Effect of cylindrical longitudinal grinding process on surface integrity of 18CrNiMo7–6 steel
-
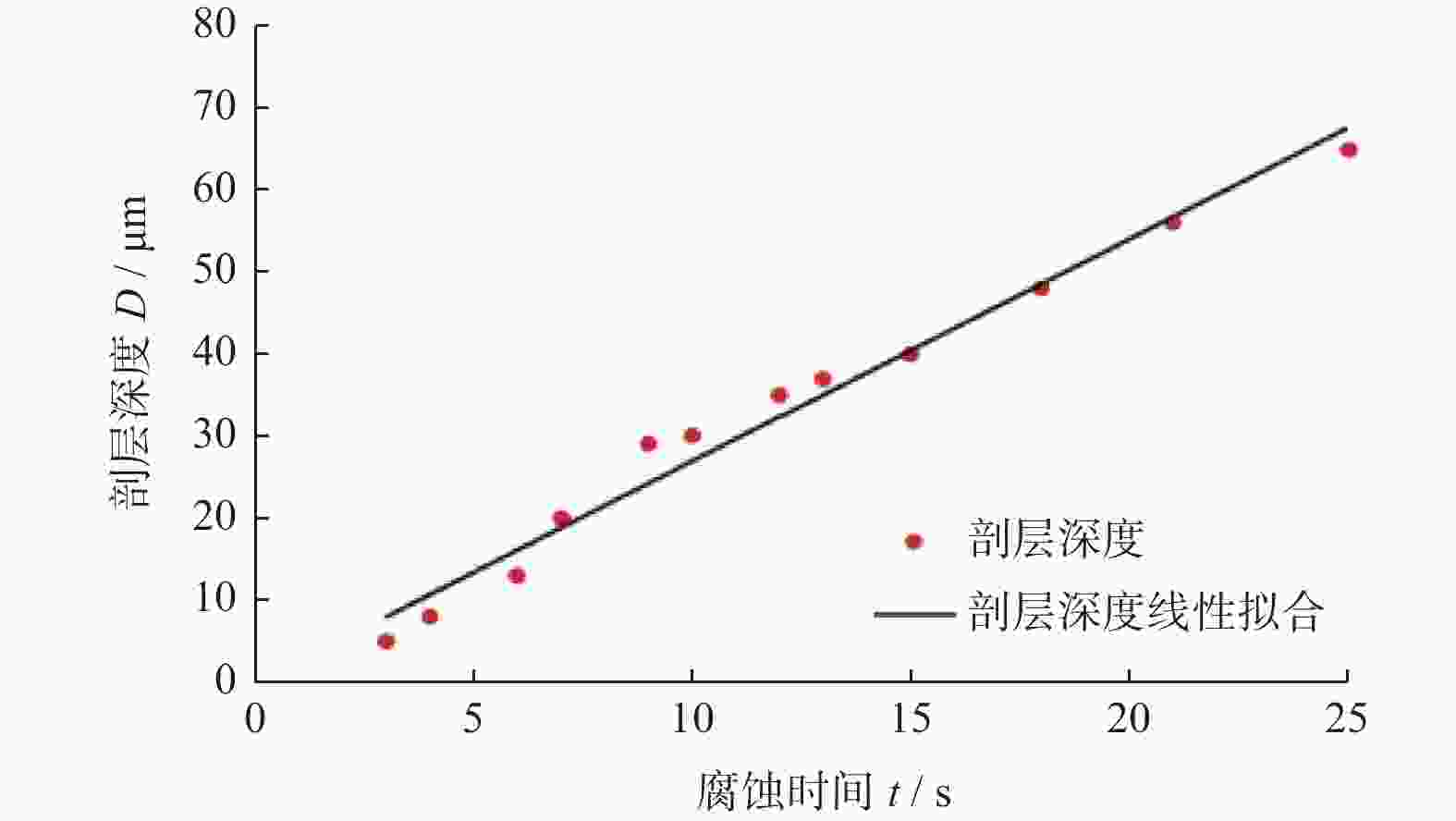
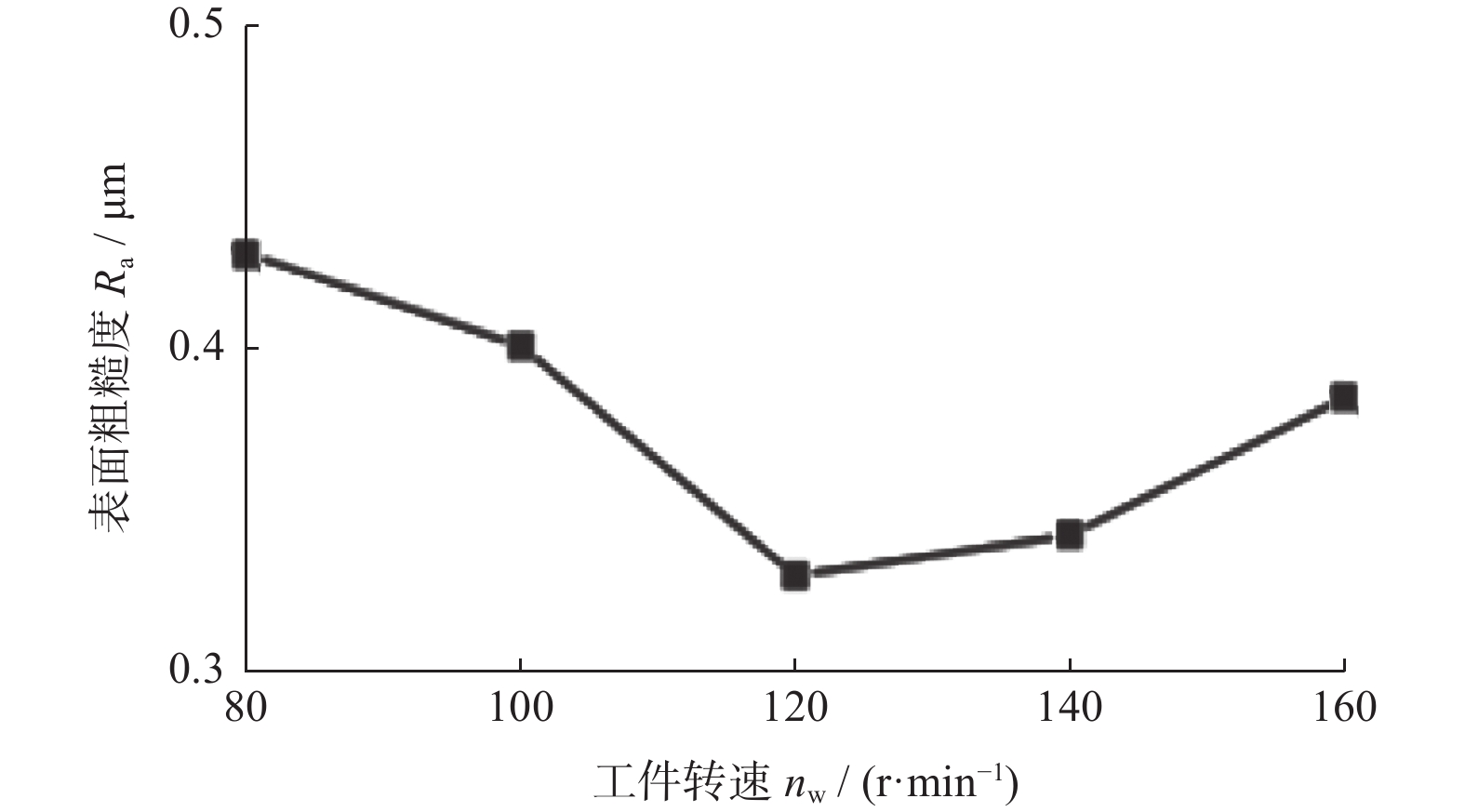
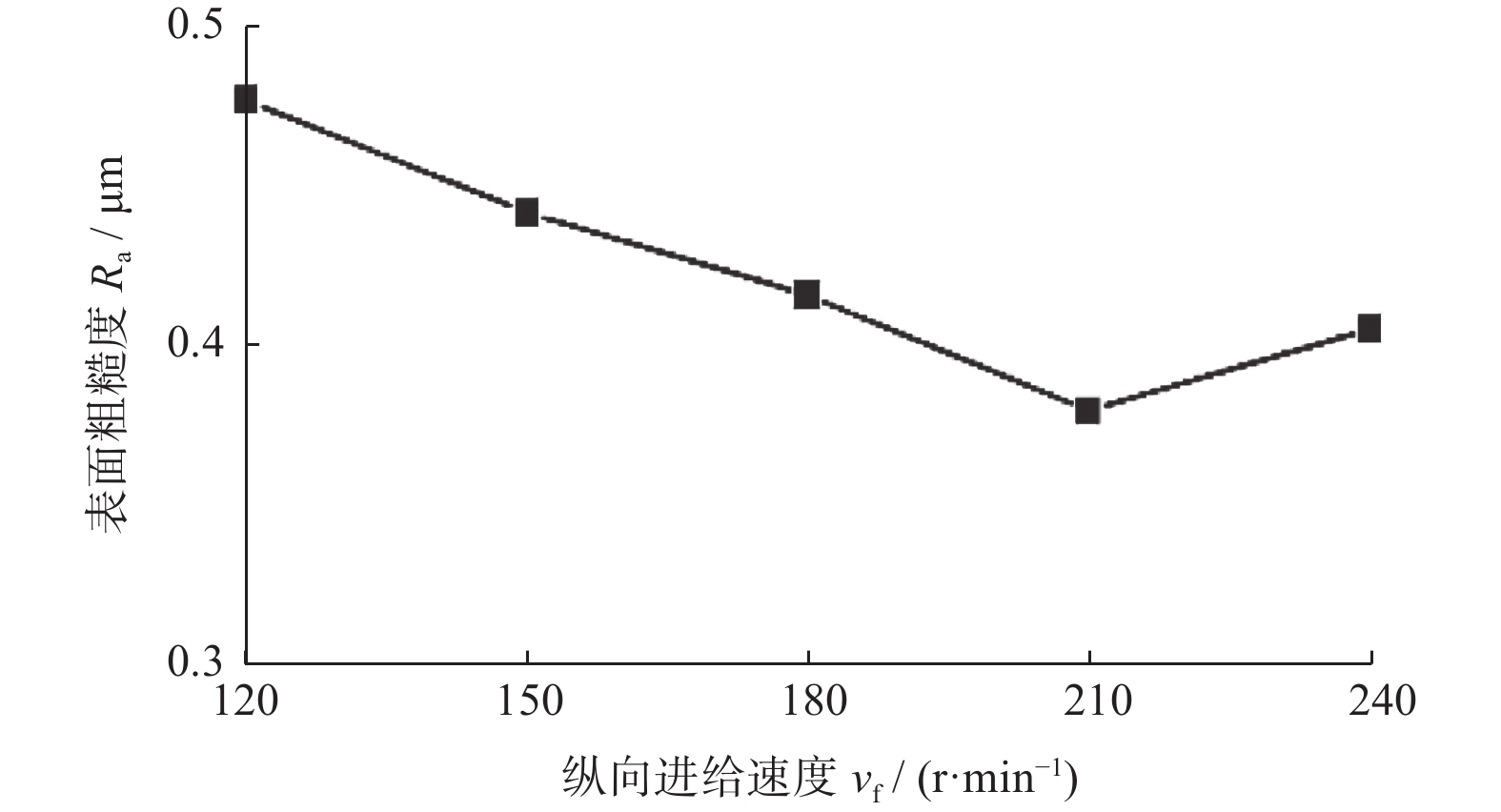
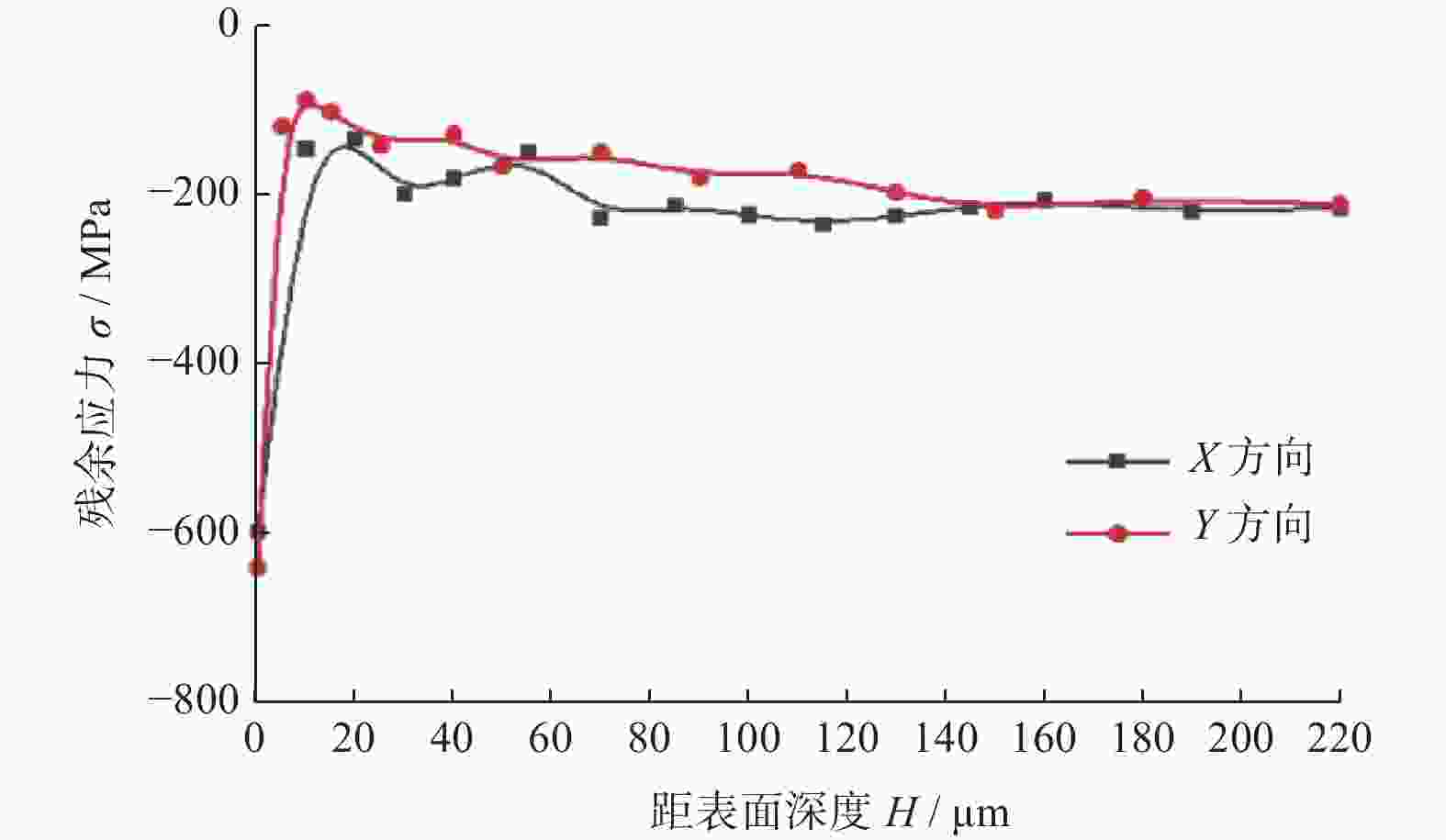
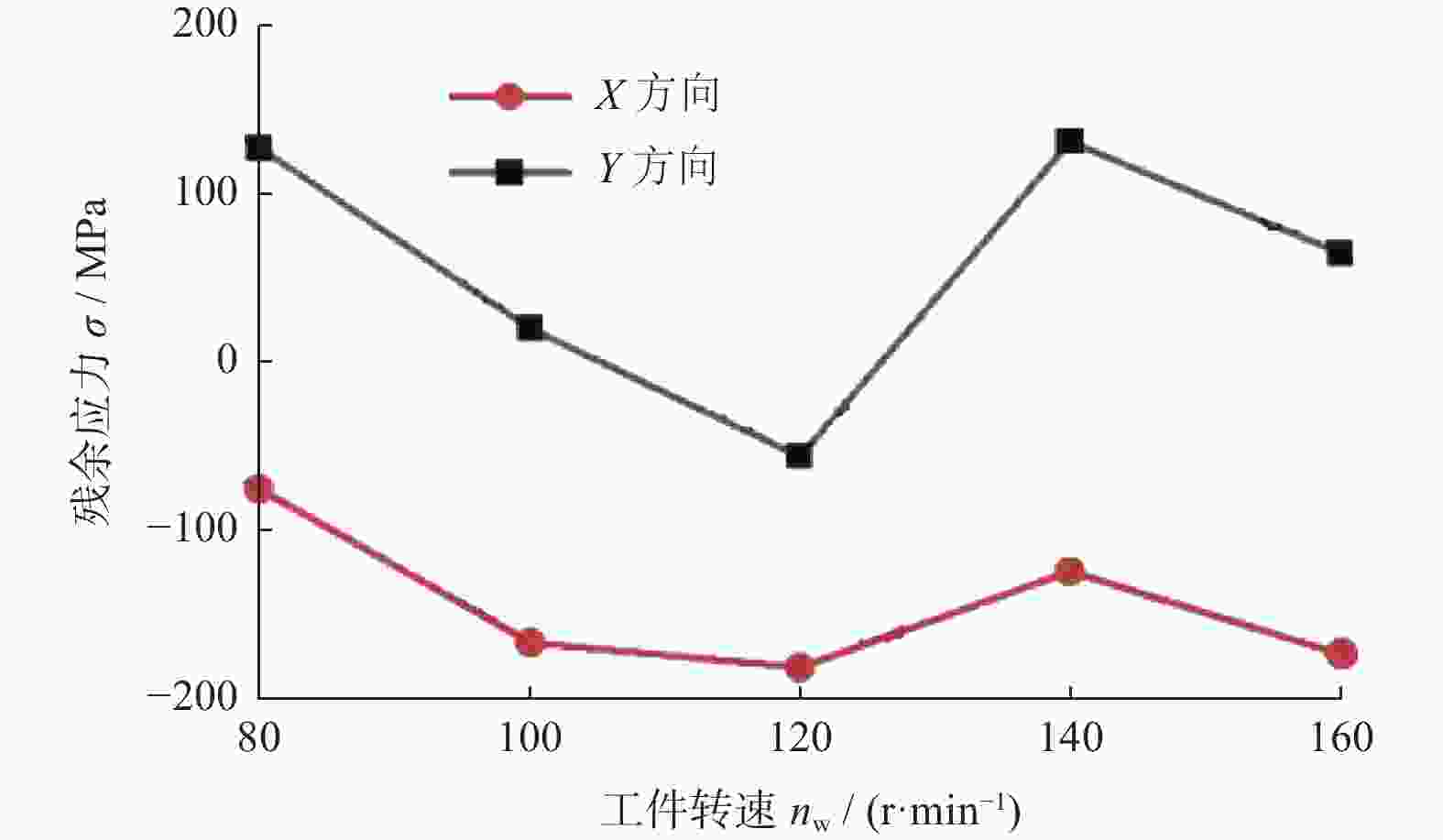
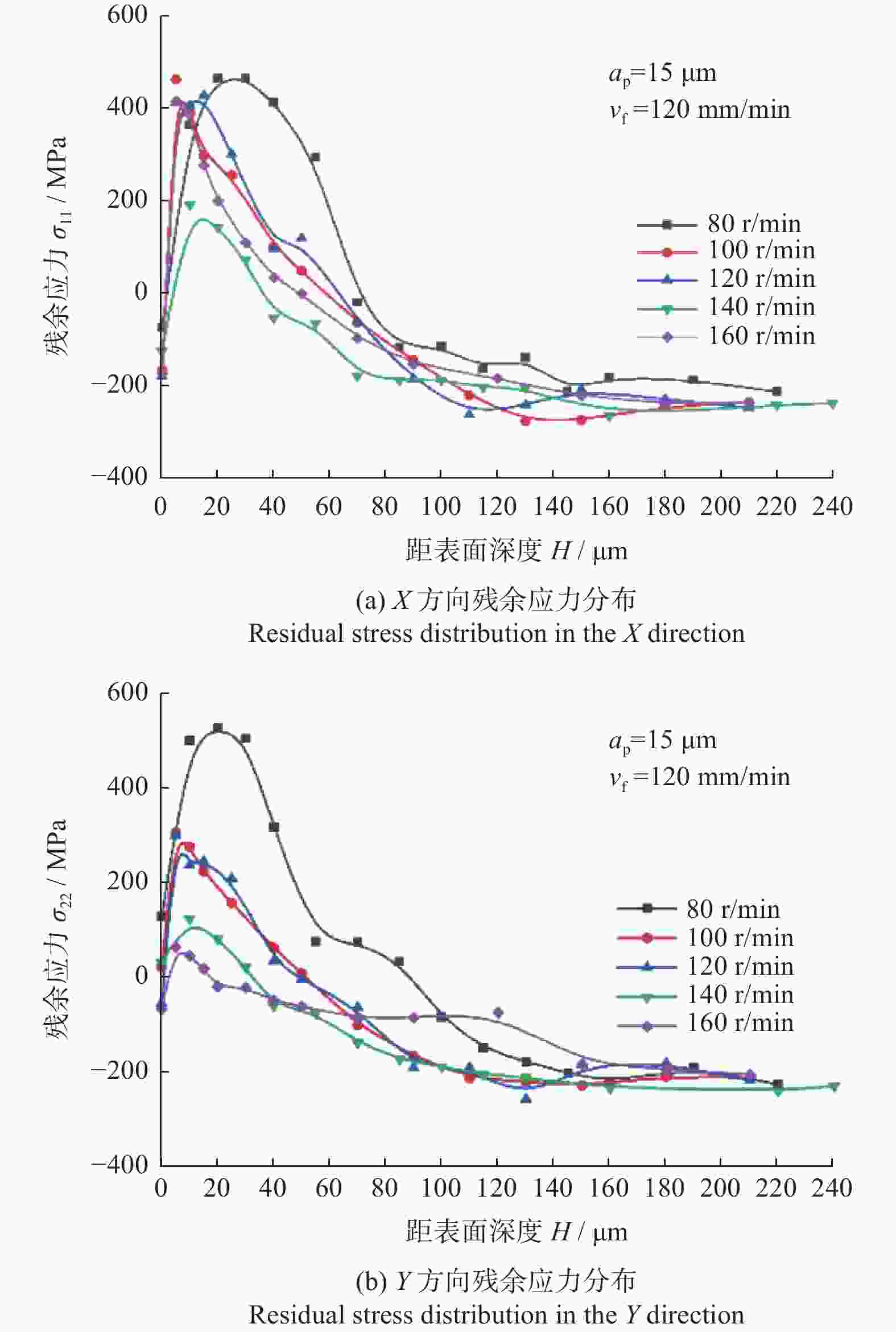
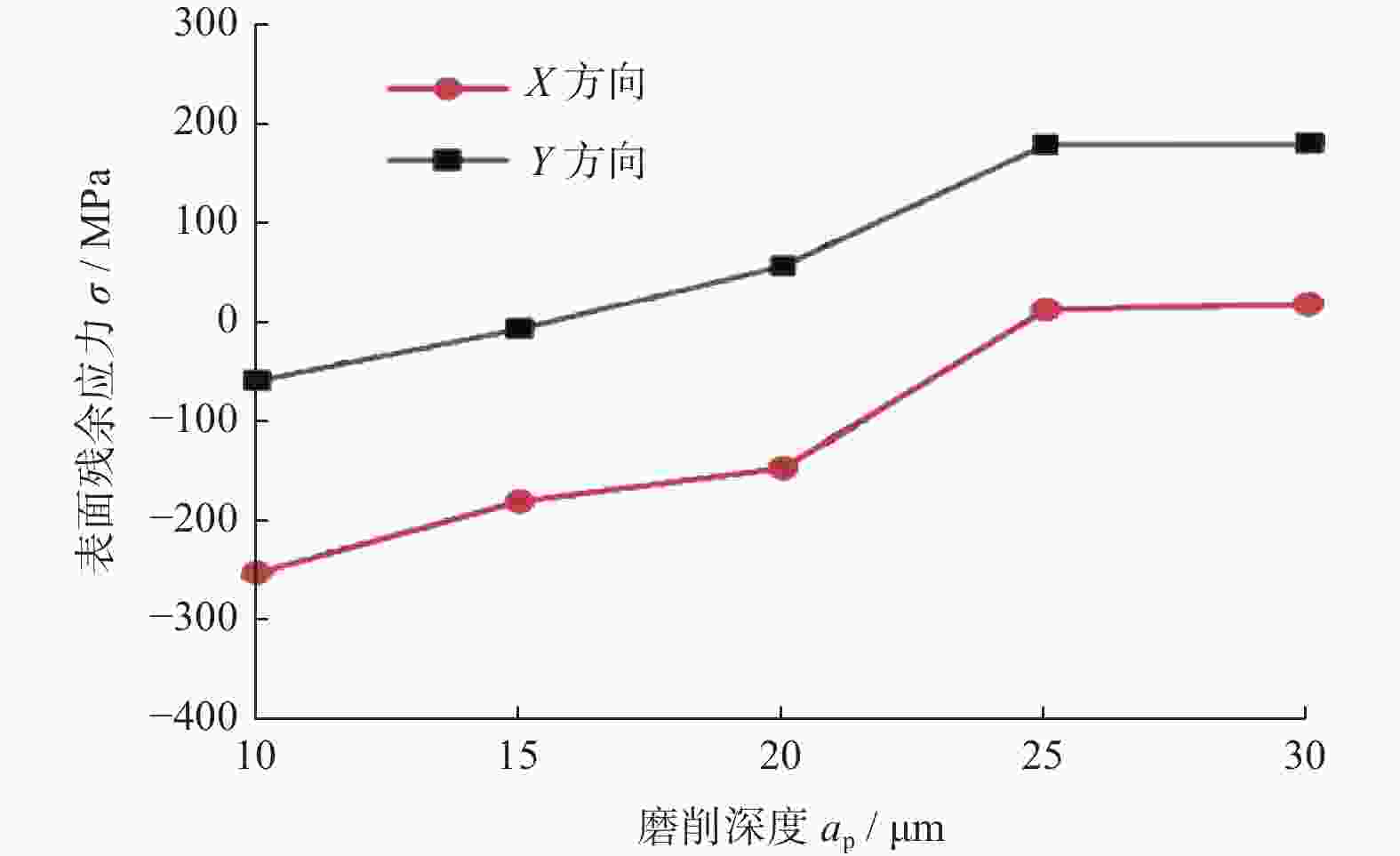
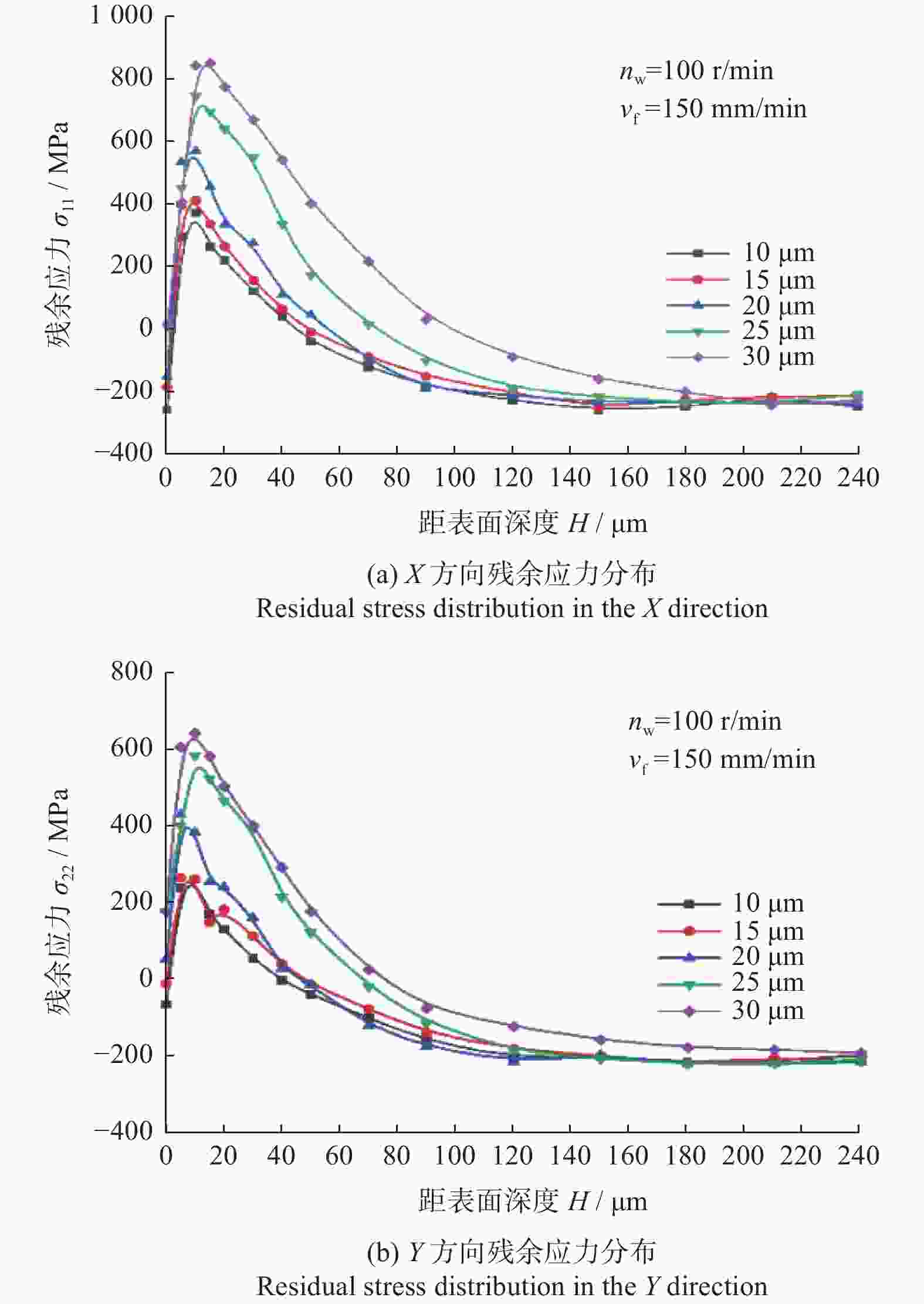
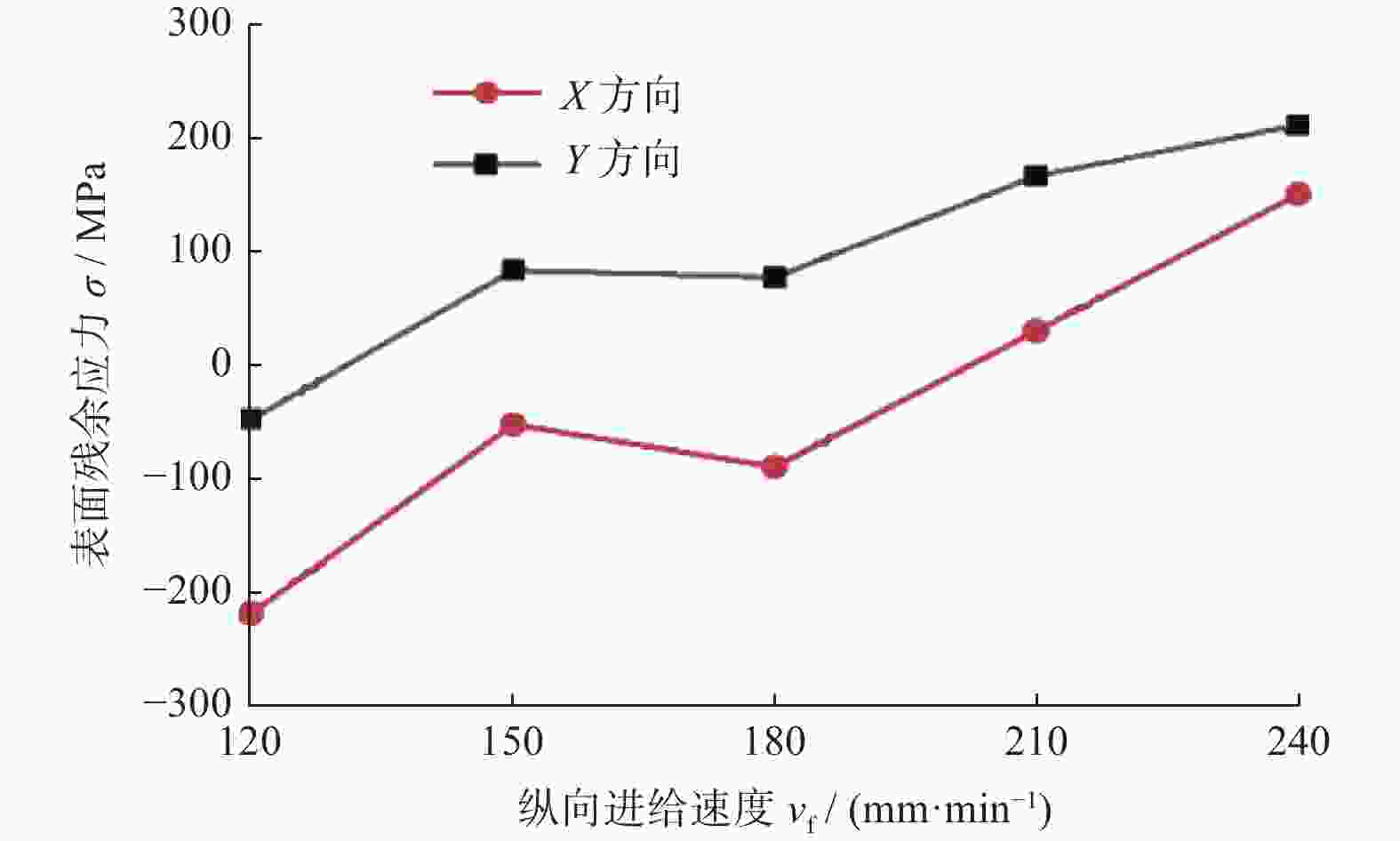
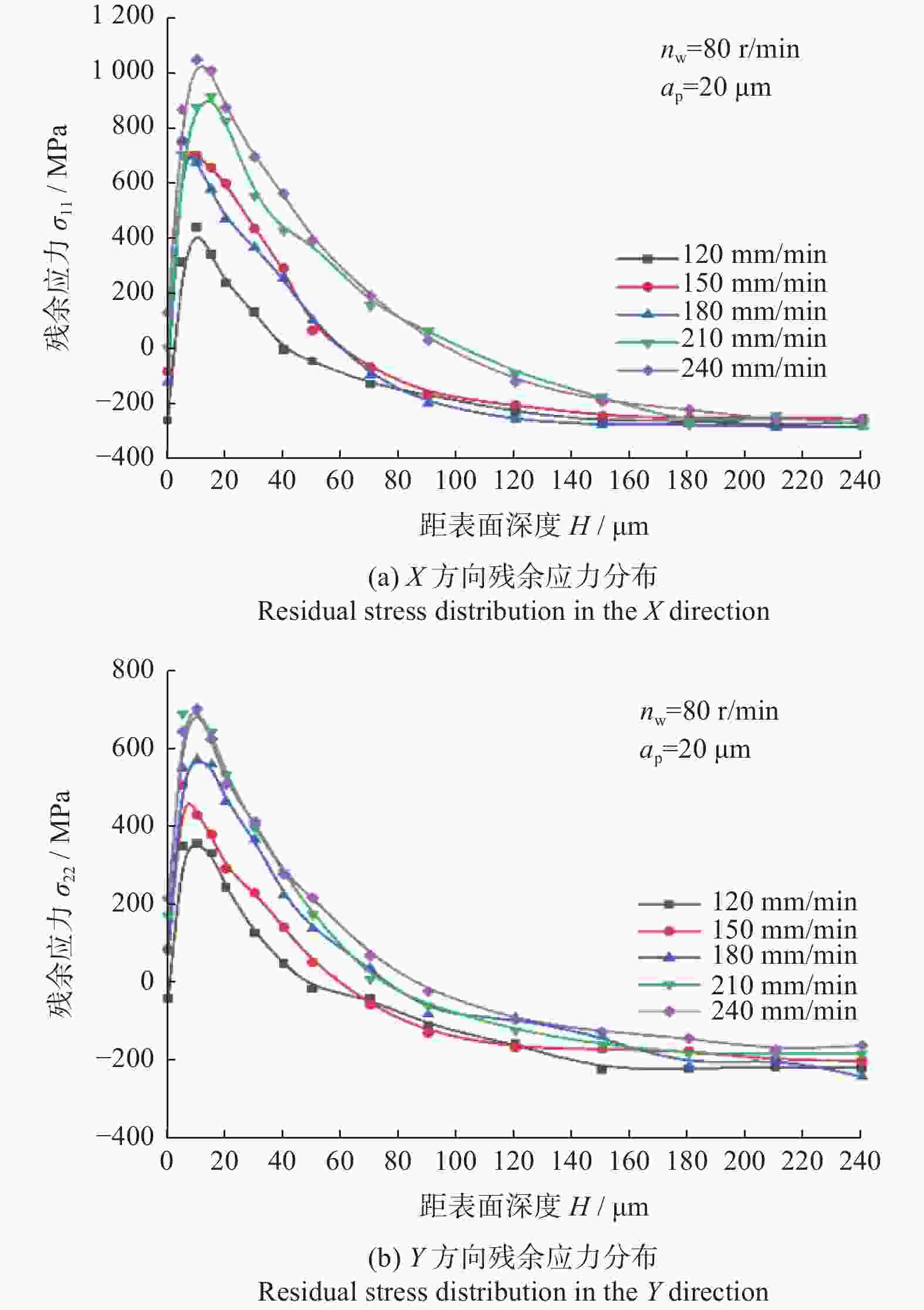
摘要: 为了探究工件转速 nw 、磨削深度 ap和纵向进给速度 vf等磨削工艺参数对18CrNiMo7–6钢表面粗糙度和表层残余应力的影响,用端面外圆磨床开展其单因素外圆纵向磨削试验。结果表明:随着nw的增大,工件表面粗糙度Ra先减小后增大,当nw为120 r/min时,Ra达到最小值,此时工件表面的残余压应力最大;当nw大于120 r/min时,工件表面残余应力出现起伏。随着ap的增大,工件表面粗糙度Ra先减小后增大,工件表面残余拉应力随着磨削深度的增大而增大。随着vf的增大,工件表面粗糙度 Ra先减小后增大,当vf为210 mm/min时,Ra值最小;且随vf的增大,工件表面残余压应力逐渐减小,并最终转变为逐渐增大的残余拉应力。
