Rapid formation of TiC coating on diamond surface through thermal explosion reaction
-
摘要:
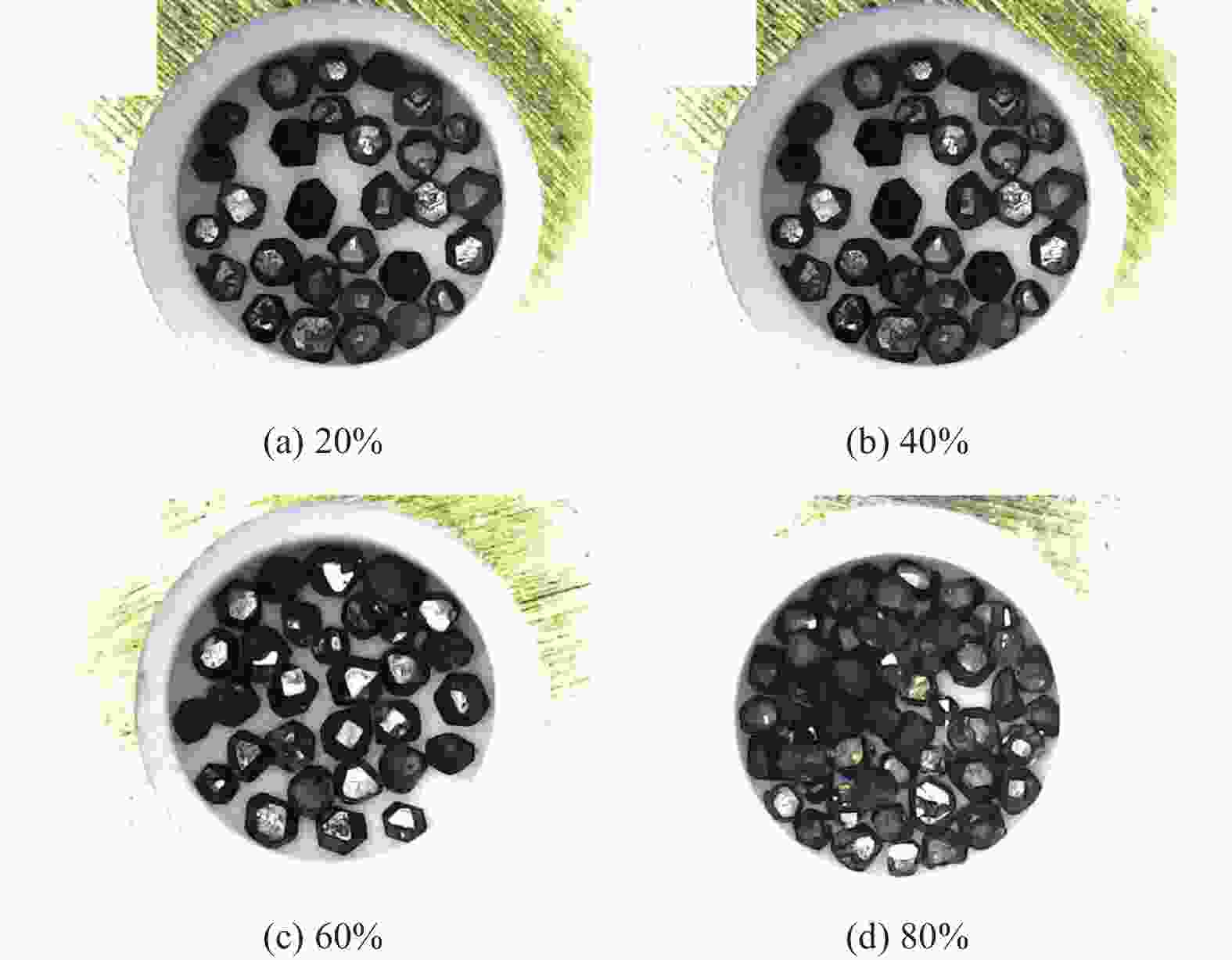
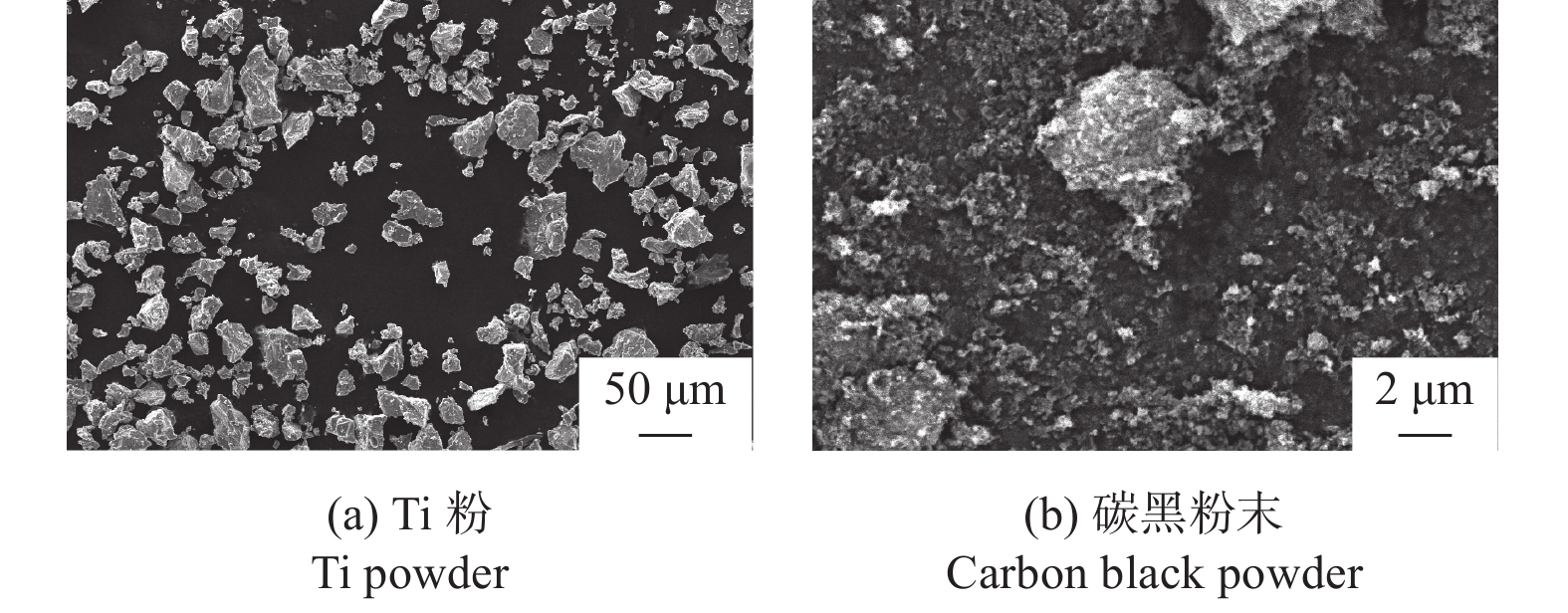
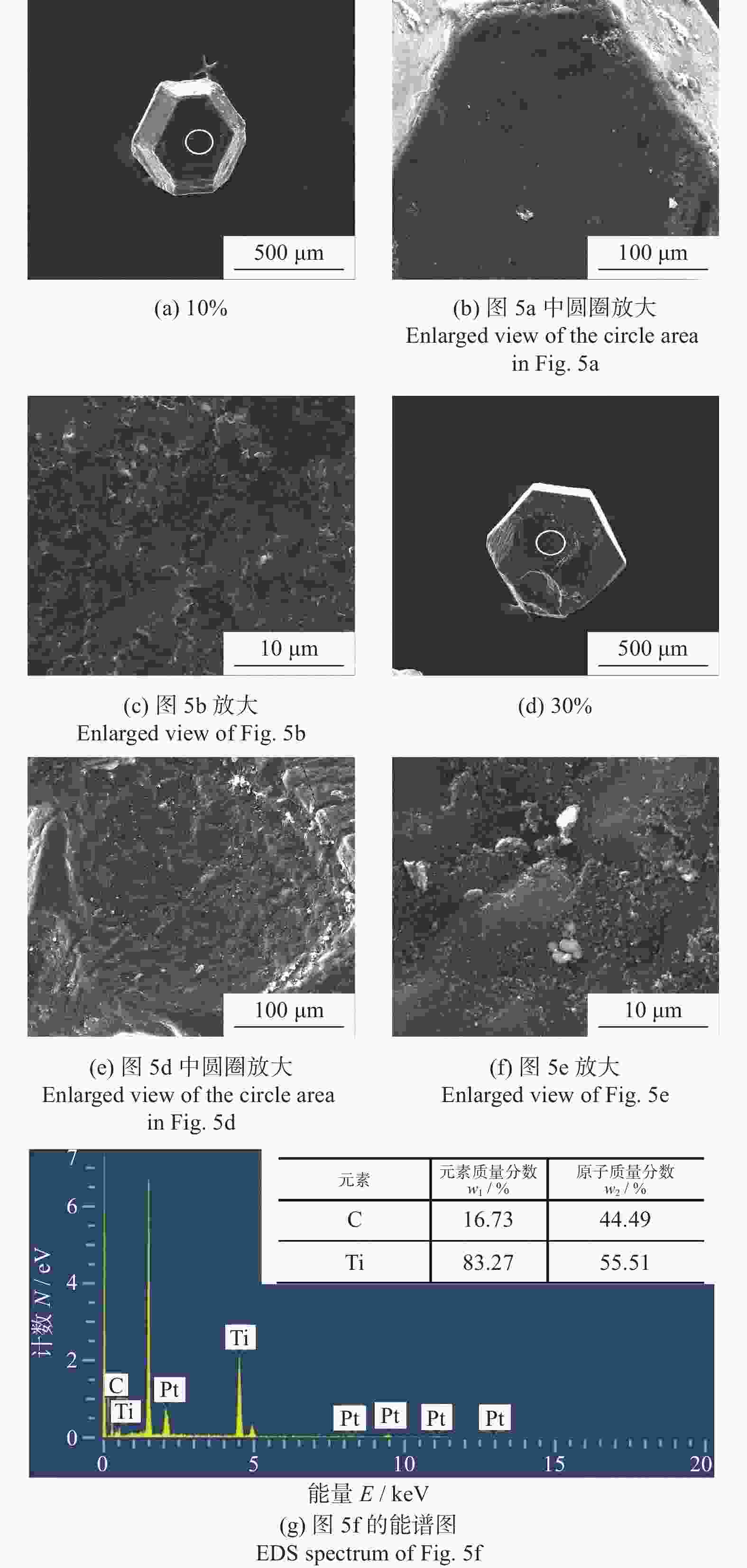
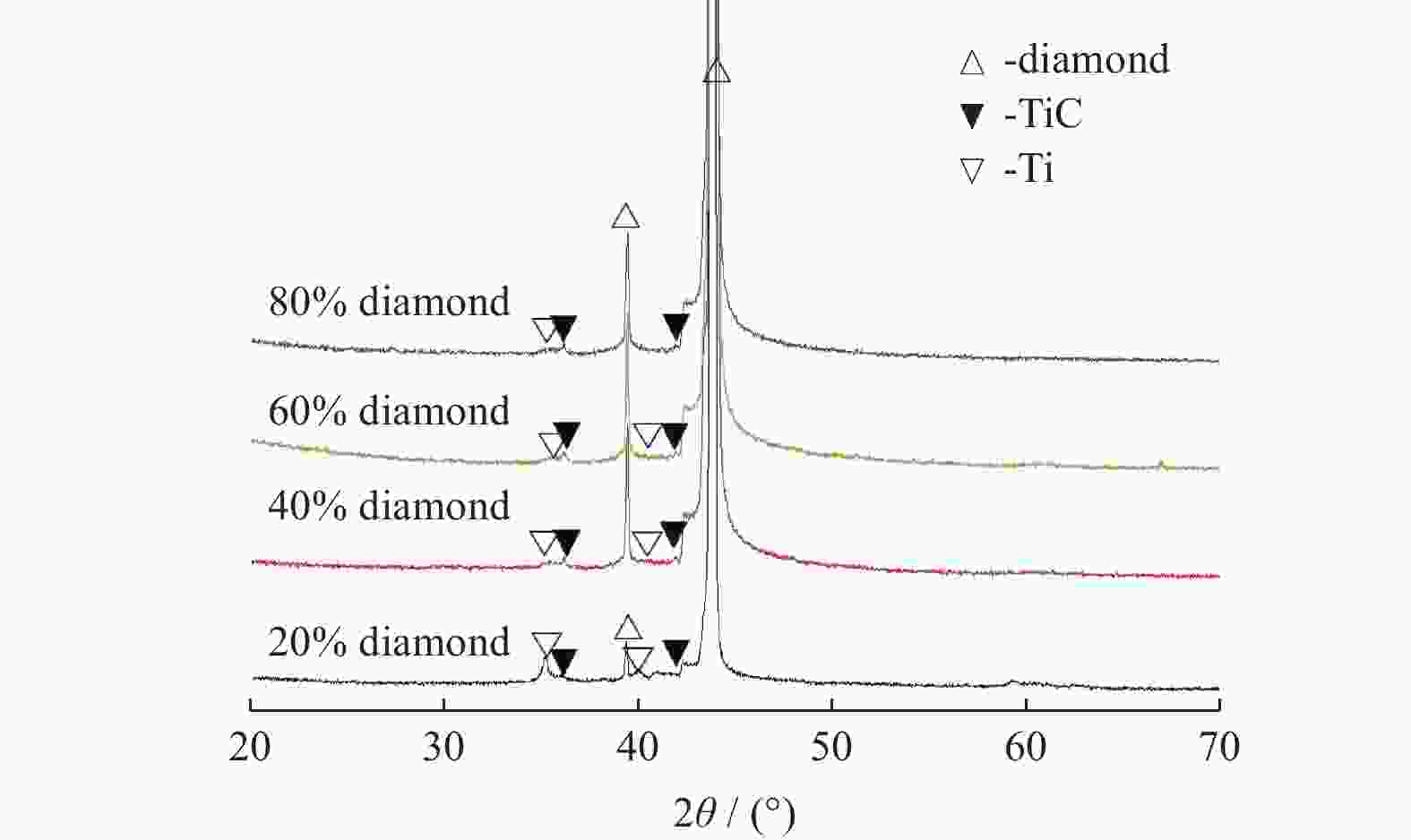
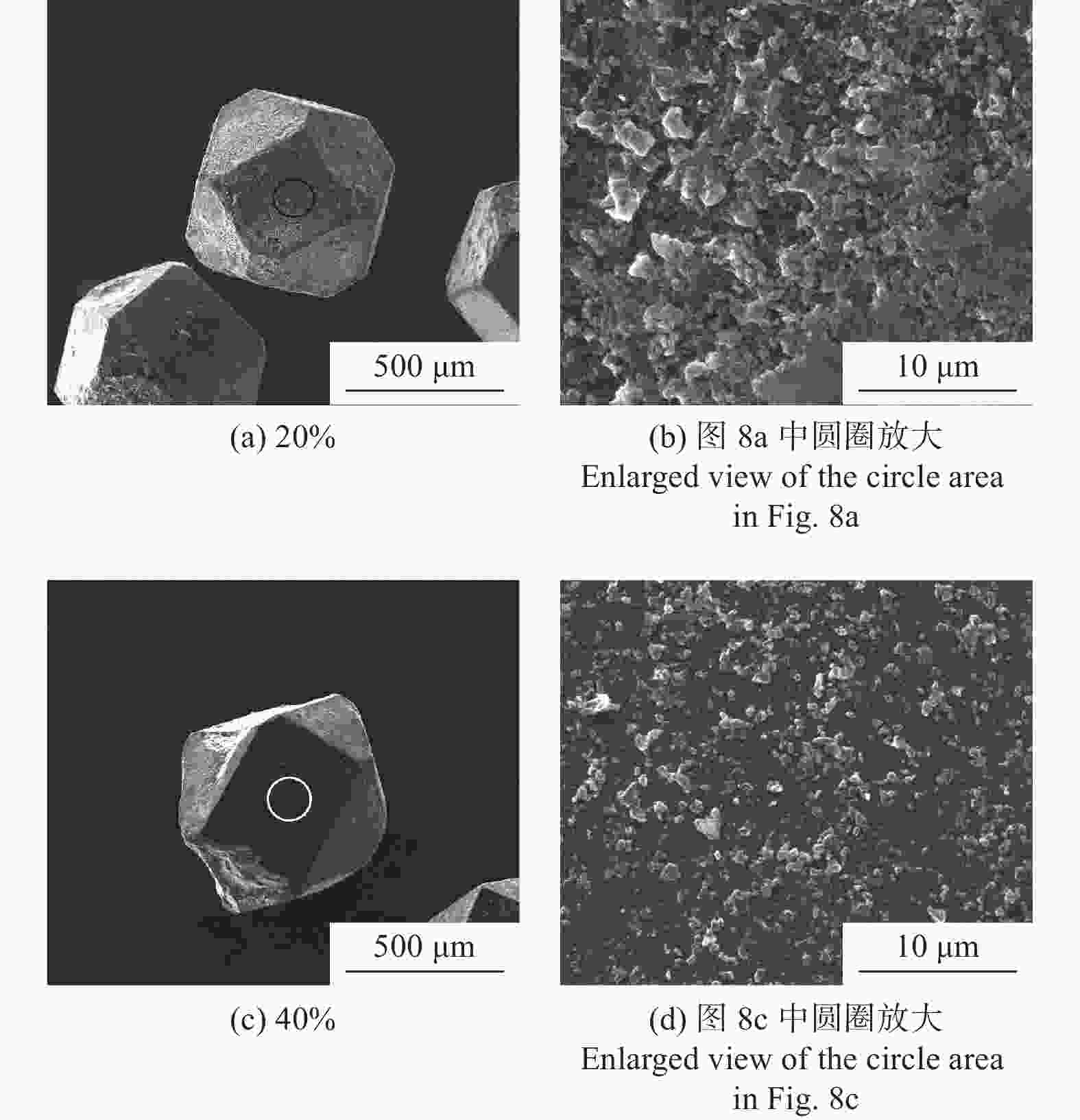
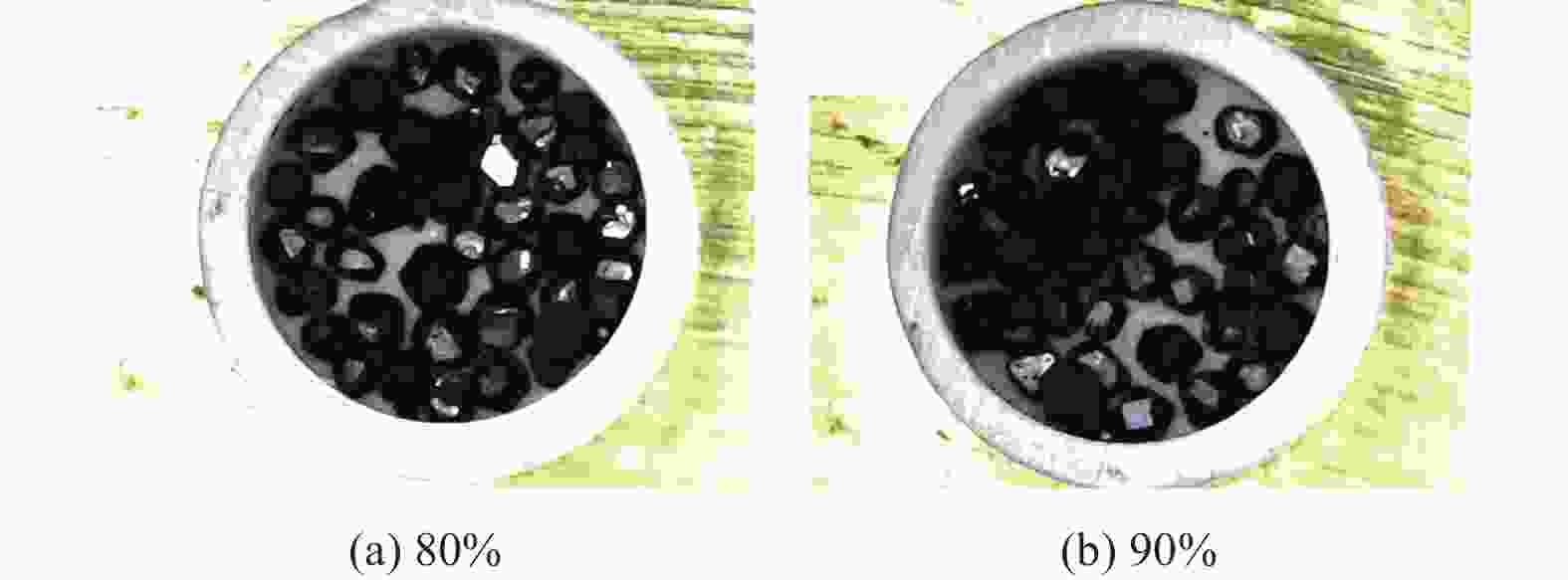
分别采用Ti/碳黑/diamond和Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond粉体为原料,通过热爆反应在金刚石颗粒表面形成以TiC为主的涂层,研究原料中金刚石含量及添加PTFE对金刚石表面TiC涂层的影响。结果表明:2种体系的原料热爆反应后基体的组成为TiC。Ti/碳黑/diamond体系中,当原料中金刚石质量分数为10%~30%时,反应后的金刚石表面均实现良好的TiC涂层涂覆。在Ti/碳黑/PTFE/diamond体系中,当原料中添加质量分数为3%的PTFE并减少原料中碳黑的质量分数时,可明显促进金刚石表面的TiC涂覆;且当原料中金刚石质量分数为80%~90%时,仍可使金刚石颗粒表面实现良好的TiC涂覆。
Abstract:Objectives: Coating treatment on the surface of diamond particles is an important technique to effectively overcome the problem of difficult bonding between diamond and substrate, and the thermal explosion reaction is a common surface coating technique for diamond particles. However, this technology has disadvantages such as difficulty in separating diamonds from the product and a low proportion of diamonds, which increases its complexity and production costs, greatly limiting the promotion and application of this technology. This article