Grinding performance of micro-texured grinding wheel on different ceramic materials
-
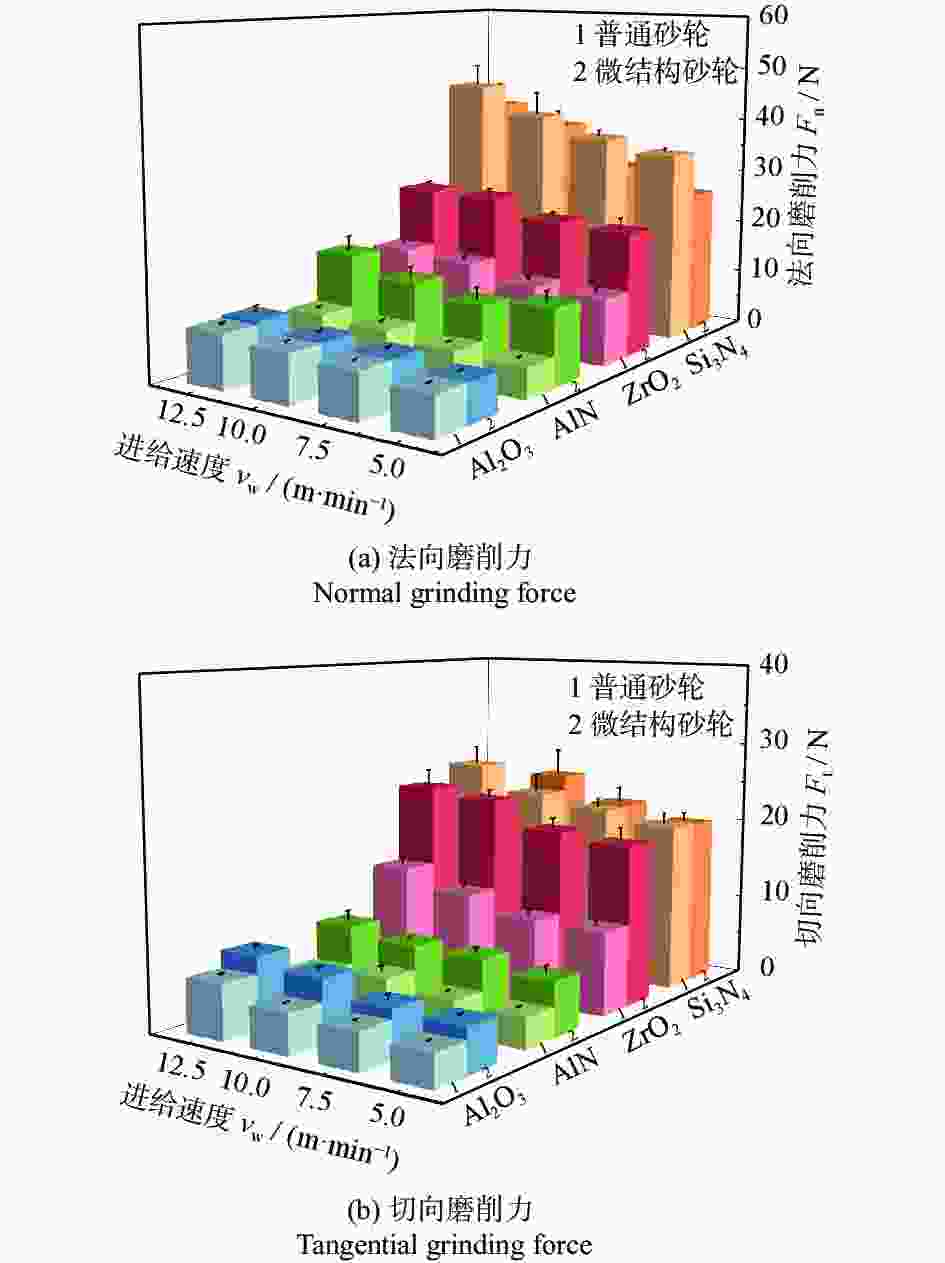
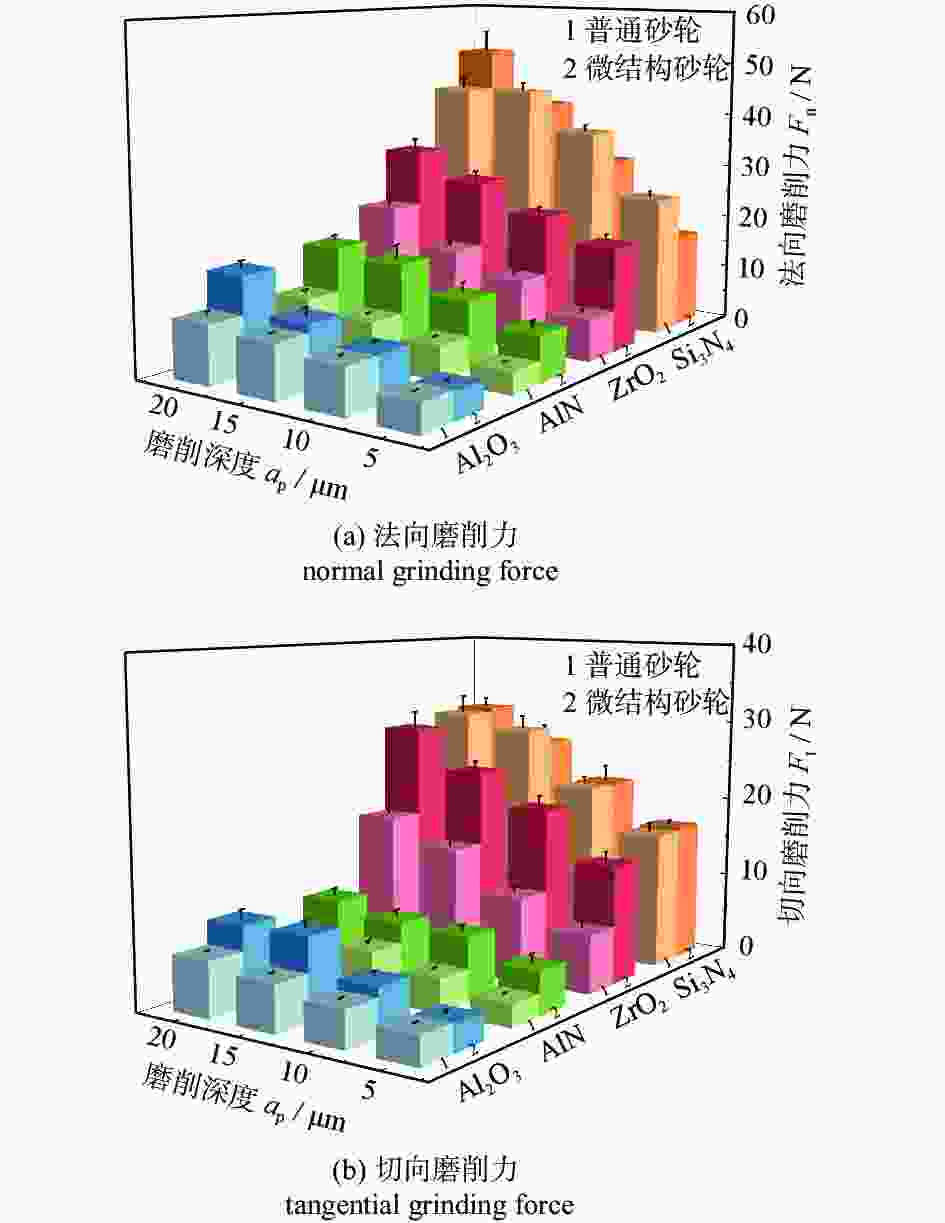
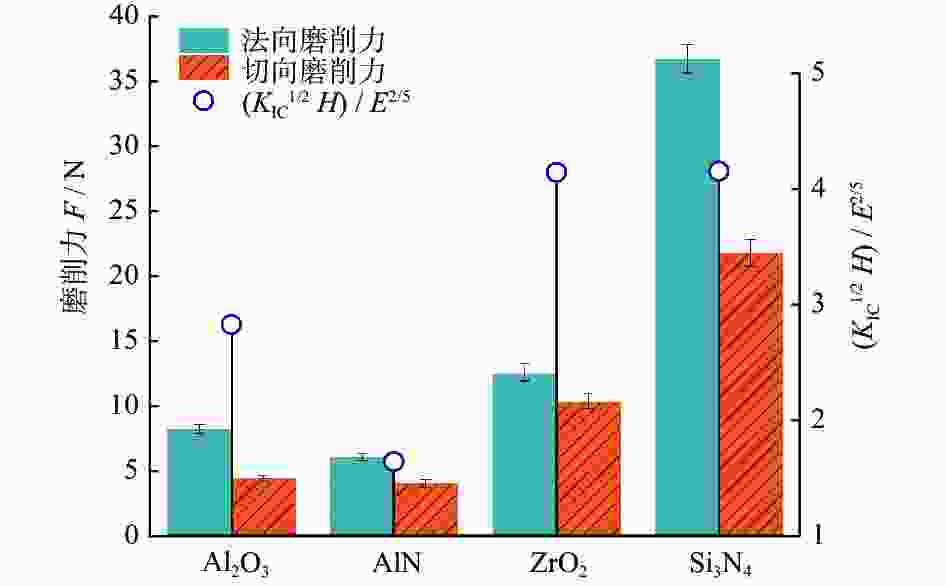
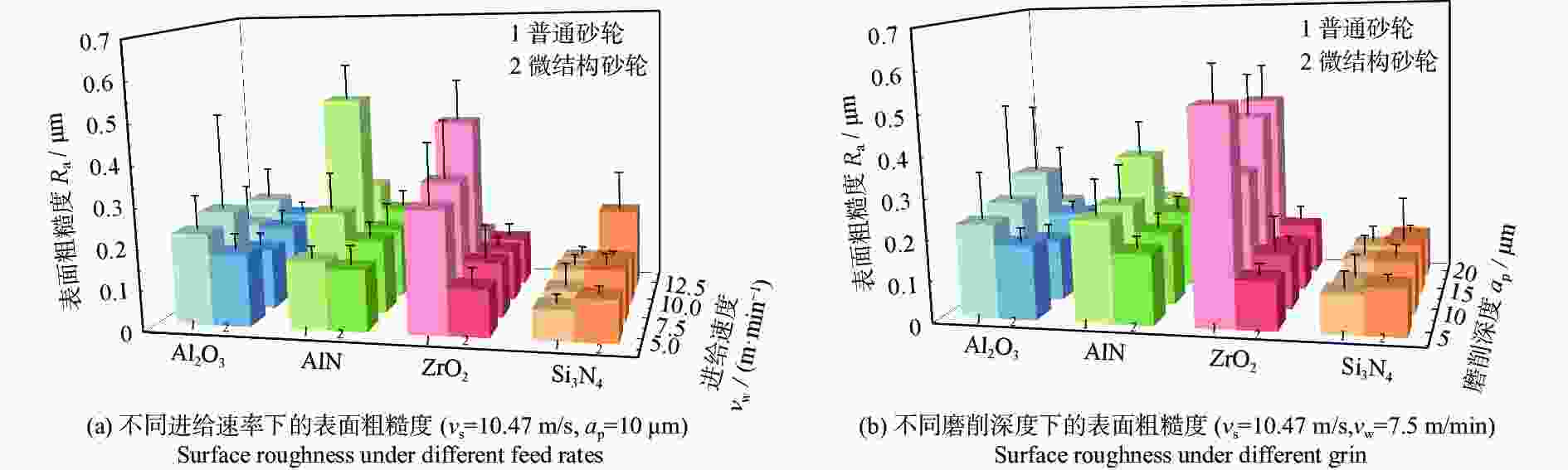
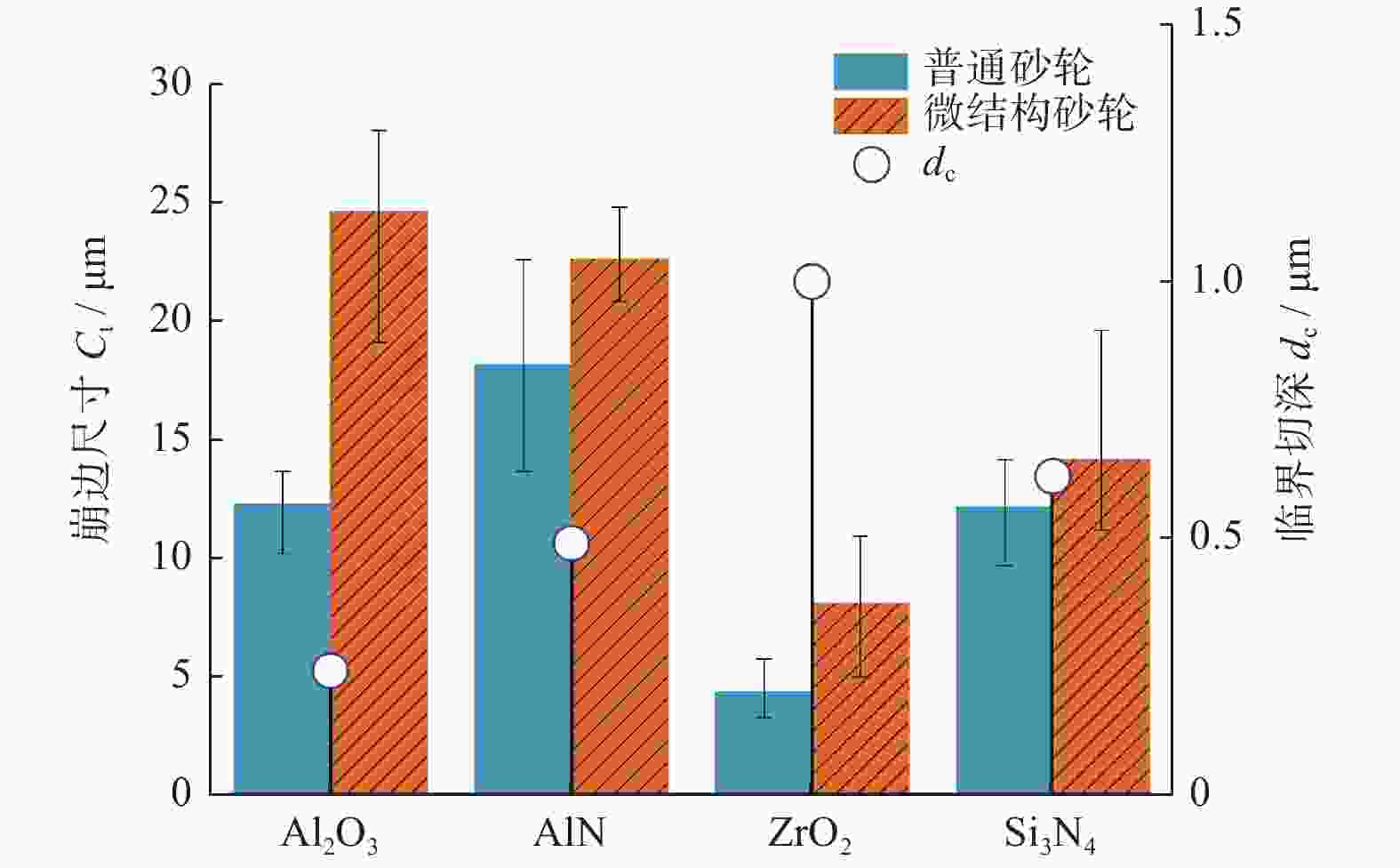
摘要: 基于阵列微孔的微结构砂轮和普通砂轮对氧化铝、氮化铝、氧化锆及氮化硅陶瓷材料的不同磨削性能,对比研究不同砂轮和不同陶瓷材料的磨削力、比磨削能、表面粗糙度及表面崩边特征。结果表明:相比普通砂轮,微结构砂轮提高了氧化铝、氮化铝及氧化锆陶瓷的磨削力和比磨削能,降低了表面粗糙度,而对氮化硅陶瓷的磨削力及表面粗糙度影响不明显;相比其他陶瓷,氮化硅陶瓷具有较高的磨削力和比磨削能。