-
关键词:
- 外圆纵向磨削 /
- 磨削工艺 /
- 表面粗糙度 /
- 残余应力 /
- 18CrNiMo7–6钢
Abstract: In order to explore the influence of the grinding process parameters on the surface roughness and surface layer residual stress of 18CrNiMo7–6 steel, the cylindrical longitudinal grinding experiment was carried out by using an end cylindrical grinder. With using the workpiece speed nw, grinding depth ap and longitudinal feed speed vf, the single-factor experimental research is carried out. The research results show that with the increase of nw, the surface roughness Ra of the workpiece decreases first and then increases. When nw is 120 r/min, the surface roughness Ra reaches the minimum value, and the surface residual compressive stress value is the largest at this condition, and when nw is greater than 120 r/min, the surface residual stress exists fluctuation. With the increase of ap, the surface roughness Ra of the workpiece decreases first and then increases, and the tensile stress influence on the surface layer of the workpiece increases with the increase of the grinding depth. The surface roughness Ra first decreases and then increases with the increase of vf. When vf is 210 mm/min, the surface roughness value Ra is the smallest. With the increase of vf, the residual compressive stress of the surface layer gradually decreases and gradually changes to increasing residual tensile stress. -
表 1 18CrNiMo7–6材料化学成分组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of 18CrNiMo7–6 material
成分 质量分数 ω / % C 0.15~0.21 Si 0.15~0.40 Mn 0.60~0.90 P <0.02 Cr 1.50~1.80 Ni 1.40~1.70 Mo 0.25~0.35 Fe <96.00 表 2 18CrNiMo7–6钢力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of 18CrNiMo7–6 steel
