Study on machining performance of fixed-abrasive lap-grinding plate with random grid structure
-
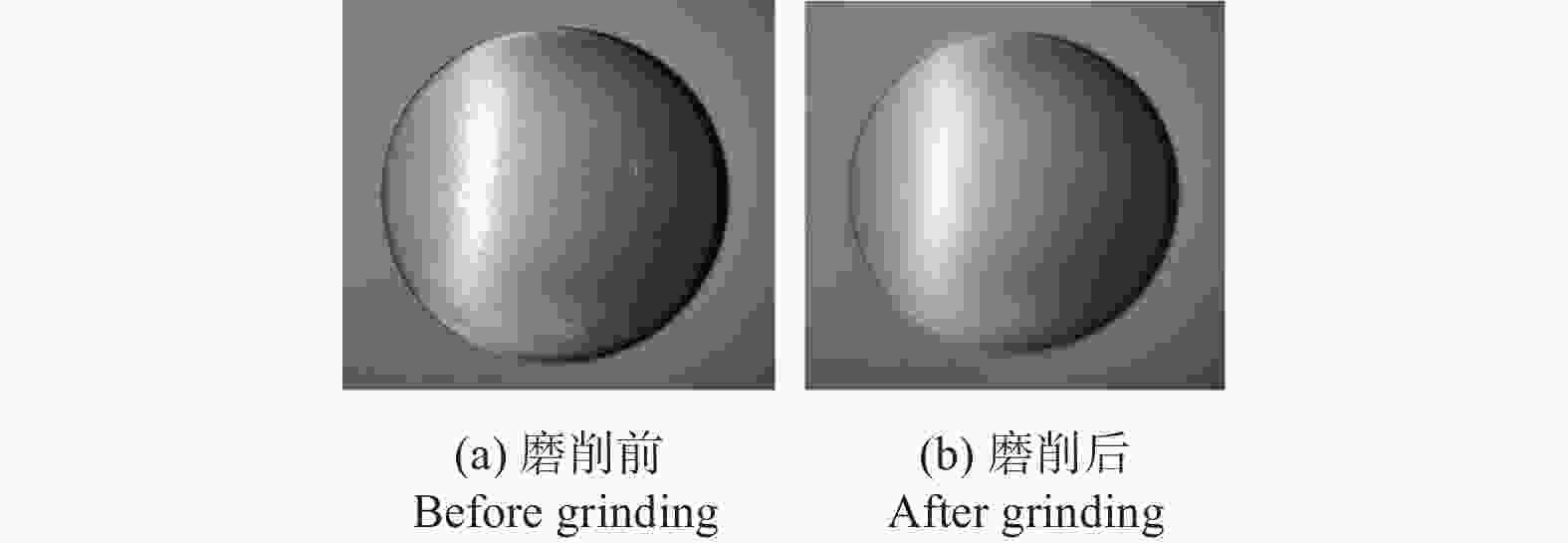
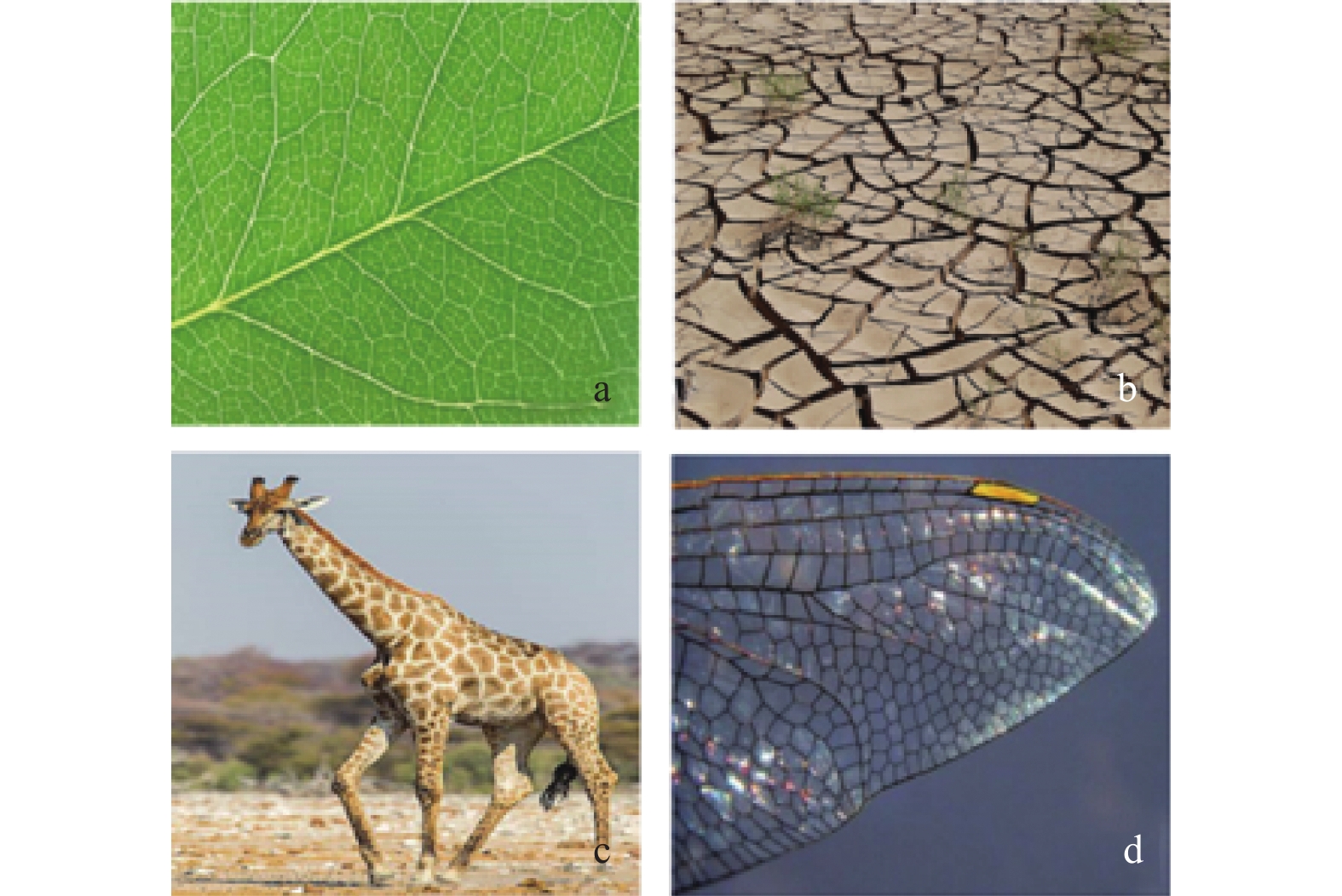
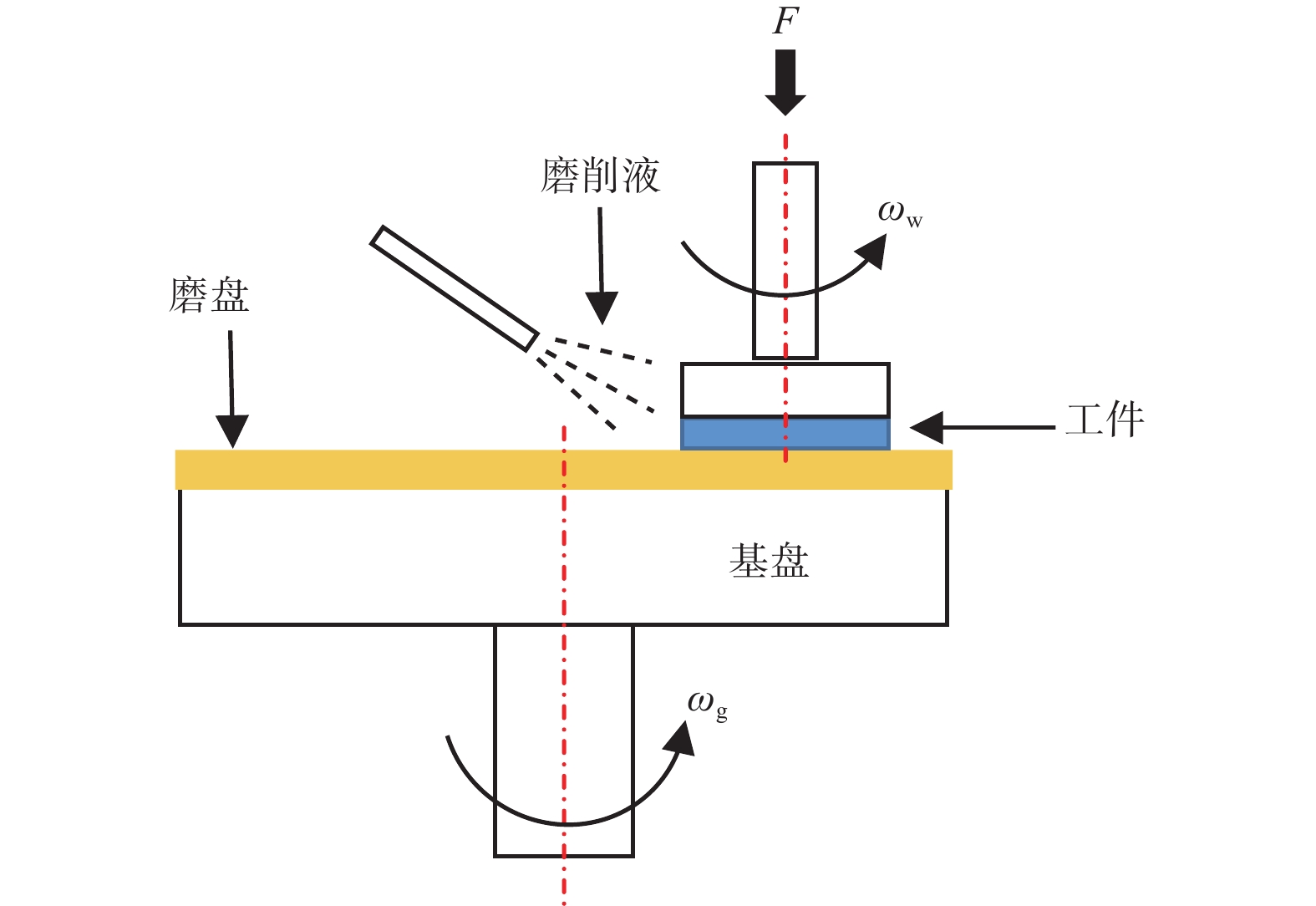
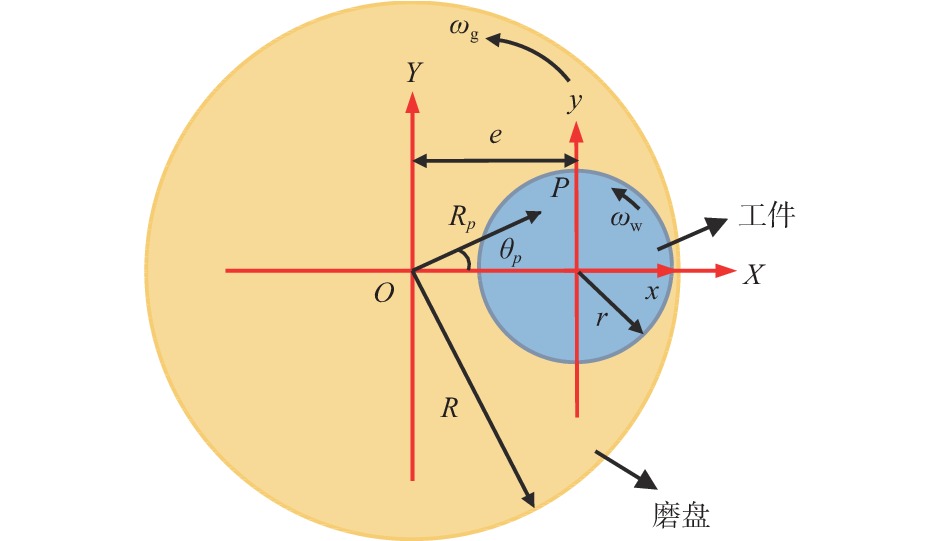
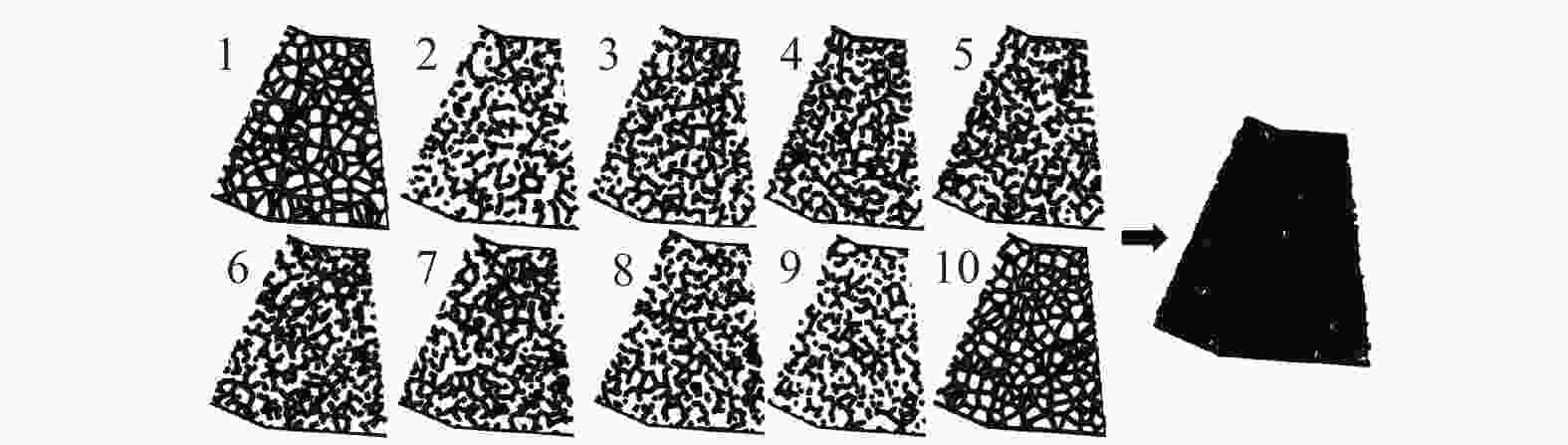
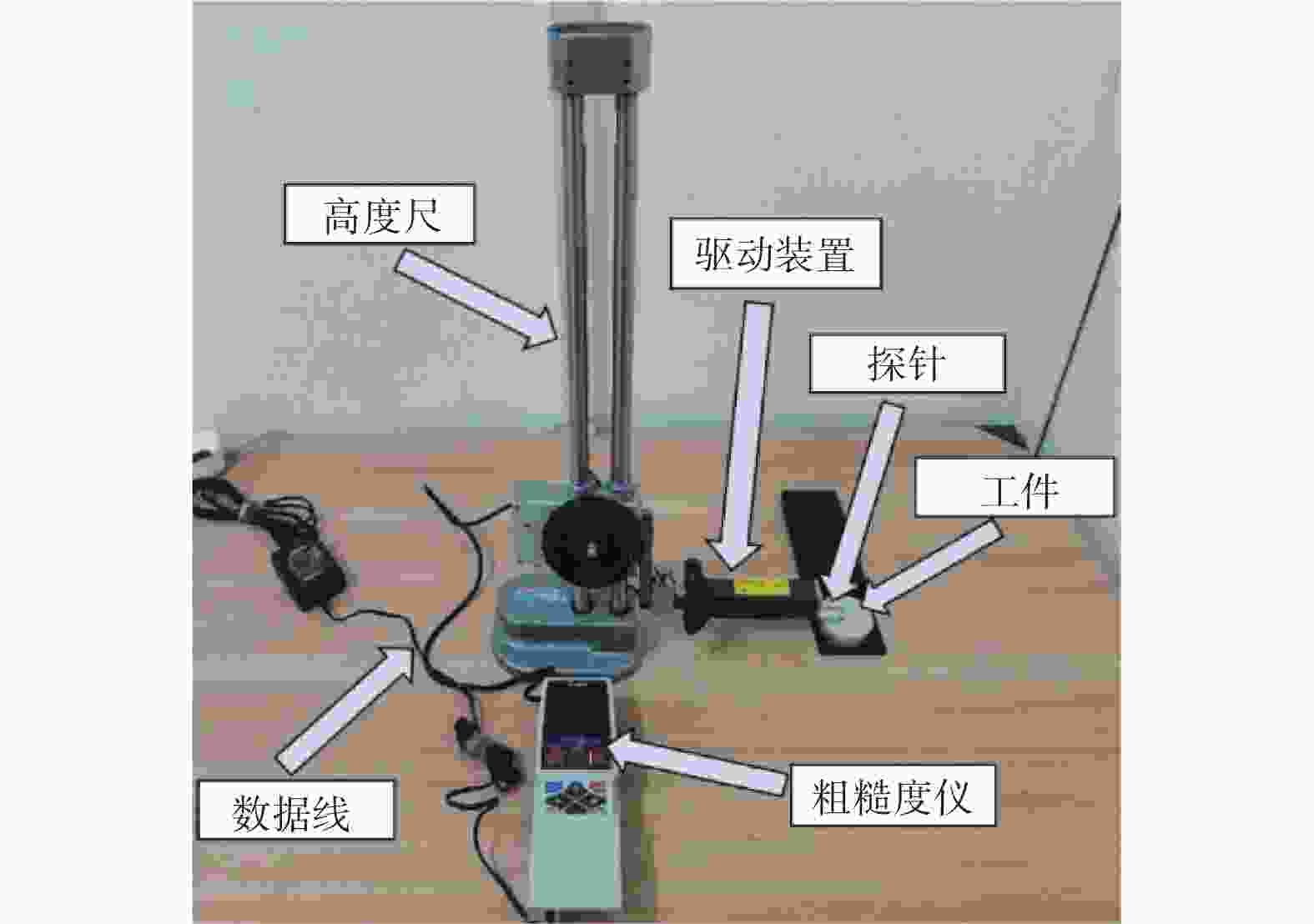
摘要: 针对超精密磨削加工过程对工件材料去除效率、表面质量、亚表面损伤等指标的复合需求,提出一种基于泰勒多边形设计的随机网格结构固结磨料磨盘(textured-fixed abrasive plate, T-FAP),并以光固化树脂作为结合剂基体材料混合微米级氧化铝磨料制备磨盘,使用MATLAB图像分析和磨抛轨迹仿真方法研究磨盘磨削过程中表面磨损时变图案特征对其加工性能的影响,并通过铝制工件的平面磨削实验对磨盘磨削过程中的材料去除率及工件表面粗糙度进行分析。实验结果表明:相比传统固结磨料磨盘,采用随机网格结构磨盘加工的工件表面粗糙度为0.84 μm,材料去除率为3.21 μm/min,能够在保证材料去除率的同时获得较高的表面精度。