从磨削加工表面特征上看,氧化铝、氮化铝陶瓷以脆性去除方式为主,氧化锆以塑性去除为主,而氮化硅则兼具塑性和脆性去除特征;微结构砂轮加工表面崩边尺寸大于普通砂轮的崩边尺寸,氧化铝和氮化铝陶瓷的表面崩边尺寸明显大于氧化锆和氮化硅陶瓷的。Abstract: The grinding performance of micro-textured grinding wheel with arrayed micro-hole and common grinding wheel are compared through experiments on alumina, aluminum nitride, zirconia and silicon nitride ceramic materials. The grinding force, the specific grinding energy, the surface roughness and the surface chipping are analyzed. In comparison with common grinding wheel, micro-textured grinding wheel improves the grinding force and the specific grinding energy in grinding of alumina, aluminum nitride and zirconia ceramics, reduces the surface roughness of these ceramics, but has a little effect on the grinding force and the surface roughness of silicon nitride ceramics. Silicon nitride has higher grinding force and specific grinding energy than other ceramic materials do. The surface characteristics of alumina and aluminum nitride mainly imply brittle removal mode, while a ductile removal mode is characterized on the surface of zirconia and silicon nitride has both plastic and brittle removal characteristics. The surface chipping thickness processed by the micro-textured grinding wheel is larger than that of the common grinding wheel, while the surface chipping thickness of both alumina and aluminum nitride ceramics is larger than those of zirconia and silicon nitride ceramics.