屈服强度
Rs / (N·mm−2)抗拉强度
Rm / (N·mm−2)延伸率
δ / %收缩率
ψ / %1 016 1 220 14 68 表 3 外圆磨削试验单因素试验参数
Table 3. Single factor test parameters of cylindrical grinding test
条件编号 工件转速
nw / (r·min−1)磨削深度
ap / μm纵向进给速度
vf / (mm·min−1)1 80,100,120,140,160 15 120 2 100 10,15,20,25,30 150 3 80 20 120,150,180,210,240 -
[1] HUA Q, ZHOU Q, ZHANG J, et al. Friction and wear characteristics of alloy steel 18CrNiMo7–6 sliding on 42CrMo4 [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2018,1074:12163. [2] FU P, ZHAN K, JIANG C. Micro-structure and surface layer properties of 18CrNiMo7–6 steel after multistep shot peening [J]. Materials and Design,2013,51:309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.04.011 [3] 刘月明. 磨削过程建模与点磨削工艺的若干研究 [D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2012.LIU Yueming. Several researches on grinding process modeling and point grinding technology [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2012. [4] 王龙, 田欣利, 王望龙, 等. 磨齿表面残余应力研究进展 [J]. 工具技术,2016,50(3):3-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2016.03.001WANG Long, TIAN Xinli, WANG Wanglong, et al. Research progress of residual stress on grinding tooth surface [J]. Tool Technology,2016,50(3):3-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2016.03.001 [5] HOFFMEISTER H W, HAHMANN W C. Influence of machining with lapping foils on surface integrity of hardened steel [J]. Procedia Engineering,2011,19:144-149. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.093 [6] FIELD M, KAHLES J F. The surface integrity of machined and ground high