aims to introduce polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) into thermal explosion reaction technology to form a coating mainly composed of TiC on the surface of diamond particles. It is expected to optimize the coating preparation process and promote the popularization and application of thermal explosion reaction technology in the field of diamond plating, so as to improve the wear resistance and service life of the diamond tools. Methods: Using two raw material systems, Ti/carbon black/diamond and Ti/carbon black/PTFE/diamond powders, the thermal explosion reaction of Ti/carbon black/diamond is induced by the chemical furnace method, and the intense chemical reaction between PTFE and titanium at low temperature ensures that the Ti/carbon black/PTFE/diamond system directly undergoes a thermal explosion reaction. At the same time, the TiC coating can be generated on the surface of diamond particles by adjusting the ratio of raw materials and triggering the thermal explosion reaction under high temperature conditions. The macroscopic morphology of diamond particles before and after coating is observed and compared by optical microscope to roughly infer the plating condition, and the phase compositions of the coating were analyzed by X-ray diffraction. Then the scanning electron microscope and the energy dispersive spectroscopy are used to observe the surface morphology of diamond particles, determine the elemental compositions, and infer the surface reaction state. Results: The thermal explosion reaction of both raw material systems can form a TiC coating on the surface of diamond. The main phase of the binder reaction product is TiC, and the main phases of the coating on the surface of diamond particles are TiC and Ti. But for the Ti/carbon black/diamond system, the chemical furnace method is needed to induce a thermal explosion reaction. When the diamond mass fraction in the raw material is 30% or lower, the TiC coating on the surface of the diamond particles is good. When a small amount of PTFE is introduced into the Ti/carbon black/diamond system, the reaction between Ti and PTFE releases a large amount of heat, which induces the thermal explosion reaction between Ti and carbon black and synthesizes TiC, and finally forms a TiC coating on the surface of diamond particles. In addition, the system does not need the chemical furnace method to detonate. When the diamond mass fraction in the raw material