Preparation and properties of intermetallic-bonded diamond grinding wheel for thinning SiC wafer
-
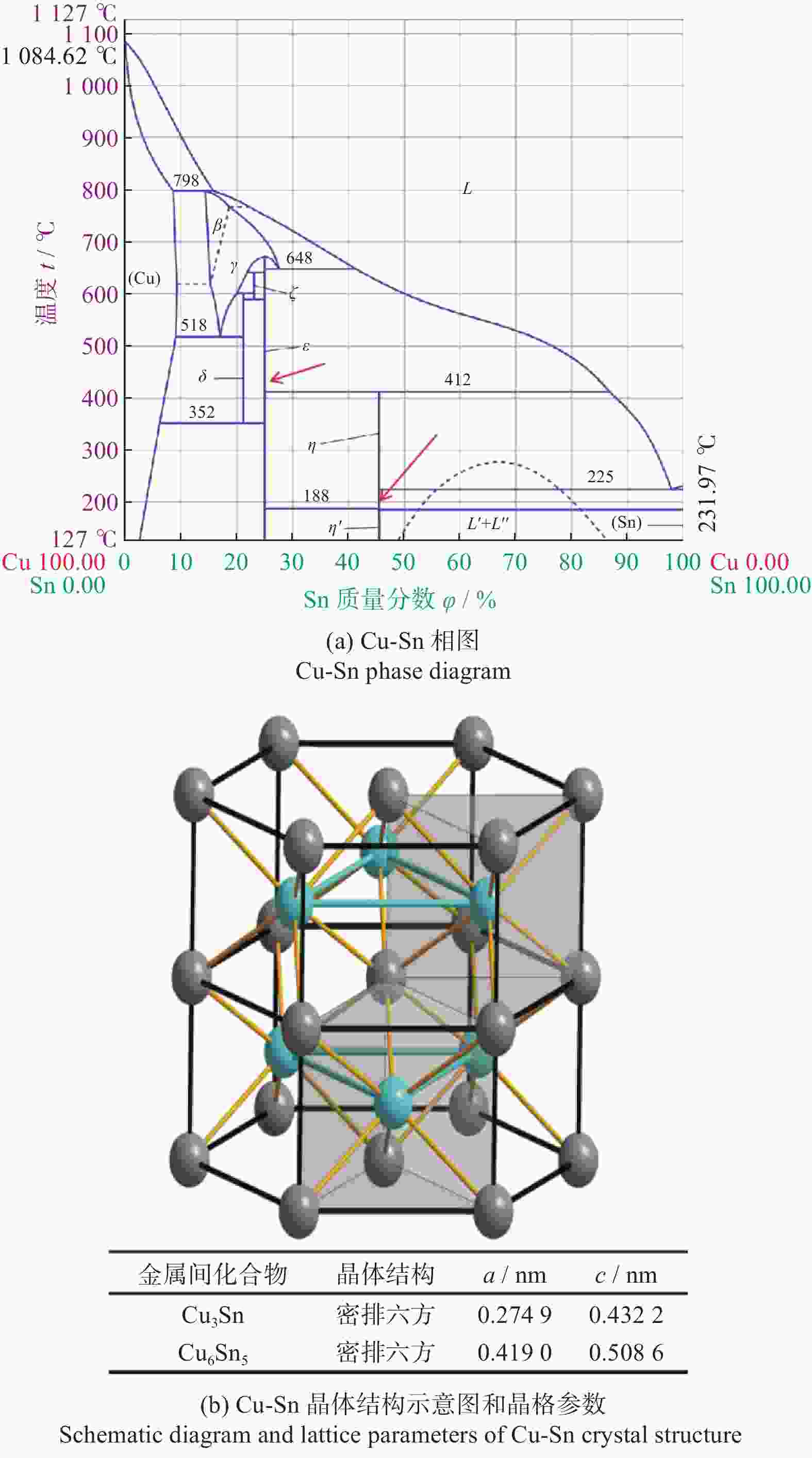
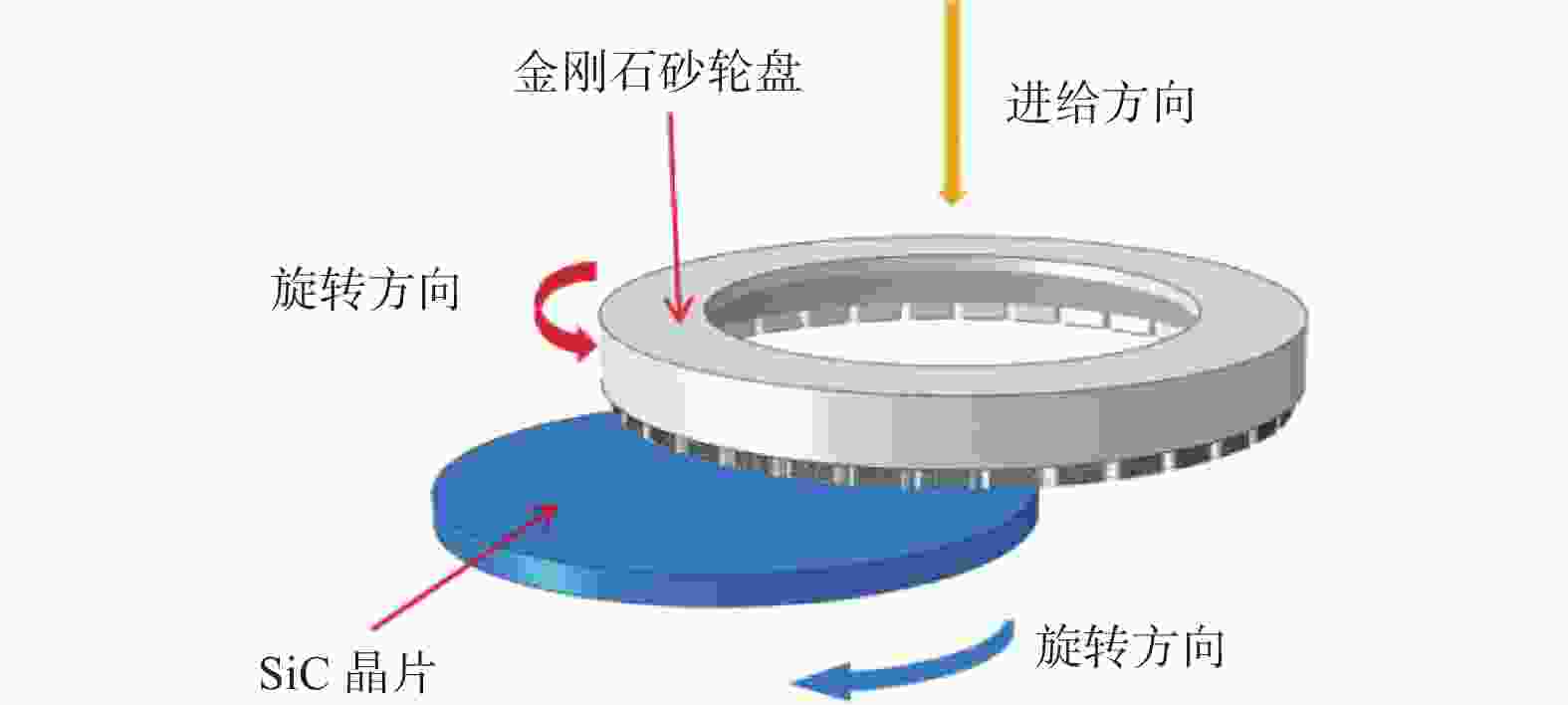
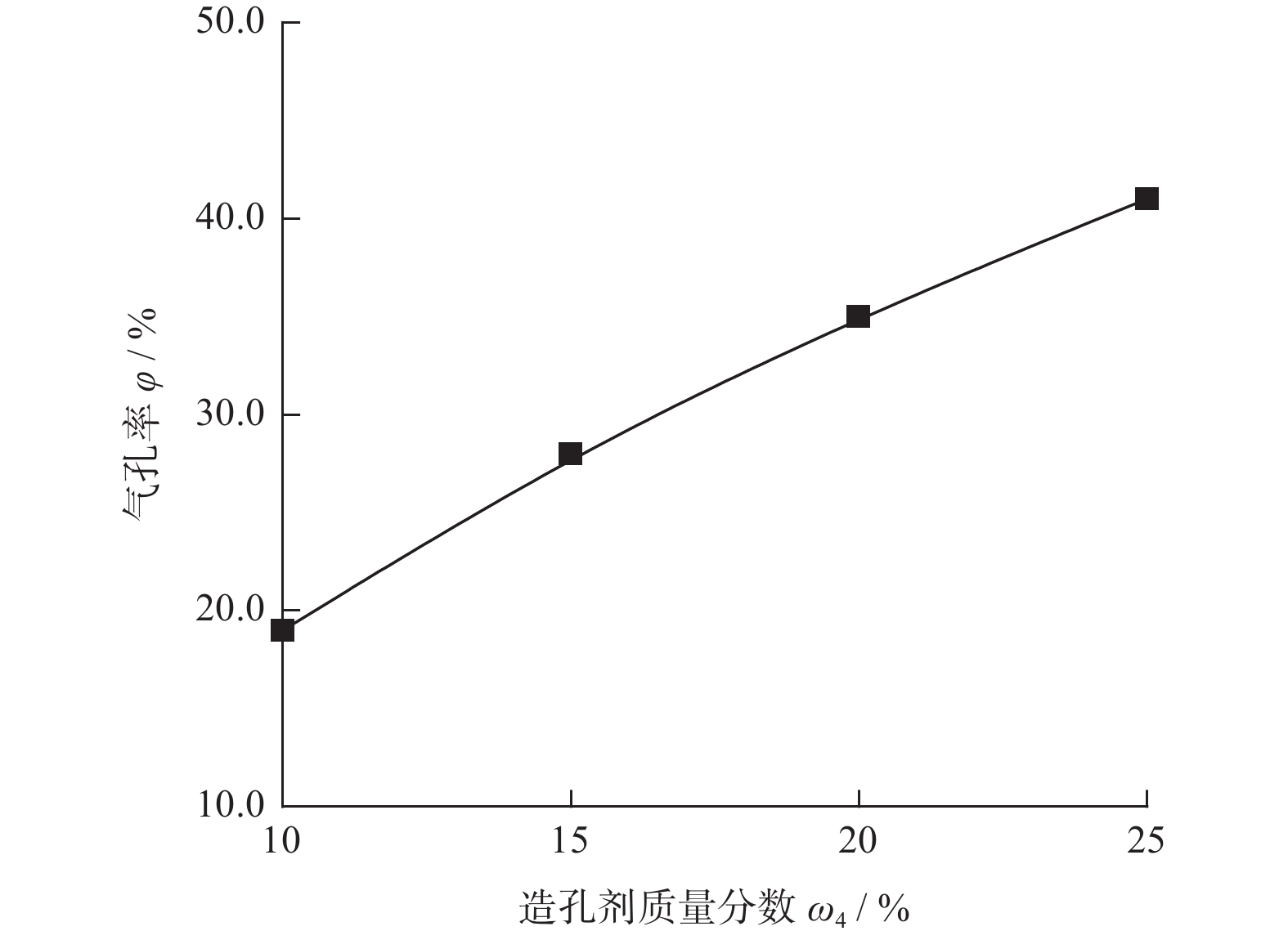
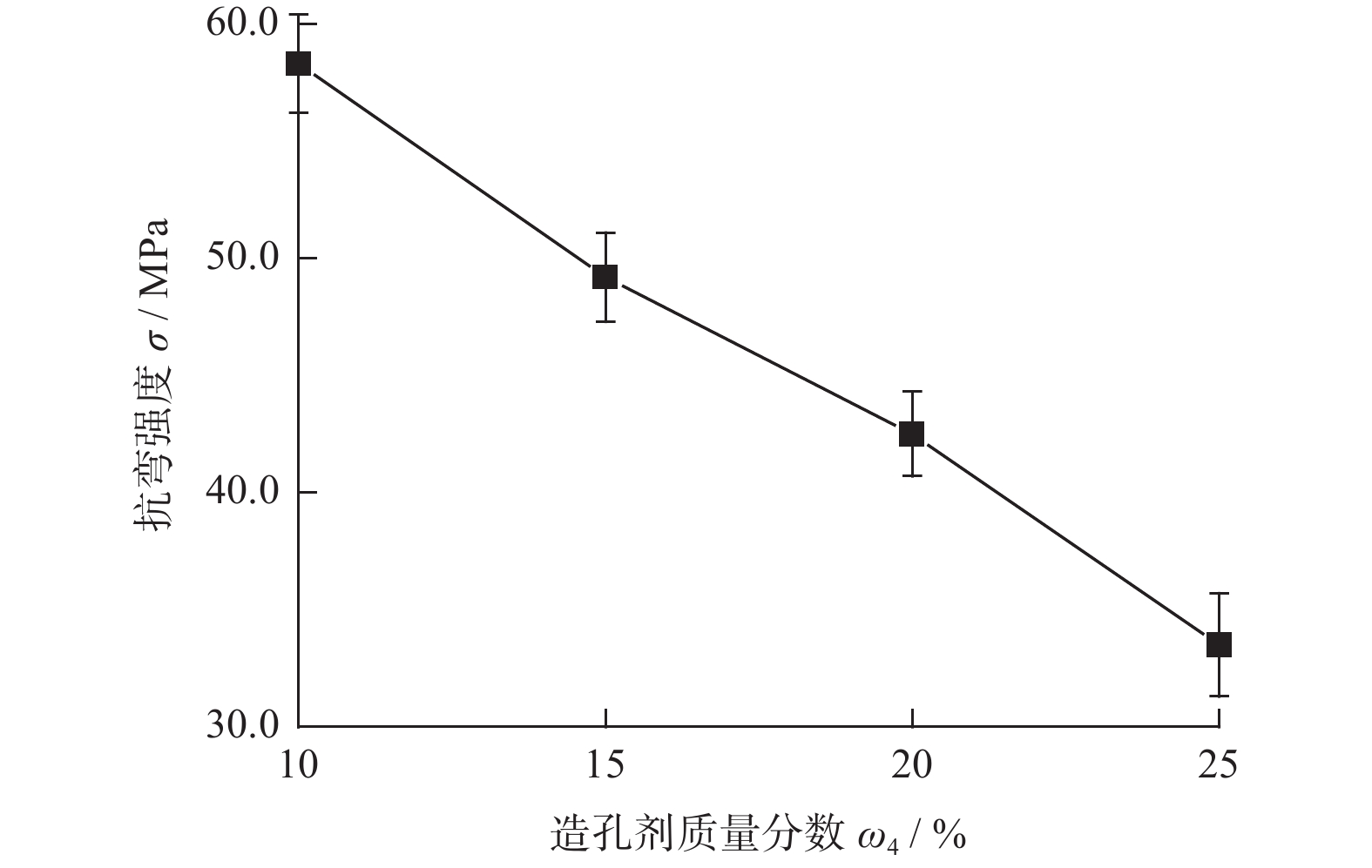
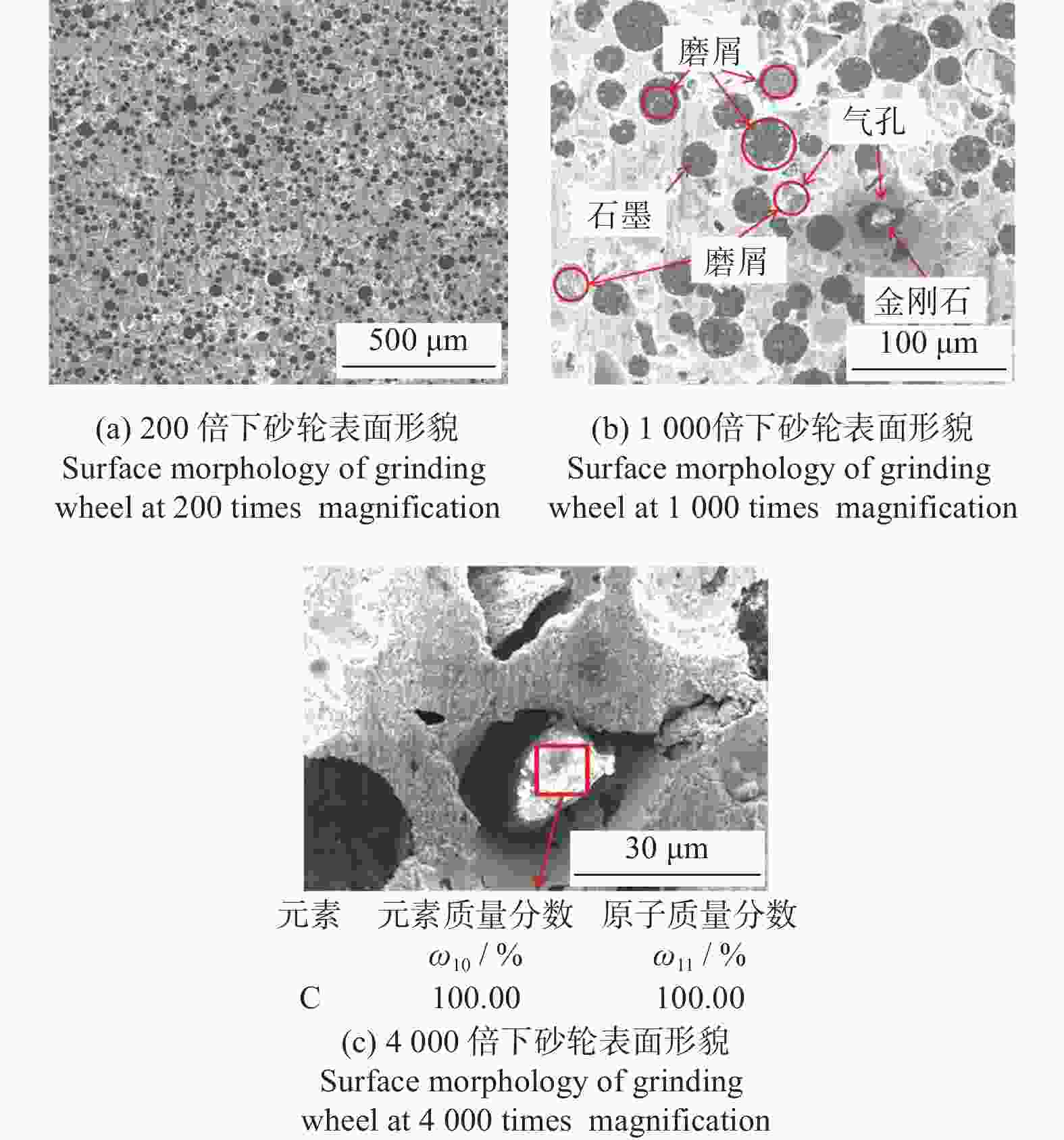
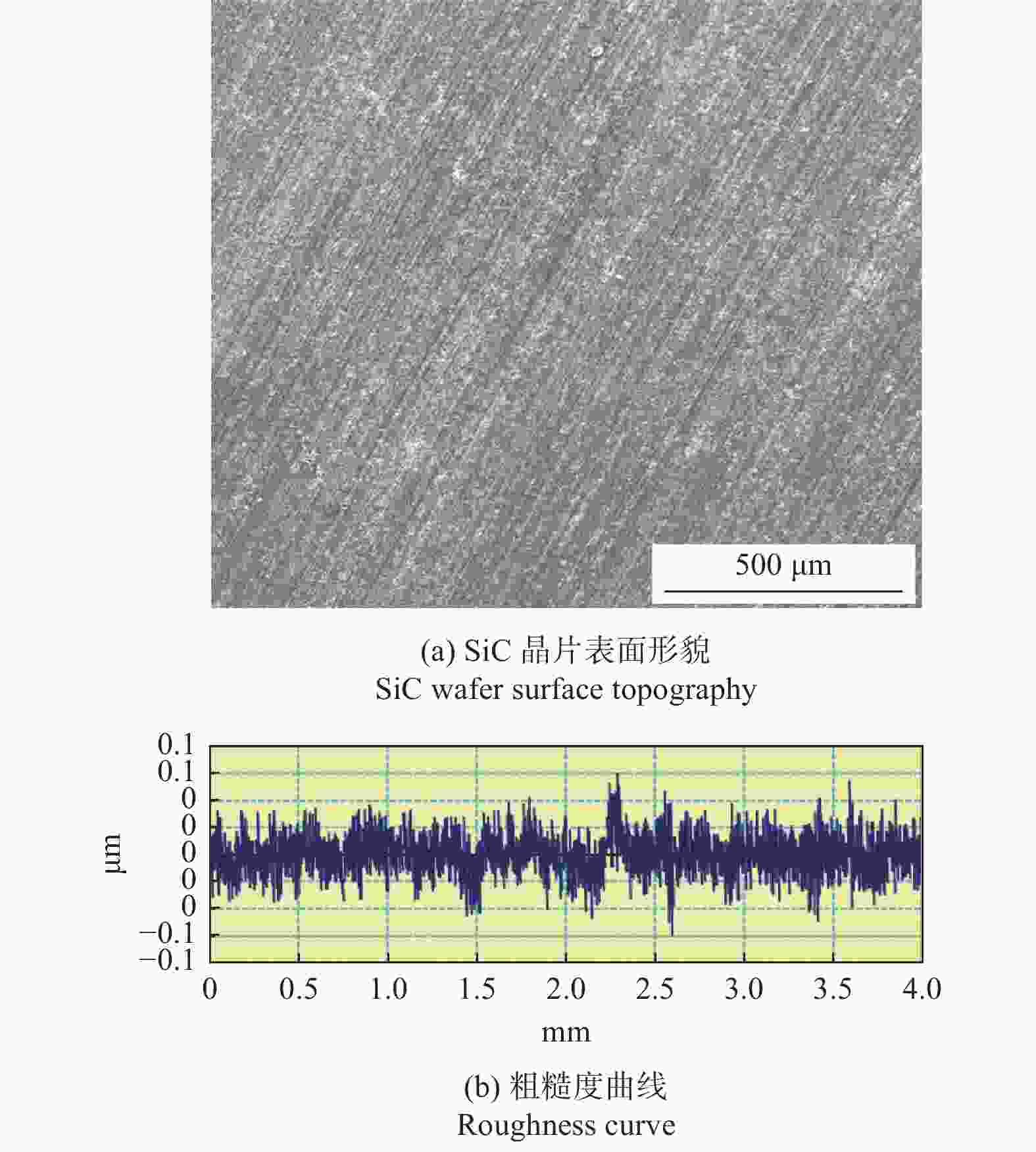
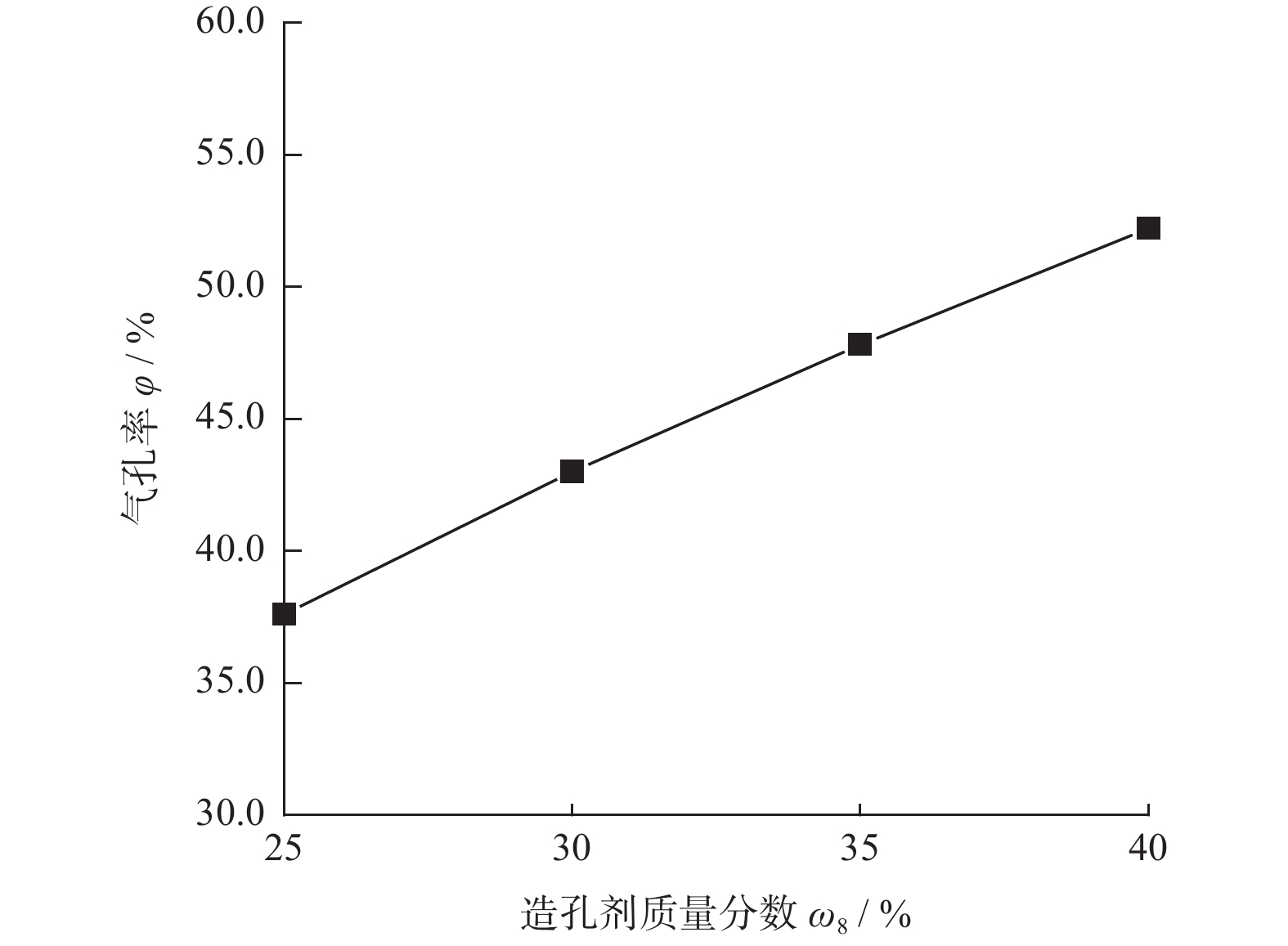
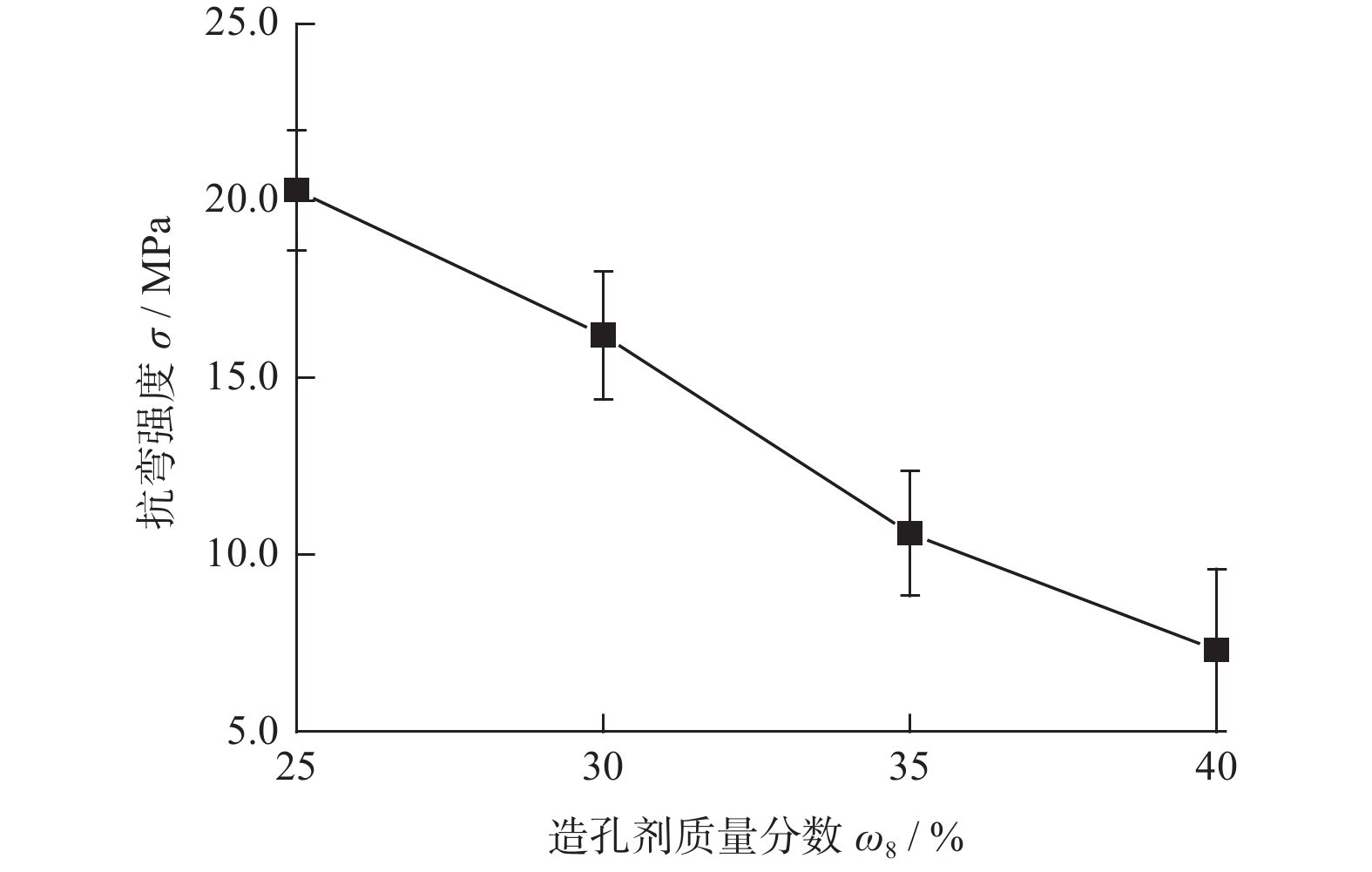
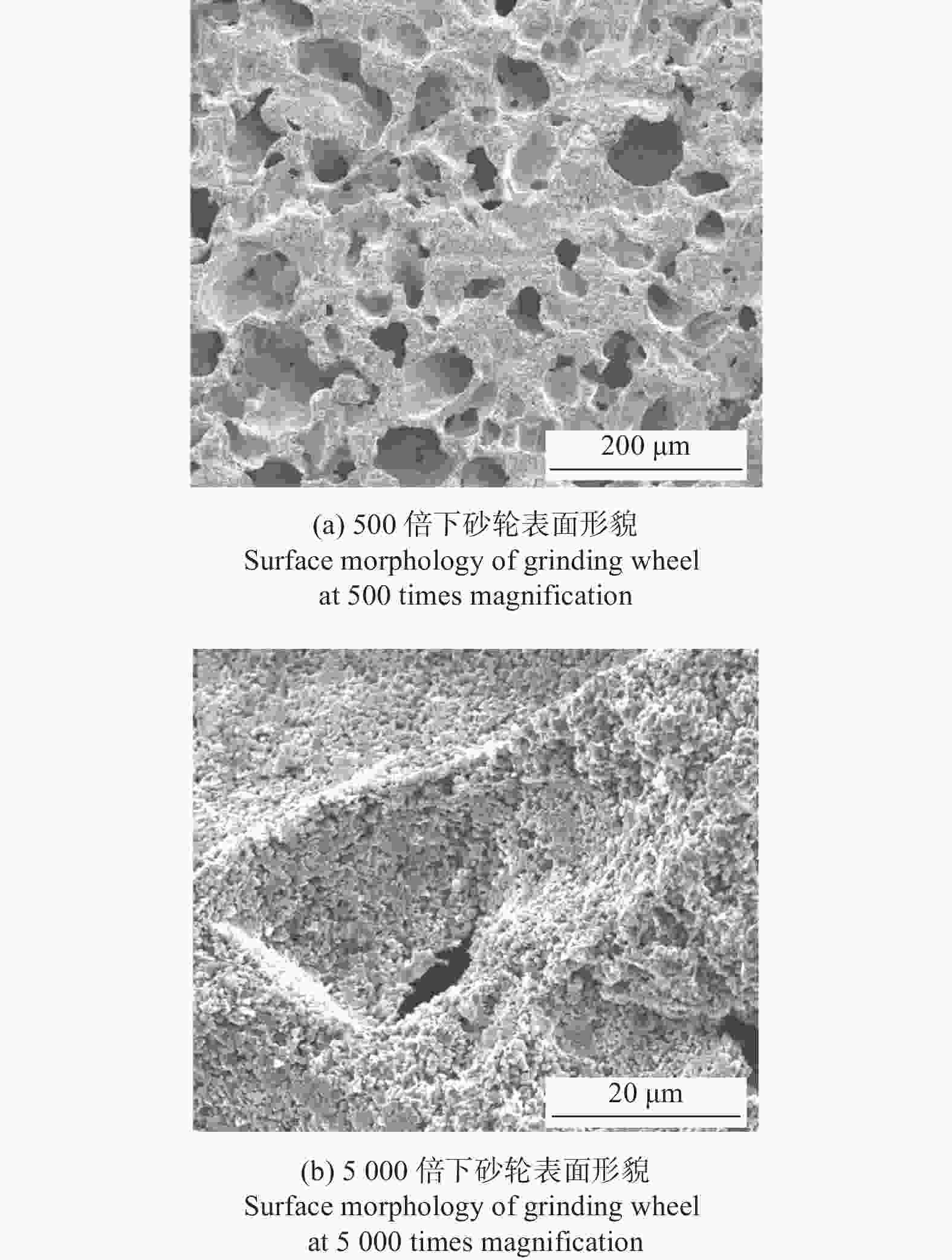
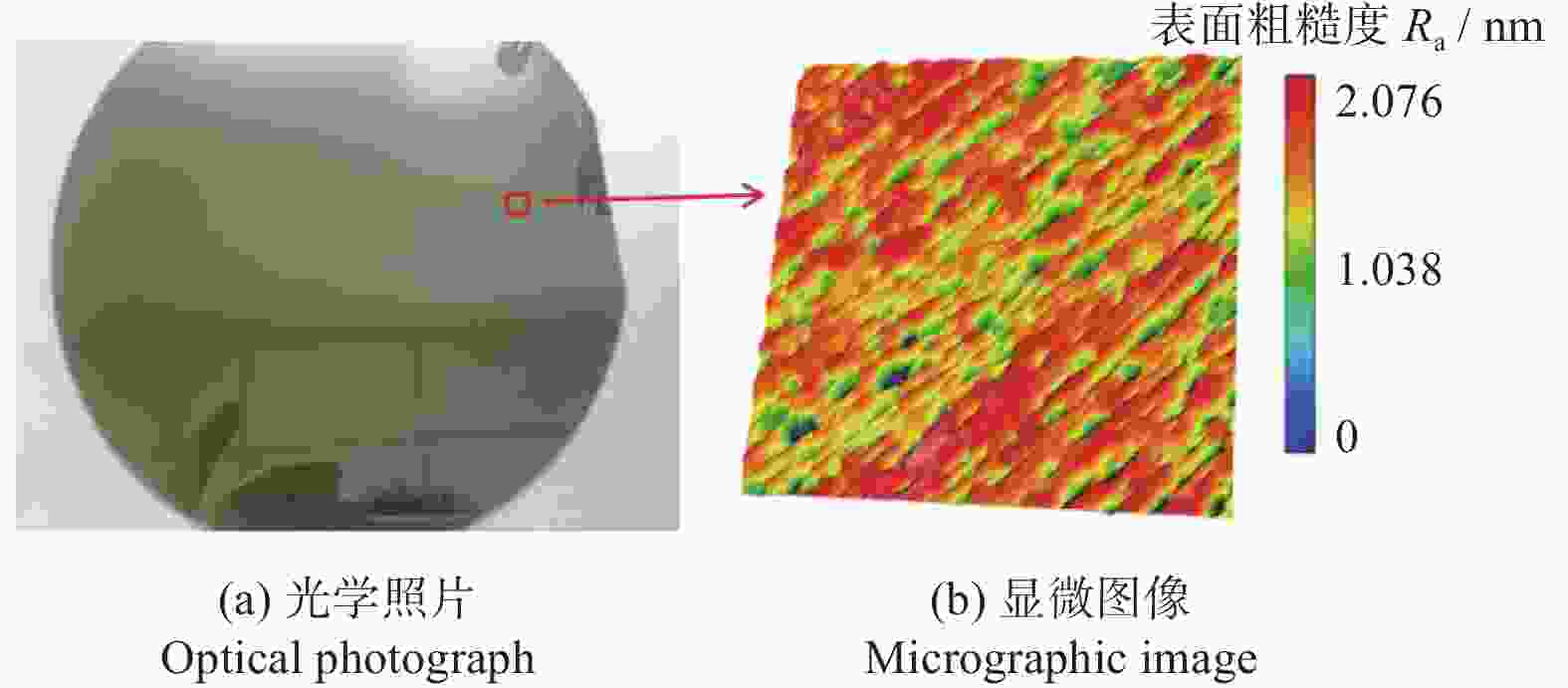
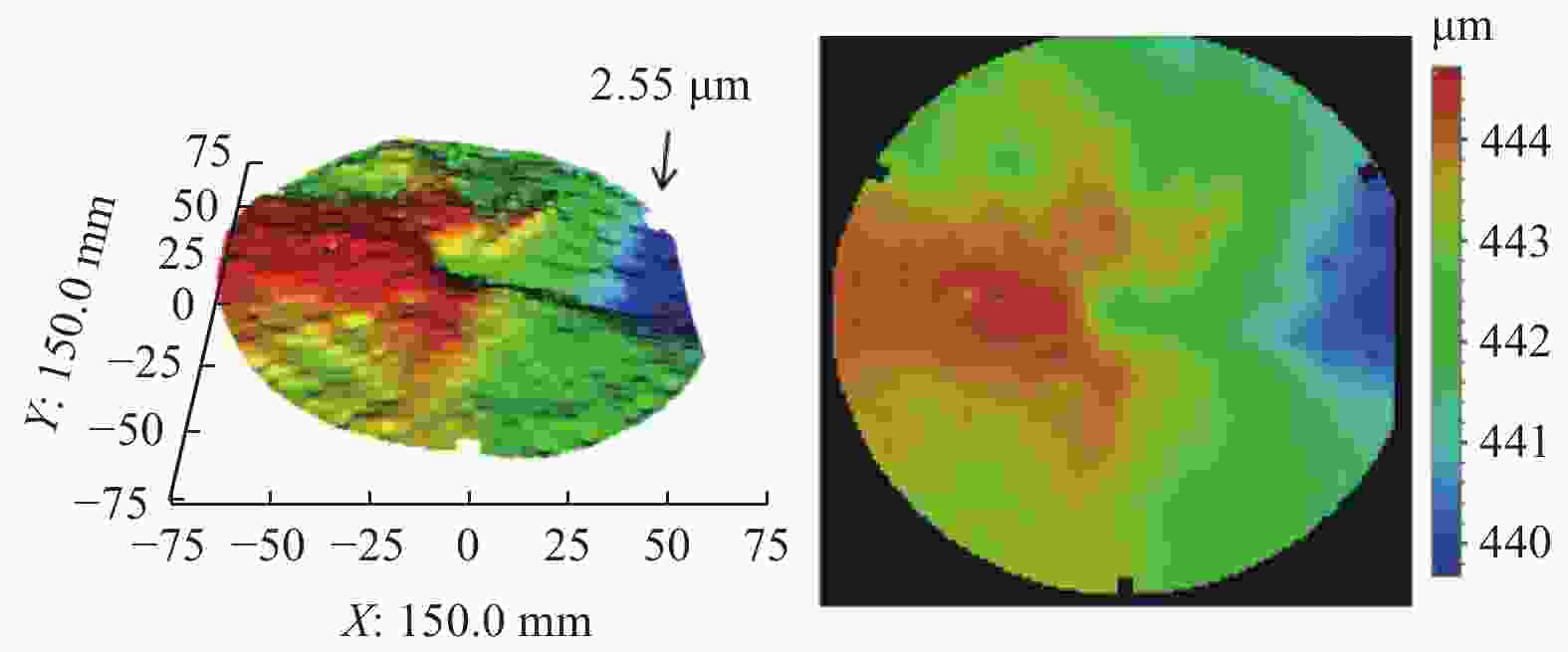
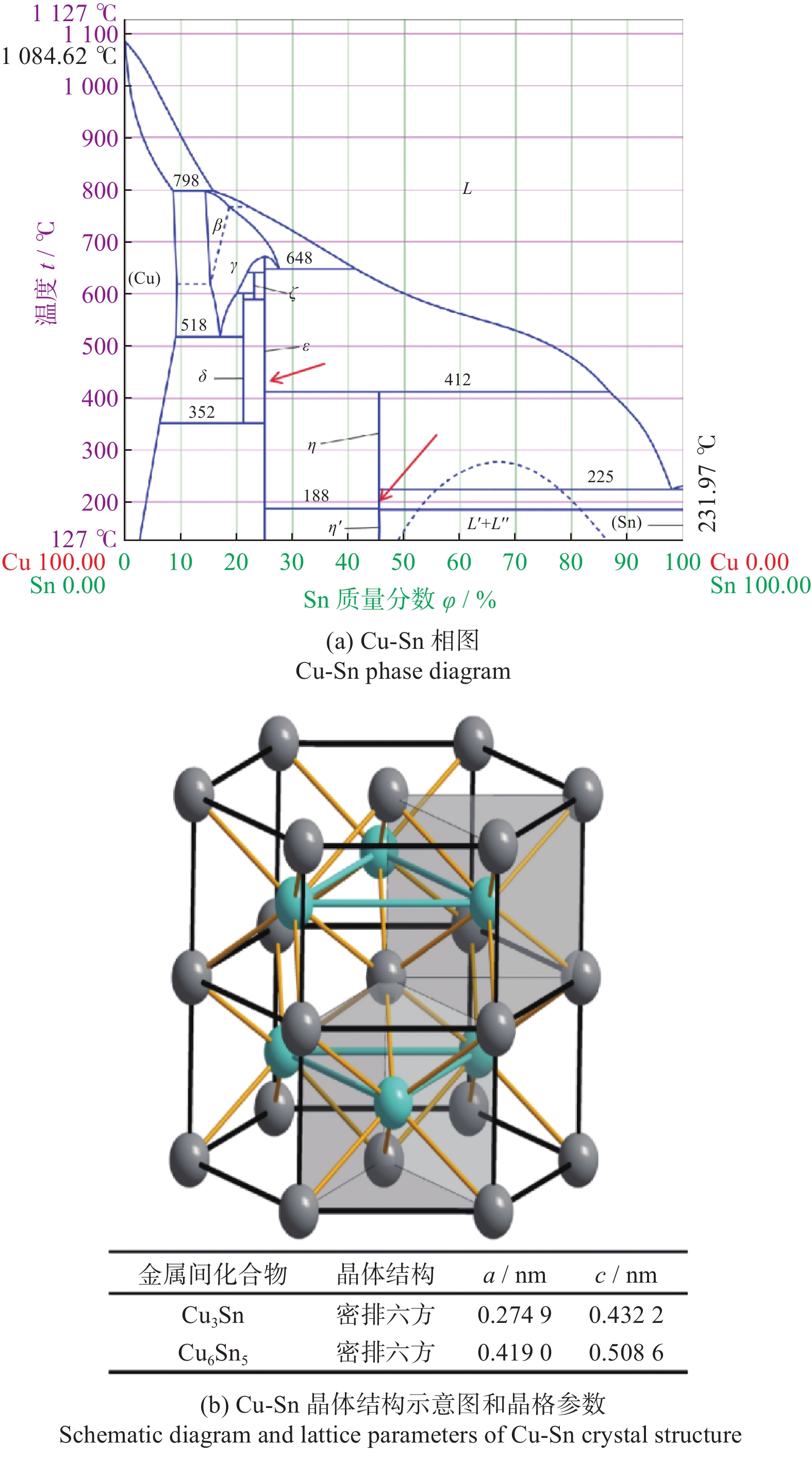
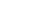
摘要: 与Si基材料相比,SiC因其导热性好、击穿电场强度高和禁带宽度大等特性成为芯片制造的理想基底材料。但SiC晶片莫氏硬度高达9.5,磨削困难。实现SiC晶片的减薄加工,降低加工成本,提高SiC晶片的加工质量,成为半导体行业亟待解决的问题。