Abstract: To meet the increasing requirements on material removal efficiency, surface quality, and subsurface damage in the ultra-precision grinding process, a textured-fixed abrasive plate (T-FAP) with random grid structure based on the Voronoi Diagram is proposed. The abrasive tool is fabricated by using UV-curable resin and micro-level alumina abrasive grains. The influence of time-varying texture characteristics of surface wear on the machining performance is studied via MATLAB image analysis and numerical simulation of the grinding trajectory. The lap-grinding experiment of the aluminum workpieces is carried out to analyze the material removal efficiency and workpiece surface roughness obtained from the T-FAP grinding process. The results show that the surface roughness of the workpiece processed with the T-FAP grinding is 0.84 μm, and that the material removal rate is 3.21 μm/min. Compared with the traditional fixed abrasive grinding tool, the T-FAP grinding ensures the material removal efficiency and obtains high surface accuracy as well.
-
Key words:
- fixed-abrasive tool /
- lap-grinding /
- surface roughness /
- material removal rate
-
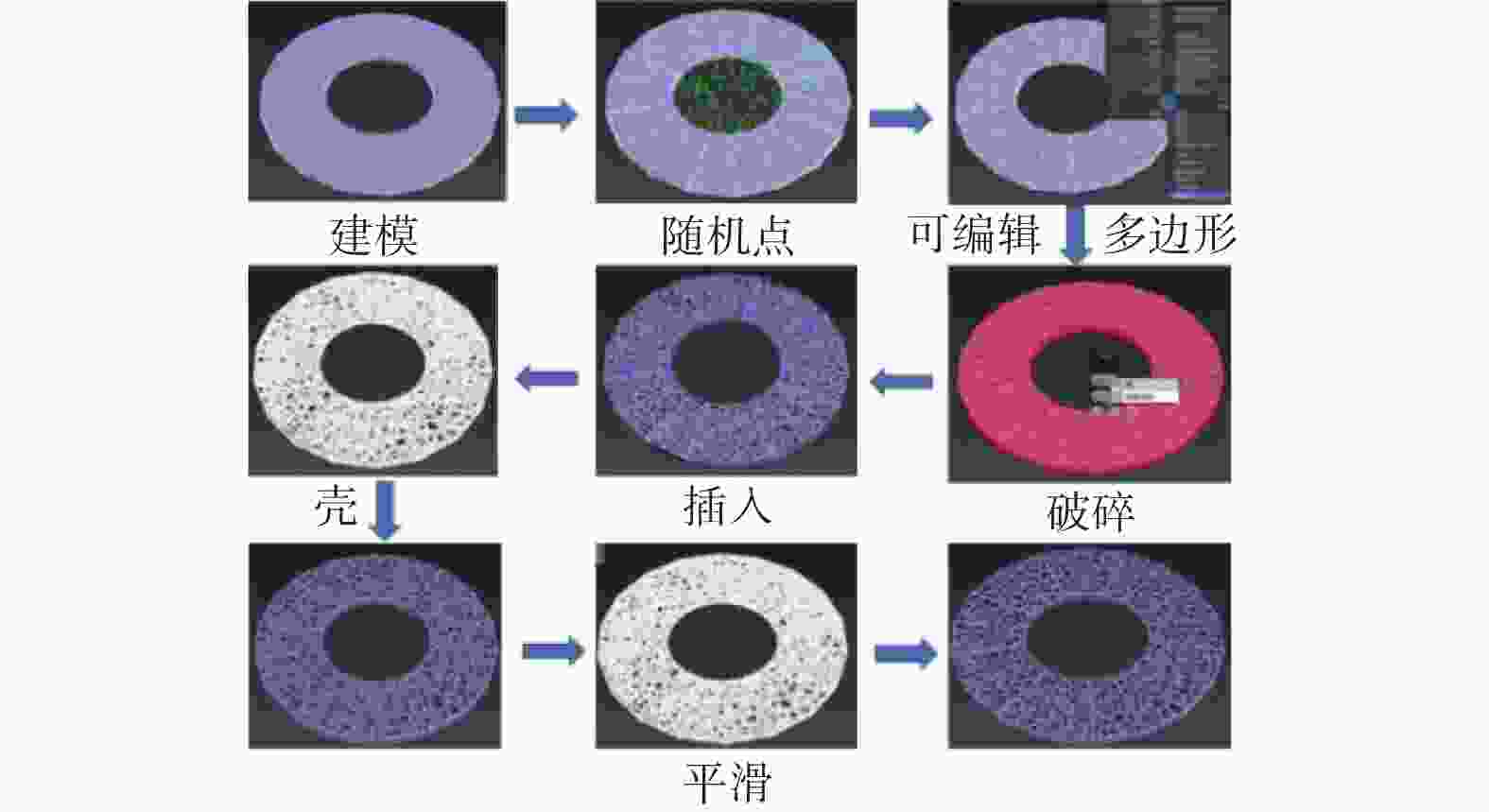
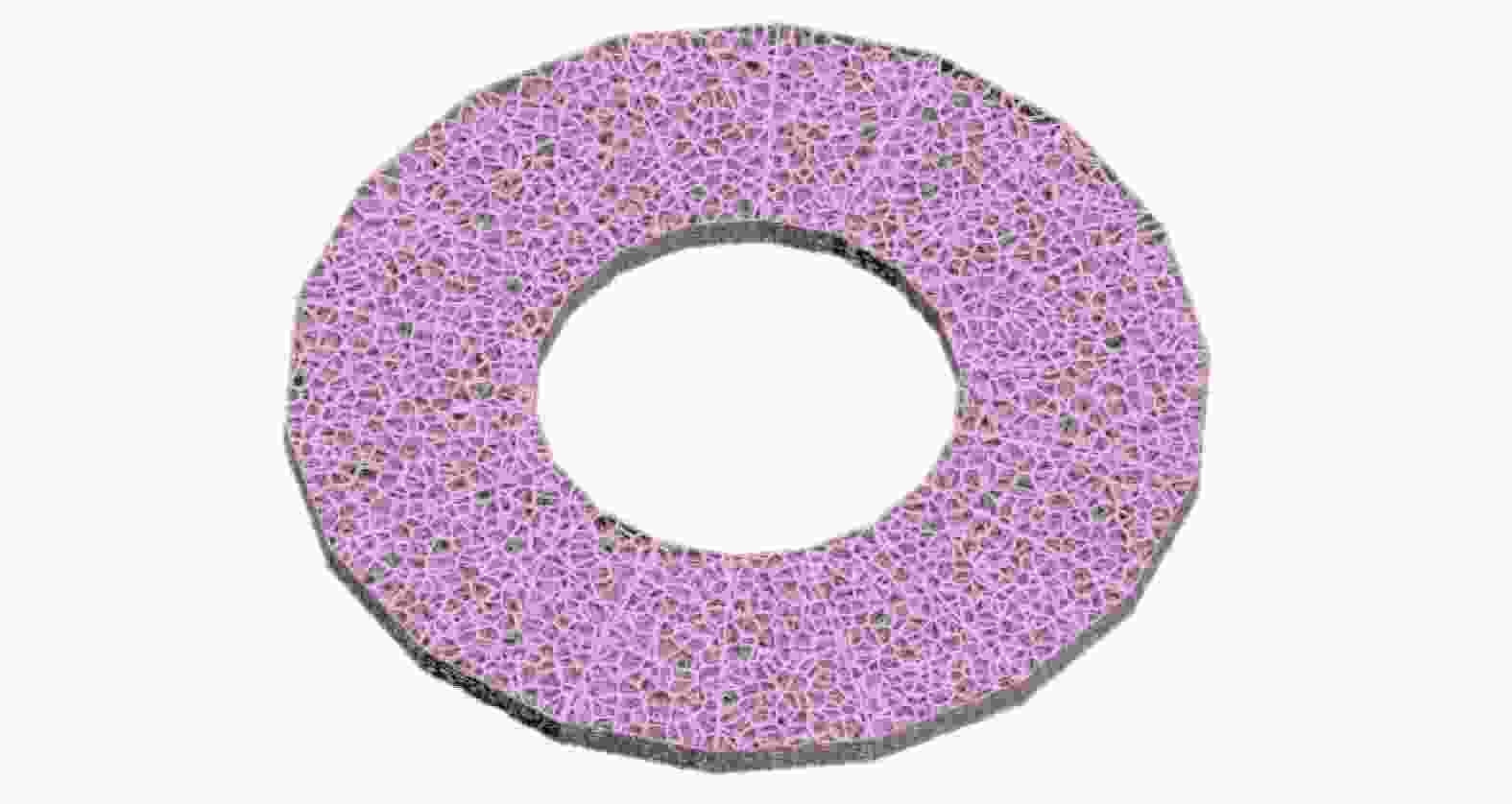
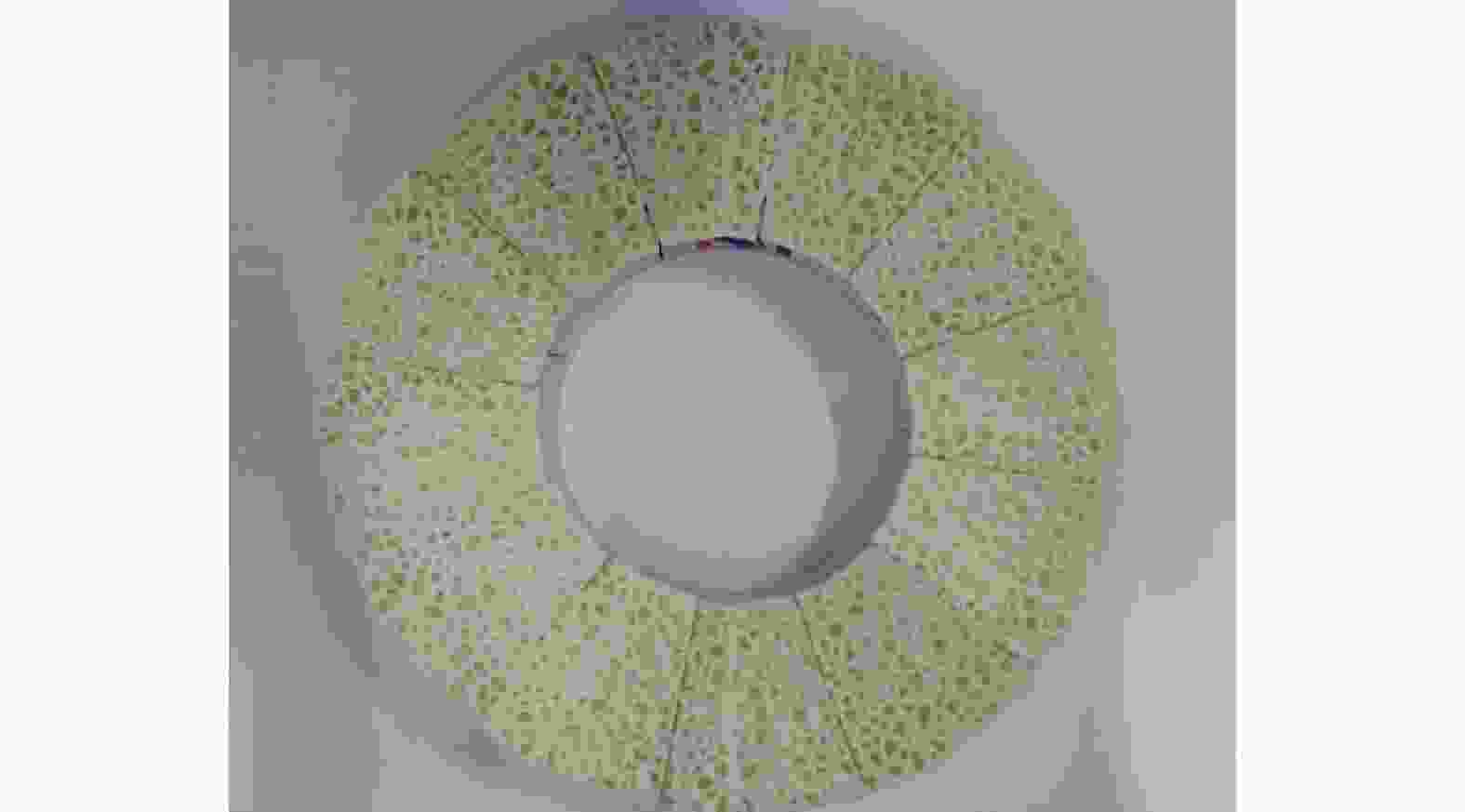
表 1 3D Max中磨盘建模参数
Table 1. Modeling parameters of the lap-grinding plate in 3D Max
参数 数值 半径1 r1 / mm 130 半径2 r2 / mm 60 高度 h / mm 10 随机点数量 n 8 000 随机种子数量 n0 10 壳内部量 nin 0 壳外部量 nout 1 网格平滑度 f 1 表 2 LCD光固化打印机与树脂材料参数
