Diamond particle clarity detection method based on CBAM-ResNet50
-
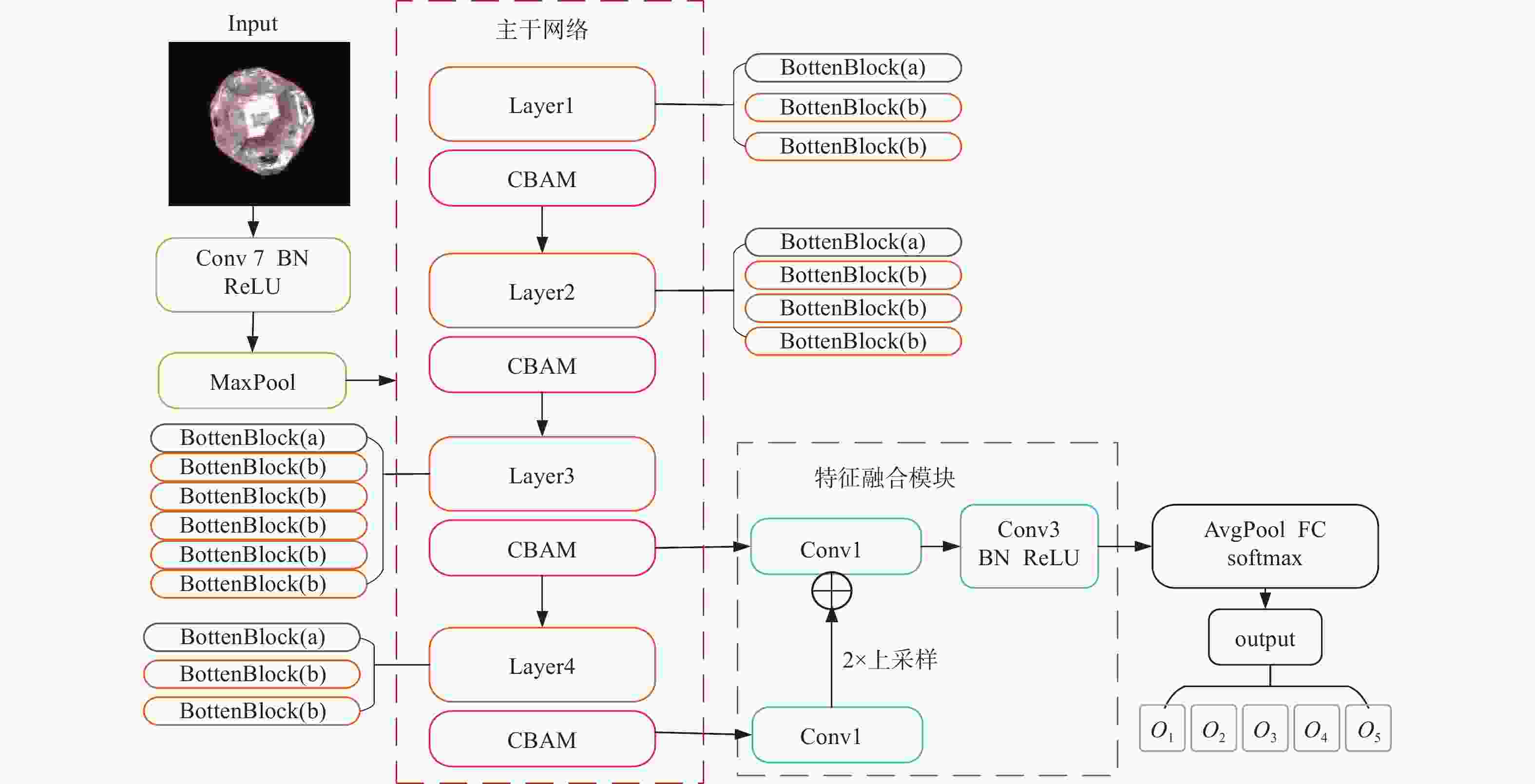
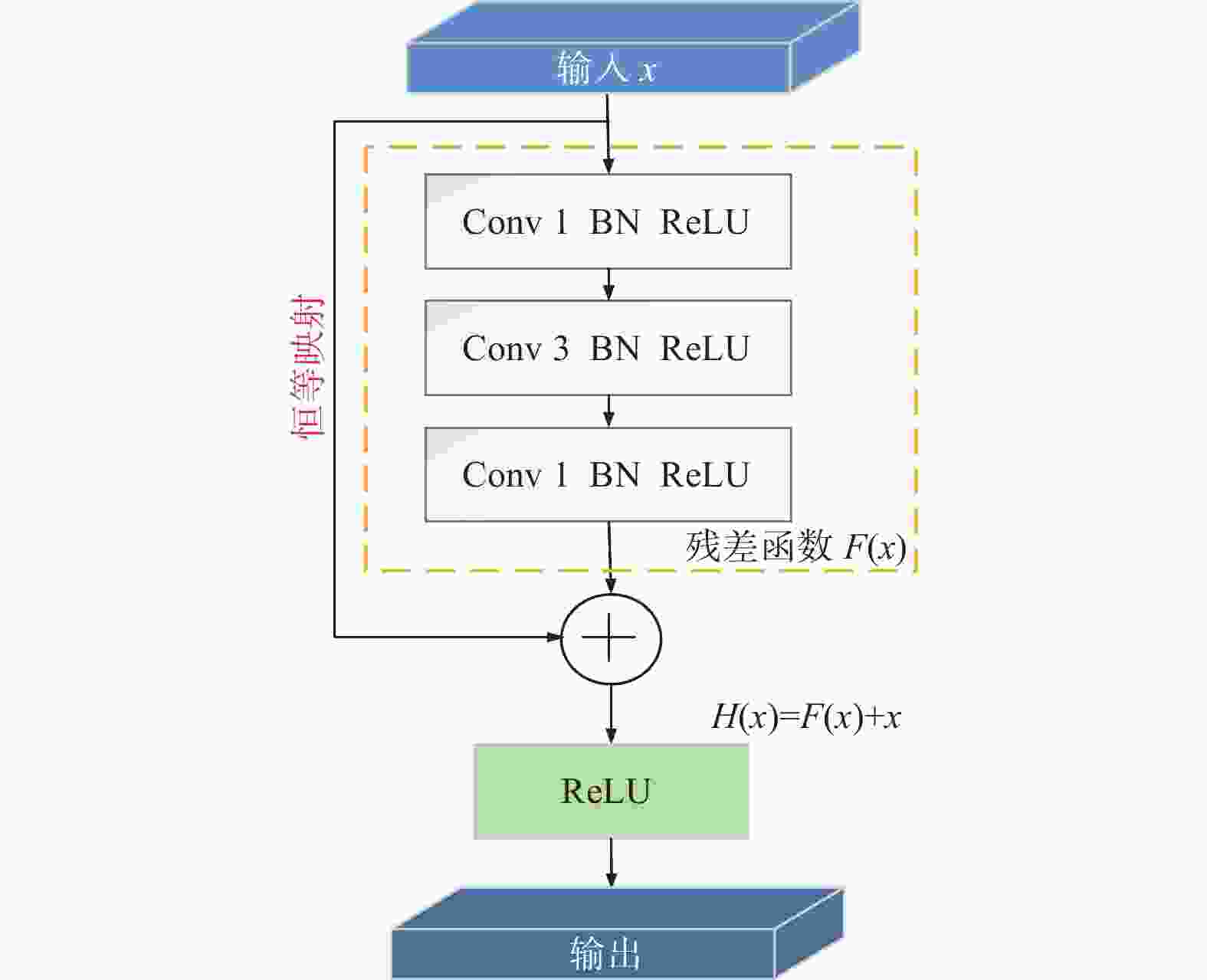
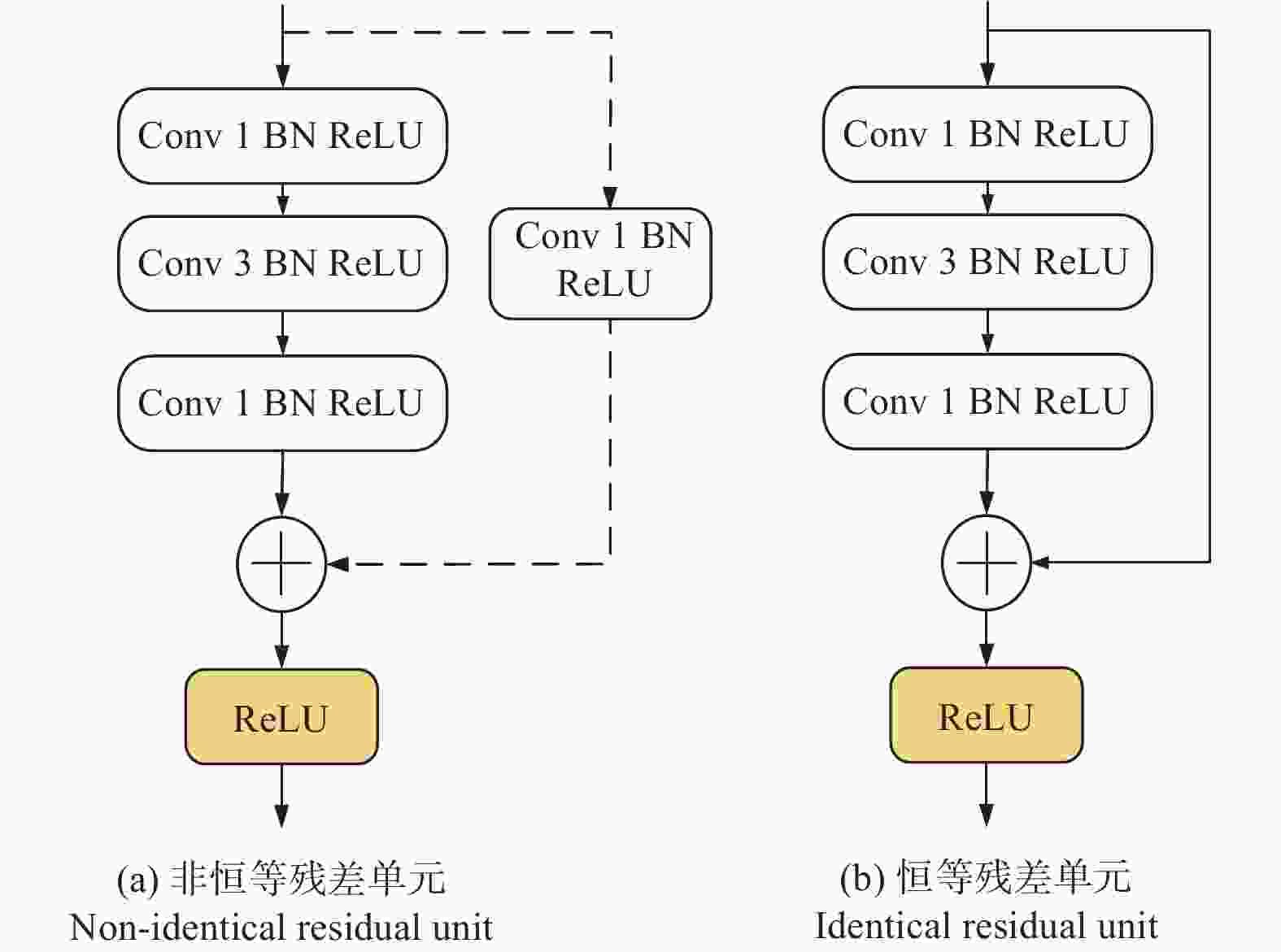
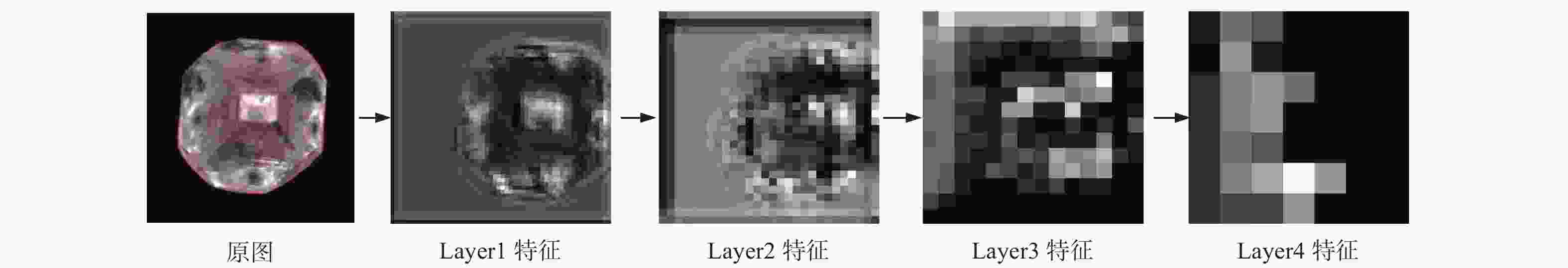
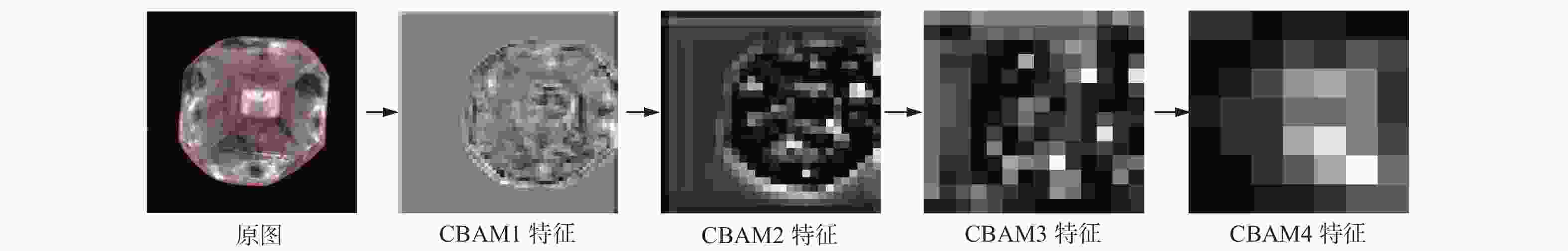
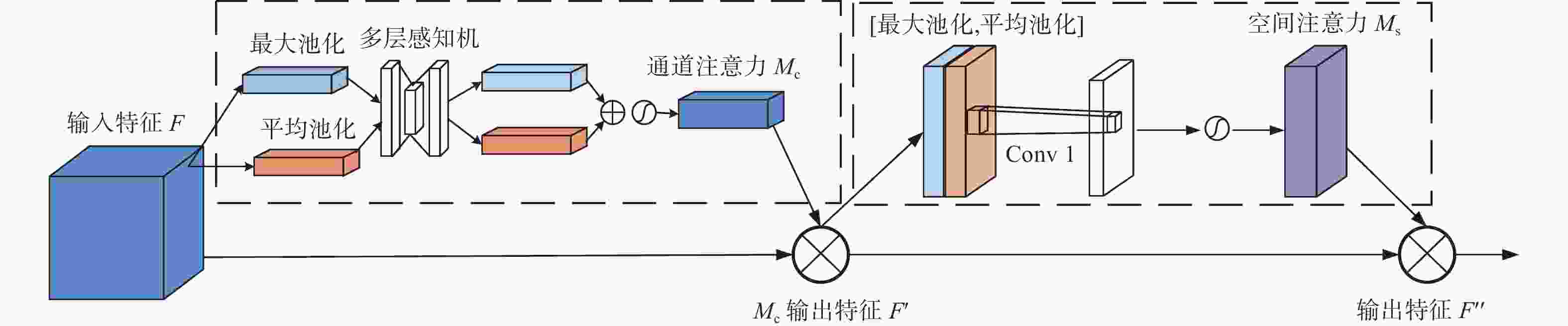
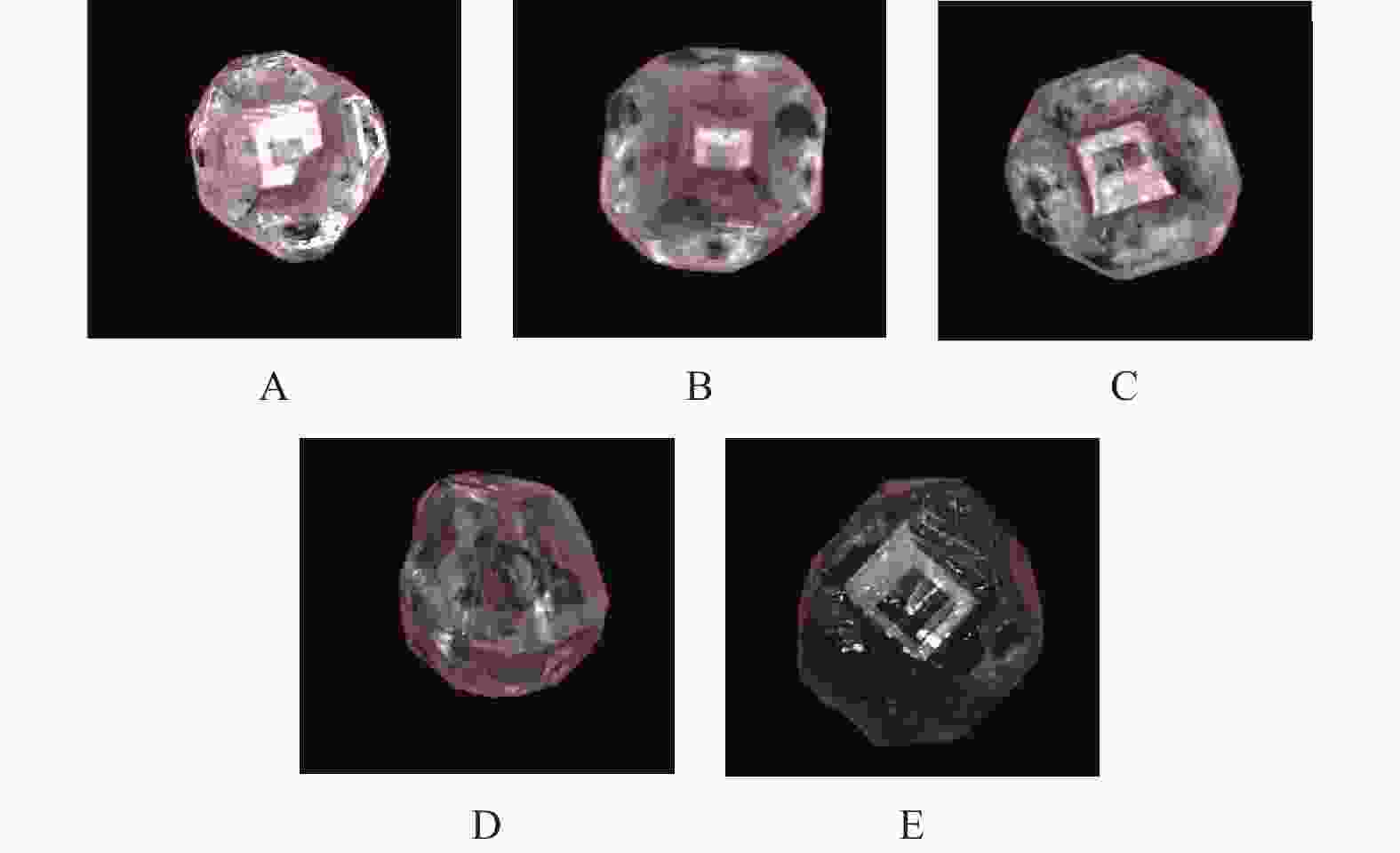
摘要: 针对金刚石颗粒净度传统检测方法效率低、准确率差的问题,提出了一种基于迁移学习和改进ResNet50的金刚石颗粒净度检测算法CBAM-ResNet50。该算法通过在ResNet50主干网络的每层中增加CBAM,以提升模型特征的提取能力;且在主干网络的Layer3和Layer4中融入FPN结构,对提取的特征进行部分特征聚合,来解决采样过程中小目标特征易丢失的问题;同时引入迁移学习方法,用交叉熵损失函数优化模型的初始参数,提升模型的泛化能力。结果表明:在学习率设置为0.000 1时,提出的CBAM-ResNet50模型训练准确率达到99.2%;根据混淆矩阵计算得到模型的精确度在99.20%以上,特异性在99.70以上%,F1分数在99.20%,分类召回率在98.70%以上,优于其他主流分类网络的结果,有效提高了金刚石颗粒净度检测的识别能力。