采用Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5金属间化合物为黏结剂,制备面向SiC晶片粗磨和精磨减薄的金刚石砂轮。结果表明:金刚石砂轮能够适用于SiC晶片的减薄加工,制备的M5/10金刚石粗磨砂轮减薄6英寸(15.24 cm)SiC晶片的磨耗比达1.0∶5.0,SiC晶片表面粗糙度为0.011 µm;制备的M1/2金刚石精磨砂轮减薄同种SiC晶片,其磨耗比为1.0∶0.6,SiC晶片表面粗糙度达2.076 nm,总厚度变化 RTTV< 3.00 µm。金刚石砂轮的减薄效果良好,可满足工业生产需要。Abstract: Objectives: Compared with Si-based materials, SiC has become an ideal substrate material for chip manufacturing due to its good thermal conductivity, high breakdown electric field strength, and large bandgap width. However, the Mohs hardness of SiC wafer is as high as 9.5, which makes it difficult to grind. The thinning process of SiC single crystal wafers, reducing processing costs, and improving the processing quality of SiC chips have become urgent problems to be solved in the semiconductor industry. This study uses Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compounds as bonders to prepare rough and fine grinding diamond wheels for thinning SiC wafers. Methods: On the basis of the research and development of intermetallic compound bonding agent superhard material grinding wheels proposed earlier, the M5/10 diamond grinding blocks and the M1/2 diamond grinding wheel teeth were prepared using raw materials such as diamond, Cu3Sn, Cu6Sn5, graphite, and pore-forming agent through a 450 ℃ hot pressing process. After grinding the upper and lower end faces of the diamond grinding wheel teeth flat, 34 pieces were selected and uniformly bonded to the aluminum substrate tooth groove with universal strong adhesive, and the diamond coarse grinding and fine grinding wheels for silicon carbide