Table 2. LCD Light-curing 3D printer and resin material characteristics
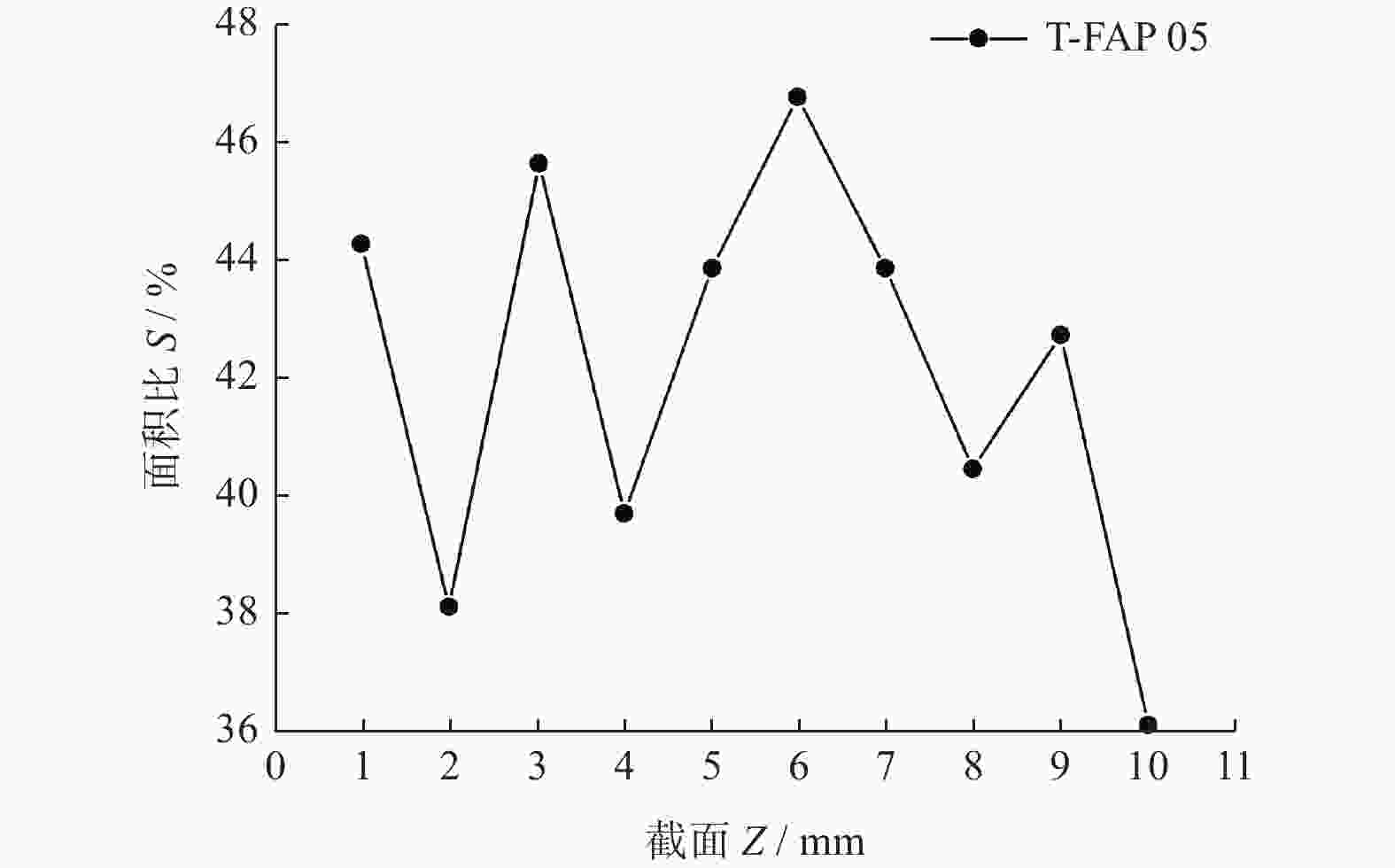
参数 数值或类型 打印层厚度 d / mm 0.01~0.20 打印速度 v / (mm·h−1) 20 额定功率 P / W 50 固化光源 LCD紫外光 材料固化密度 ρ / (g·cm−3) 1.05~1.25 材料固化波长 λ / nm 355~410 材料固化硬度 H 80 D 材料固化收缩率 β / % 3.72~4.24 表 3 不同磨盘磨粒轨迹所形成的面积占比
Table 3. Area ratio by abrasive grain trajectory of different lap-grinding plates
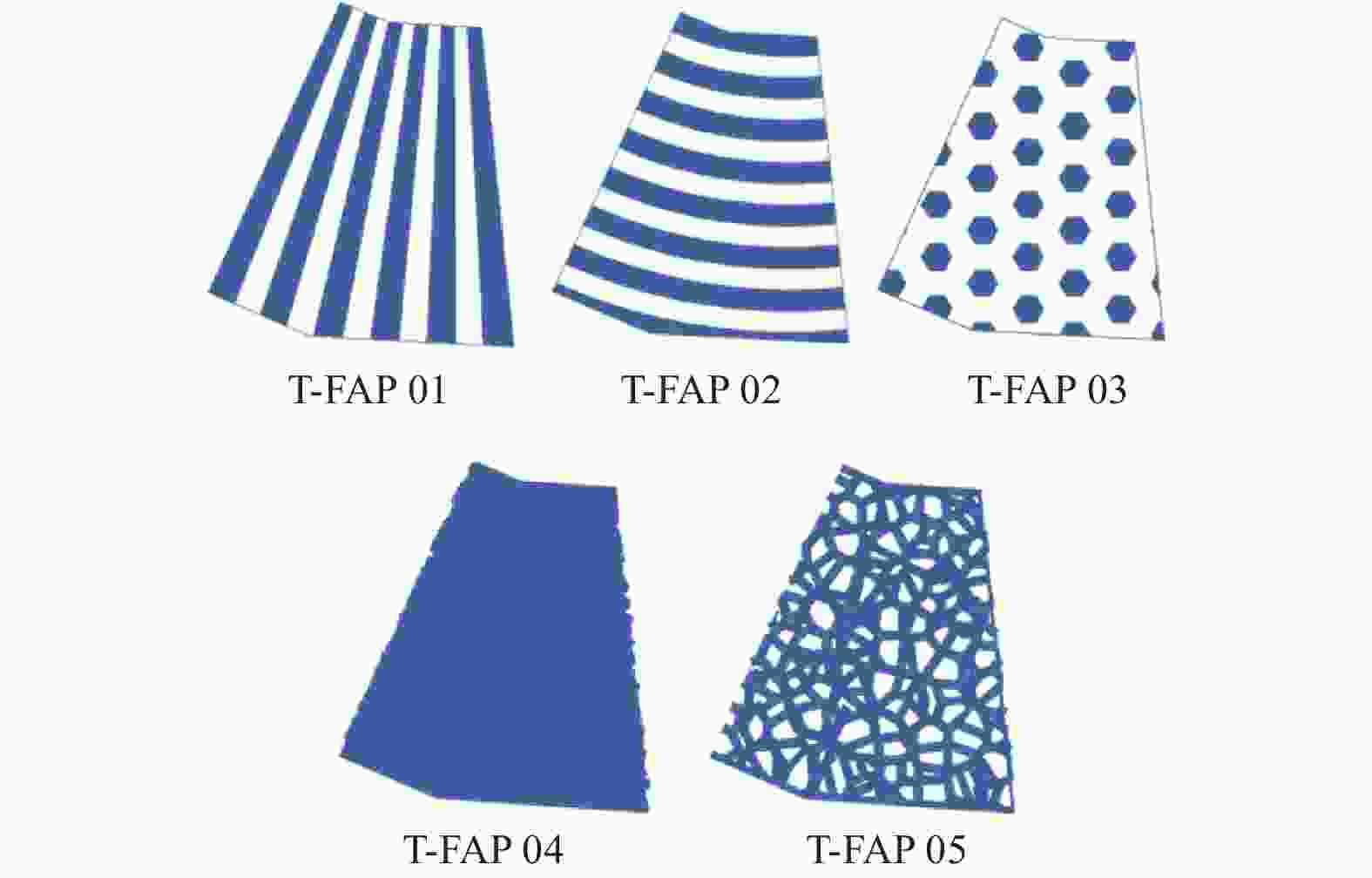
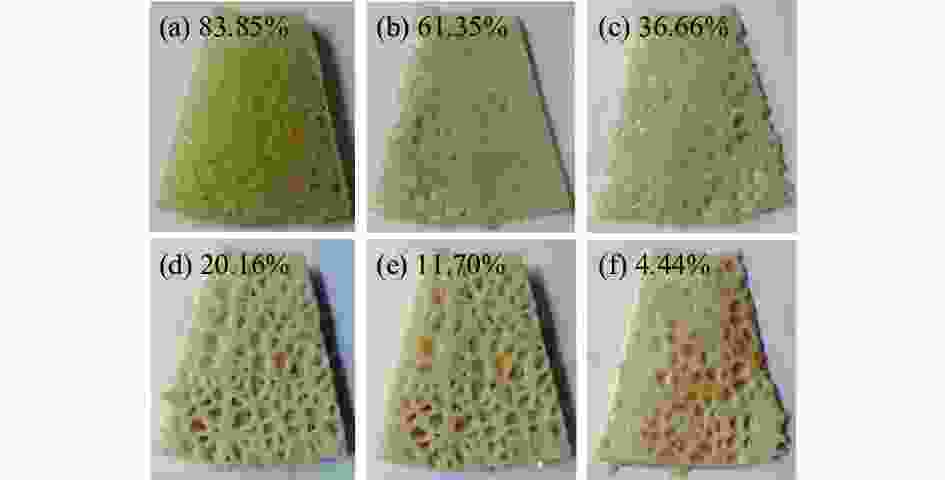
名称 轨迹面积比 S / % T-FAP 01 33.702 T-FAP 02 36.003 T-FAP 03 30.735 T-FAP 04 43.293 表 4 磨削实验参数表
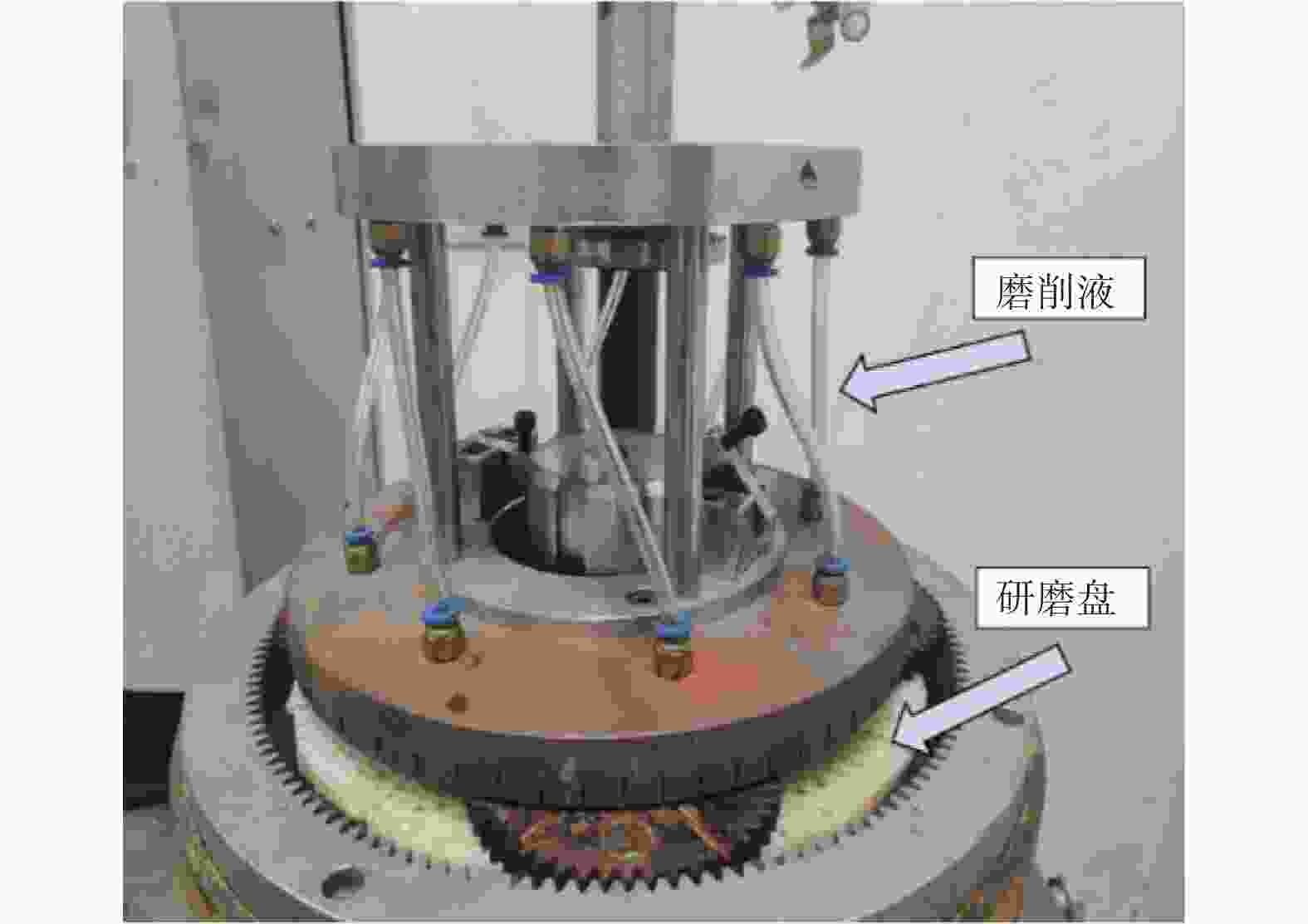
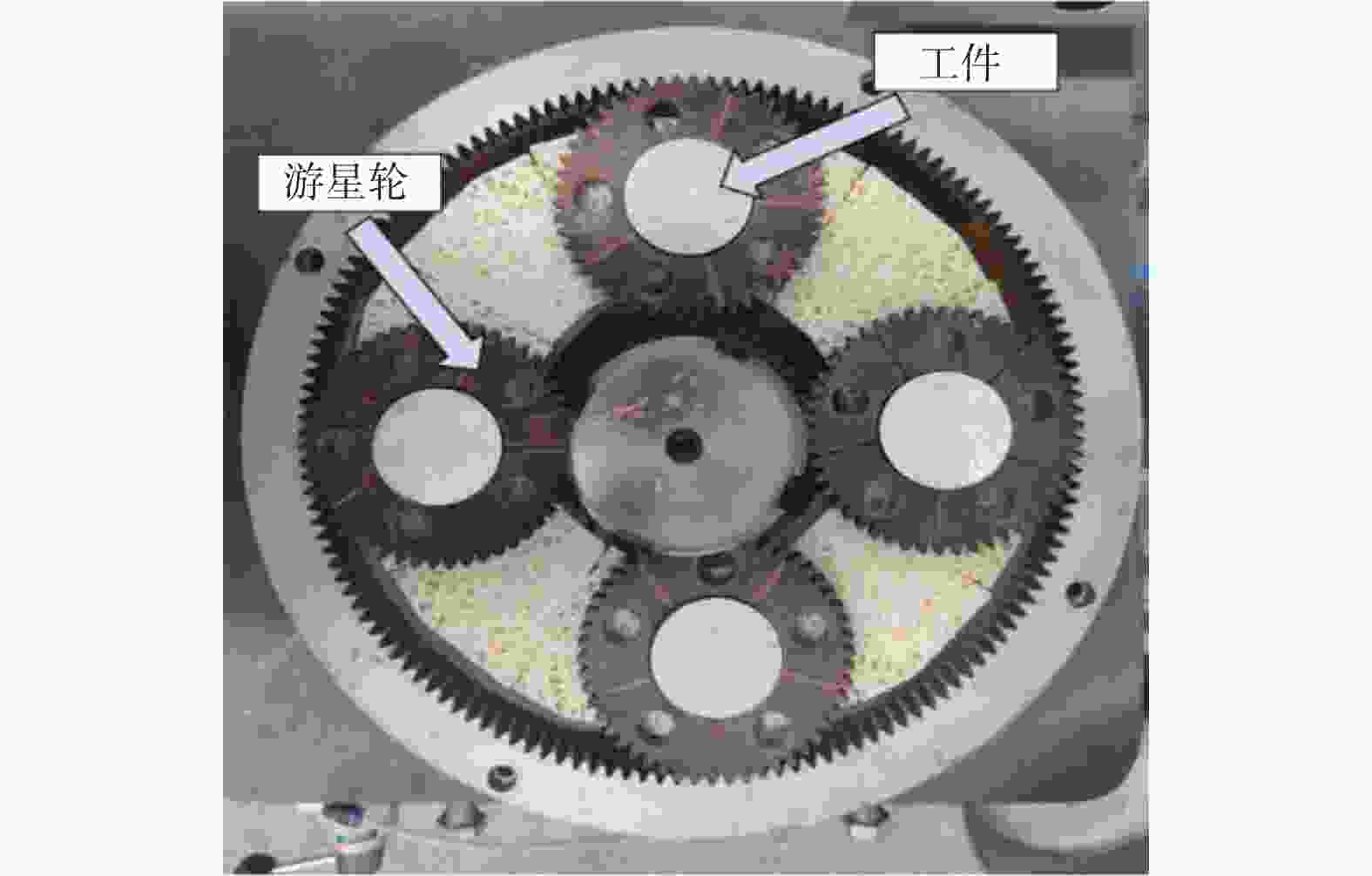
Table 4. Parameters of lap-grinding experiment
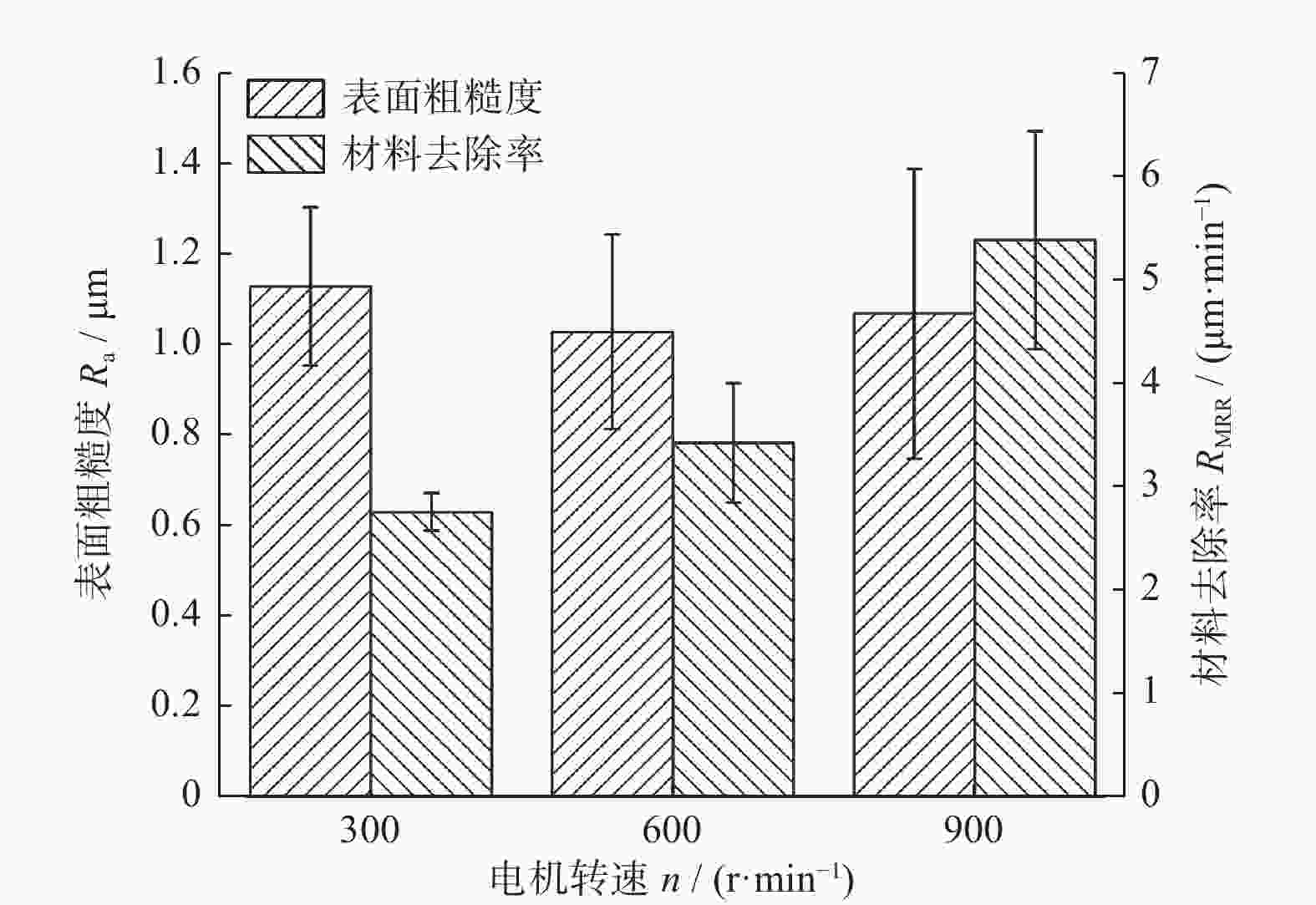
