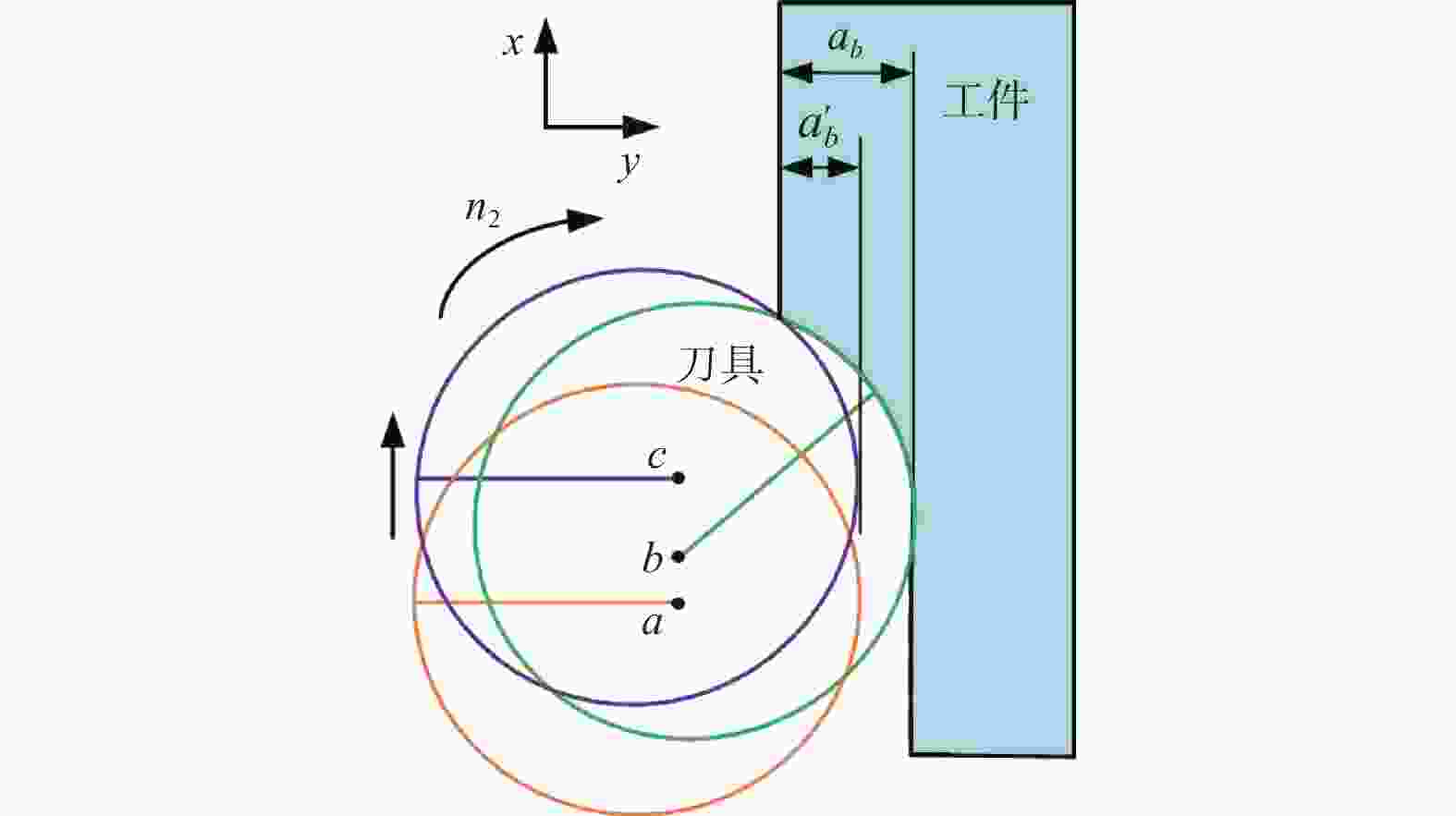
参数 取值 主轴转速 n1 / (r·min−1) 15 000 进给速度 vf / (mm·min−1) 30 切削深度 ap / mm 3 切削宽度 ae / mm 0.5 重复试验次数 N 5 表 2 磨棒磨损试验参数设置
Table 2. Grinding rod wear test parameter setting
参数 取值 主轴转速 n2 / (r·min−1) 25 000 进给速度 vf / (mm·min−1) 10 切削深度 ap / mm 3 切削宽度 ae / mm 0.1 表 3 工艺试验参数设置
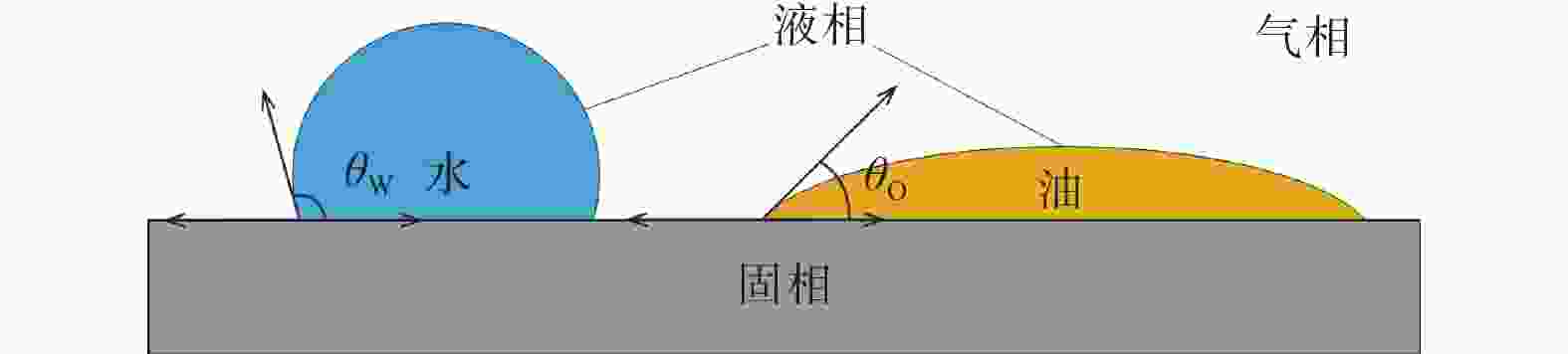
Table 3. Process test parameter setting
试验参数 试验设置 主轴转速 n / (r·min−1) 10 000,15 000,20 000,
25 000进给速度 vf / (mm·min−1) 10,18,26,34 切削深度 ap / mm 3 切削宽度 ae / mm 0.2 -
[1] 刘舜尧, 张春友. GT35钢结硬质合金应用技术研究 [J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金,2001,29(2):25-29, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2001.02.007LIU Shunyao, ZHANG Chunyou. Study of applied techniques for GT35 steel-bonded carbides [J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides,2001,29(2):25-29, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2001.02.007 [2] ZHANG Z, YAO P, WANG J, et al. Analytical modeling of surface roughness in precision grinding of particle reinforced metal matrix composites considering nanomechanical response of material [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,157/158:243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.04.047 [3] 赵昌盛, 孔东祥. 钢结硬质合金模具热处理及应用 [J]. 模具制造,2006,6(10):80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3508.2006.10.029ZHAO Changsheng, KONG Dongxiang. Heat treatment and application of steel structure cemented carbide die [J]. Die & Mould Manufacture,2006,6(10):80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3508.2006.10.029 [4] 王京锋, 刘景林, 闫亚超, 等. 半球形动压气体轴承陀螺电机设计及性能测试 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2017,46(9):144-150. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201701041WANG Jingfeng, LIU Jinglin, YAN Yachao, et al. Design and performance testing of hemispheric aerodynamic bearing gyro motor [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2017,46(9):144-150. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201701041 [5] 孟昊. 钢结硬质合金轴的精密点磨削工艺及砂轮在位修整方法研究 [D]. 山东: 山东大学, 2016.MENG Hao. Precision point grinding technology for steel bonded carbide axles and on-Machine conditioning of grinding wheel [D]. Shandong: Shandong University, 2016. [6] 吕程昶. 双转盘偏心槽精密球体研磨机理及其工艺研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.LU Chengchang. Research on ball lapping mechanism and technology using eccentric lapping method with two rotatable lapping plates [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016. [7] 于殿勇, 吴永孝. 钢结硬质合金的超精密磨削 [J]. 磨料磨具与磨削,1994(3):17-20.YU Dianyong, WU Yongxiao. Ultra-precision grinding of steel-jointed carbides [J]. Abrasives and Grinding,1994(3):17-20. [8] 王平, 唐一平, 张飞虎, 等. TiC系钢结硬质合金镜面微浮凸磨削机理的研究 [J]. 西安交通大学学报,1998(5):82-84, 88.WANG Ping, TANG Yiping, ZHANG Feihu. Mirror micro-relief grinding mechanism of TiC series steel-matrix carbide alloys [J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University,1998(5):82-84, 88. [9] 关佳亮, 仇忠臣, 赵增强, 等. 钢结硬质合金的ELID高效磨削试验研究 [J]. 机械设计与制造,2008(11):107-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2008.11.042GUAN Jialiang, QIU Zhongchen, ZHAO Zengqiang, et al. Research on ELID grinding performance of steel bonded carbide [J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture,2008(11):107-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2008.11.042 [10] WANG Z, LIN T, HE X, et al. Fabrication and properties of the TiC reinforced high-strength steel matrix composite [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2016, 58: 14-21. [11] 杨雄, 冉小丰, 帅玉妹, 等. GT35钢结硬质合金电火花加工工艺试验 [J]. 