wafer thinning were obtained. At the same time, the processing load and wear ratio of the silicon carbide grinding wheel, and the roughness and RTTV (total thickness deviation) of the silicon carbide wafer were systematically characterized. Results: (1)The bending strength and the impact toughness of Cu3Sn material subjected to 450 ℃ hot pressing are 206.6 MPa and 0.45 J/cm2, respectively. The bending strength and the impact toughness of Cu6Sn5 material are 142.0 MPa and 0.31 J/cm2, respectively. (2)With the increase of pore-forming agent amount, the porosity of the grinding wheel teeth significantly increases, while its bending strength rapidly decreases. When the mass fraction of the added pore-forming agent is 20%, the porosity and the bending strength of the grinding wheel teeth are 35.0% and 42.5 MPa, respectively. (3)During the grinding process, the higher the bending strength of the grinding wheel teeth, the greater the holding force of the binder on the diamond, and the grinding wheel is prone to load alarms. However, too low bending strength of grinding wheel teeth will lead to excessive wear of the grinding wheel, easy edge breakage, and even broken teeth. (4) The wear ratio of M5/10 diamond rough grinding and thinning wheel with a mass fraction of 20% pore-forming agent for grinding 6-inch SiC chips reaches 1.0∶5.0, the surface smoothness of SiC chips reaches 0.011 µm, and the fragmentation rate is less than 0.2%. (5) When the mass fraction of the pore-forming agent added is 30%, the porosity and the bending strength of M1/2 fine grinding