strength steels [R]. DMIC Report, 1964, 210: 54-58. [7] MAMALIS A G, KUNDRÁK J, GYÁNI K. On the surface integrity of precision-ground steel cylindrical parts [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2003,18(5):835-845. doi: 10.1081/AMP-120024979 [8] 朱大虎. 难加工材料高速外圆磨削机理及其表面完整性研究 [D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2011.ZHU Dahu. Research on the mechanism and surface integrity of high-speed cylindrical grinding of difficult-to-machine materials [D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2011. [9] ICHIDA Y, SATO R, MORIMOTO Y. Formation mechanism of finished surface in ultra high-speed grinding with CBN wheels [J]. JSME International Journal,2006,49(1):100-105. [10] 王栋, 王建军, 李宁. 外圆磨削18CrNiMo7–6表面完整性研究 [J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,34(4):76-86.WANG Dong, WANG Jianjun, LI Ning. Research on surface integrity of 18CrNiMo7–6 cylindrical grinding [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,34(4):76-86. [11] 杨鑫, 张银霞, 原少帅, 等. 18CrNiMo7–6钢高速外圆磨削的残余应力 [J]. 中国机械工程,2021,32(5):540-546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.05.005YANG Xin, ZHANG Yinxia, YUAN Shaoshuai, et al. Residual stress of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel high-speed cylindrical grinding [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2021,32(5):540-546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2021.05.005 [12] 张银霞, 周星, 王子乐, 等. 金刚石滚轮修整对18CrNiMo7–6钢磨削残余应力影响 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2020(12):153-155.ZHANG Yinxia, ZHOU Xing, WANG Zile, et al. The influence of diamond roller dressing on the residual stress of 18CrNiMo7–6 steel grinding [J]. Modular Machine Tool and Automatic Processing Technology,2020(12):153-155. [13] 李国发, 王龙山, 丁宁. 基于进化神经网络外圆纵向磨削表面粗糙度的在线预测 [J]. 中国机械工程,2005,16(3):223-226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.011LI Guofa, WANG Longshan, DING Ning. On-line prediction of surface roughness in cylindrical longitudinal grinding based on evolutionary neural network [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2005,16(3):223-226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.011 [14] 陈鑫, 王栋, 刘昱范. 高速磨削对18CrNiMo7–6表面完整性的影响研究 [J]. 表面技术,2018,47(9):259-265.CHEN Xin, WANG Dong, LIU Yufan. Influence of high-speed grinding on the surface integrity of 18CrNiMo7–6 [J]. Surface Technology,2018,47(9):259-265. -





 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