硬质合金,2009,26(4):236-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7292.2009.04.008YANG Xiong, RAN Xiaofeng, SHUAI Yumei, et al. Electrical discharge machining (EDM) technological test of GT35 steel-bonded carbide [J]. Cemented Carbide,2009,26(4):236-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7292.2009.04.008 [12] BONNY K, DEBAETS P, OST W, et al. Influence of electrical discharge machining on the reciprocating sliding wear response of WC-Co cemented carbides [J]. Wear,2009,266(1/2):84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.05.009 [13] KUMMEL J, BRAUN D, GIBMEIER J, et al. Study on micro texturing of uncoated cemented carbide cutting tools for wear improvement and built-up edge stabilisation [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2015,215:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.07.032 [14] KAWASEGI N, SUGIMORI H, MORIMOTO H, et al. Development of cutting tools with microscale and nanoscale textures to improve frictional behavior [J]. Precision Engineering,2009,33(3):248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.07.005 [15] 李克华, 熊华军, 郜永娟, 等. CBN磨料特性对树脂砂轮磨削性能的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2017,37(3):19-22, 34.LI Kehua, XIONG Huajun, GAO Yongjuan, et al. Influence of different CBN grains on grinding performance of resin bonged CBN grinding wheel [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2017,37(3):19-22, 34. [16] HEJAZI V, NOSONNVSKY M. Contact angle hysteresis in multiphase systems [J]. Colloid and Polymer Science,2013,291(2):329-338. doi: 10.1007/s00396-012-2838-0 [17] ARUNACHALAM N, ANANDPS P, VIJAYARAGHAVAN L. Investigation of tribological conditions on grinding of bioceramic material using diamond grinding wheel under different cooling and lubrication environment [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,71:550-564. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.09.004 [18] 石淼淼. 切削中的摩擦与切削液 [M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1994.SHI Miaomiao. Friction in cutting and cutting fluids [M]. Beijing: China Rail Way Publishing House, 1994. -




 下载:
下载:










 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