-
表 1 陶瓷材料的理化性能及用途
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of ceramic materials and their applications
表 2 陶瓷材料的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of ceramic materials
陶瓷 硬度 H / GPa 弹性模量 E / GPa 断裂韧性 KIC / (MPa·m1/2) Al2O3 16.1 422 3.9 AlN 9.8 342 3.0 Si3N4 14.7 268 7.0 ZrO2 13.5 257 8.0 表 3 磨削实验参数
Table 3. Grinding parameters
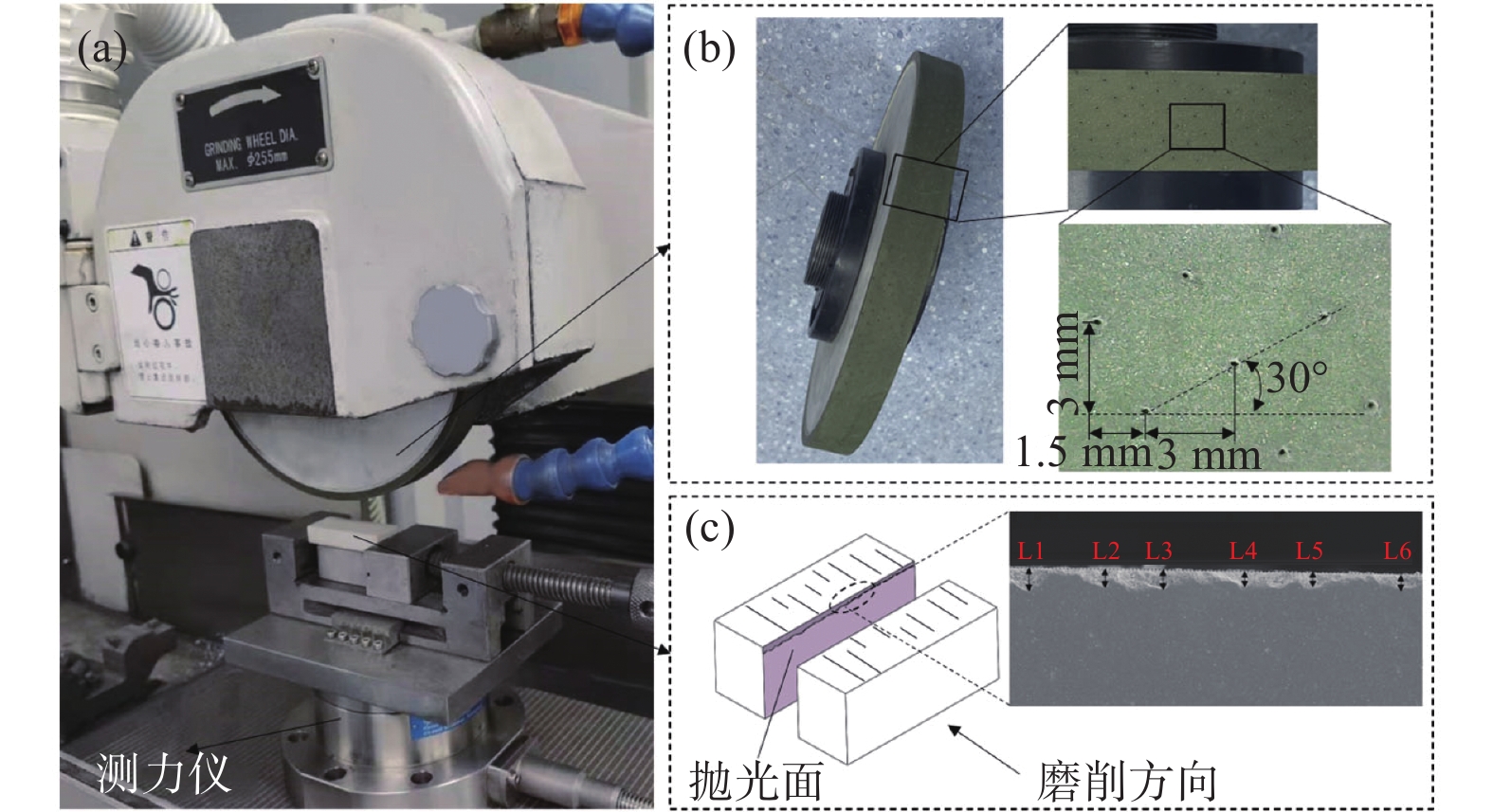
参数类型 取值 砂轮线速度vs / (m·s−1) 10.47 进给速度vw / (m·min−1) 5.0,7.5,10.0,12.5 磨削深度ap / μm 5,10,15,20 -
[1] 谢志鹏, 许靖堃, 安迪. 先进陶瓷材料烧结新技术研究进展 [J]. 中国材料进展,2019,38(9):821-830. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201906007XIE Zhipeng, XU Jingkun, AN Di. Research progress of novel sintering technology for advanced ceramic materials [J]. Materials China,2019,38(9):821-830. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201906007 [2] CHOUDHARY A, PAUL S. The wear mechanisms of diamond grits in grinding of alumina and yttria-stabilized zirconia under different cooling-lubrication schemes [J]. Wear,2020,454/455:203315. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2020.203315 [3] CHOUDHARY A, NASKAR A, PAUL S. Effect of minimum quantity lubrication on surface integrity in high-speed grinding of sintered alumina using single layer diamond grinding wheel [J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(14):17013-17021. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.144 [4] CHOUDHARY A, NASKAR A, PAUL S. An investigation on application of nano-fluids in high speed grinding of sintered alumina [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2018,35:624-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.09.013 [5] 孙跃. 氧化铝陶瓷磨削去除率模型的建立与试验研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2012.SUN Yue. Experimental study of the alumina ceramic grinding removal rate model [D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2012. [6] ZHANG B, ZHENG X L, TOKURA H, et al. Grinding induced damage in ceramics [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2003,132(1/2/3):353-364. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00952-4 [7] RABIEY M. Dry grinding with CBN wheels, the effect of structuring [M]. Heimsheim: Jost Jetter Verlag, 2011. [8] ZHANG X H, WEN D D, SHI Z Y, et al. Grinding performance improvement of laser micro-structured silicon nitride ceramics by laser macro-structured diamond wheels [J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(1):795-802. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.034 [9] LI H N, AXINTE D. Textured grinding wheels: A review [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2016,109:8-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.07.001 [10] NGUYEN T, ZHANG L C. Performance of a new segmented grinding wheel system [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture,2009,49:291-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.10.015 [11] AZARHOUSHANG B. Wear of non-segmented and segmented diamond wheels in high-speed deep grinding of carbon fibre-reinforced ceramics [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2014,74(9/10/11/12):1293-1302. doi: 10.1007/s00170-014-6082-2 [12] 郭兵, 金钱余, 赵清亮, 等. 