is less than or equal to 60%, the diamond particle surface coated with TiC coating is good. At the same time, appropriately reducing the content of carbon black in the raw materials can enable diamond to obtain a good TiC coating on its surface even when the mass fraction of diamond is 90% or higher. Conclusions: TiC coatings are prepared on the surface of diamond particles using thermal explosion reaction technology, and the important effects of raw material compositions and PTFE additives on the formation of diamond particles' surface coating are revealed. Adding an appropriate amount of PTFE can directly induce the thermal explosion reaction, which greatly promotes the increase of the proportion of diamond in the raw material, and effectively improves the formation quality of the coating. This can greatly save binder powder, thereby reducing production costs, while obtaining loose powder products that are easy to separate from diamonds. In addition, drawing on the work of this study, other carbide materials (such as SiC) can be analogously extended for coating on the surface of diamond particles, thereby promoting the promotion and the application of thermal explosion reactions in diamond coating.
-
Key words:
- Ti-TiC coating /
- diamond /
- thermal explosion /
- PTFE
-
-
[1] TONSHOFF H K, DENKENA B, APMANN H H. Diamond tools for wire sawing metal components [J]. Key Engineering Materials,2003,250:33-40. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.250.33 [2] TONSHOFF H K, DENKENA B, APMANN H H, et al. Diamond tools in stone and civil engineering industry: Cutting principles, wear and applications [J]. Key Engineering Materials,2003(250):103-109. [3] 朱振东, 刘豪, 张甜, 等. 金刚石表面镀覆技术与应用的研究进展 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2021(3):28-32.ZHU Zhendong, LIU Hao, ZHANG Tian, et al. Research progress of plating technology on the diamond surface and its application [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2021(3):28-32. [4] 黄本生, 李慧, 江仲英, 等. 金刚石CVD金属化及其应用 [J]. 真空科学与技术学报,2011,31(6):754-759.HUANG Bensheng, LI Hui, JIANG Zhongying, et al. Diamond metallization by chemical vapor deposition and its applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology,2011,31(6):754-759. [5] HU G, YANG J, LIU Y. Deposition of tungsten - titanium carbides on surface of diamond by reactive PVD [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,1999,9(4):838-841. [6] MIYAKE S, SHINDO T, MIYAKE