Research of brittle-plastic behavior of SiCp/Al composites based on nano-indentation/scratch
-
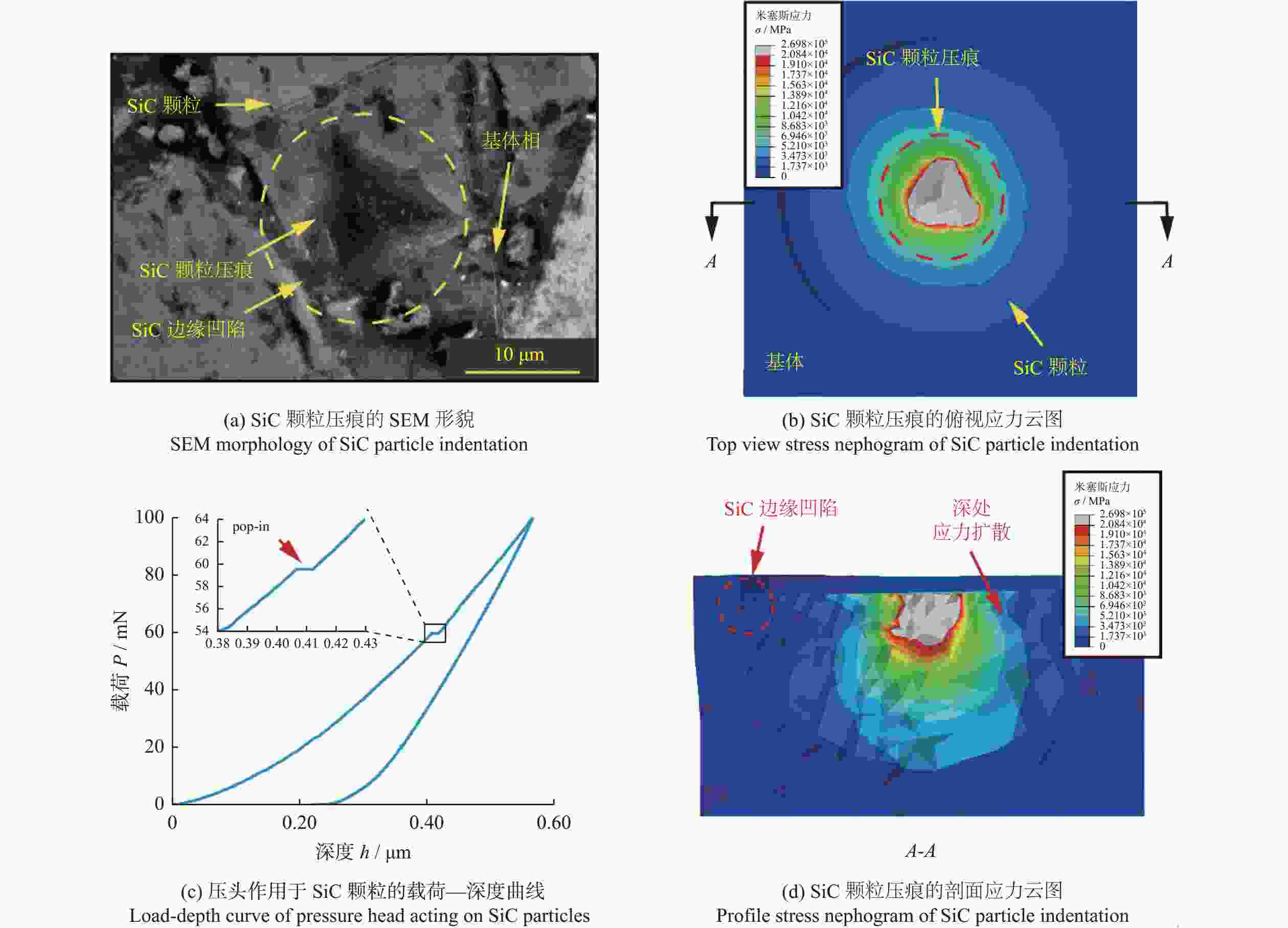
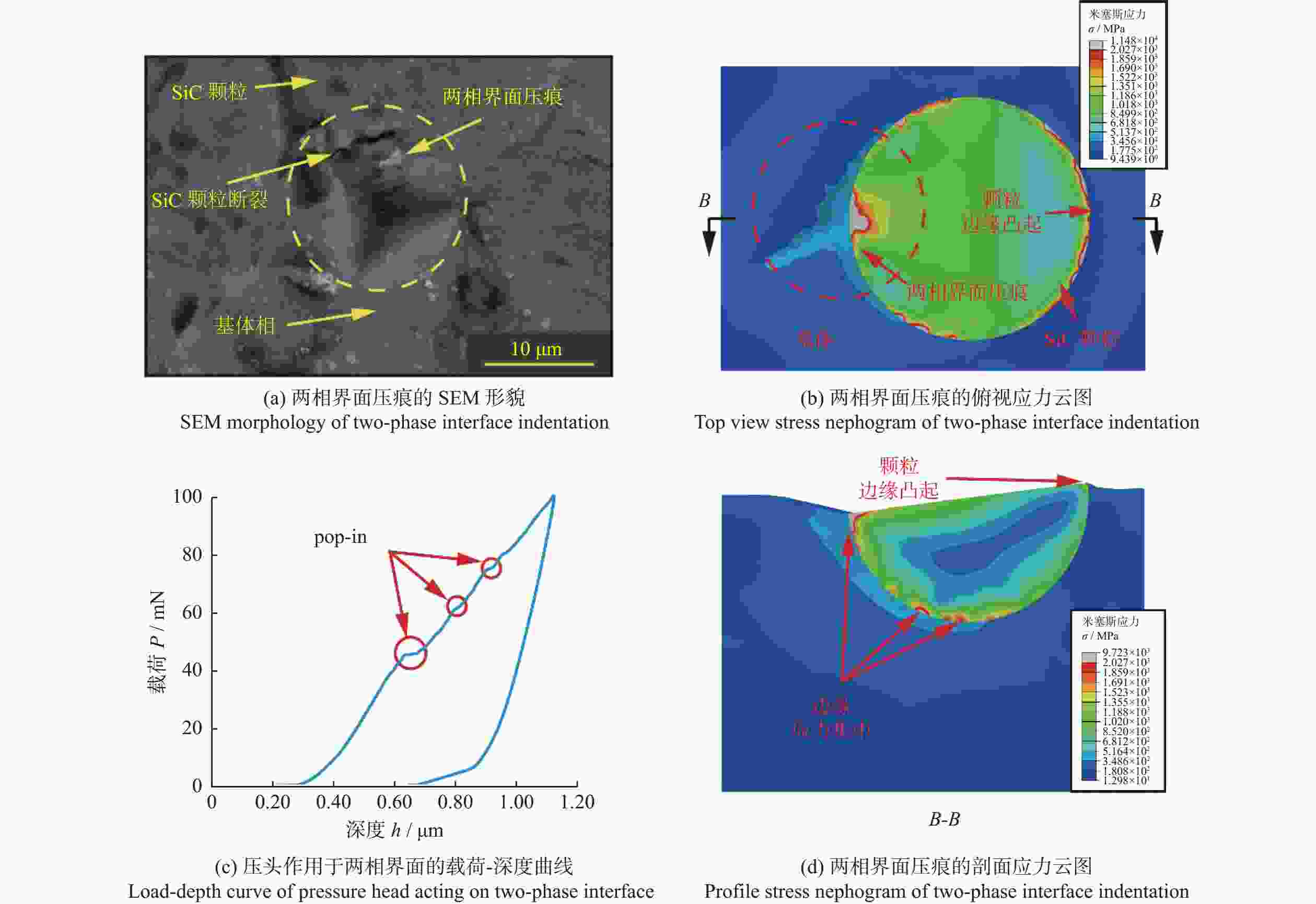
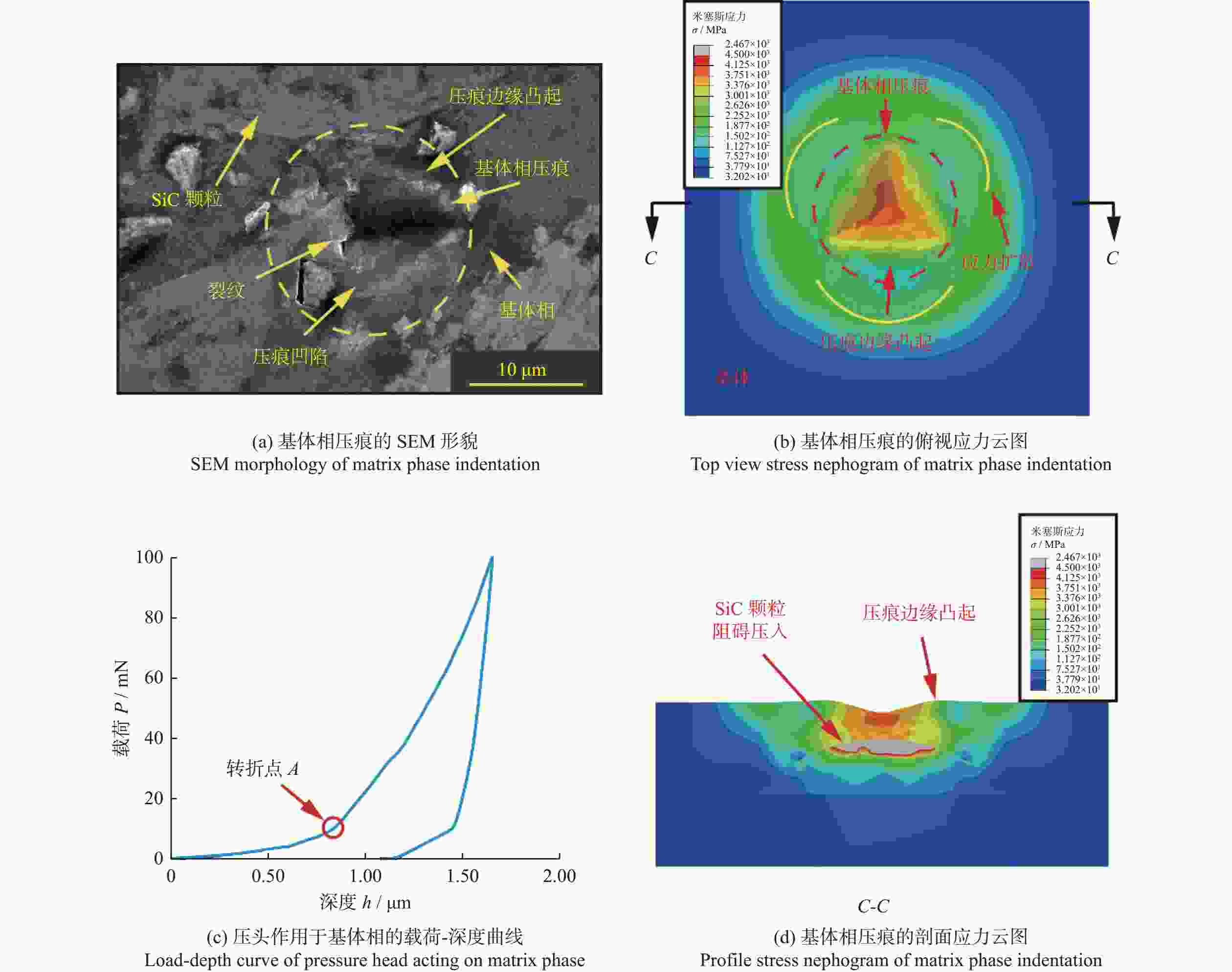
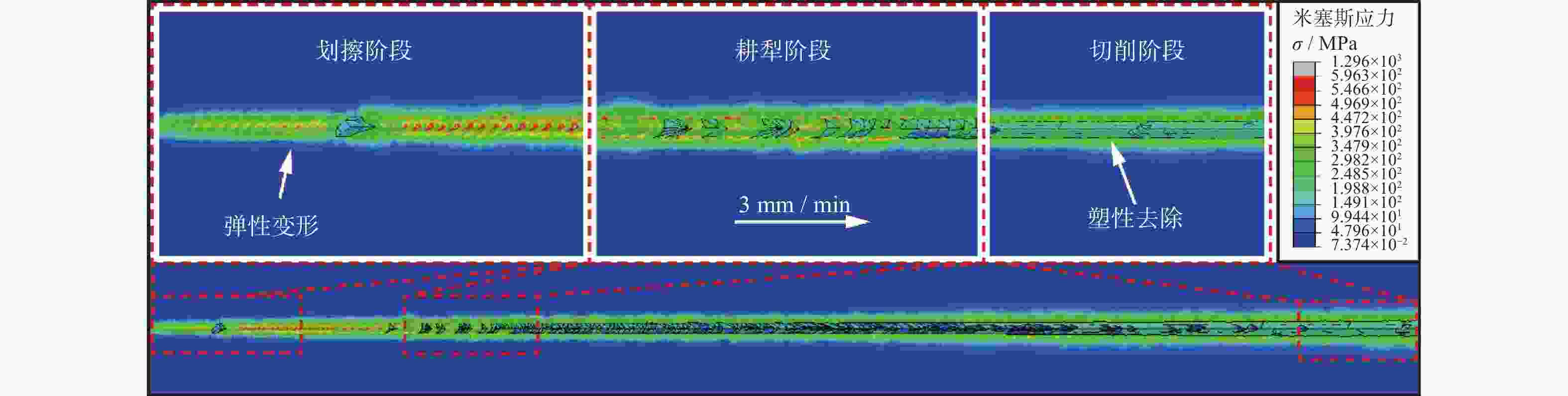
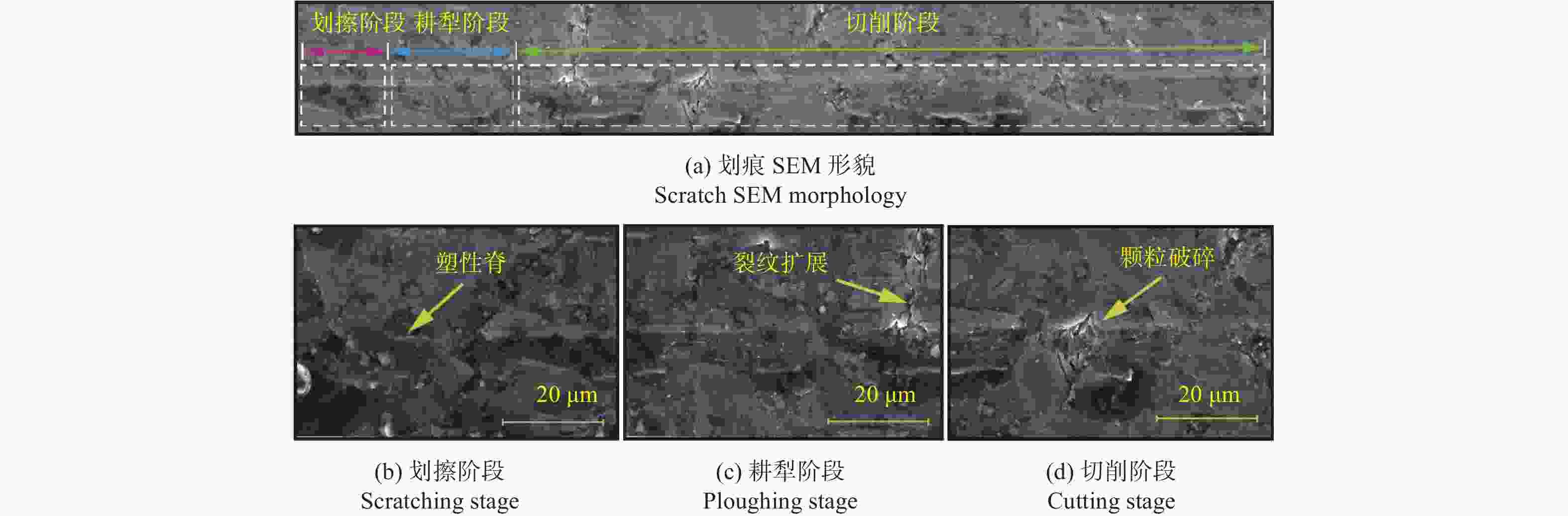
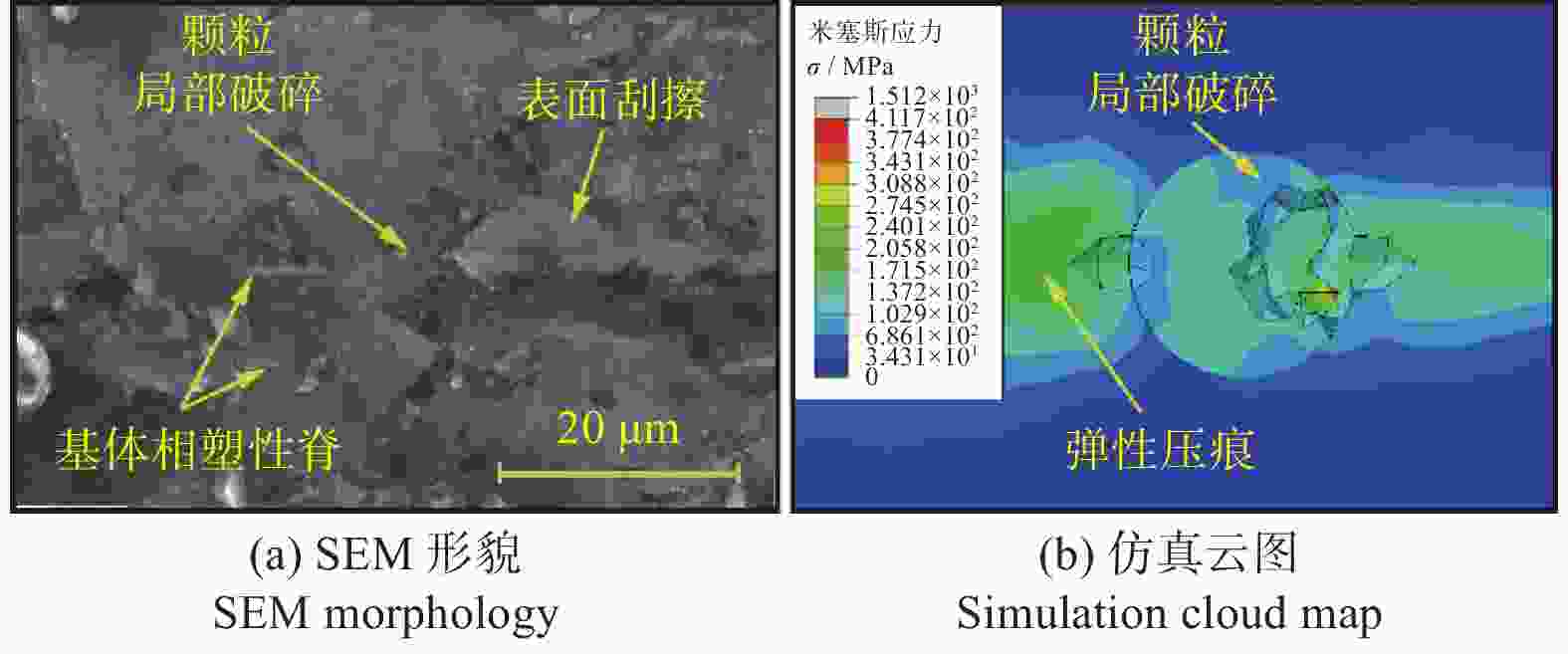
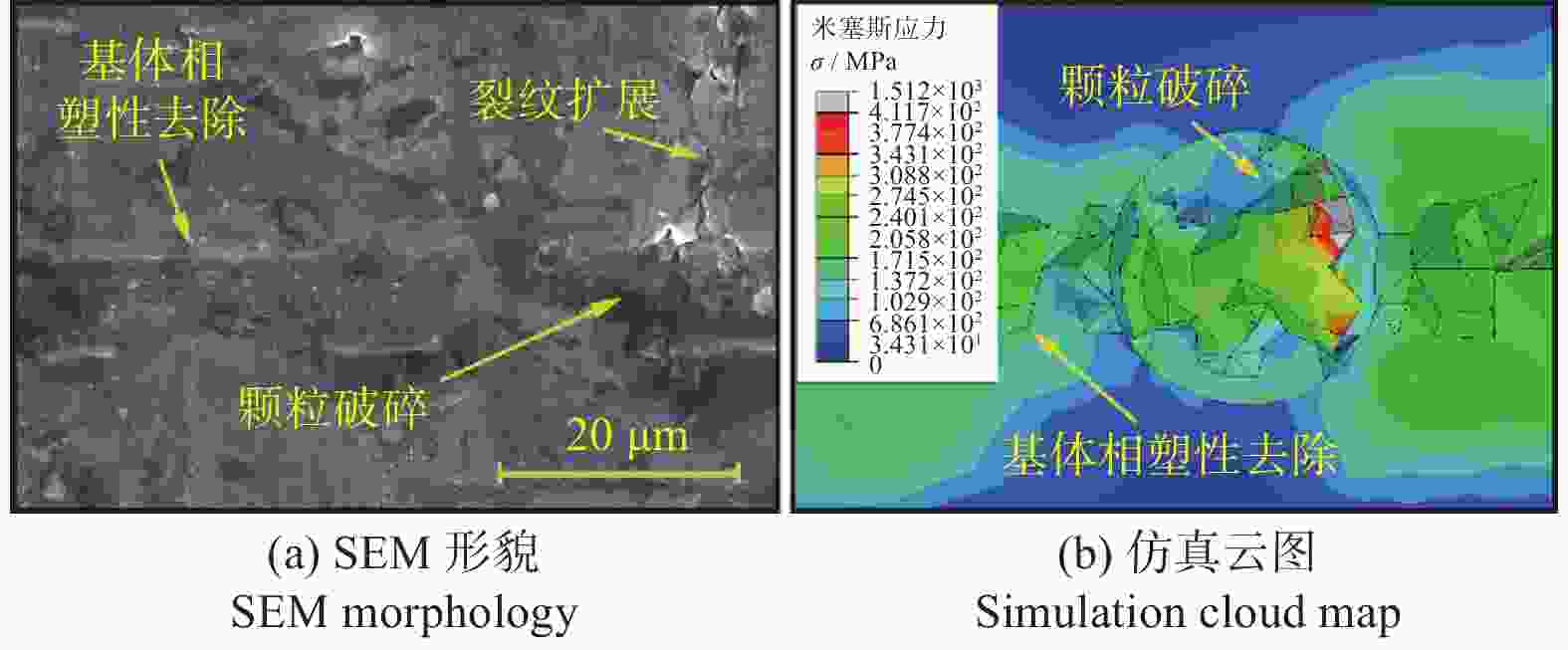
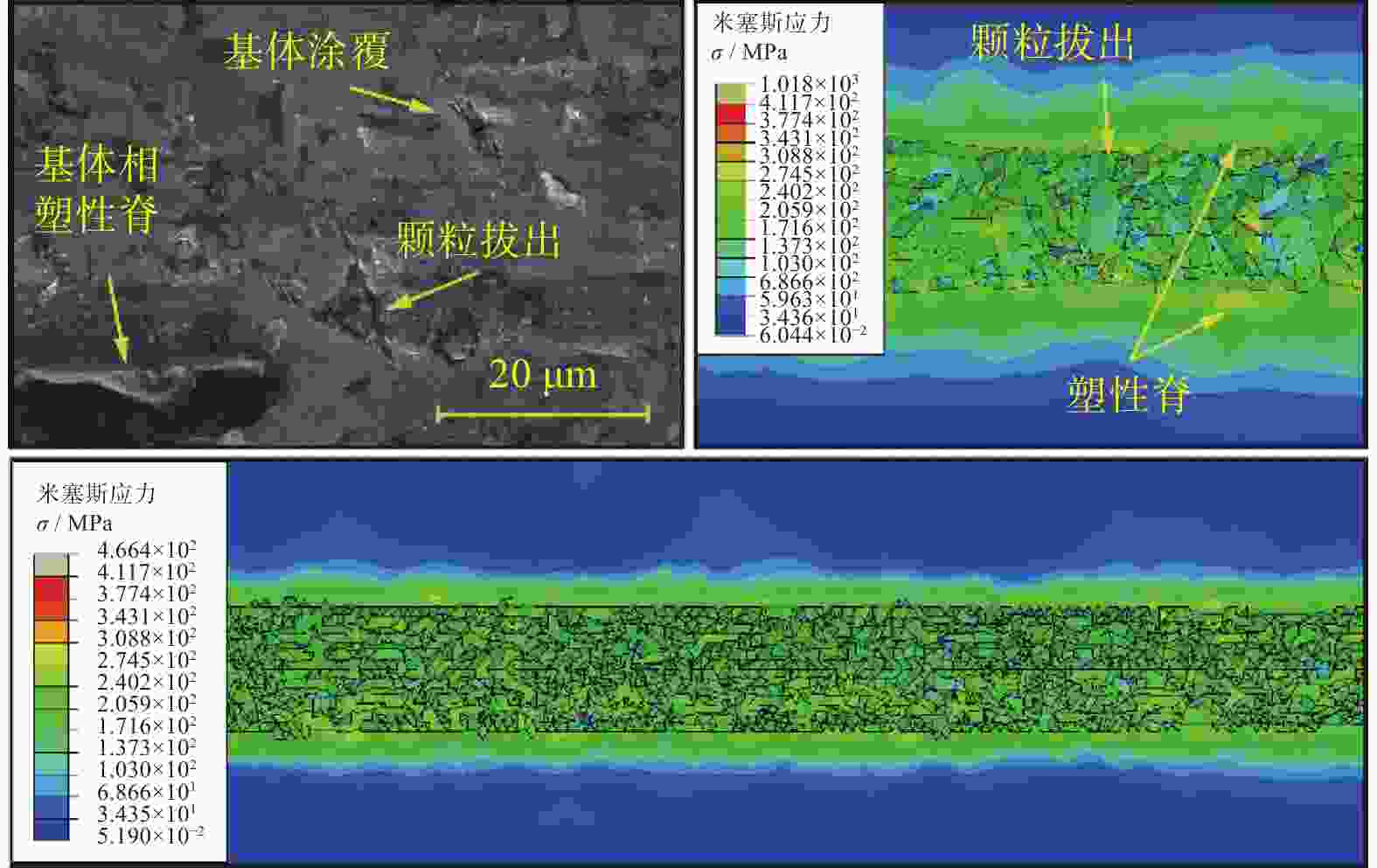
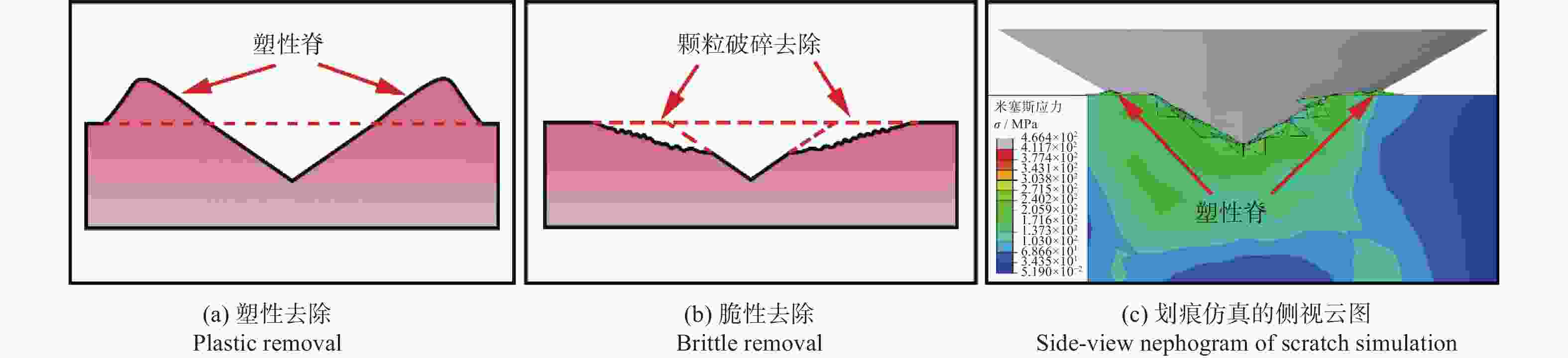
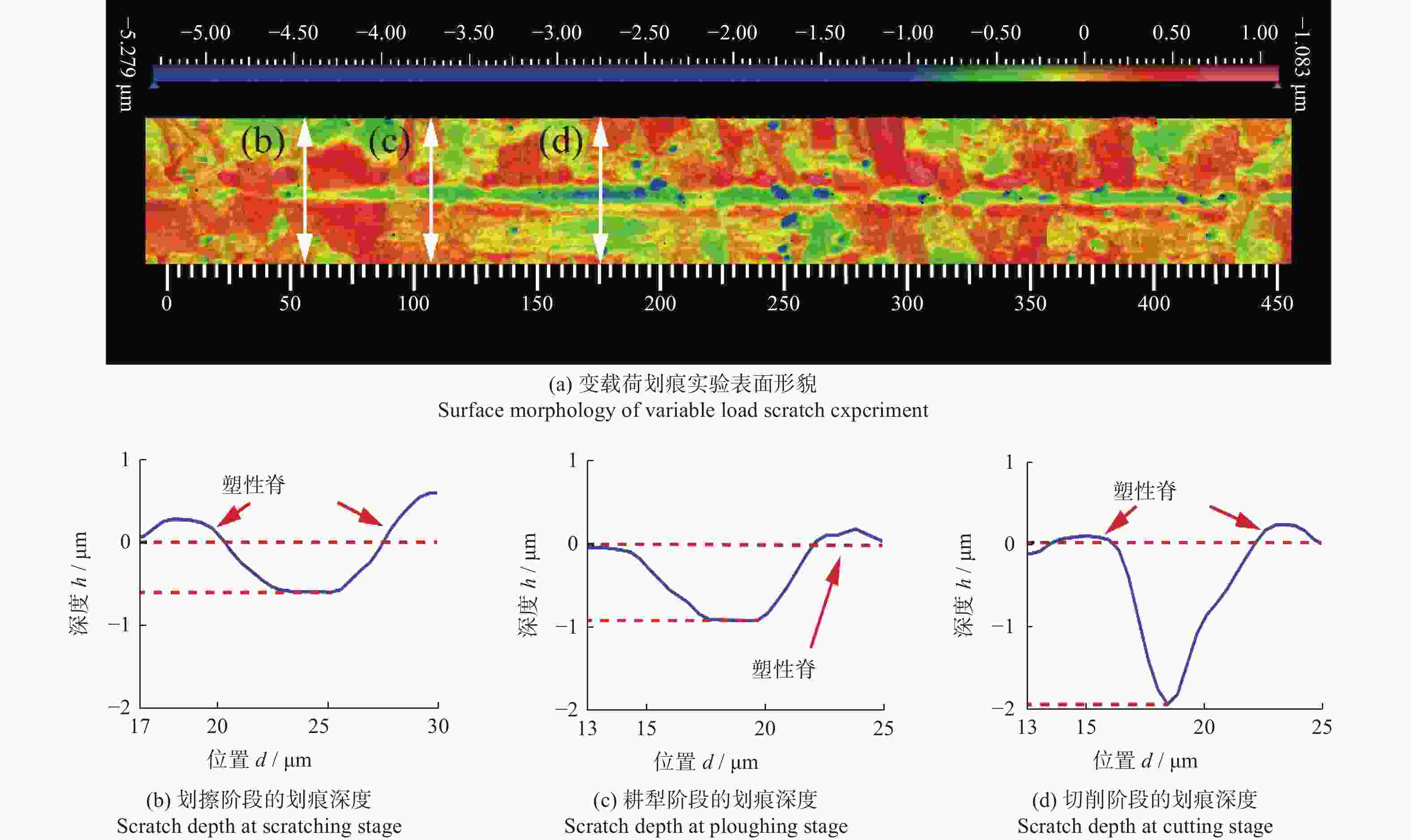
摘要: 为探究SiCp/Al复合材料中两相材料相互作用引起的力学性能差异,研究微观尺度下法向载荷变化对SiCp/Al复合材料形变和去除的影响。采用纳米压痕实验,基于Oliver-Pharr法测得其硬度和弹性模量,并对其压痕表面进行观察,结合有限元仿真分析产生力学性能差异的原因;同时,根据纳米压痕实验所得力学参数进行变载荷纳米划痕仿真,并配合实验后划痕表面观察结果分析材料的形变和脆塑性行为。结果表明:当金刚石压头作用于SiC颗粒时,颗粒出现破碎和二次压入现象,所测硬度与弹性模量小于单晶SiC的理论值;当金刚石压头作用于基体相时,由于SiC颗粒阻碍基体压入,复合材料的硬度与弹性模量测量结果偏大。在纳米划痕过程中,复合材料的去除形式随载荷变化体现为划擦、耕犁和切削阶段,其中的基体相通过塑性流动产生塑性脊堆积并伴随有涂覆现象,SiC颗粒则以脱黏、断裂破碎和拔出等脆性机制而去除,且SiC颗粒的二次压入、断裂、破碎和拔出是导致复合材料力学性能与单晶SiC的力学性能产生巨大差异的主要原因。随着划痕载荷增加,SiC体积分数为45 %的SiCp/Al复合材料的去除机制更多取决于以塑性去除为主的基体相,而SiC颗粒则主要表现为脆性去除。
-
关键词:
- 纳米压痕/划痕 /
- SiCp/Al复合材料 /
- 有限元仿真 /
- 力学性能 /
- 去除机制
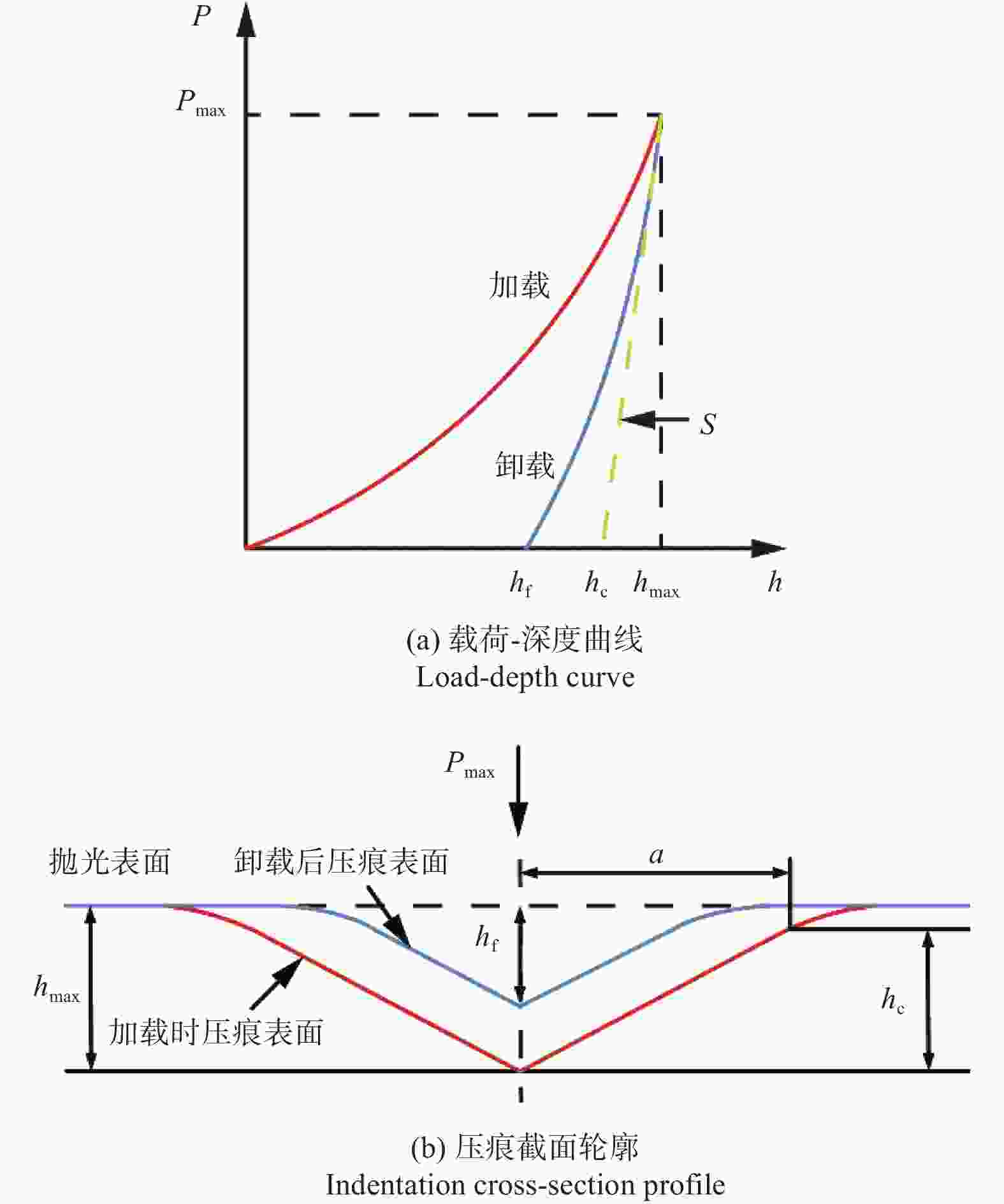
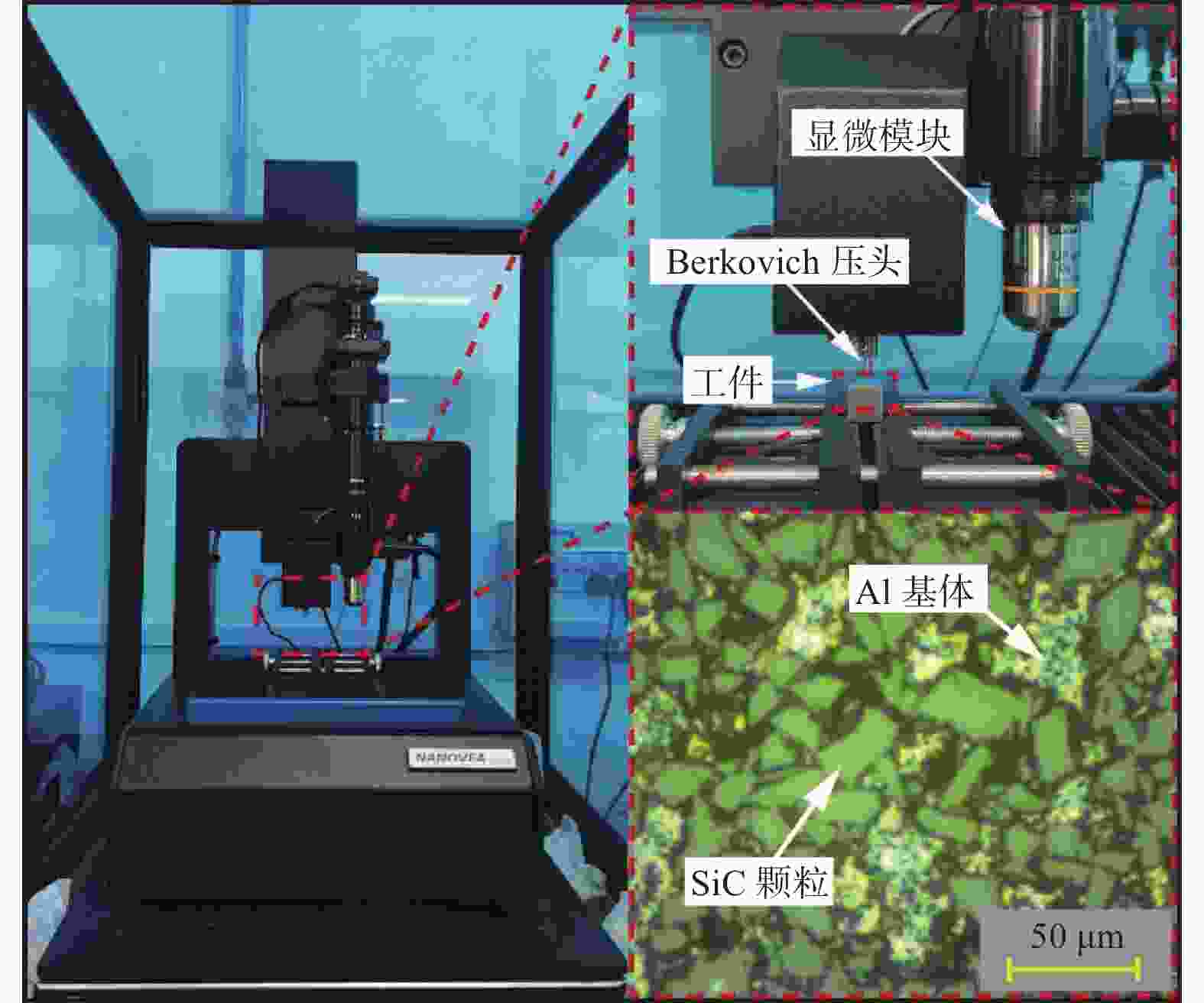
Abstract: Objectives: SiCp/Al composite is a kind of particle-reinforced metal matrix composite, which offers high specific strength and low density. It is widely used in electronic packaging, aerospace and automobile manufacturing. Although the presence of a large number of SiC particles improves the mechanical properties of the material, it also presents significant challenges in processing. As the volume fraction of SiCp/Al composite material increases, its mechanical parameters such as hardness improve, but a large number of surface defects appear during processing.To improve the surface machining quality and select better machining parameters, it is crucial to investigate the mechanical properties and the removal mechanism of SiCp/Al composites with medium or high volume fraction. Methods: Nanoindentation is a commonly used method