表面结构化砂轮磨削加工技术研究进展 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2016,48(7):1-13. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2016.07.001GUO Bing, JIN Qianyu, ZHAO Qingliang, et al. Research progress of grinding technology with surface structured wheels [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2016,48(7):1-13. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2016.07.001 [13] WU M T, GUO B, ZHAO Q L, et al. Precision grinding of a microstructured surface on hard and brittle materials by a microstructured coarse-grained diamond grinding wheel [J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(7):8026-8034. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.243 [14] GUO B, WU M T, ZHAO Q L, et al. Improvement of precision grinding performance of CVD diamond wheels by micro-structured surfaces [J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(14):17333-17339. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.197 [15] GUO B, ZHAO Q L, FANG X Y. Precision grinding of optical glass with laser micro-structured coarse-grained diamond wheels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2014,214(5):1045-1051. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.12.013 [16] ZHANG X H, ZHANG Z C, DENG Z H, et al. Precision grinding of silicon nitride ceramic with laser macro-structured diamond wheels [J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2019,109:418-428. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.08.021 [17] WALTER C, KOMISCHKE T, KUSTER F, et al. Laser-structured grinding tools – Generation of prototype patterns and performance evaluation [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2014,214(4):951-961. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.11.015 [18] 林志兵, 杜志军, 李明聪, 等. 刃–孔协同分布钎焊金刚石微结构端面磨头加工氧化铝陶瓷性能的研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(2):36-41. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.2.0007LIN Zhibing, DU Zhijun, LI Mingcong, et al. Preparation of edge-hole co-distributed brazed diamond microstructure end-grinding wheel and its grinding performance on alumina ceramics [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(2):36-41. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.2.0007 [19] 刘杰, 曹剑锋, 孙正斌, 等. 树脂金刚石砂轮加工氧化铝陶瓷的磨削工艺试验研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2016,36(4):79-83. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2016.4.0016LIU Jie, CAO Jianfeng, SUN Zhengbin, et al. Experimental study on process of grinding alumina ceramics with resin bond diamond grinding wheel [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2016,36(4):79-83. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2016.4.0016 [20] TANG P, FENG J Y, WAN Z P, et al. Influence of grain orientation on hardness anisotropy and dislocation behavior of AlN ceramic in nanoindentation [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(14):20298-20309. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.038 [21] SUN R, YANG X, ARIMA K, et al. High-quality plasma-assisted polishing of aluminum nitride ceramic [J]. CIRP Annals,2020,69(1):301-304. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2020.04.096 [22] 卞平艳. 二维超声振动磨削纳米氧化锆陶瓷的温度场分布特性研究 [D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2007.BIAN Pingyan. Study on two dimensional ultrasonic vibration grinding temperature field distribution character of nano ZrO2 ceramics [D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2007. [23] 毛亚男. 氧化锆/氧化铝复合陶瓷制备工艺研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2016.MAO Yanan. Research on preparation technology of ZrO2/Al2O3 nano-composite ceramics [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2016. [24] PIOSIK A, ŻUROWSKI K, PIETRALIK Z, et al. Structural studies of degradation process of zirconium dioxide tetragonal phase induced by grinding with dental bur [J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research,2017,411:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2017.07.024 [25] 李颂华, 王科冲, 孙健, 等. 氧化锆陶瓷磨削工艺优化和粗糙度控制研究 [J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(1):271-277.LI Songhua, WANG Kechong, SUN Jian, et al. Research on grinding process optimization and roughness control of zirconia ceramics [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(1):271-277. [26] 吴玉厚, 王浩, 孙健, 等. 氮化硅陶瓷磨削表面质量的建模与预测 [J]. 表面技术,2020,49(3):281-289. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2020.03.036WU Yuhou, WANG Hao, SUN Jian, et al. Modeling and prediction of surface quality of silicon nitride ceramic grinding [J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(3):281-289. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2020.03.036 [27] HUANG H, LIU Y C. Experimental investigations of machining characteristics and removal mechanisms of advanced ceramics in high speed deep grinding [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2003,43(8):811-823. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00050-6 [28] 谢桂芝. 工程陶瓷高速深磨机理及热现象研究 [D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2009.XIE Guizhi. The investigation of mechanism and thermal phenomena in high speed deep grinding of advanced ceramics [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2009. [29] CHEN J Y, SHEN J Y, HUANG H, et al. Grinding characteristics in high speed grinding of engineering ceramics with brazed diamond wheels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2010,210(6/7):899-906. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.02.002 [30] 王攸. 氧化铝陶瓷磨削温度的有限元仿真及试验研究 [D]. 厦门: 华侨大学, 2017.WANG You. Finite element simulation and experimental study on grinding temperature of alumina ceramics [D]. Xiamen: Huaqiao University, 2017. [31] 鲁慧峰. 