Effect of boron concentration and gas pressure on the electrochemical oxidation performance changes of HFCVD diamond films on Ti substrates
-
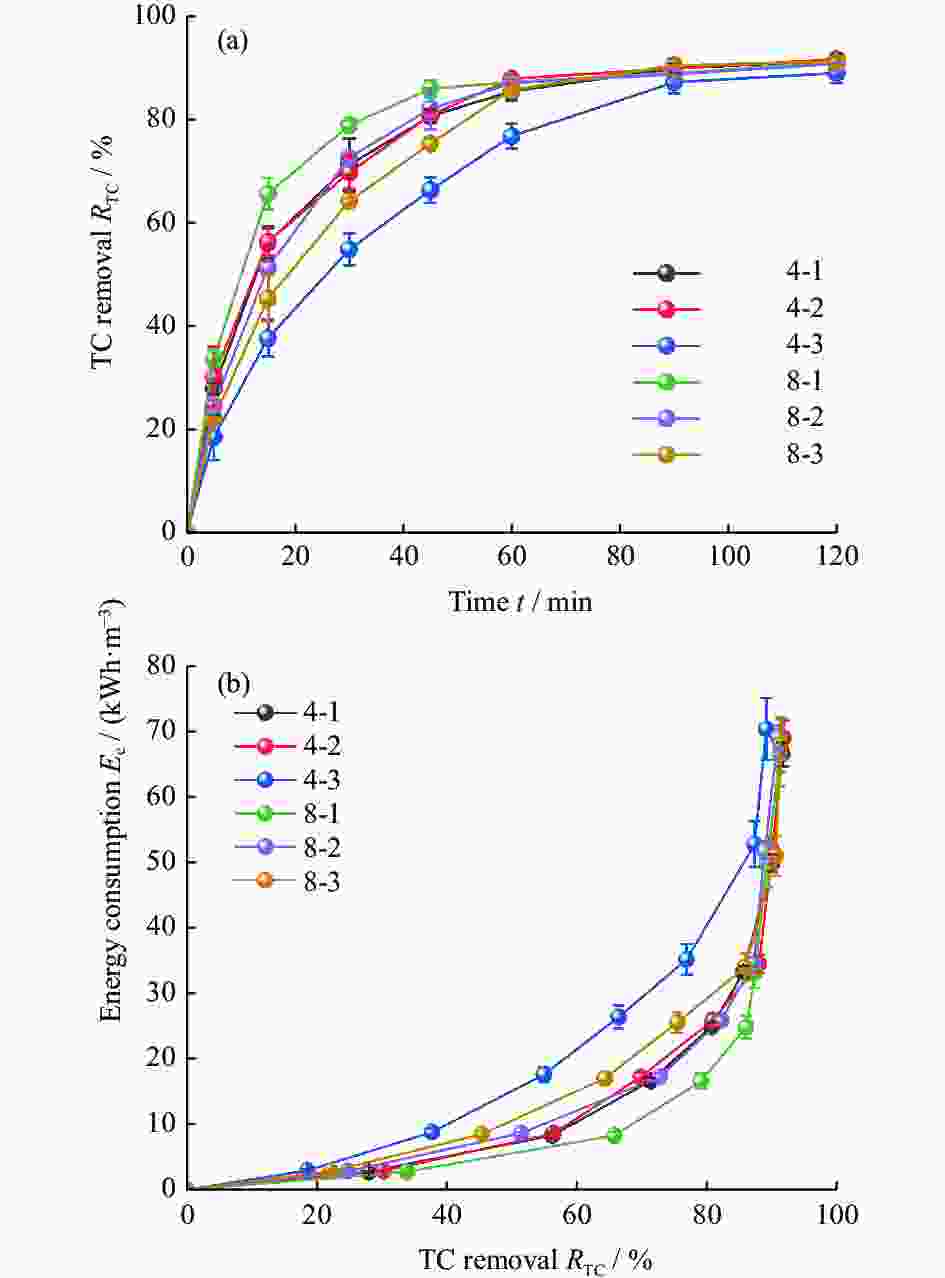
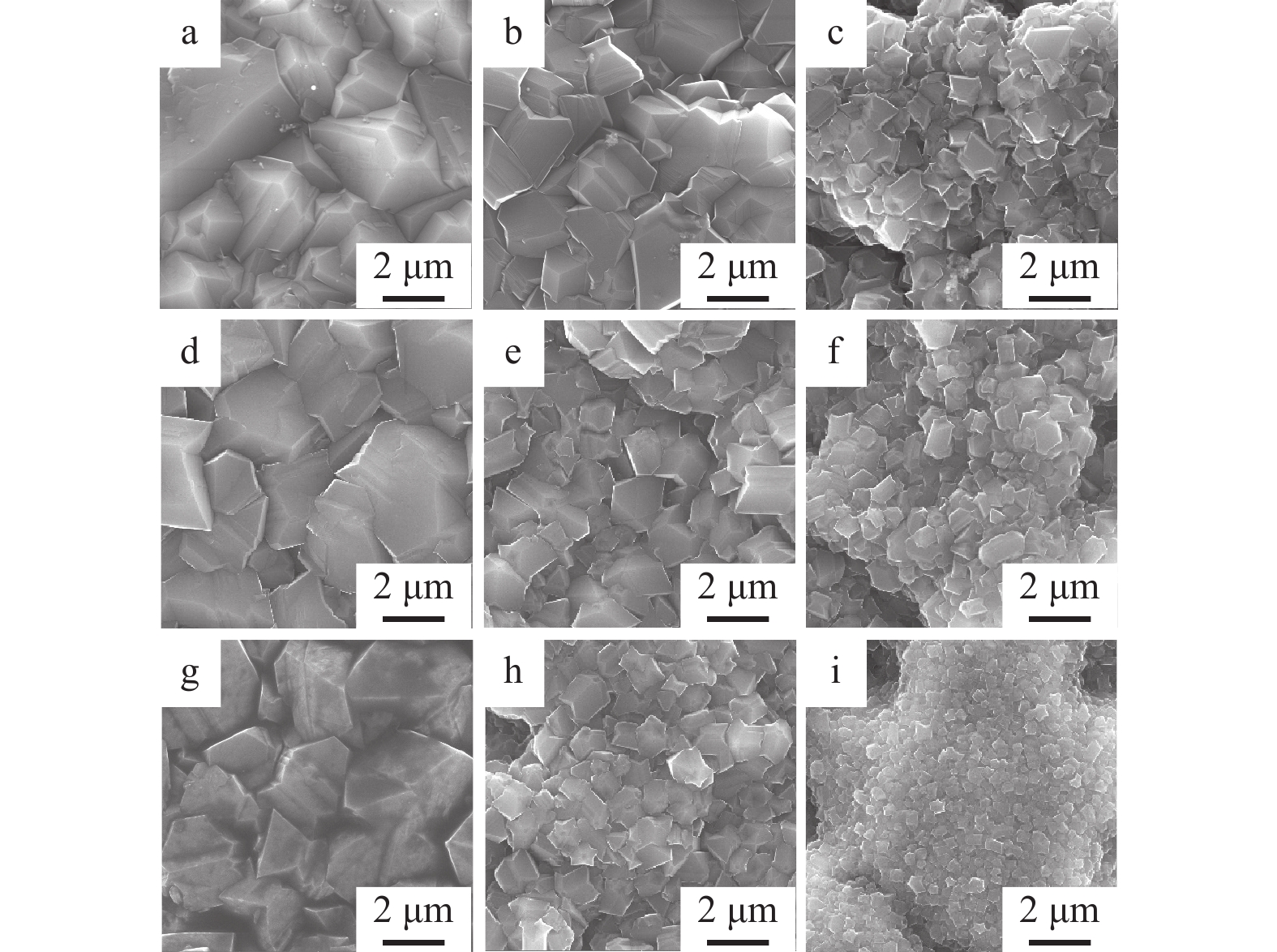
摘要: 探究在热丝化学气相沉积生长硼掺杂金刚石的过程中,掺硼浓度与沉积气压对钛基硼掺杂金刚石薄膜的微观结构与电化学氧化性能的影响,并以四环素作为模拟污染物进行电化学氧化降解实验。使用扫描电子显微镜、拉曼光谱、紫外分光光度计以及电化学工作站对电极表面形貌、成分以及电化学性能进行表征。结果表明:随着掺硼浓度与沉积气压的增大,金刚石薄膜表面晶粒明显细化,生长速率下降;然而随着沉积气压的升高,金刚石的晶粒质量逐渐降低,但硼原子掺杂则会提高金刚石晶粒质量;在高掺硼浓度和低沉积气压的条件下,金刚石薄膜表面的硼原子浓度更高;高掺硼浓度和低沉积气压下所生成的较大晶粒尺寸和更高硼原子浓度的硼掺杂金刚石电极具有更优越的电化学性能、更高的降解效率以及更低的降解能耗。
-
关键词:
- 钛基硼掺杂金刚石薄膜电极 /
- 电化学氧化 /
- 掺硼浓度 /
- 沉积气压 /
- 四环素
Abstract: The effects of boron concentration and deposition pressure on the microstructure and electrochemical oxidation performance of Ti/BDD electrodes during HFCVD growth were systematically investigated. The electrode's surface morphology, composition, and electrochemical performance were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, ultraviolet spectrophotometry, and an electrochemical workstation. Tetracycline served as a simulated pollutant to evaluate the