Abstract: Objectives: With the improvement of production technology, the traditional diamond particle cleanliness detection method can no longer meet the requirements of high precision, high quality and high automation in the diamond industry due to its low efficiency and poor accuracy. The rapid development of computer technology, optical, and electronic technologies has led to the widespread application of visual inspection and deep learning in image classification and detection, providing new methods for diamond clarity detection. Therefore, based on transfer learning and combined with the convolutional block attention module (CBAM) attention mechanism and the feature pyramid network (FPN) structure, an improved ResNet50 diamond particle clarity detection algorithm, CBAM-ResNet50, is proposed. Methods: The CBAM-RESnet50 clarity detection algorithm uses ResNet50 as the backbone network and adds CBAM to each layer of the backbone network to improve the feature extraction ability of the model. In addition, the FPN structure is integrated into Layer 3 and Layer 4 of the backbone network, where part of the extracted features are aggregated to address the issues of losing features of small and medium-sized targets during the sampling process. At the same time, the transfer learning method is introduced to optimize the model's initial parameters with a cross-entropy loss function, thereby improving the generalization ability and robustness of the model. Moreover, multi-angle diamond images are collected on a diamond clarity detection device, a diamond particle clarity dataset is established, and the improved CBAM-ResNet50 network model is experimentally compared and verified using the data set. Results: Firstly, when compared with other classic mainstream