M. Regression analysis of the effect of bias voltage on nano- and macrotribological properties of diamond-like carbon films deposited by a filtered cathodic vacuum arc ion-plating method [J]. Journal of Nanomaterials,2014(1/2):1-13. [7] DAOUSH W M, PARK H S, HONG S H. Fabrication of TiN/cBN and TiC/diamond coated particles by titanium deposition process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2014,24(11):3562-3570. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63502-0 [8] JIAO X Y, CAI X P, NIU G, et al. Rapid reactive synthesis of TiAl3 intermetallics by thermal explosion and its oxidation resistance at high temperature [J]. Progress in Natural Science:Materials International,2019,29(4):447-452. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2019.05.002 [9] LIU Y, SUN Z, CAI X, et al. Fabrication of porous FeAl-based intermetallics via thermal explosion [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2018,28(6):1141-1148. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64737-5 [10] LIANG B, DAI Z, ZHANG Q, et al. Coating of diamond by thermal explosion reaction [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2021,119:108572. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108572 [11] ZHAO H, YIN X, WANG Y. Coating diamond surfaces in a Ti/Si/carbon black/diamond system via thermal explosion [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022,127:109195. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109195 [12] LI Q, ZHANG Q, LIANG B, et al. Coating on the surface of diamond particles by thermal explosion reaction method [J]. Journal of Superhard Materials,2022,44(3):191-197. doi: 10.3103/S1063457622030042 [13] 殷声. 燃烧合成 [M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1999.YIN Sheng. Combustion synthesis [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999. [14] YANG K, YANG Y, LIN Z M, et al. Mechanical-activation-assisted combustion synthesis of SiC powders with polytetrafluoroethylene as promoter [J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2007,42(9):1625-1632. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2006.11.037 [15] ZURNACHYAN A R, KHARATYAN S L, KHACHATRYAN H L, et al. Self-propagating high temperature synthesis of SiC–Cu and SiC–Al cermets: Role of chemical activation [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2011,29(2):250-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2010.11.002 [16] BAGHDASARYAN A M, HOBOSYAN M