electrochemical oxidation degradation performance of BDD electrodes fabricated with different boron concentrations and deposition pressures. As air pressure increases, the grain quality of the diamond gradually decreases, yet boron atom doping enhances the grain quality of the diamond. Under high boron concentration and low pressure conditions, the boron atom concentration on the diamond film's surface is elevated. BDD electrodes with larger grain sizes and higher boron atom concentrations, prepared under these conditions, exhibit superior electrochemical performance, increased degradation efficiency, and reduced degradation energy consumption. -
表 1 硼烷流量和沉积气压
Table 1. Boron flow rate and gas pressure
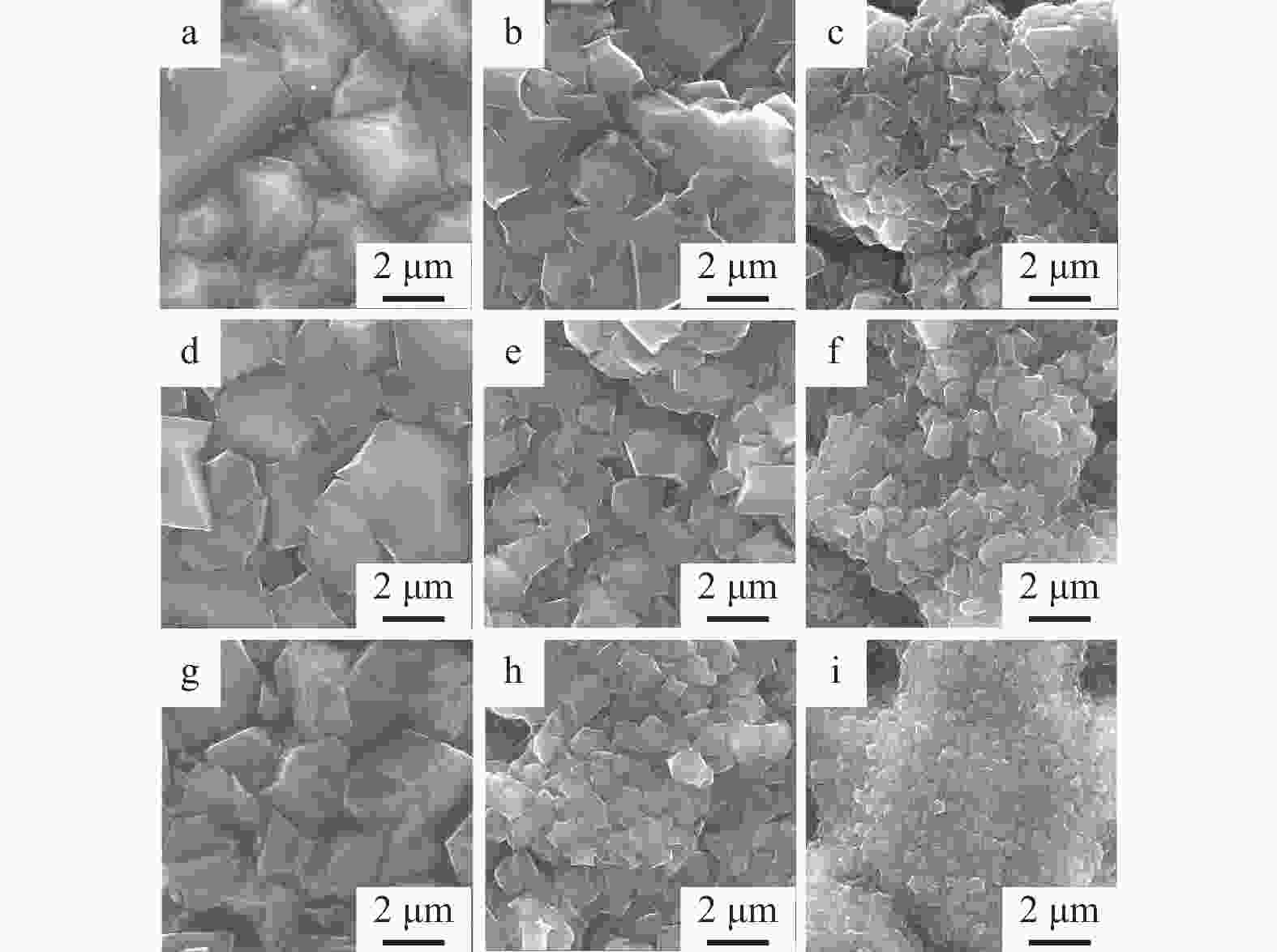
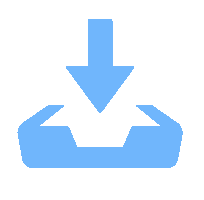
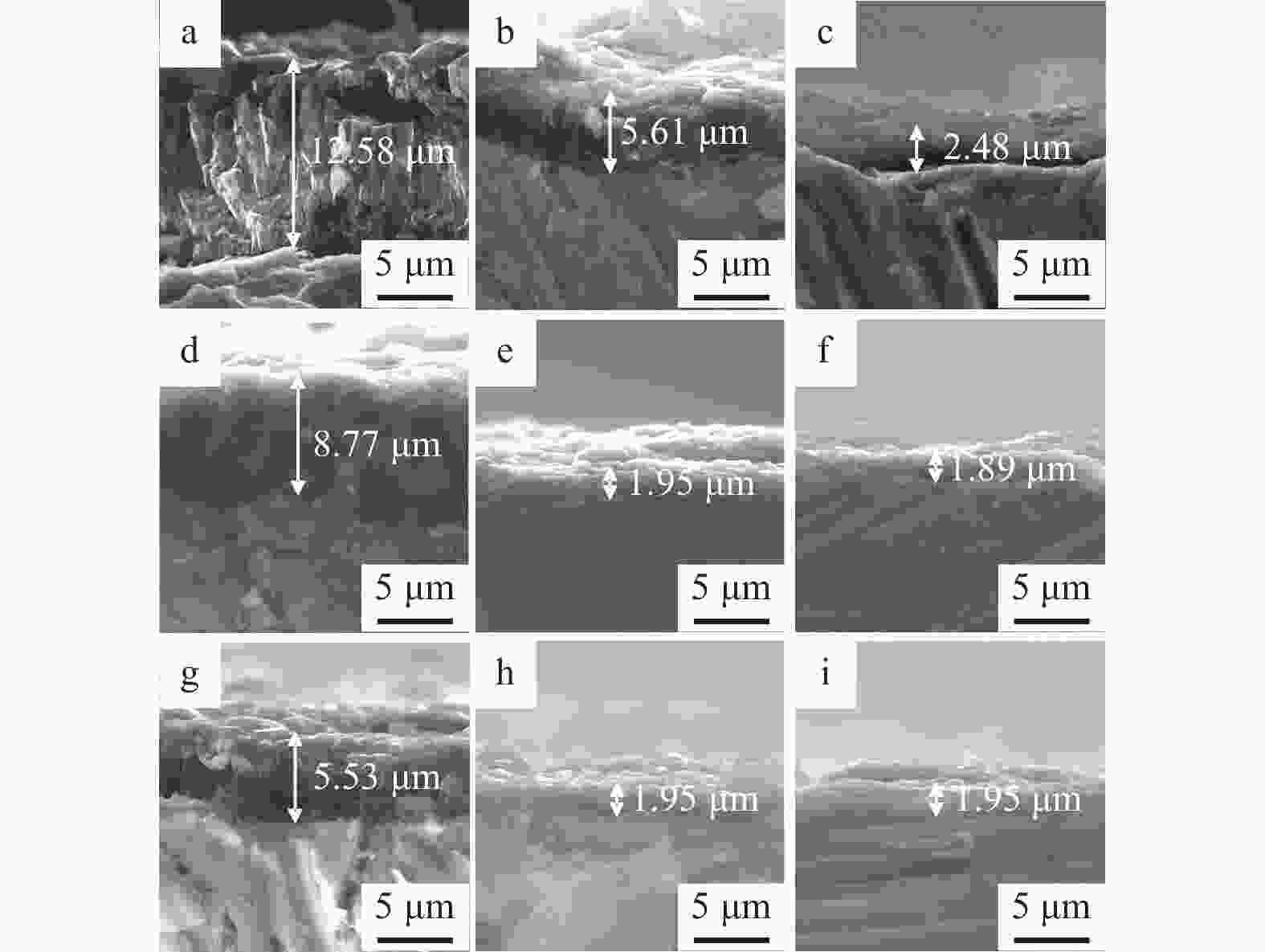
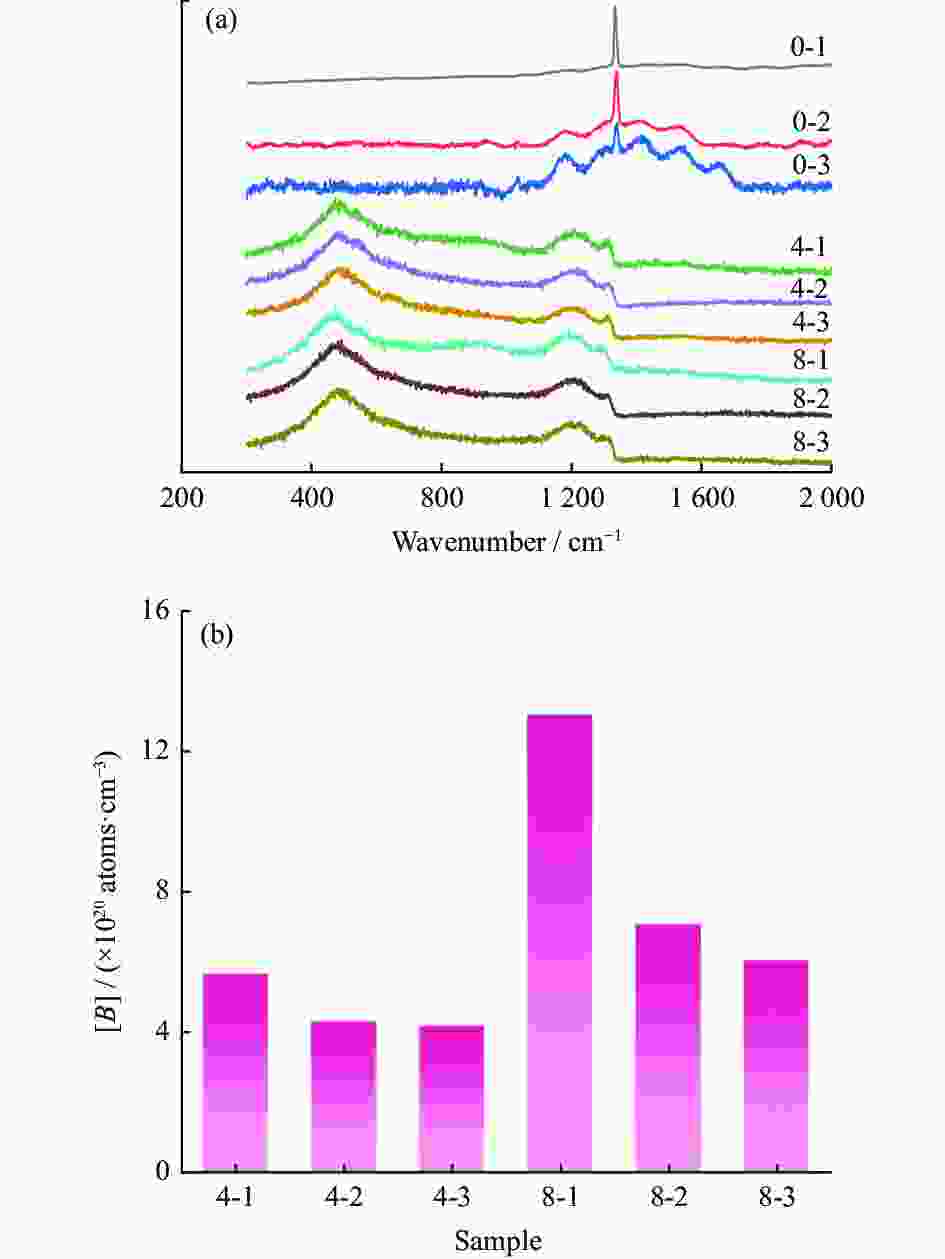
样品编号 硼烷流量 QB / sccm 沉积气压 p / kPa 0-1 0 1 0-2 0 2 0-3 0 3 4-1 0.4 1 4-2 0.4 2 4-3 0.4 3 8-1 0.8 1 8-2 0.8 2 8-3 0.8 3 表 2 HFCVD生长金刚石薄膜的沉积参数
Table 2. Synthesis parameters of various diamond films by HFCVD method