wheel teeth are 43.0% and 16.2 MPa , respectively. In addition, there are a large number of pores on the surface of the thinning grinding wheel, forming a honeycomb shape, ensuring that the grinding wheel has good chip holding and chip removal effects during the grinding process. At the same time, the wear ratio of the diamond wheel for grinding 6-inch SiC wafer is 1.0∶0.6, the surface smoothness of SiC wafer is 2.076 nm, and the RTTV is 2.55 µm. The process of grinding is smooth with a stable load. Conclusions: Cu3Sn material has high strength and can be used to prepare coarse grinding wheels for thinning SiC wafers. Cu6Sn5 material has good brittleness and can be used to prepare fine grinding wheels for thinning SiC wafers. During the grinding process, the pores in the grinding wheel can play a role in accommodating and removing chips, and can also accommodate failed and detached diamonds, thereby ensuring good surface quality of SiC wafers. The coarse and fine grinding diamond wheels prepared in this paper have obtained good grinding results. However, the diamond used in the grinding wheel for thinning SiC wafers is developing to M0/0.5 at present, which is hoped to achieve the better surface roughness and the lowest surface damage layer of SiC wafers, in order to reduce the processing amount of the CMP process. The follow-up work will further improve the brittleness of Cu6Sn5 material through ceramicization to enhance the sharpness of the grinding wheel, and carry out research on M0/0.5 diamond precision grinding and thinning grinding wheels.
