Simulation and intelligent control during grinding process for difficult-to-machine materials in aerospace
-
摘要:
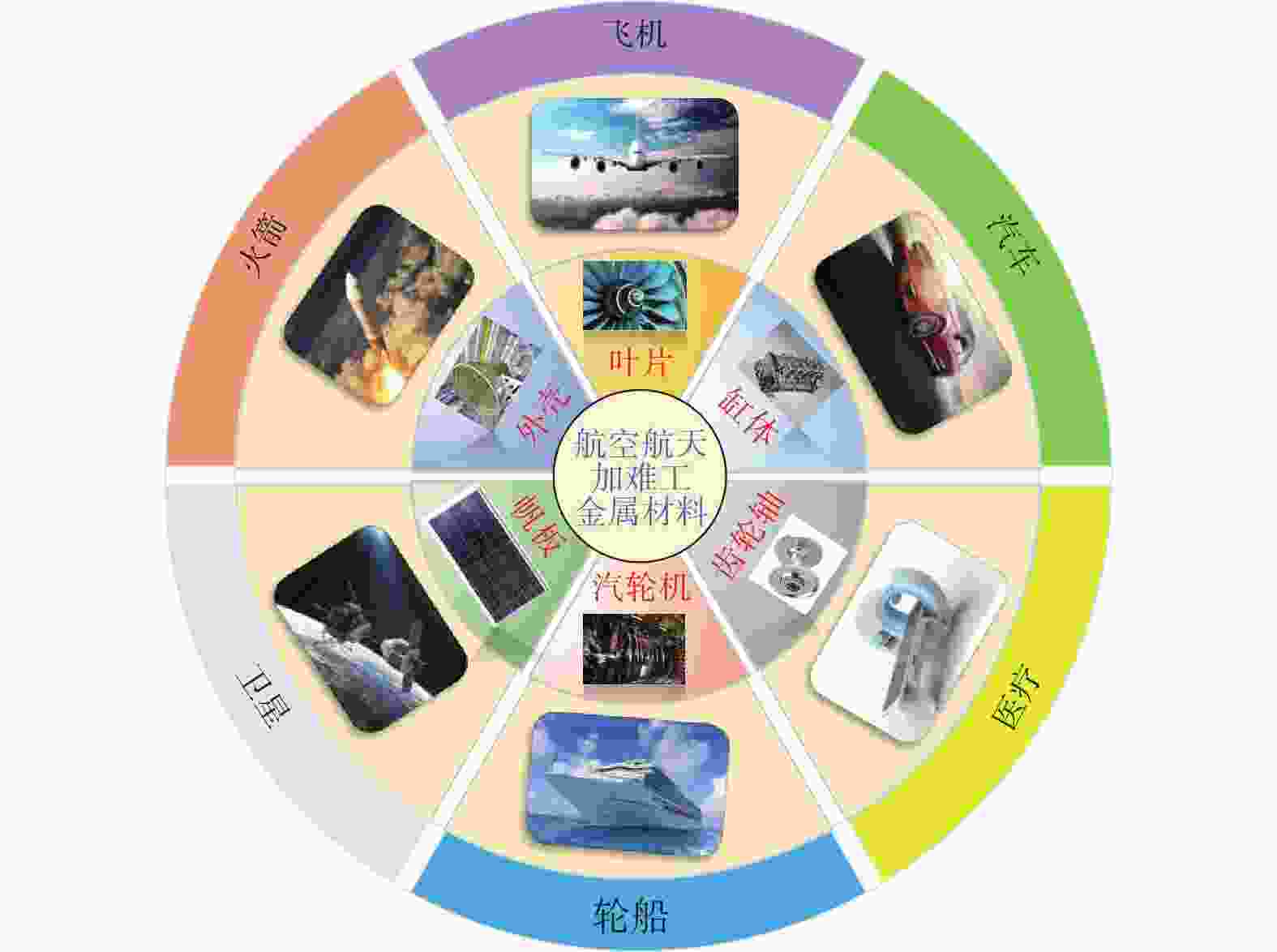
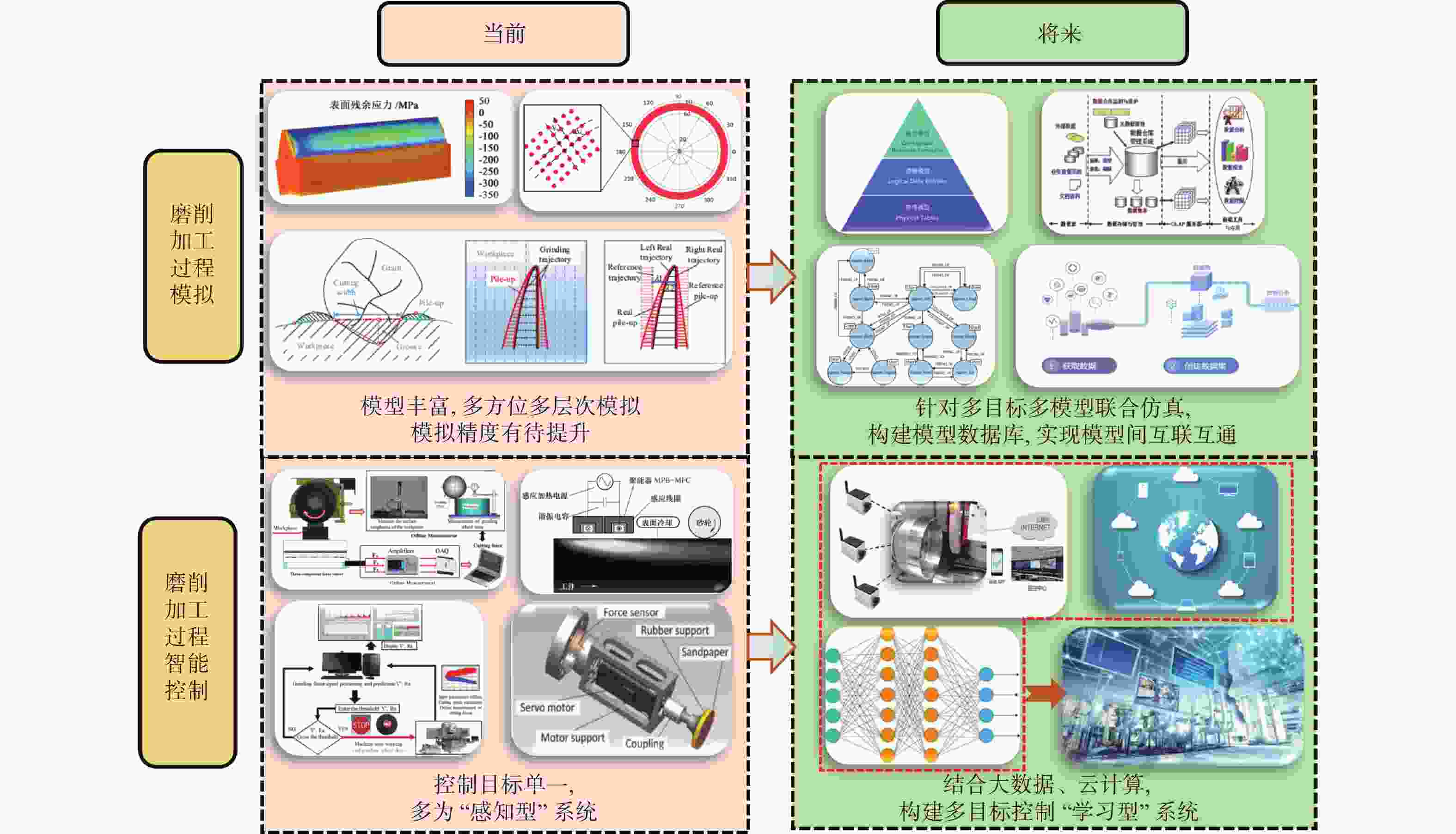
近年来,钛合金、高温合金、金属间化合物、高强度钢等难加工材料凭借优异性能广泛应用于航空航天领域关键构件。磨削作为难加工材料及关键构件精密制造的终加工方法,对制造质量与生产效率具有直接影响。然而,由于材料的难加工特性以及磨削过程的复杂性,导致磨削过程极易出现磨削力大、磨削温度高、砂轮磨损严重以及加工质量差等问题。本文针对航空航天难加工材料,以磨削加工过程模拟与智能控制技术为主线,总结了磨削过程力、温度、砂轮磨损及表面完整性等方面的研究进展和现存问题。最后,本文针对当前研究存在的主要问题,对未来磨削过程模拟与智能控制技术的发展趋势进行了展望。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The difficult-to-machine materials (e.g. titanium alloys, superalloys, intermetallics and high-strength steels, etc) have attracted increasing attentions in manufacturing the key components in aerospace fields in recent years, resulting from their superior mechanical properties. Grinding, as the final machining method, has been employed to fabricate those materials and the associated key components, playing an important influence in the manufacturing quality and efficiency. However, there are problems such as large grinding force and temperature, severe wear of wheels, and poor grinding quality, owing to the difficult machining property of those materials and the complexity of grinding processes. This paper summarized the research progresses and existed problems in view of the grinding force, the grinding temperature, the wheel wear and the ground surface quality. The research object was the difficult-to-machine materials in aerospace fields and the main discussion topics focused on the simulation during grinding processes and intelligent control techniques. Finally, the future development trends of grinding process simulation and intelligent control technology were prospected regarding the main problems existing in current researches.
-
Key words:
- grinding /
- intelligent control /
- tool wear /
- surface integrity
-
-
[1] 李本凯, 丁文锋, 马艳艳, 等. 新型刚玉砂轮磨削GH4169镍基高温合金的性能评价研究 [J]. 航空制造技术,2021,64(4):14-19. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.04.014LI Benkai, DING Wenfeng, MA Yanyan, et al. Performance evaluation on grinding of nickel-based superalloy GH4169 using new corundum abrasive wheel [J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2021,64(4):14-19. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.04.014 [2] KUANG W J, MIAO Q, DING W F, et al. Fretting wear behaviour of machined layer of nickel-based superalloy produced by creep-feed profile grinding [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,35:401-411. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.10.007 [3] 韩璐, 康仁科, 张园, 等. GH4169超声辅助磨削表面完整性研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(5):46-51. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.5.0008HAN Lu, KANG Renke, ZHANG Yuan, et al. Research on surface integrity of GH4169 machined by ultrasonic assisted grinding [J]. Diamond and Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(5):46-51. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.5.0008 [4] LI H N, YU T B, ZHU L D, et al. Modeling and simulation of grinding wheel by discrete element method and experimental validation [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2015,81:1921-1938. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7205-0 [5] LI H N, YU T B, WANG Z X, et al. Detailed modeling of cutting forces in grinding process considering variable stages of grain-workpiece micro interactions [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2017,126:319-339. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.11.016 [6] LI H N, AXINTE D. On a stochastically grain-discretized model for 2D/3D temperature mapping prediction in grinding [J]. International journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2017,116:60-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.01.004 [7] 赵庆军, 尹胜, 向瑶, 等. 基于ABAQUS切削仿真加工技术应用 [J]. 工具技术,2022,56(2):76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2022.02.017ZHAO Qingjun, YIN Sheng, XIANG Yao, et al. Application of cutting simulation technology based on ABAQUS [J]. Tool Engineering,2022,56(2):76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2022.02.017 [8] WEN J, TANG J Y, ZHOU W H. Study on formation mechanism and regularity of residual stress in ultrasonic vibration grinding of high strength alloy steel [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,66:608-622. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.04.040 [9] 闫艳燕, 闫浩哲, 刘俊利, 等. TC4钛合金纵扭超声磨削力热耦合模型及其试验研究 [J]. 中国机械工程,2022,10:1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.01.001Yan Yanyan, Yan Hanzhe, Liu Junli. et al. The thermo-mechanical coupling model and experimental research of longitudinal and torsional ultrasonic grinding of TC4 titanium alloy [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2022,10:1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.01.001 [10] LEI X F, XIANG D H, PENG P C, et al. Establishment of dynamic grinding force model for ultrasonic-assisted single abrasive high-speed grinding [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2022,300:117420. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117420 [11] 张银霞, 韩程宇, 杨鑫, 等. GCr15钢平面磨削力仿真分析与实验研究 [J]. 表面技术,2019,48(10):342-348. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2019.10.042ZHANG Yinxia, HAN Chengyu, YANG Xin, et al. Simulation analysis and experimental research on surface grinding force of GCr15 steel [J]. Surface Technology,2019,48(10):342-348. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2019.10.042 [12] MOSLEH A O, MIKHAYLOVSKAYA A V, KOTOV A D, et al. Experimental, modelling and simulation of an approach for optimizing the superplastic forming of Ti-6% Al-4% V titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2019,45:262-272. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.06.033 [13] YASMEEN T, SHAO Z T, ZHAO L, et al. Constitutive modeling for the simulation of the superplastic forming of TA15 titanium alloy [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,164:105178. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105178 [14] 夏江, 丁文锋, 仇博, 等. 镍基高温合金高速超高速磨削成屑过程的三维仿真研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2020,40(6):58-69. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.6.0011XIA Jiang, DING Wenfeng, QIU Bo, et al. 3D simulation study on the chip formation process in high speed and ultra-high speed grinding of nickel-based superalloy [J]. Diamond and Abrasives Engineering,2020,40(6):58-69. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2020.6.0011 [15] 田欣利, 王龙, 刘谦, 等. 20CrMnTi钢齿面磨削力模型构建与分析 [J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(3):227-232. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.03.227TIAN Xinli, WANG Long, LIU Qian, et al. Construction and analysis of grinding force model of 20CrMnTi steel tooth surface [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2018,54(3):227-232. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.03.227 [16] 段继豪, 牛强, 杨元, 等. TC4钛合金磨削机理和仿真研究 [J]. 计算机仿真,2022,39(1):218-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2022.01.047DUAN Jihao, NIU Qiang, YANG Yuan, et al. Study on grinding mechanism and simulation of TC4 titanium alloy [J]. Computer Simulation,2022,39(1):218-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2022.01.047 [17] LI B K, DAI C W, DING W F, et al. Prediction on grinding force during grinding powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloy FGH96 with electroplated CBN abrasive wheel [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2021,34(8):65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.05.002 [18] MA X F, CAI Z Q, YAO B, et al. Dynamic grinding force model for face gear based on the wheel-gear contact geometry [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2022,306:117633. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117633 [19] 马志飞, 梁国星, 张昊, 等. 单颗磨粒高速磨削Ti6Al4V仿真与试验验证 [J]. 工具技术,2019,53(4):49-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2019.04.012MA Zhifei, LIANG Guoxing, ZHANG Hao, et al. Simulation and experimental investigation of high-speed grinding Ti6Al4V with single grain [J]. Tool Engineering,2019,53(4):49-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2019.04.012 [20] GRIMMERT A, WIEDERKEHR P. Macroscopic process simulation of surface and profile grinding processes estimating forces for the production of turbine blades [J]. Procedia CIRP,2021,102:126-131. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2021.09.022 [21] NOSENKO V A, DANILENKO M V. Mathematical simulation of cutting force during grinding using theory of Markov processes [J]. Materials Today:Proceedings,2021,38:1602-1606. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.163 [22] GHANDEHARIUN A, HUSSEIN H M, KISHAWY H A. Machining metal matrix composites: novel analytical force model [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2016,83:233-241. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7554-8 [23] 谢黎明, 邹崇磊, 沈浩, 等. 冷作磨具钢Cr12MoV磨削温度场解析模型的建立 [J]. 机械与电子,2010,2:126-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2257.2010.02.023XIE Liming, ZOU Chonglei, SHEN Hao, et al. Establishment of analytical model in grinding temperature field of cold steel Cr12MoV [J]. Machinery and electronics,2010,2:126-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2257.2010.02.023 [24] JIANG J L, GE P Q, SUN S F, et al. From the microscopic interaction mechanism to the grinding temperature field: an integrated modelling on the grinding process [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2016,110:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.08.004 [25] JAMSHIDI H, BUDAK E. Grinding temperature modeling based on a time dependent heat source [J]. Procedia CIRP,2018,77:299-302. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2018.09.020 [26] YANG S Y, CHEN W F, NONG S, et al. Temperature field modelling in the form grinding of involute gear based on high-order function moving heat source [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,81:1028-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.014 [27] CHEN T, MIAO Q, XIONG M Y, et al. On the residual stresses of turbine blade root of γ-TiAl intermetallic alloys induced by non-steady-state creep feed profile grinding [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,82:800-817. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.08.051 [28] 王龙, 汪刘应, 唐修检, 等. 成形法磨削齿轮的磨削温度模型构建与分析 [J]. 机械工程学报,2022,58(3):295-304. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.03.295WANG Long, WANG Liuying, TANG Xiujian, et al. Construction and analysis of grinding temperature model for gear processed by form grinding technology [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2022,58(3):295-304. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.03.295 [29] HANDA D, KUMAR S, SURENDRAN S B, et al. Simulation of intermittent grinding for Ti-6Al-4V with segmented wheel [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2021,44:2537-2542. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.626 [30] NASKAR A, CHOUDHARY A, PAUL S. Wear mechanism in high-speed superabrasive grinding of titanium alloy and its effect on surface integrity [J]. Wear,2020,462:203475. [31] 蓝善超, 王宏芳, 李文斌. 磨料粒度对电镀CBN砂轮磨损影响的有限元仿真分析 [J]. 工具技术,2012,46(1):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2012.01.006LAN Shanchao, WANG Hongfang, LI Wenbin. Finite element simulation and analysis of influence of grain size on wear of electroplated CBN grinding wheel [J]. Tool Engineering,2012,46(1):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2012.01.006 [32] AGNARD S, LIU Z H, HAZEL B. Material removal and wheel wear models for robotic grinding wheel profiling [J]. Procedia Manufacturing,2015,2:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2015.07.007 [33] AHRENS M, DAMM J, DAGEN M, et al. Estimation of dynamic grinding wheel wear in plunge grinding [J]. Procedia CIRP,2017,58:422-427. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.247 [34] MIAO Q, DING W F, KUANG W J, et al. Tool wear behavior of vitrified microcrystalline alumina wheels in creep feed profile grinding of turbine blade root of single crystal nickel-based superalloy [J]. Tribology International,2020,145:106144. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2019.106144 [35] 周生合, 王军, 吕玉山, 等. 磨粒有序排布的电镀CBN砂轮磨削表面粗糙度仿真 [J]. 工具技术,2015,49(5):98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2015.05.029ZHOU Shenghe, WANG Jun, LV Yushan, et al. Simulation of grinding surface roughness of electroplated CBN grinding wheel with pattern [J]. Tool Engineering,2015,49(5):98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2015.05.029 [36] MOHAMMAD R, JOSEPH L Z W. Simulation of workpiece surface roughness after flat grinding by electroplated wheel [J]. Procedia CIRP,2018,77:303-306. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2018.09.021 [37] 肖军民, 谢晋. 20CrMnTi高速外圆磨削试验研究及参数优化 [J]. 机床与液压,2015,43(11):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2015.11.016XIAO Junmin, XIE Jin. Experimental research and parameters optimization of high-speed cylindrical grinding for 20CrMnTi [J]. Machine Tool and Hydraulics,2015,43(11):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2015.11.016 [38] WANG Y Z, LIU Y, CHU X M, et al. Calculation model for surface roughness of face gears by disc wheel grinding [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2017,123:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2017.08.002 [39] LING H, YANG C M, FENG S C, et al. Predictive model of grinding residual stress for linear guideway considering straightening history [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2020,176:105536. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105536 [40] WANG Y Z, ZHANG W, LIU Y. Analysis model for surface residual stress distribution of spiral bevel gear by generating grinding [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory,2018,130:477-490. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.08.027 [41] KUANG W J, MIAO Q, DING W F, et al. Residual stresses of turbine blade root produced by creep-feed profile grinding: three-dimensional simulation based on workpiece-grain interaction and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,62:67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.11.045 [42] 雷瑛, 李达, 罗森怡. 磨削加工件表面残余应力测试及其线性回归预测分析 [J]. 