network models, the accuracy of the CBAM-ResNet50 model during training is 99.2%, and the precision is 99.7%, ourperforming the classification results of other network models and significantly improving the identification ability for diamond particle clarity detection. The average detection time of the CBAM-ResNet50 model is 0.01629s, which meets the real-time requirements for industrial detection. Secondly, the CBAM-ResNet50 model is evaluated and ablated on diamond particles of various grades. The results show that the CBAM-ResNet50 model achieves an accuracy of over 99.2%, a classification recall rate of over 98.7%, specificity of over 99.7%, and an F1 score of over 99.2% for classifying diamonds of different grades. The ablation experiment results show that adding the CBAM attention mechanism and FPN feature fusion module significantly improves the classification performance of different grades of diamond particles. The ResNet50+CBAM model achieves a classification accuracy and recall rate of 100.0% for A and E grade diamonds, indicating that the CBAM module helps focus the network's attention on the black impurity features inside the diamond particles, reduces attention to irrelevant information, and improves classification accuracy. The CBAM-ResNet50, with the addition of the FPN feature fusion module, further enhances the classification accuracy and recall rate for B, C, and D grade diamonds. This improvement suggests that the FPN fuses both high-level and low-level feature information, enriching the small target features in the feature map, and enhances classification performance for B, C, and D grade diamonds with similar characteristics. Conclusions: Deep learning technology has been applied to the cleanliness detection of diamond particles, with the ResNet50 network, known for its strong feature extraction ability, serving as the backbone model. Based on the cleanliness features in diamond particle images, the CBAM attention mechanism, the FPN feature fusion module, transfer learning, and the entropy loss function are respectively integrated to address the challenges of insufficient feature extraction, the loss of small target features, and limited generalization in network models. By comparing experiments with other mainstream networks and conducting network ablation experiments, the impact of various improvements on the performance of the diamond particle cleanliness classification network is studied, confirming the effectiveness of the improved network model.