for testing hardness, which can quantitatively characterize the hardness, elastic modulus and other mechanical parameters of materials. It provides a theoretical basis for predicting machined surface roughness. The load-depth curves of SiCp/Al composites under specific indentation load and rate can be obtained through nanoindentation experiments. The hardness and elastic modulus of SiCp/Al composites are determined using the Oliver-Pharr method. Due to the presence of a large number of SiC particles in the SiCp/Al composite, different failure behaviors are observed when the diamond indenters applies loads to the SiC particles, Al matrix, and two-phase interfaces, resulting in significant differences in measured hardness and elastic modulus. After the indentation experiment, scanning electron microscope (SEM) is used to observe the indentation surface morphology, and the ABAQUS finite element software is used to simulate the indentation process of SiCp/Al composites. The reasons for the differences in mechanical properties are then analyzed based on the finite element simulation results and the experimental indentation surface defects. Results: It is found that when the diamond indenter acts on SiC particles, the experimental values of hardness and elastic modulus of the material are the largest, with average values of 22.75 GPa and 190.78 GPa, respectively. When the indenter acts on the matrix phase, the average values of hardness and elastic modulus are 1.39 GPa and 66.52 GPa, respectively. For the interface between the two phases, the average hardness and elastic modulus measured are 4.62 GPa and 84.38 GPa, respectively. Additionally, the nanoscratch experiment simplifies the complex interaction between abrasive particles and the workpiece during grinding. It explores the brittle-plastic transformation behavior and potensial surface defects of the material surface by applying loads to the workpiece. This is an effective method for studying the material removal form. The hardness