-
Key words:
- intermetallic compound /
- diamond grinding wheel /
- SiC wafer /
- grinding quality
-
表 1 Si和SiC指标参数
Table 1. Si and SiC index parameters
材料 禁带宽度
E1 / eV饱和电子
漂移率
μ / (cm·S−1)击穿场强 E2 /
(MV·cm−1)热导率 K /
[W·(cm.K)−1]莫氏硬度
HMSi 1.12 1 × 107 0.3 1.5 7.0 SiC 3.20 2 × 107 3.5 4.0 9.5 表 2 Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5材料的基础性能
Table 2. Basic properties of Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 materials
金属间
化合物烧结温度
θ / ℃密度
ρ / (g·cm−3)抗弯强度
σ / MPa硬度 / HV 冲击韧性
KIC / (J·cm−2)Cu3Sn 450 8.89 206.6 389.0 0.45 Cu6Sn5 450 8.30 142.0 387.2 0.31 表 3 粗磨金刚石砂轮化学组成(质量分数)
Table 3. Chemical compositions of rough diamond grinding wheels (mass fraction )
砂轮
编号金刚石
ω1 / %Cu3Sn
ω2 / %石墨
ω3 / %造孔剂
ω4 / %其他
ω5 / %A 10~20 70 5~10 10 3~6 B 10~20 65 5~10 15 3~6 C 10~20 60 5~10 20 3~6 D 10~20 55 5~10 25 3~6 表 4 精磨金刚石砂轮化学组成(质量分数)
Table 4. Chemical compositions of fine diamond grinding wheels (mass fraction )
砂轮
编号金刚石
ω6 / %Cu6Sn5
ω7 / %造孔剂
ω8 / %其他
ω9 / %E 30~40 35 25 3~6 F 30~40 30 30 3~6 G 30~40 25 35 3~6 H 30~40 20 40 3~6 表 5 金刚石砂轮C粗磨减薄SiC晶片时的批量使用效果
Table 5. Batch use effect of diamond grinding wheel C for rough grinding and thinning of SiC wafers
参数 类型或取值 粗磨砂轮 C 砂轮转速 n1 / (r·min−1) 2 000 进给速率 vw1 / (µm·s−1) 0.5 磨耗比 R1 1.0∶5.0 表面粗糙度 Ra1 / µm 0.011 磨床最大负载值 La1 / % 30~35 破片率 Rr / % <0.2 表 6 精磨金刚石砂轮的使用效果
Table 6. Application effects of fine diamond grinding wheels
砂轮编号 造孔剂质量分数 ω8 / % 使用效果 E 25 负载报警 F 30 正常 G 35 砂轮齿崩边 H 40 断齿 表 7 金刚石砂轮F精磨SiC晶片的实际效果
Table 7. Actual effect of fine grinding SiC wafer with diamond grinding wheel F
参数 类型或取值 精磨砂轮 F 砂轮转速 n2 / (r·min−1) 2 000 进给速率 vw2 / (µm·s−1) 0.3 磨耗比 R2 1.0∶0.6 表面粗糙度 Ra2 / nm 2.076 磨床最大负载值 La2 / % 35~40 RTTV / µm 2.55 -
[1] PATTEN J A, JACOB J. Comparison between numerical simulations and experiments for single-point diamond turning of single-crystal silicon carbide [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2008,10(1):28-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2008.08.001 [2] WU R, ZHOU K, YUE C Y, et al. Recent progress in synthesis, properties and potential applications of SiC nanomaterials [J]. Progress in Materials Science,2015,72:1-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.003 [3] 张鹏. 碳化硅单晶衬底超精密抛光关键技术研究 [D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017.ZHANG Peng. Research on the key technology for ultra-precision polishing of silicon carbide single crystal substrate [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017. [4] 张波, 邓小川, 张有润, 等. 宽禁带半导体SiC功率器件发展现状及展望 [J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报,2009,4(2):111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2009.02.001ZHANG Bo, DENG Xiaochuan, ZHANG Yourun, et al. Recent development and future perspective of silicon carbide power device: Opportunity and challenge [J]. Journal of Chinese Academy of Electronic Sciences,2009,4(2):111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2009.02.001 [5] 李丽婷. 碳化硅半导体材料研究进展及其产业发展建议 [J]. 厦门科技,2016(5):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1563.2016.05.001LI Liting. Research progress of silicon carbide semiconductor materials and its suggestions for industrial development [J]. Xiamen Science and Technology,2016(5):1-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1563.2016.05.001 [6] 刘宇浩. 碳化硅材料性能优异, 应用迎来发展良机 [J]. 中国集成电路,2023,32(5):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1681-5289.2023.05.003LIU Yuhao. Silicon carbide material has excellent performance and ushers in a good opportunity for development in the application field [J]. China IC,2023,32(5):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1681-5289.2023.05.003 [7] 肖强, 李言, 李淑娟. SiC单晶片CMP 超精密加工技术现状与趋势 [J]. 宇航材料工艺,2010,40(1):9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2010.01.003XIAO Qiang, LI Yan, LI Shujuan. Situation and development trends of CMP for SiC monocrystal slice [J]. Aerospace Materials Technology,2010,40(1):9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2010.01.003 [8] HARA H, SANO Y, MIMURA H, et al. Novel abrasive-free planarization of 4H-SiC (0001) using catalyst [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2006,35(8):11-14. doi: 10.1007/s11664-006-0218-6 [9] NAMBA Y, KOBAYASHI H, SUZUKI H, et al. Ultraprecision surface grinding of chemical vapor deposited silicon carbide for X-ray mirrors using resinoid-bonded diamond wheels [J]. CIRP Annals:Manufacturing Technology,1999,48(1):277-280. doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63183-7 [10] ETO H, LIN W, WATANABE Y, et al. 407 ELID grinding of large SiC mirror [J]. The Manufacturing & Machine Tool Conference: The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2006: 61-62. doi: 10.1299/jsmemmt.2006.6.61 [11] 王超超, 张凤林, 欧阳承达, 等. 用于磨削6H-SiC晶片的陶瓷结合剂金刚石砂轮制备及磨削试验研究 [J]. 工具技术,2022,56(12):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2022.12.009WANG Chaochao, ZHANG Fenglin, OUYANG Chengda, et al. Experimental study on preparation of vitrified bond diamond grinding wheel for grinding 6H-SiC wafers [J]. Tools Technology,2022,56(12):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2022.12.009 [12] 李论. 振动辅助单颗磨粒划擦碳化硅晶体的数值仿真研究 [D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2020.LI Lun. Numerical simulation study on vibration-assisted single abrasive grain scratching silicon carbide crystals [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2020. [13] CHEN Z, ZHANG X H, WEI D D, et al. Improved grinding performance of SiC using an innovative bionic vein-like structured grinding wheel optimized by hydrodynamics [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2023,101:195-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.06.010 [14] 王照. 磨削硬脆材料多孔陶瓷结合剂金刚石磨具的研究 [D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2023.WANG Zhao. Study on Diamond abrasives for grinding porous ceramic bond of hard and brittle materials [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2023. [15] LI W, HU X L, GUI L, et al. Grain wear properties and grinding performance of porous diamond grinding wheels [J]. Wear, 2023, 93: 530-531. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2023.204993 [16] 刘小磐. 陶瓷结合剂金刚石砂轮的制备及磨削性能研究 [D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2013.LIU Xiaopan. Study on preparation and grinding properties of vitrified bond diamond wheel [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2013. [17] 苏宏华. 新型金属结合剂金刚石工具技术的基础研究 [D]. 南京:南京航空航天大学, 2009.SU Honghua. Fundamental research on fabrication and application technology of metal bonded diamond [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009. [18] 宋冬冬. 金属—陶瓷复合结合剂金刚石砂轮制备及性能研究 [D]. 长沙:湖南大学, 2018.SONG Dongdong. Study on preparation and performance of metal-vitrified composite bond diamond grinding wheels [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2018. [19] PENG J W, ZHANG F L, HUANG Y J, et al. Comparative study on NiAl and FeAl intermetallic-bonded diamond tools and grinding performance for Si3N4 ceramic [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47:32736-32746. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.170 [20] HUANG L, YU J, KIPSANG B, et al. Wetting mechanism of Cu3Ni, Cu3Zn, Cu3Sn on diamond surface: A first-principles calculation [J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter,2013,613:412993. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2021.412993 [21] CHEN S P, KANG X Y, HE Y H. Study on the preparation of Ni–Al intermetallic-bonded diamond grinding block and grinding performance for sapphire [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022,130:109490. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109490 [22] POLVI J, HEINOLA K, NORDLUND K. An interatomic potential for W–N interactions [J]. Modelling & Simulation in Materials Science & Engineering,2016,24(6):065007. doi: 10.1088/0965-0393/24/6/065007 [23] 桑夏晗. 铜锡合金中金属间化合物的电子显微学研究 [D]. 北京: 中国科学院金属研究所, 2008.SANG Xiahan. Electron microscopy of intermetallics in Cu-Sn alloys [D]. Beijing: Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008. [24] 李伯民, 赵波, 李清. 磨料、磨具与磨削技术 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015.LI Bomin, ZHAO Bo, LI Qing. Abrasive, abrasive tools and grinding techniques [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2015. [25] 廖翠姣. 多孔金属结合剂金刚石砂轮的开发研究 [D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2006.LIAO Cuijiao. The development of porous metal bonded diamond grinding wheels [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2006. -



 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