-
表 1 不同模型训练结果
Table 1. Training results of different models
模型 验证准
确率
A1 / %训练准
确率
A2 / %平均训
练时间
t1 / s平均检
测时间
t2 / sVGG16 87.8 95.8 33.456 0.02435 AlexNet 87.6 92.5 20.931 0.00826 ResNet50 98.6 98.8 23.839 0.01588 CBAM-ResNet50 98.7 99.2 24.143 0.01629 表 2 金刚石颗粒测试集混淆矩阵
Table 2. Confusion matrix of diamond particle test set
预测类别 A B C D E 真实标签 A 400 0 0 0 0 B 0 766 1 3 0 C 0 2 622 6 0 D 0 2 0 1148 0 E 0 0 0 0 50 表 3 CBAM-ResNet50模型金刚石颗粒分类结果
Table 3. CBAM-ResNet50 model diamond particle classification results
金刚石
等级精确度
P / %召回率
R / %特异性
S / %F1 / % A 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 B 99.50 99.50 99.80 99.50 C 99.80 98.70 99.70 99.20 D 99.20 99.80 99.90 99.50 E 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 表 4 不同模型的金刚石颗粒分类结果
Table 4. Classification results of diamond particles of different models
金刚石等级 模型 精确度
P / %召回率
R / %特异性
S / %F1 / % A ResNet50 96.15 100.00 100.00 98.04 ResNet50 + FPN 99.01 100.00 100.00 99.50 ResNet50 + CBAM 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 CBAM-ResNet50 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 B ResNet50 97.92 94.00 98.51 95.92 ResNet50 + FPN 98.00 98.00 99.50 98.00 ResNet50 + CBAM 98.99 98.00 99.50 98.49 CBAM-ResNet50 99.50 99.50 99.80 99.50 C ResNet50 98.98 97.00 99.25 97.98 ResNet50 + FPN 99.49 98.50 99.62 98.99 ResNet50 + CBAM 99.49 98.50 99.62 98.99 CBAM-ResNet50 99.80 98.70 99.70 99.20 D ResNet50 96.04 97.00 99.25 96.52 ResNet50 + FPN 97.24 97.50 99.25 97.38 ResNet50 + CBAM 98.01 98.50 99.62 98.25 CBAM-ResNet50 99.20 99.80 99.90 99.50 E ResNet50 99.01 100.00 100.00 99.50 ResNet50 + FPN 99.01 100.00 100.00 99.50 ResNet50 + CBAM 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 CBAM-ResNet50 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 -
[1] 周青超, 沈锡田. 从专利角度分析人造金刚石技术的发展 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2021,33(5):29-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2021.05.007ZHOU Qingchao, SHEN Xitian. Analysis of the development of synthetic diamond technology from the perspective of patents [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2021,33(5):29-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2021.05.007 [2] 熊辉. 基于模板匹配的金刚石颗粒图像识别 [D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2005.XIONG Hui. The image recognition of the diamond particles based on the template matching [D]. Chengdou: Sichuan University, 2005. [3] 郭树青. 金刚石颗粒形貌检测系统关键技术研究 [D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2016.GUO Shuqing. Research on the key technology of diamond particle morphology detection system [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2005. [4] WANG W, CAI L. Inclusion extraction from diamond clarity images based on the analysis of diamond optical properties [J]. Optics Express,2019,27(19):27242. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.027242 [5] WANG W, CAI L. On the development of an effective image acquisition system for diamond quality grading [J]. Applied Optics,2018,57(33):9887-9897. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.009887 [6] 石广丰, 王雪, 王淑坤, 等. 基于机器视觉的金刚石原石检测系统 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2019,39(6):7-12. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2019.6.0002SHI Guangfeng, WANG Xue, WANG Shukun, et al. Diamond raw detection system based on machine vision [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2019,39(6):7-12. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2019.6.0002 [7] 狄超雄. 钻石净度检测系统研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021.DI Chaoxiong. Research on diamond clarity detection system [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2021. [8] 季长清, 高志勇, 秦静, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的图像分类算法综述 [J]. 