and elastic modulus values obtained from the nanoindentation experiment are introduced into the scratch finite element simulation. A variable load of 0 to 400 mN is applied to the SiCp/Al composite, with the scratch speed fixed at 0.05 mm/s. The results show that the removal form of the material changes with the load during the scraping, ploughing and cutting stages. The matrix phase undergoes plastic plastic flow, causing plastic ridge accumulation with coating phenomenon, while the SiC particles are removed by brittle mechanisms such as debonding, breaking, and pulling out. Conclusions: In the indentation experiment, secondary indentation of SiC particles in SiCp/Al composites results in significant differences between the mechanical properties of SiC particles and the theoretical mechanical properties of SiC crystals. Due to fracture and breakage of the particles during the loading process of the diamond indenter, the test results tend to be exaggerated. As the scratch load increases, the removal form of SiCp/Al composites with a volume fraction of 45% replies more on the plastic removal of the matrix phase, while the removal form of SiC particles is mainly brittle. The brittle-plastic behavior of the material surface during machining, as analyzed by the nanoindentation/scratch experiments, provides a theoretical basis for predicting the material's surface quality during machining. -
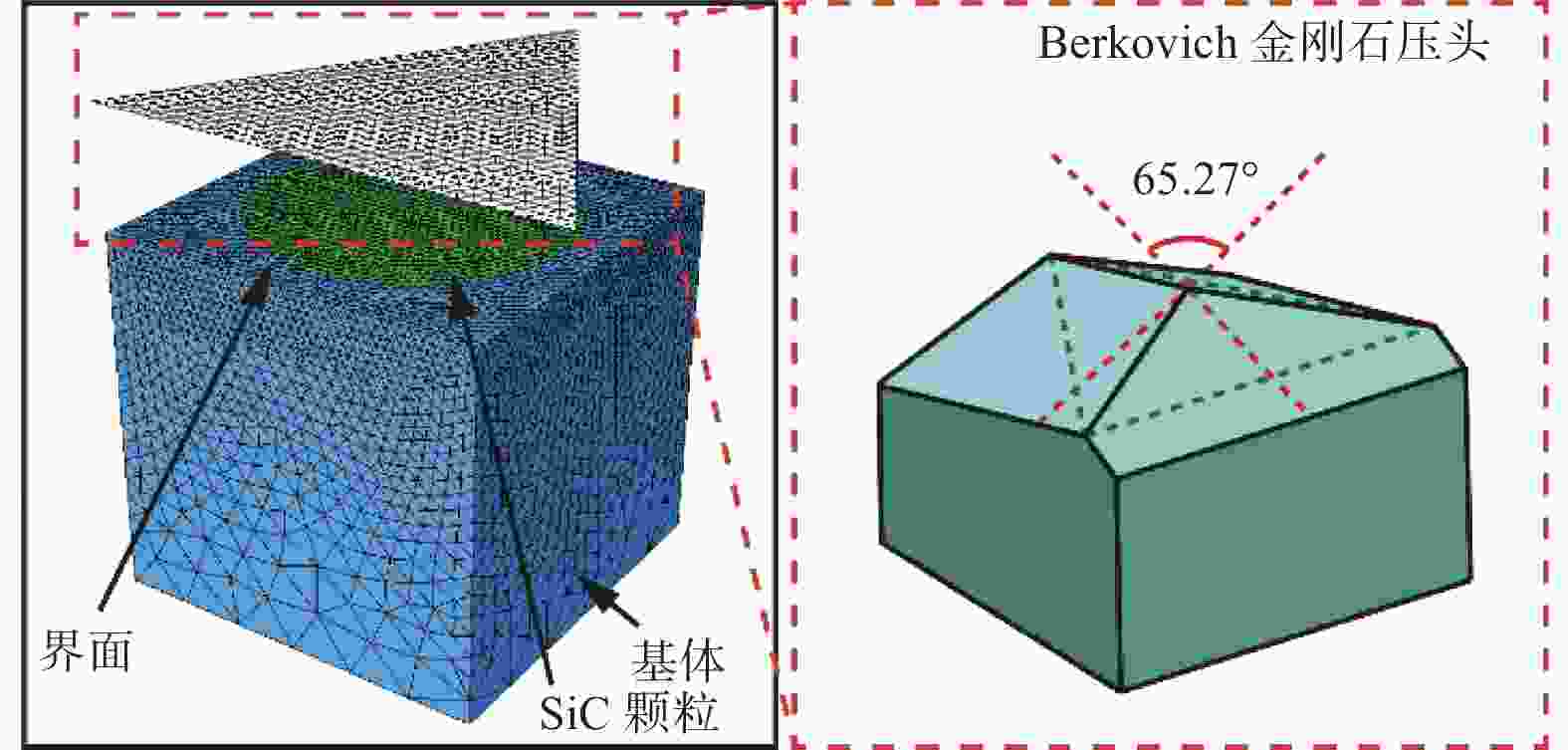
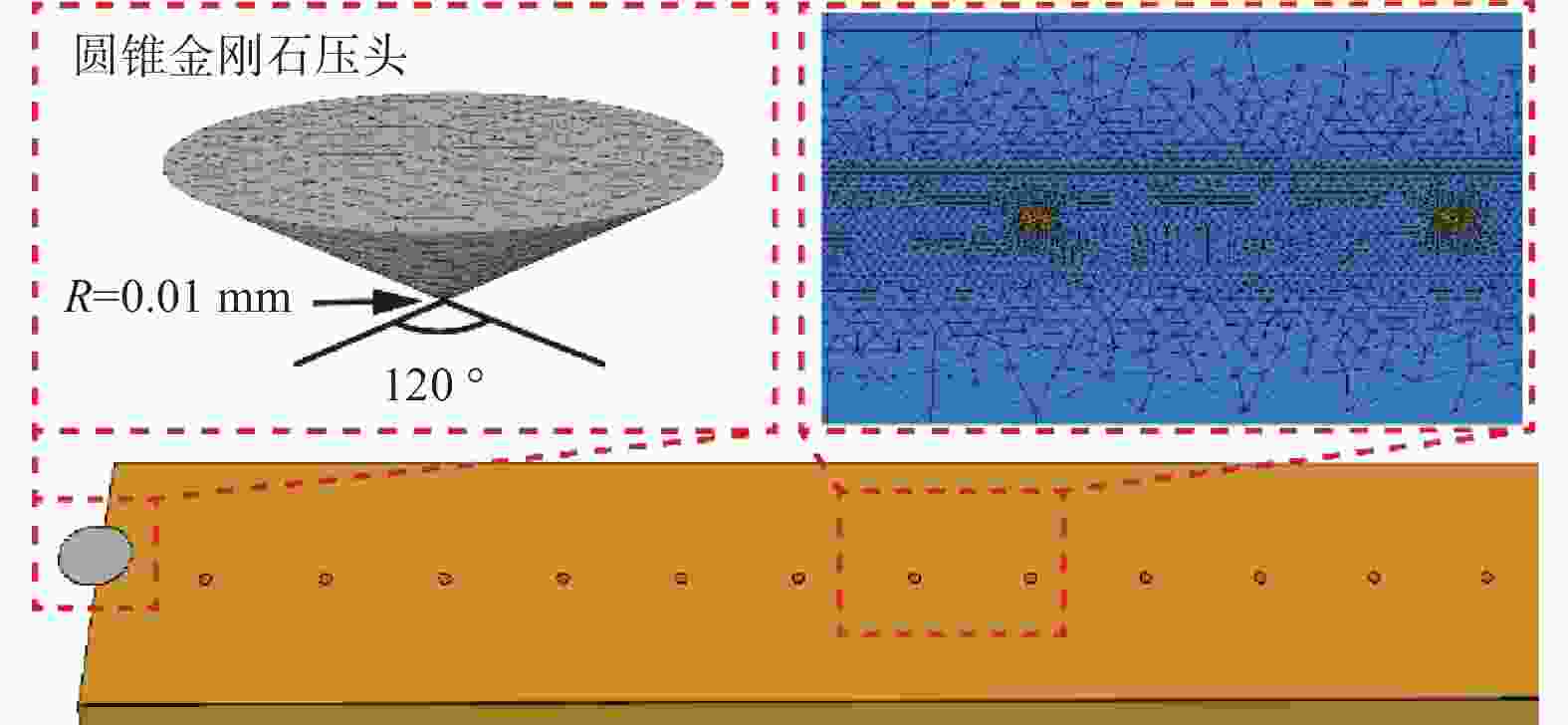
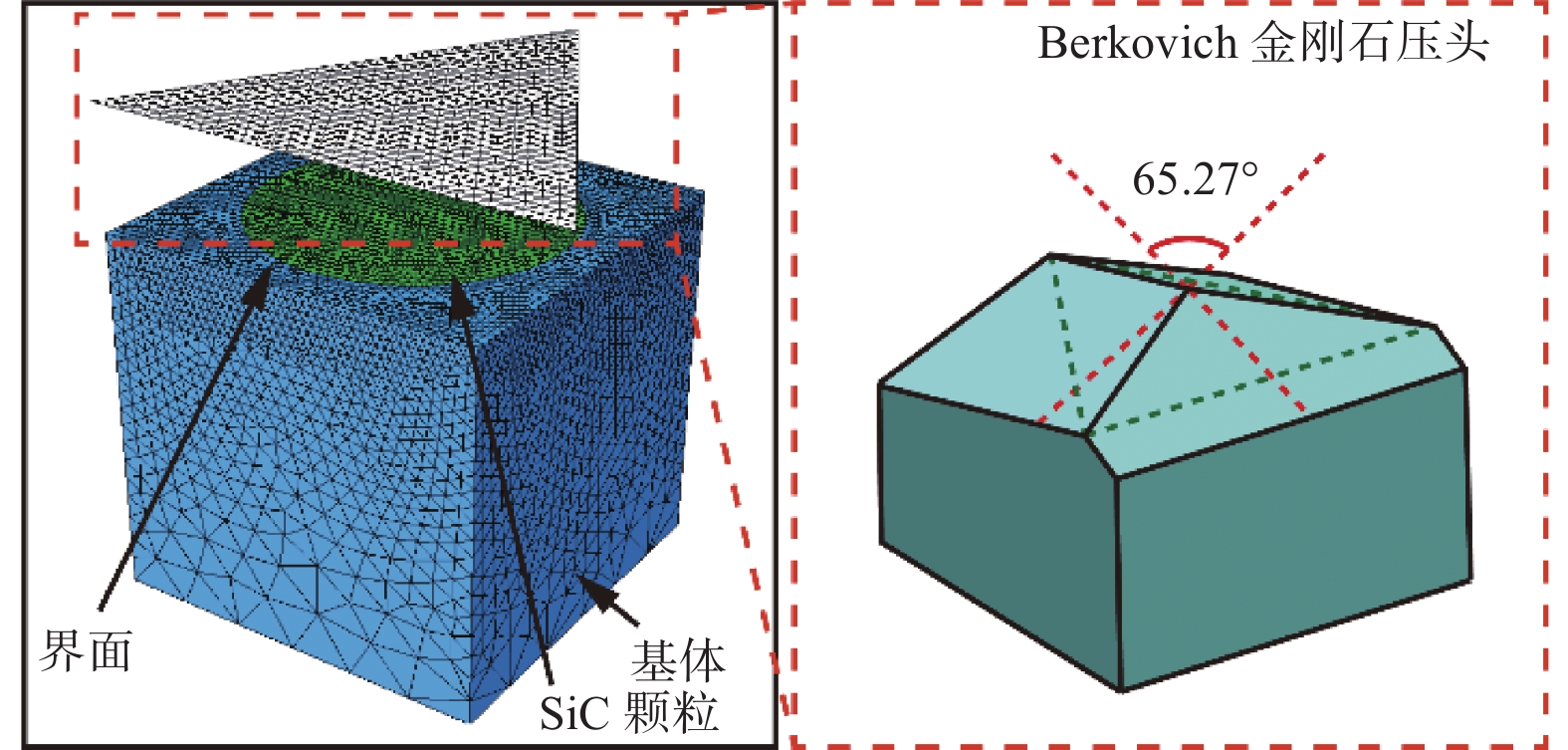
表 1 工件与压头材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of workpiece and indenter
参数 复合材料 金刚石压头 Al SiC 密度 ρ / (t·mm−3) 2.70 × 10−9 3.13 × 10−9 4.25 × 10−9 杨氏模量 E / MPa 70 000 420 000 1 147 000 泊松比 ν 0.30 0.14 0.07 表 2 SiCp/Al复合材料的微观力学性能参数
Table 2. Micromechanical properties parameters of SiCp/Al composite materials
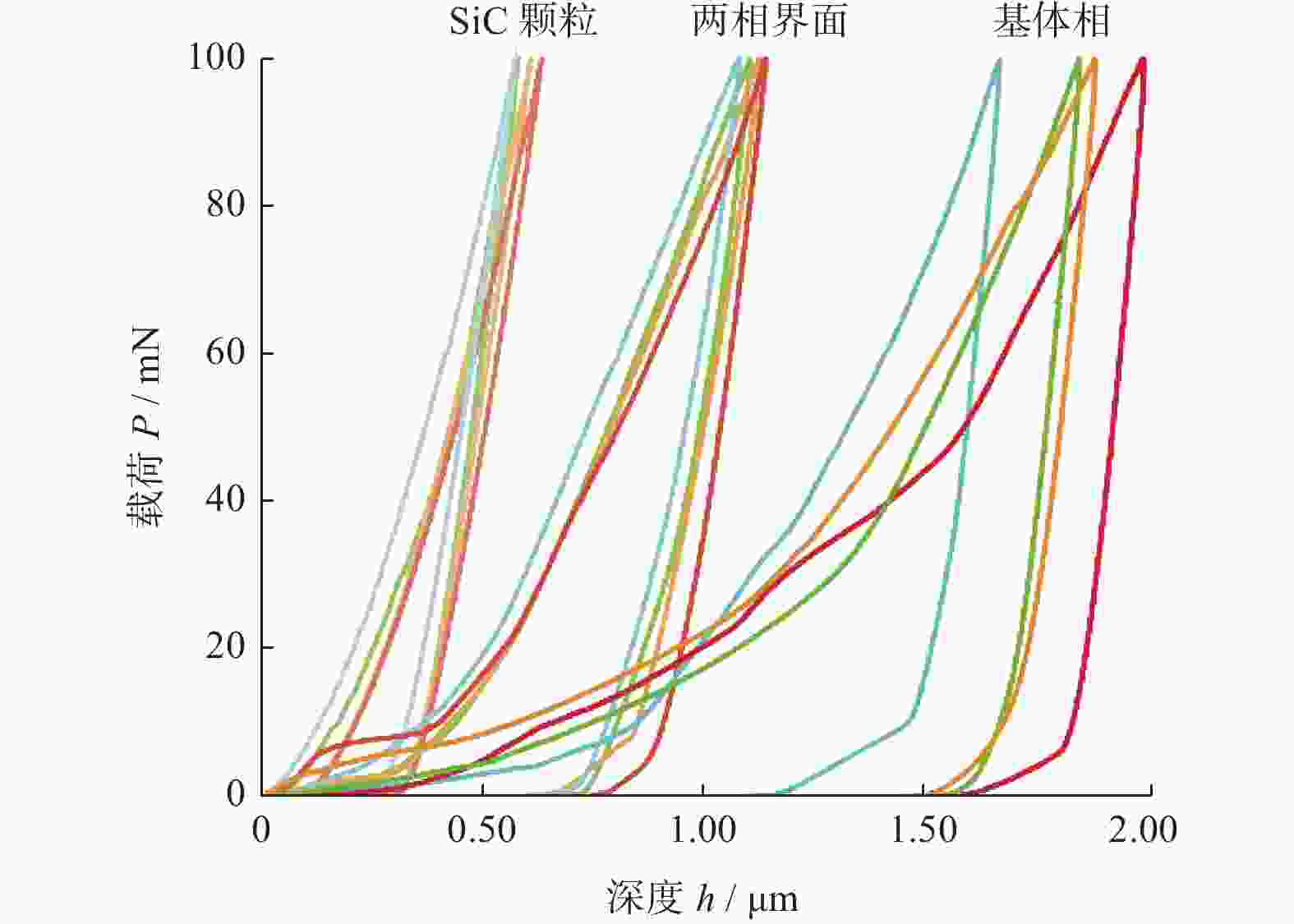
力学性能参数 SiC颗粒 两相界面 基体相 硬度
H / GPa范围 20.14~26.24 4.22~5.01 1.15~1.69 平均值 22.75 4.62 1.39 弹性模量