沉积参数 数值 热丝功率 P / W 560 基底温度 θ / ℃ 800±10 甲烷流量 QC / sccm 2 氢气流量 QH / sccm 98 丝底距 d / mm 14 沉积时间 t / h 5 表 3 不同BDD电极的析氧电位与电势窗口参数
Table 3. Oxygen evolution potentials and potential windows of various BDD films
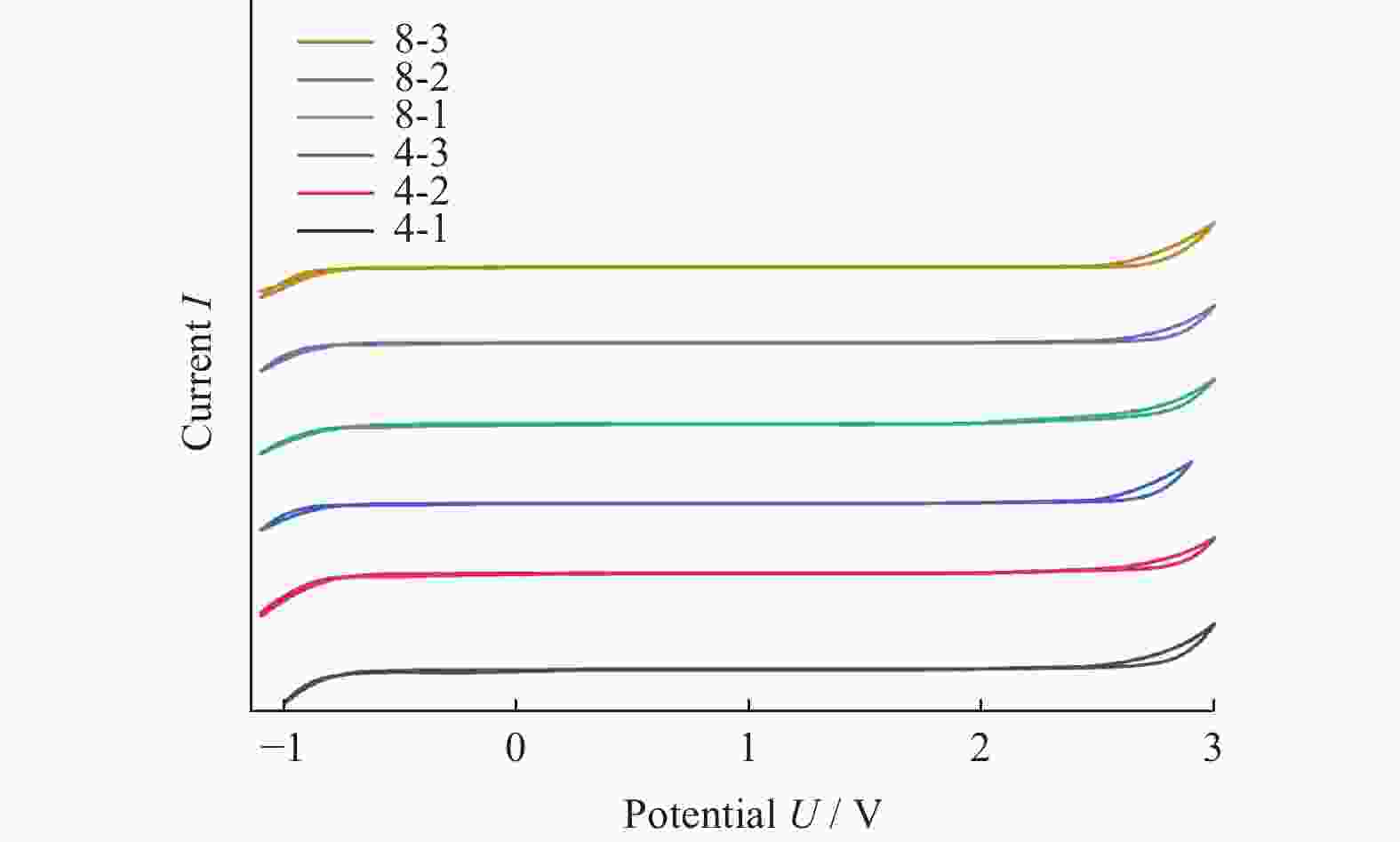
电极 析氧电位 u / V 电势窗口 U / V 4-1 2.69 3.40 4-2 2.70 3.48 4-3 2.59 3.42 8-1 2.72 3.55 8-2 2.69 3.53 8-3 2.68 3.53 表 4 不同BDD电极的Cdl参数
Table 4. Cdl parameters of various BDD electrodes
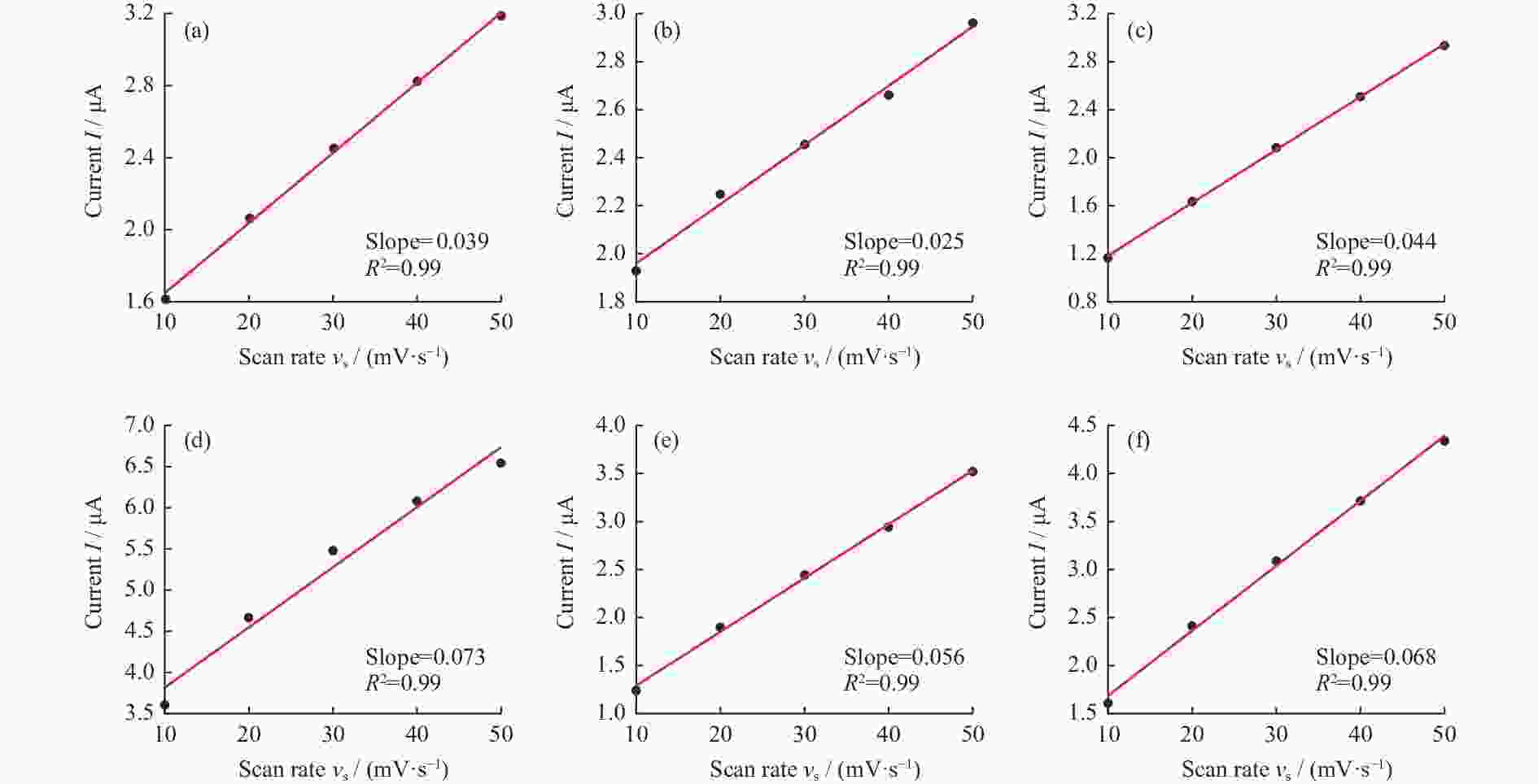
电极 Cdl / μF 4-1 0.039 4-2 0.025 4-3 0.044 8-1 0.073 8-2 0.056 8-3 0.068 表 5 不同BDD电极的EIS值
Table 5. EIS parameters of various BDD electrodes
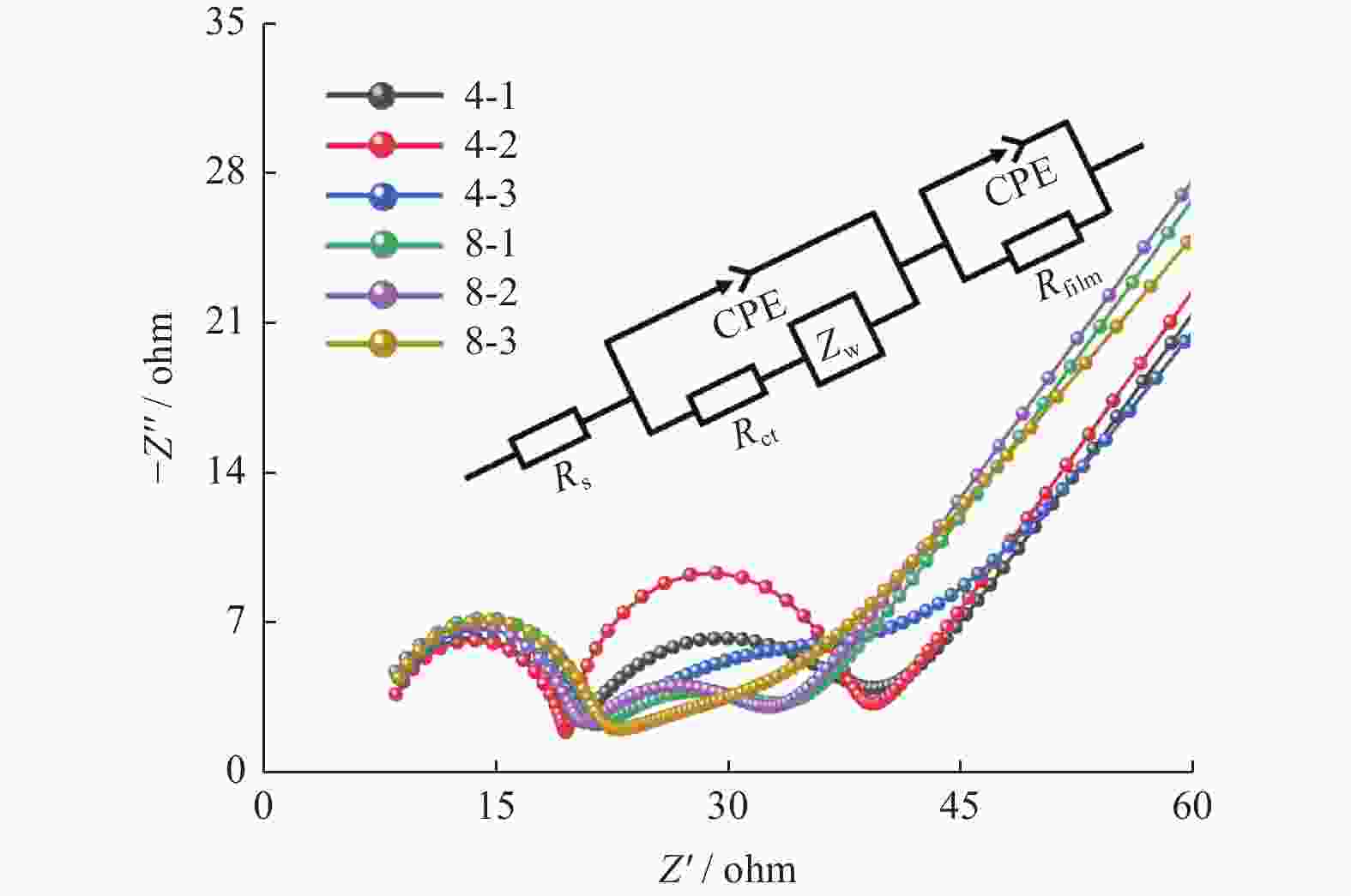
电极 Rct / Ω Rs / Ω Rfilm / Ω Zw / Ω 4-1 19.9 7.2 12.0 0.02 4-2 18.0 7.4 12.2 0.02 4-3 25.0 7.1 12.6 0.02 8-1 13.3 7.0 13.7 0.02 8-2 13.2 6.6 13.1 0.02 8-3 21.5 6.6 13.0 0.02 -
[1] 束蒋成. 改性钛基二氧化铅电极电化学降解水中四环素的研究 [D]. 常州: 常州大学, 2022.SHU Jiangcheng. Electrochemical degradation of tetracycline in water by modified titanium based lead dioxide electrode [D]. Changzhou: Changzhou University, 2022. [2] NIDHEESH P V, DIVYAPRIYA G, OTURAN N, et al. Environmental