计算机应用,2022,42(4):1044-1049. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021071273JI Changqing, GAO Zhiyong, QIN Jing, et al. Review of image classification algorithms based on convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Computer Applications,2022,42(4):1044-1049. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021071273 [9] 邢延动, 李远. BP神经网络在金刚石锯片磨粒识别中的应用 [J]. 超硬材料过程,2014(1):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2014.01.001XING Yandong, LI Yuan. Application of BP neural network in diamond saw blade abrasive particle recognition [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2014(1):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2014.01.001 [10] 潘秉锁, 潘文超, 刘子玉. 基于空洞卷积神经网络的金刚石图像语义分割 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2019,39(6):20-24. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2019.6.0004PAN Bingsuo, PAN Wenchao, LIU Ziyu. Semantic segmentation of diamond image using dilated convolutional neural network [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2019,39(6):20-24. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2019.6.0004 [11] 林振坤. 基于深度学习的金刚石品质检测技术与实现 [D]. 郑州: 郑州航空工业管理学院, 2020.LIN Zhenkun. Diamond quality detection technology and implementation based on deep learning [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Aeronautics, 2020. [12] 杨建新, 兰小平, 赵振, 等. 基于改进郊狼算法与极限学习机的工业金刚石检测 [J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2023,29(2):449-459. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2023.02.008YANG Jianxin, LAN Xiaoping, ZHAO Zhen, et al. Industrial diamond detection method based on improved coyote optimization algorithm and extreme learning machine [J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems,2023,29(2):449-459. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2023.02.008 [13] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M, et al. MobileNetV2: Iinverted residuals and linear bottlenecks: 2018 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) [C]. Salt Lake: IEEE, 2018. [14] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) [C]. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016. [15] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module: European conference on computer vision (ECCV) [C]. Munich: CVPR, 2018. [16] LIN T, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) [C]. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017. [17] 沈微微, 李颖, 杨志豪, 等. 防止过拟合的属性约简 [J]. 计算机应用研究,2020,37(9):2665-2668. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.05.0116SHEN Weiwei, LI Ying, YANG Zhihao, et al. Attribute reduction with avoiding overfitting [J]. Application Research of Computers,2020,37(9):2665-2668. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.05.0116 [18] 邓建国, 张素兰, 张继福, 等. 监督学习中的损失函数及应用研究 [J]. 大数据,2020,6(1):60-80. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020006DENG Jianguo, ZHANG Sulan, ZHANG Jifu, et al. Loss function and application research in supervised learning [J]. Big Data Research,2020,6(1):60-80. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020006 [19] PAN S, YANG Q. A survey on transfer learning [J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering,2010,22(10):1345-1359. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [20] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition: 3rd international conference on learning representations (ICLR 2015) [C]. San Diego: arXiv, 2015. [21] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks: 25th international conference on neural Information processing systems (NeurIPS 2012) [C]. New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2012. -




 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