E1 / GPa范围 150.50~224.23 76.35~88.60 60.69~77.12 平均值 190.78 84.38 66.52 表 3 Al基体相J-C本构模型参数
Table 3. J-C constitutive model parameters of Al matrix phase
参数 取值 A / MPa 270 B / MPa 134 C 0.008 2 m 0.703 n 0.514 Tmelt / ℃ 600 Troom / ℃ 20 ${\bar \varepsilon ^{{\mathrm{pl}}}}/ {\mathrm{S}}^{-1}$ 0.001 表 4 Al基体相的J-C损伤参数
Table 4. J-C damage parameters of Al matrix phase
参数 取值 D1 0.13 D2 0.13 D3 −1.551 D4 0.011 D5 0 表 5 SiC颗粒脆性断裂的本构模型参数
Table 5. Constitutive model parameters for brittle fracture of SiC particles
参数 取值 $ {\sigma _{\mathrm{b}}} $/ MPa 1 500 $ G_{\mathrm{f}}^{\mathrm{I}} $/ (J·m−2) 30 $ p $ 1 $ {\varepsilon _{\max }^{{\mathrm{ck}}}} $ 0.001 -
[1] FAN Y, XU Y, HAO Z, et al. Cutting deformation mechanism of SiCp/Al composites based on strain gradient theory [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2022,299:117345. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117345 [2] YIN W, DUAN C, LI Y, et al. Dynamic cutting force model for cutting SiCp/Al composites considering particle characteristics stochastic models [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(24):35234-35247. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.09.066 [3] XIANG D, LIU G, PENG P, et al. Micro-removal characteristics of SiCp/Al by ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratch [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2022,37(16):1829-1836. doi: 10.1080/10426914.2022.2065007 [4] 房玉鑫, 王优强, 张平, 等. SiCp/Al复合材料高速切削去除机理及表面质量研究 [J]. 表面技术,2022,51(10):293-300. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2022.10.031FANG Yuxin, WANG Youqiang, ZHANG Ping, et al. High-speed cutting removal mechanism and surface quality of SiCp/Al composites [J]. Surface Technology,2022,51(10):293-300. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2022.10.031 [5] ZHU C, GU P, WU Y, et al. Surface roughness prediction model of SiCp/Al composite in grinding [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,155:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.02.025 [6] LAGHARI R A, JAMIL M, LAGHARI A A, et al. A critical review on tool wear mechanism and surface integrity aspects of SiCp/Al MMCs during turning: Prospects and challenges [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2023,126(7/8):2825-2862. doi: 10.1007/s00170-023-11178-7 [7] SHEN H, BROUSSEAU E, KULASEGARAM S. Assessment and validation of SPH modeling for nano-indentation [J]. Computational Particle Mechanics,2023,10(3):603-6132. doi: 10.1007/s40571-022-00514-5 [8] YUAN Z, SHEN Q, LIU H, et al. Damage behavior and mechanism of SiCp/Al composites under biaxial tension [J]. Materials Characterization,2021,180:111402. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111402 [9] AKINWAMIDE S O, AKINRIBIDE O J, OLUBAMBI P A. Microstructural evolution, mechanical and nanoindentation studies of stir cast binary and ternary aluminium based composites [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,850:156586. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156586 [10] ZHANG Z, YAO P, WANG J, et al. Analytical modeling of surface roughness in precision grinding of particle reinforced metal matrix composites considering nanomechanical response of material [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,157:243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.04.047 [11] LIU Y, WANG Q, LU C, et al. Microscopic residual stress evolution at the SiC/Al interface during nanoindentation via molecular dynamics simulation [J]. Surfaces and Interfaces,2022:102210. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102210 [12] KONG X, WANG B, WANG M, et al. Microscratch characteristic and deformation mechanism of SiC particle-reinforced composites at elevated temperatures [J]. Advanced Composites Letters,2020,29:1-11. doi: 10.1177/2633366X19898694 [13] SUN X, YAO P, QU S, et al. Material properties and machining characteristics under high strain rate in ultra-precision and ultra-high-speed machining process: A review [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,120(11/12):7011-7042. doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09111-5 [14] 卢守相, 杨秀轩, 张建秋, 等. 