氮化铝粉末制备及注射成形研究 [D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2020.LU Huifeng. Study on preparation and injection molding of aluminum nitride powder [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2020. [32] CAI L Q, GUO X G, GAO S, et al. Material removal mechanism and deformation characteristics of AlN ceramics under nanoscratching [J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(16):20545-20554. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.034 [33] YANG Z C, ZHU L D, LIN B, et al. The grinding force modeling and experimental study of ZrO2 ceramic materials in ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding [J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(7):8873-8889. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.216 [34] HUANG H, YIN L, ZHOU L B. High speed grinding of silicon nitride with resin bond diamond wheels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2003,141(3):329-336. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00284-X [35] 郑彧, 童亚琦, 张伟儒. 高导热氮化硅陶瓷基板材料研究现状 [J]. 真空电子技术,2018(4):13-17. doi: 10.16540/j.cnki.cn11-2485/tn.2018.04.03ZHENG Yu, TONG Yaqi, ZHANG Weiru. Research on high thermal conductivity silicon nitride ceramic substrate materials [J]. Vacuum Electronics,2018(4):13-17. doi: 10.16540/j.cnki.cn11-2485/tn.2018.04.03 [36] AGARWAL S, VENKATESWARA R P. Predictive modeling of force and power based on a new analytical undeformed chip thickness model in ceramic grinding [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2013,65:68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2012.10.006 [37] XU H, JAHANMIR S, IVES L K. Mechanisms of material removal in abrasive machining of ceramics [J]. InterCeram: International Ceramic Review,1998,46(6):380-385. [38] MALKIN S. Grinding technology: Theory and applications of machining with abrasives [M]. Oxford, UK: Pergamon Press, 1991. [39] 吴志远, 梁克高, 田欣利, 等. 烷烃磨削液应用于Si3N4陶瓷磨削时的砂轮堵塞机理及改性研究 [J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报,2010,24(6):85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1497.2010.06.020WU Zhinyuan, LIANG Kegao, TIAN Xinli, et al. Research on blocking mechanism and chemical modification for alkane grinding fluid applied for Si3N4 ceramic grinding [J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering,2010,24(6):85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1497.2010.06.020 [40] 吴志远, 时小军, 王淑卉, 等. 有机磨削液在氮化硅陶瓷磨削过程中的清洗机理研究 [J]. 现代制造工程,2011(12):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3133.2011.12.016WU Zhinyuan, SHI Xiaojun, WANG Shuhui, et al. The cleaning mechanisms on organic grinding fluid applied for ceramic grinding [J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering,2011(12):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3133.2011.12.016 [41] BIFANO T G, DOW T A, SCATTERGOOD R O. Ductile-regime grinding: A new technology for machining brittle materials [J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry,1991,113(2):184-189. doi: 10.1115/1.2899676 -




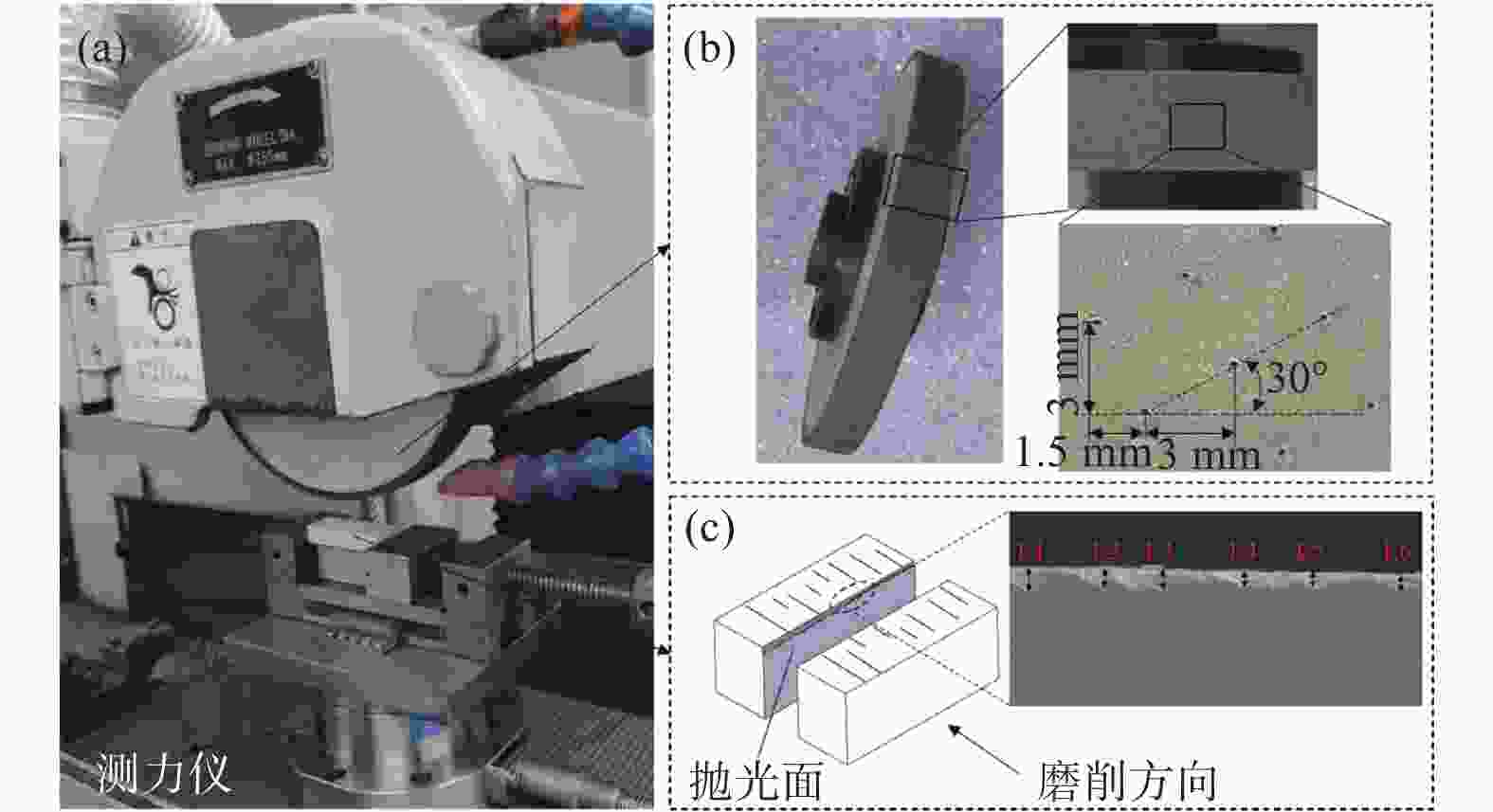
 下载:
下载:










 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