工具技术,2021,55(10):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2021.10.004LEI Ying, LI Da, LUO Senyi. Surface residual stress measurement and linear regression prediction analysis of grinding workpiece [J]. Tool Engineering,2021,55(10):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2021.10.004 [43] ZHOU W H, TANG J Y, SHAO W. Study on surface generation mechanism and roughness distribution in gear profile grinding [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2020,187:105921. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105921 [44] 巩亚东, 苏志朋, 孙瑶, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金微磨削形貌仿真及实验研究 [J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(7):949-954. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2020.07.007GENG Yadong, SU Zhipeng, SUN Yao, et al. Morphology simulation and experimental study on micro-grinding of nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2020,41(7):949-954. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2020.07.007 [45] XIAO Y L, WANG S L, MA C, et al. Numerical modeling of material removal mechanism and surface topography for gear profile grinding [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,76:719-739. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.02.052 [46] 杨磊, 李郝林, 迟玉伦. 基于自适应模糊神经网络的砂轮磨损评估 [J]. 轻工机械,2020,38(6):72-76.YANG Lei, LI Haolin, CHI Yulun. Wear evaluation of grinding wheel based on adaptive fuzzy neural network [J]. Light Industry Machinery,2020,38(6):72-76. [47] 苏史博, 毕果, 郑守红, 等. 基于LSTM和声发射的金刚石砂轮磨损状态识别 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2021,8:169-172.SU Shibo, BI Guo, ZHENG Shouhong, et al. Identification of wear status of diamond grinding wheel based on LSTM and acoustic emission [J]. Modular Machine Tool and Automatic Manufacturing Technique,2021,8:169-172. [48] 张铁, 胡广, 陈首彦. 基于模糊自整定PID的力控制磨削实验研究 [J]. 现代制造工程,2016,9:121-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2895.2020.06.014ZHANG Tie, HU Guang, CHEN Shouyan. Experiment research on force control grinding based on fuzzy-PID [J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering,2016,9:121-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2895.2020.06.014 [49] LI D W, YANG J X, ZHAO H, et al. Contact force plan and control of robotic grinding towards ensuring contour accuracy of curved surfaces [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2022,227:107449. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107449 [50] 王雨, 孙龙, 王玉伟, 等. 风电叶片打磨机器人柔性末端磨削力抗扰控制 [J]. 计算机仿真,2020,37(7):384-390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.07.076WANG Yu, SUN Long, WANG Yuwei, et al. Auto disturbance rejection control of the flexible end grinding force of a wind turbine blade grinding robot [J]. Computer Simulation,2020,37(7):384-390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.07.076 [51] MITROFANOV A, PARSHEVA K, NOSENKO V. Simulation of an artificial neural network for predicting temperature and cutting force during grinding using CAMQL [J]. Materials Today:Proceedings,2021,38:1508-1511. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.139 [52] HEININEN A, PROD’HON R, MOKHTARIAN H, et al. Finite element modelling of temperature in cylindrical grinding for future integration in a digital twin [J]. Procedia CIRP,2021,104:875-880. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2021.11.147 [53] 路建萍, 董涛, 侯丽雅. 基于神经网络的磨削温度在线监测预报系统 [J]. 南京理工大学学报,2000,24(3):273-276. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2000.03.019LU Jianping, DONG Tao, HOU Liya. On-line monitoring and forecasting system for grinding arc temperature based on artificial neural network [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,2000,24(3):273-276. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2000.03.019 [54] PENG R T, TONG J W, TANG X Z, et al. Application of a pressurized internal cooling method in grinding Inconel 718: Modeling-simulation and testing-validation [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2021,189:105985. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105985 [55] SHARMIN I, MOON M, TALUKDER S, et al. Impact of nozzle design on grinding temperature of hardened steel under MQL condition [J]. Materials Today:Proceedings,2021,38:3232-3237. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.717 [56] XU X P, YU Y Q, HUANG H. Mechanisms of abrasive wear in the grinding of titanium (TC4) and nickel (K417) alloys [J]. Wear,2003,255:1421-1426. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00163-7 [57] CARAGUAY S J, BOARON A, WEINGAERTNER W L, et al. Wear assessment of microcrystalline and electrofused aluminum oxide grinding wheels by multi-sensor monitoring technique [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,80:141-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.05.052 [58] 郭维诚, 李蓓智, 杨建国, 等. 磨削过程信号监测与砂轮磨损预测模型构建 [J]. 上海交通大学学报,2019,53(12):1475-1481. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2019.12.010GUO Weicheng, LI Beizhi, YANG Jianguo, et al. Monitoring of grinding signals and development of wheel wear prediction model [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2019,53(12):1475-1481. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2019.12.010 [59] 丁宁, 段景淞, 石建, 等. 基于声发射砂轮磨损监测系统的研究 [J]. 南京航空航天大学学报,2020,52(1):48-52. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2020.01.005DING Ning, DUAN Jingsong, SHI Jian, et al. Research on grinding wheel wear monitoring system based on acoustic emission [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2020,52(1):48-52. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2020.01.005 [60] XU L M, NIU M, ZHAO D, et al. Methodology for the immediate detection and treatment of wheel wear in contour grinding [J]. Precision Engineering,2019,60:405-412. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.09.006 [61] NGUYEN D T, YIN S H, TANG Q C, et al. Online monitoring of surface roughness and grinding wheel wear when grinding Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy using ANFIS-GPR hybrid algorithm and Taguchi analysis [J]. Precision Engineering,2019,55:275-292. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.09.018 [62] 尹国强, 王东, 关云匀, 等. 基于声发射监测的砂轮磨损实验 [J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2022,43(8):1127-1133. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.08.009YIN Guoqiang, WANG Dong, GUAN Yunyun, et al. Grinding wheel wear experiment based on acoustic emission [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2022,43(8):1127-1133. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.08.009 [63] MAHATA S, SHAKYA P, BABU N R. A robust condition monitoring methodology for grinding wheel wear identification using Hilbert Huang transform [J]. Precision Engineering,2021,70:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.01.009 [64] 陈廉清, 郭建亮, 杨勋, 等. 基于进化神经网络的磨削粗糙度预测模型 [J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2013,19(11):2854-2863. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2013.11.chenlianqing.2854.10.20131123CHEN Lianqing, GUO Jianliang, YANG Xun, et al. Grinding roughness prediction model based on evolutionary artificial neural network [J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems,2013,19(11):2854-2863. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2013.11.chenlianqing.2854.10.20131123 [65] LI Y, LIU Y H, TIAN Y B, et al. Application of improved fireworks algorithm in grinding surface roughness online monitoring [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,74:400-412. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.12.046 [66] GOPAN V, WINS K L D, SURENDRAN A. Integrated ANN-GA approach for predictive modeling and optimization of grinding parameters with surface roughness as the response [J]. Materials today:proceedings,2018,5(5):12133-12141. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.02.191 [67] ALI Y M, ZHANG L C. Estimation of residual stresses induced by grinding using a fuzzy logic approach [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,1997,63(1-3):875-880. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02742-2 [68] WANG P Z, HE Z S, ZHANG Y S, et al. Control of grinding surface residual stress of Inconel 718 [J]. Procedia Engineering,2017,174:504-511. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.01.174 [69] 李峰, 李学崑, 融亦鸣. 强化感应加热辅助磨削Inconel718的残余应力主动调控 [J]. 机械工程学报,2018,3:216-226. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.03.216LI Feng, LI Xuekun, RONG Yiming. Active control of the residual stress in Inconel718 grinding assisted by the strengthen induction heating [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2018,3:216-226. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.03.216 -





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
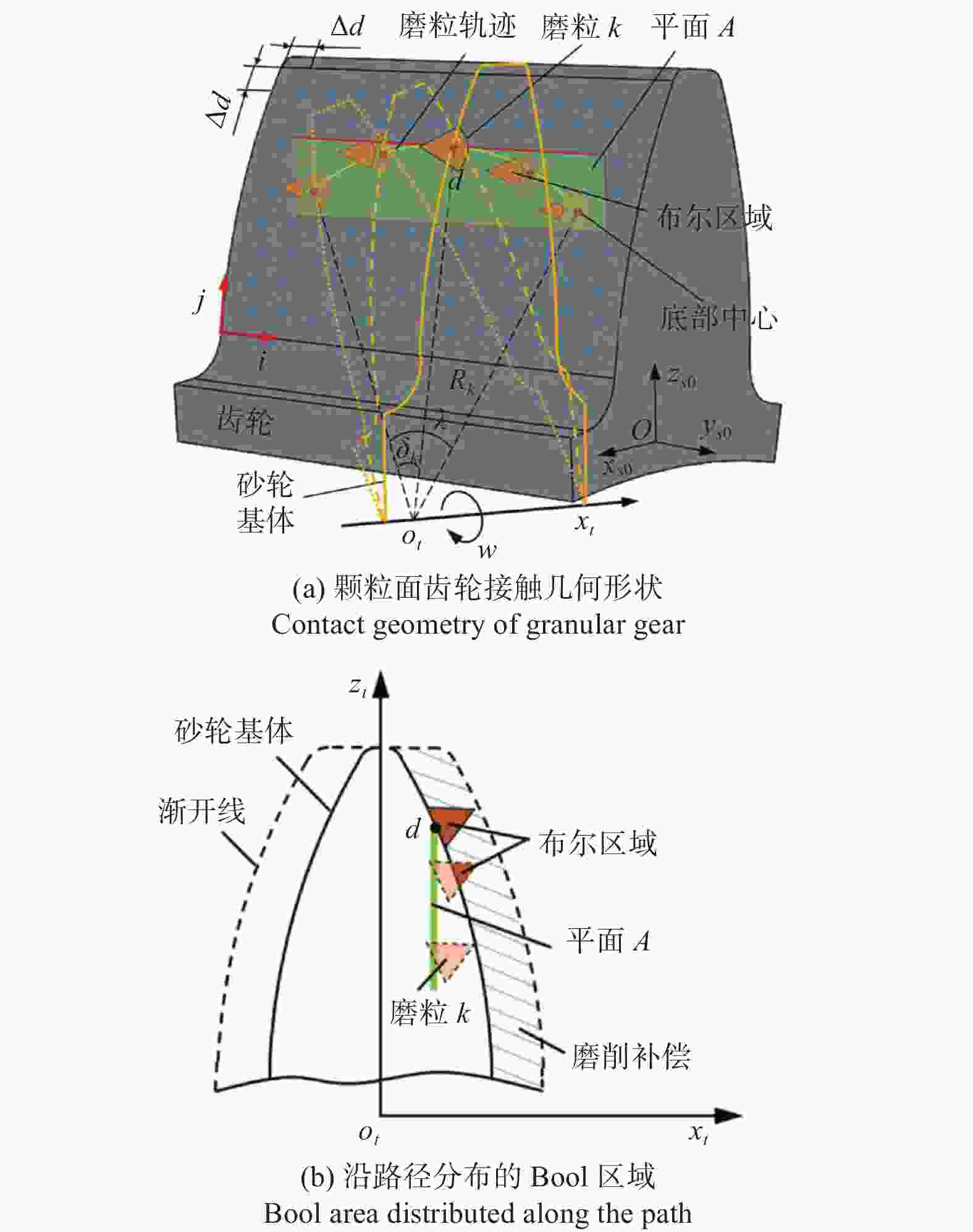
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