关于硬脆材料去除机理与加工损伤的理性思考 [J]. 机械工程学报,2022,58(15):31-45. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.15.031LU Shouxiang, YANG Xiuxuan, ZHANG Jianqiu, et al. Rational discussion on material removal mechanisms and machining damage of hard and brittle materials [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2022,58(15):31-45. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.15.031 [15] ZHANG Y, WU T, LI C, et al. Numerical simulations of grinding force and surface morphology during precision grinding of leucite glass ceramics [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2022,231:107562. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107562 [16] LI C, ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Nanoindentation and nanoscratch tests of YAG single crystals: An investigation into mechanical properties, surface formation characteristic, and theoretical model of edge-breaking size [J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(3):3382-3393. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.048 [17] FU J, KAMALI-BERNARD S, BERNARD F, et al. Comparison of mechanical properties of CSH and portlandite between nano-indentation experiments and a modeling approach using various simulation techniques [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,151:127-138. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.05.043 [18] LUU H T, DANG S L, HOANG T V, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoindentation in Al and Fe: On the influence of system characteristics [J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,551:149221. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149221 [19] SONG H, YAVAS H, VAN D G E, et al. Discrete dislocation dynamics simulations of nanoindentation with pre-stress: Hardness and statistics of abrupt plastic events [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,2019,123:332-347. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2018.09.005 [20] ZHANG Z, NI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Multiscale simulation of surface defects influence nanoindentation by a quasi-continuum method [J]. Crystals,2018,8(7):291. doi: 10.3390/cryst8070291 [21] XIAO X, LI S, YU L. Effect of irradiation damage and indenter radius on pop-in and indentation stress-strain relations: Crystal plasticity finite element simulation [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2021,199:106430. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106430 [22] LICHINCHI M, LENARDI C, HAUPT J, et al. Simulation of Berkovich nanoindentation experiments on thin films using finite element method [J]. Thin Solid Films,1998,312(1/2):240-248. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(97)00739-6 [23] LI H, CHEN J, CHEN Q, et al. Determining the constitutive behavior of nonlinear visco-elastic-plastic PMMA thin films using nanoindentation and finite element simulation [J]. Materials & Design,2021,197:109239. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109239 [24] 李洪钢. LED封装基板超精密磨削表面材料去除机理[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021.LI Honggang. Research on material removal mechanism in ultra-precision grinding of LED package substrate[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2021. [25] GU P, ZHU C, TAO Z, et al. Micro-removal mechanism of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composite in grinding based on cohesive theory [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2021,117:243-265. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07578-2 [26] 刘亚龙. 材料微纳米尺度压痕硬度检测的仿真研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010.LIU Yalong. Research on material micro-nano indentation hardness measurement simulation [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. [27] OLIVER W C, PHARR G M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments [J]. Journal of Materials Research,1992,7(6):1564-1583. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1992.1564 [28] 张杰. 基于纳米压痕法AZ31BMg/6061Al复合材料连接界面行为研究 [D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021.ZHANG Jie. Study on interface behavior of AZ31BMg/6061Al composite based on nanoindentation method[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. [29] GUO X, GUO Q, NIE J, et al. Particle size effect on the interfacial properties of SiC particle-reinforced Al-Cu-Mg composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2018,711:643-649. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.068 [30] WANG Y, LIAO W, YANG K, et al. Simulation and experimental investigation on the cutting mechanism and surface generation in machining SiCp/Al MMCs [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,100:1393-1404. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2769-0 [31] 魏斌. 加热辅助切削SiCp/Al复合材料的切削力和表面质量研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020.WEI Bin. Research on cutting force and surface quality of heating-assisted cutting SiCp/Al composite[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020. [32] ZHANG H, RAMESH K T, CHIN E S C. Effects of interfacial debonding on the rate-dependent response of metal matrix composites [J]. Acta Materialia,2005,53(17):4687-4700. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.07.004 [33] 田达, 傅宏俊, 吴利伟, 等. 增韧复合材料的GI断裂韧性有限元模拟 [J]. 复合材料科学与工程,2018,(1):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2018.01.003TIAN Da, FU Hongjun, WU Liwei, et al. Finite element simulation of GI fracture toughness of toughened composites [J]. Composites Science and Engineering,2018,(1):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2018.01.003 [34] 郑伟. SiCp/Al复合材料超声振动磨削材料去除及表面质量研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.ZHENG Wei. Research on material removal and surface finish in ultrasonic vibration grinding of SiCp/Al composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. -




 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