A, KHACHATRYAN H L, et al. The role of chemical activation on the combustion and phase formation laws in the Ni–Al-promoter system [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,188:210-215. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.137 [17] LEE I, REED R R, BRADY V L, et al. Energy release in the reaction of metal powders with fluorine containing polymers [J]. Therm Anal Calorim,1997,49(3):1699-1705. doi: 10.1007/BF01983730 [18] 鱼银虎, 汪涛, 张洪敏, 等. PTFE促发TiC陶瓷粉体低温固相合成研究 [J]. 无机材料学报,2015,30(3):272-276. doi: 10.15541/jim20140307YU Yinhu, WANG Tao, ZHANG Hongmin, et al. Low temperature combustion synthesis of TiC powder induced by PTFE [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2015,30(3):272-276. doi: 10.15541/jim20140307 [19] DUNMEAD S D, READEY D W, SEMLER C E, et al. Kinetics of combustion synthesis in the Ti-C and Ti-C-Ni systems [J]. Journal of American Ceram Society,1989,72(12):2318-2324. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb06083.x -




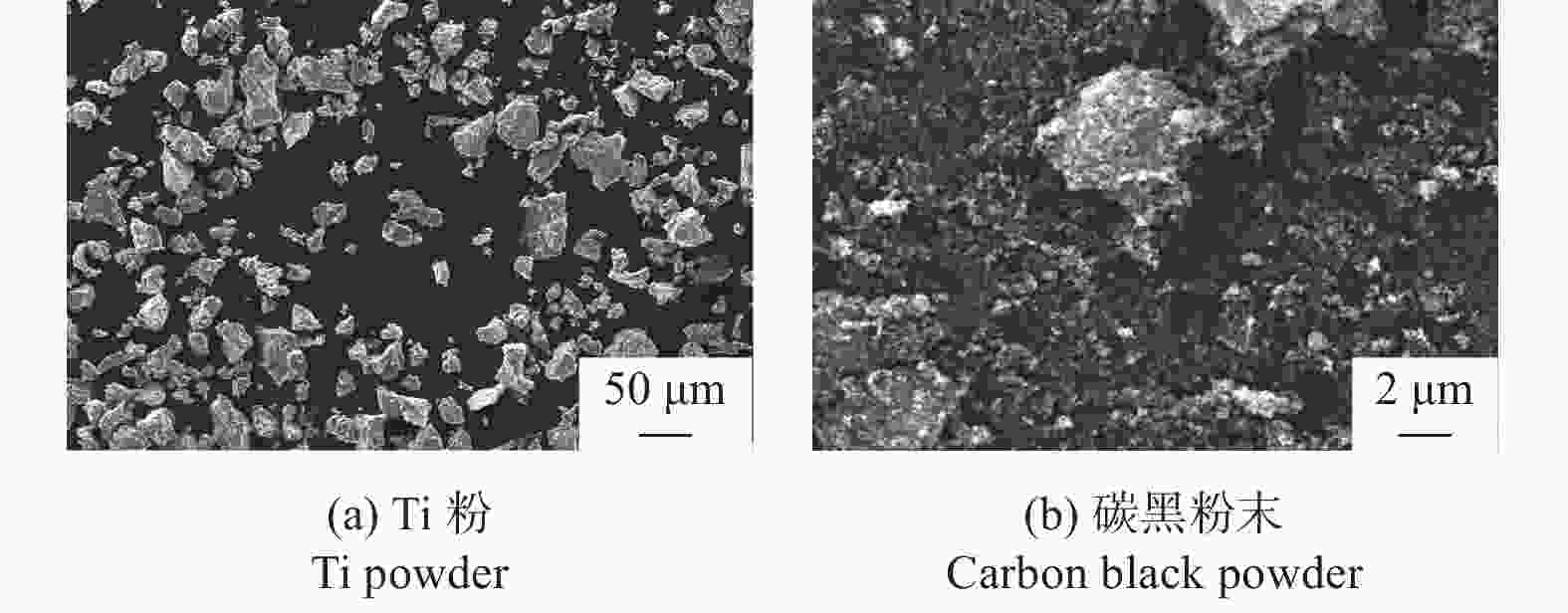
 下载:
下载:
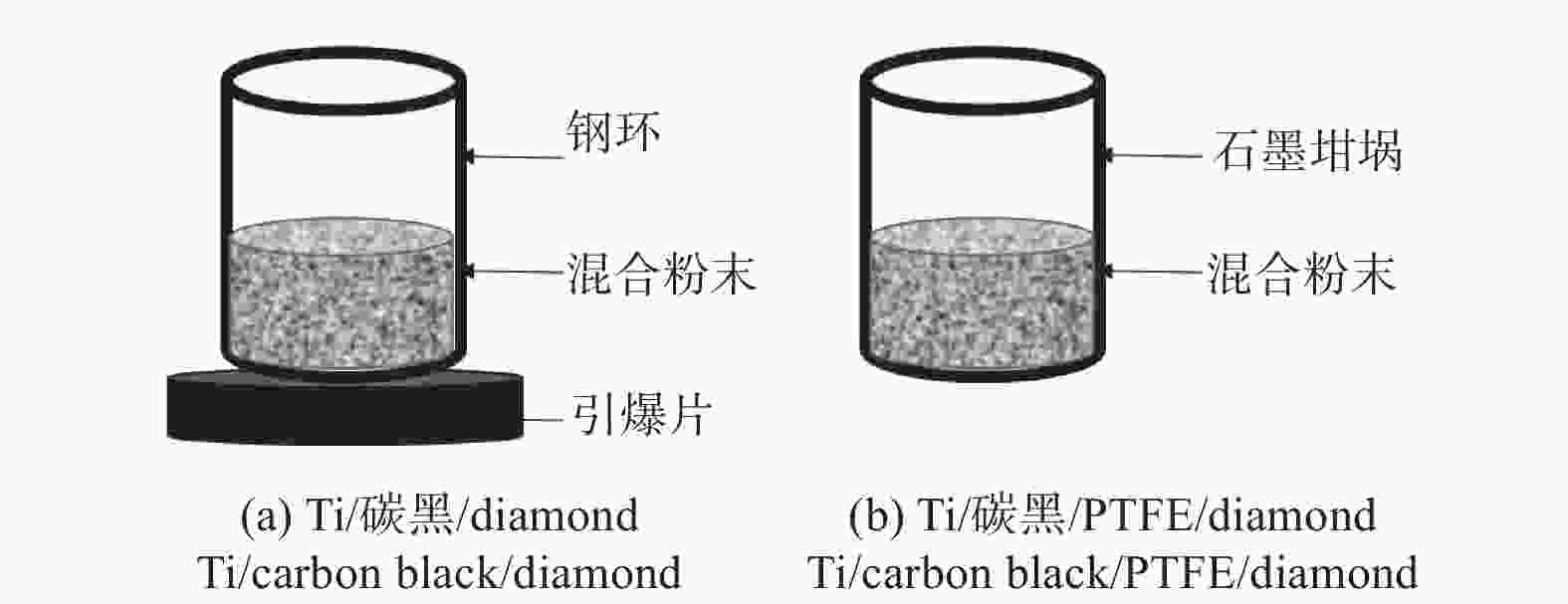
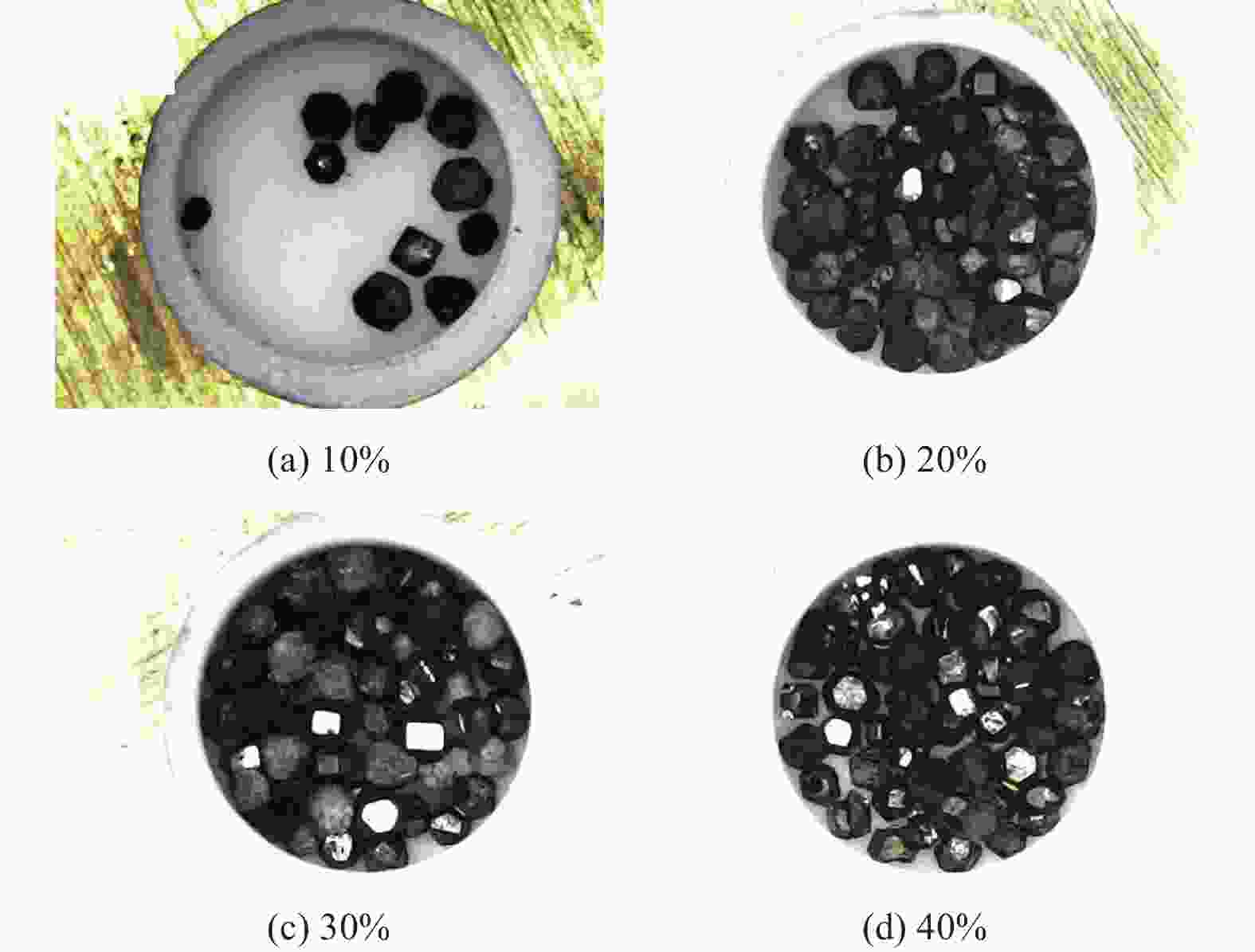
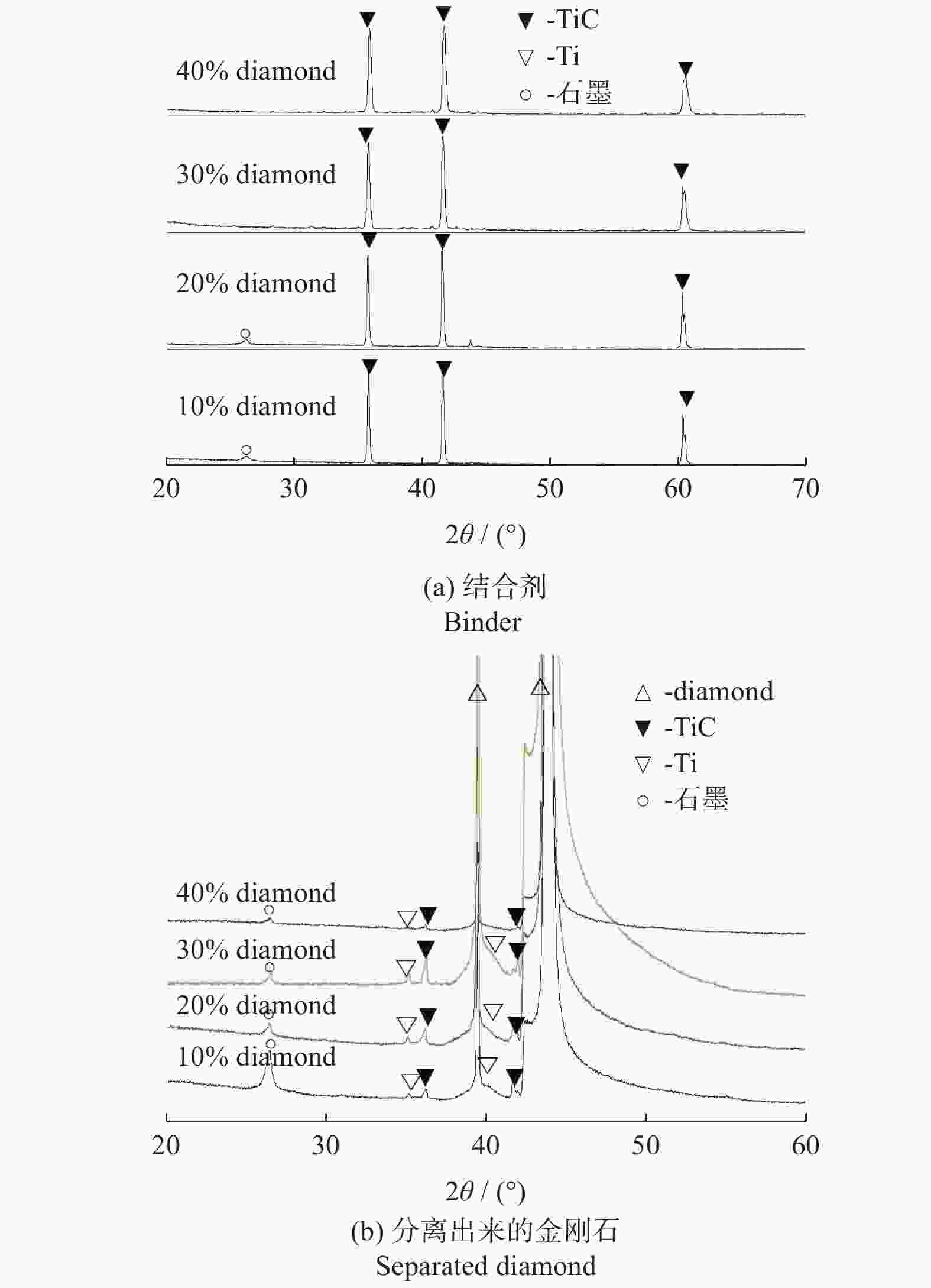




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