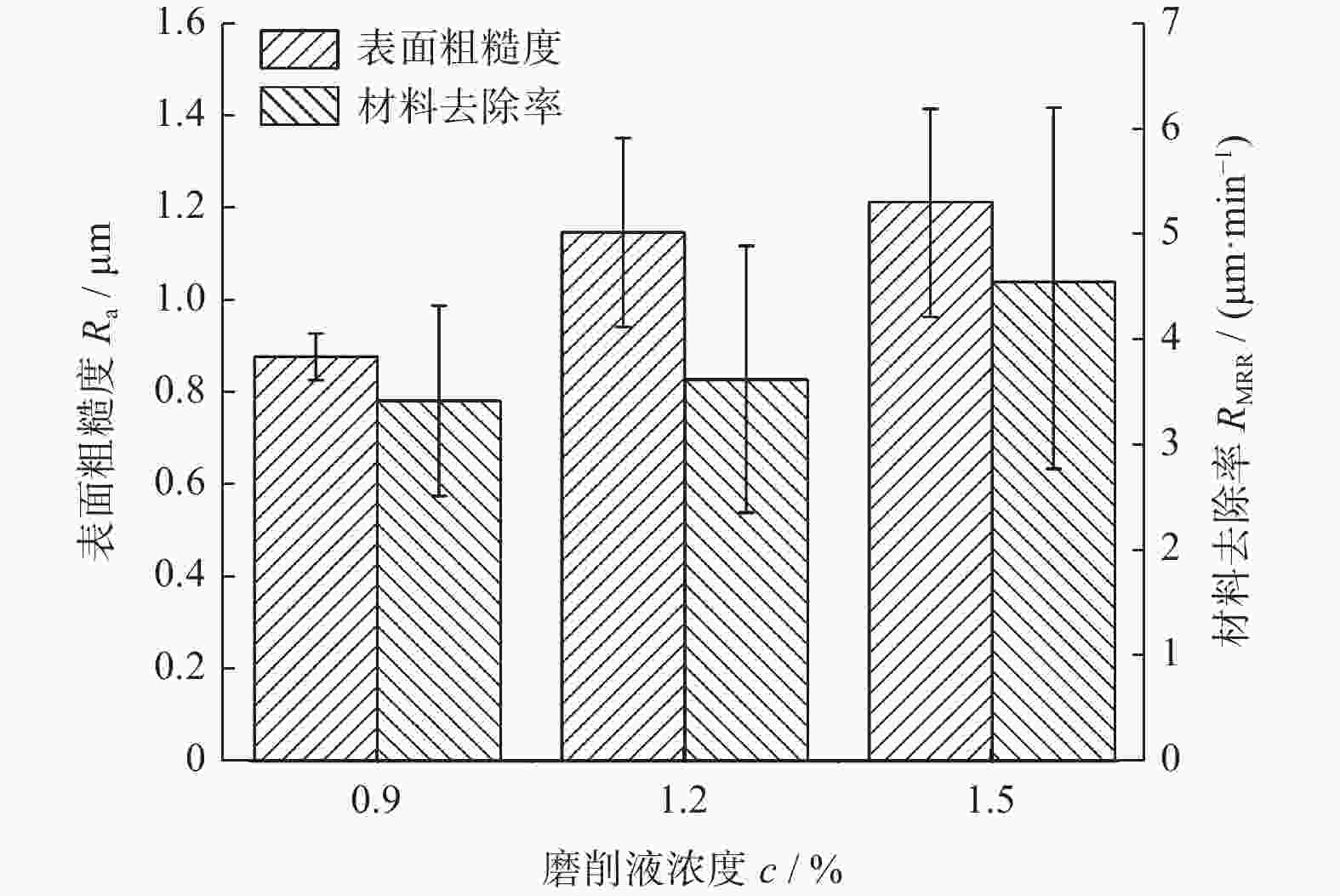
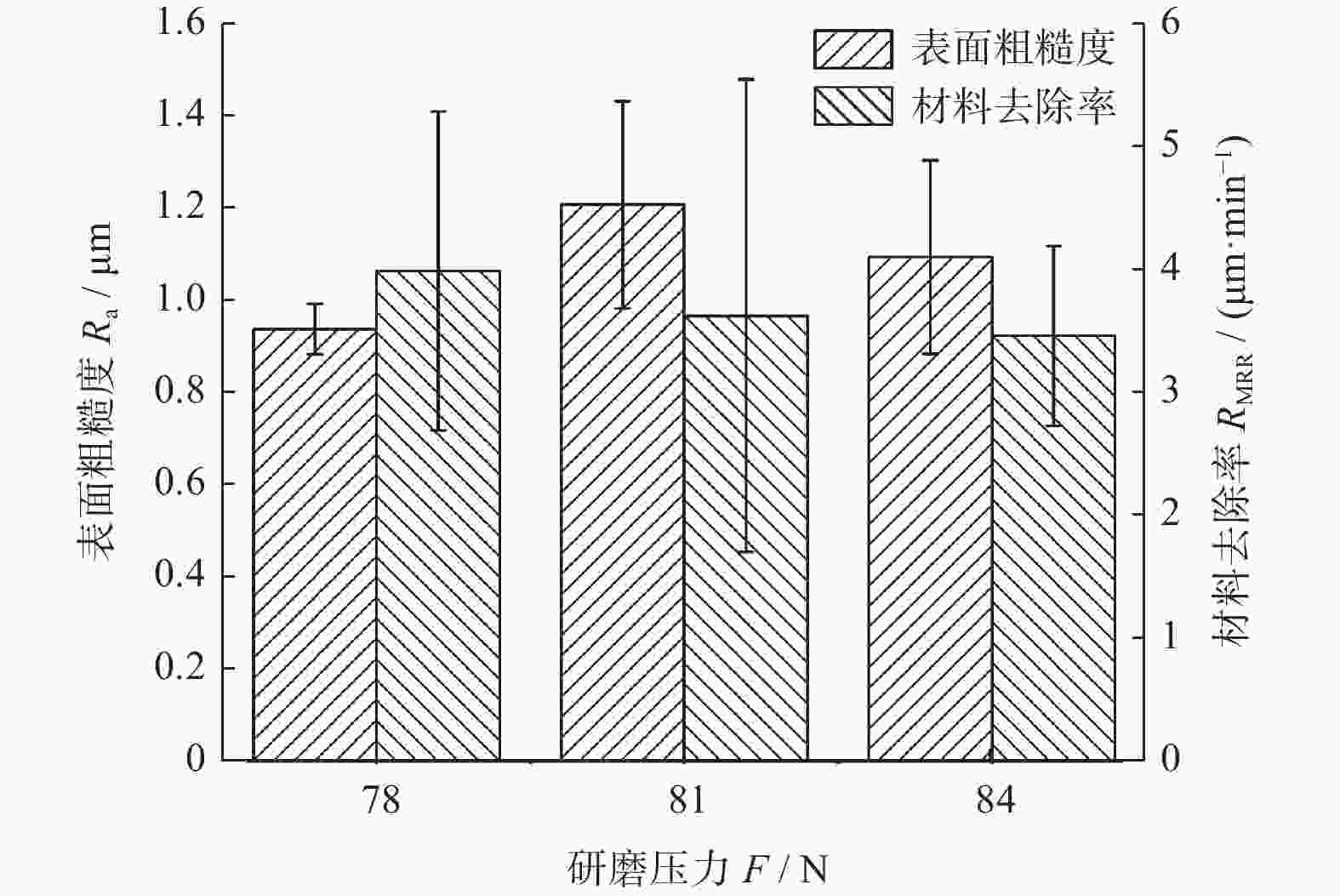
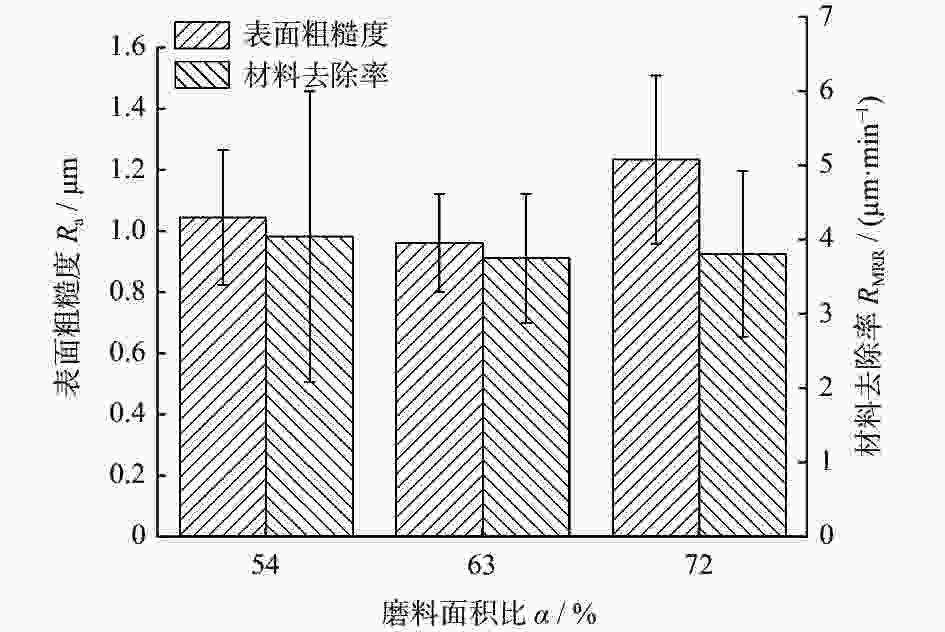
因素 水平 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ 电机转速 n / (r·min−1) 300 600 900 磨削液浓度 c / % 0.9 1.2 1.5 磨削压力 F / N 78 81 84 磨盘有效面积比 α / % 72 54 63 -
[1] TAWAKOLI T, AZARHOUSHANG B. Influence of ultrasonic vibrations on dry grinding of soft steel [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture: Design, Research and Application,2008,48(14):1585-1591. [2] HASHIMOTO F, SILVA E J, GUO C, et al. Industrial challenges in grinding [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2009,58(2):663-680. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2009.09.006 [3] BRINKSMEIER E, MUTLUGUNES Y, KLOCKE F, et al. Ultra-precision grinding [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2010,59(2):652-671. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.05.001 [4] TAWAKOLI T, AZARHOUSHANG B. Intermittent grinding of ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) utilizing a developed segmented wheel [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture,2011,51(2):112-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.11.002 [5] LEE K W, WONG P K, ZHANG J H. Study on the grinding of advanced ceramics with slotted diamond wheels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2000,100(1):230-235. [6] 杨张一. 开槽冰冻固结磨料抛光垫的抛光性能研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.YANG Zhangyi. Study on polishing performance of ice fixed abrasive polishing pad with grooves [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013. [7] TSAI M Y, WANG S M, TSAI C C, et al. Investigation of increased removal rate during polishing of single-crystal silicon carbide [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2015,80(9/10/11/12):1511-1520. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7023-4 [8] FANG C F, ZHAO Z X, LU L Y, et al. Influence of fixed abrasive configuration on the polishing process of silicon wafers [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2017,88(1/2/3/4):575-584. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-8808-9 [9] FANG C F, ZHAO Z X, HU Z W. Pattern optimization for phyllotactic fixed abrasive pads based on the trajectory method [J]. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing,2017,30(1):78-85. doi: 10.1109/TSM.2016.2637058 [10] FANG C F, YAN Z, HU Z W, et al. Pattern design of fixed abrasive pads inspired by the bee colony theory [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2018,97(5/6/7/8):2563-2574. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2114-7 [11] 林魁. 固结磨料研磨抛光垫的性能评价及自修整机理的研究 [D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.LIN Kui. Performance evaluation and self-conditioning of fixed-abrasive pad [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010. -




 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