applications of boron-doped diamond electrodes: 1. Applications in water and wastewater treatment [J]. Chemelectrochem,2019,6:2124-2142. doi: 10.1002/celc.201801876 [3] MACPHERSON J V. A practical guide to using boron doped diamond in electrochemical research [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2015,17(5):2935-2949. doi: 10.1039/C4CP04022H [4] HUTTON L A, IACOBINI J G, BITZIOU E, et al. Examination of the factors affecting the electrochemical performance of oxygen-terminated polycrystalline boron-doped diamond electrodes [J]. Analytical Chemistry,2013,85(15):7230-7240. doi: 10.1021/ac401042t [5] 胡靖源, 马莉, 朱成武, 等. 微观结构与降解温度对掺硼金刚石薄膜电极电氧化降解活性橙X-GN染料废水的影响 [J]. 表面技术,2018,47(11):17-25.HU Jingyuan, MA Li, ZHU Chengwu, et al. Effects of microstructure and degradation temperature on electrochemical oxidation degradation of reactive orange X-GN dye wastewater by boron doped diamond [J]. Surface technology,2018,47(11):17-25. [6] MARTÍNEZ-HUITLE C A, RODRIGO M A, SIR´ES I, et al. A critical review on latest innovations and future challenges of electrochemical technology for the abatement of organics in water [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2023,328:122430. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122430 [7] GERGER I, HAUBNER R. The behaviour of Ti-substrates during deposition of boron doped diamond [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials,2008,26(5):438-443. [8] PENG J H, XIONG C, LIAO J C, et al. Study on the effect of ar-containing work gas on the microstructure and tribological behavior of nanocrystalline diamond coatings [J]. Tribology International,2021,153:106667. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106667 [9] WANG H, WANG C C, WANG X C, et al. Effects of carbon concentration and gas pressure with hydrogen-rich gas chemistry on synthesis and characterizations of HFCVD diamond films on WC-Co substrates [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2021,409:126839. [10] WEI Q P, ASHFOLD M N R, MANKELEVICH Y A, et al. Diamond growth on WC-Co substrates by hot filament chemical vapor deposition: Effect of filament–substrate separation [J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2011,20:641-650. [11] LIN Q, CHEN S L, JI Z, et al. A novel growth model for depositing ultrananocrystalline diamond films in CH4/H2 chemistry [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2021,419:127280. [12] WANG L, SHEN B, SUN F H, et al. Effect of pressure on the growth of boron and nitrogen doped HFCVD diamond [J]. Surface Interface Analysis,2015,47:572-586. doi: 10.1002/sia.5748 [13] LI L A, LI H D, LU X Y, et al. Dependence of reaction pressure on deposition and properties of boron-doped freestanding diamond films [J]. Applied Surface Science,2010,256:1764-1768. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.09.109 [14] GUO L, CHEN G H. High-quality diamond film deposition on a titanium substrate using the hot-filament chemical vapor deposition method [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2007,16(8):1530-1540. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2006.12.016 [15] RAMAMURTI R, BECKER M, SCHUELKE T, et al. Boron doped diamond deposited by microwave plasma-assisted CVD at low and high pressures [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2008,17(4/5):481-485. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2007.08.042 [16] LIU Z L, LI H J, LI M J, et al. Preparation of polycrystalline BDD/Ta electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic matter [J]. Electrochimica Acta,2018,290:109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.09.058 [17] BOGDANOWICZ R, FABIAŃSKA A, GOLUNSKI L, et al. Influence of the boron doping level on the electrochemical oxidation of the azo dyes at Si/BDD thin film electrodes [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2013,39:82-88. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2013.08.004 [18] WEI J J, LI C M, GAO X H, et al. The influence of boron doping level on quality and stability of diamond film on Ti substrate [J]. Applied Surface Science,2012,258:6909-6913. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.03.134 [19] YANG W L, TAN J L, CHEN Y H, et al. Relationship between substrate type and BDD electrode structure, performance and antibiotic tetracycline mineralization [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 890: 161760. [20] ZHANG J, YU X, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Influence of pore size of Ti substrate on structural and capacitive properties of Ti/boron doped diamond electrode [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,777:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.120 [21] WANG Z L, LU C, LI J J, et al. Influence of growth pressure on the electrical properties of boron-doped polycrystalline diamond films [J]. Applied Surface Science,2009,255:9522-9525. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.07.086 [22] STETER J R, BRILLAS E, SIRES I. On the selection of the anode material for the electrochemical removal of methylparaben from different aqueous media [J]. Electrochimica Acta,2016,222:1464-1474. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.11.125 [23] LIANG X B, WANG L, ZHU H L, et al. Effect of pressure on nanocrystalline diamond films deposition by hot filament CVD technique from CH4/H2 gas mixture [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2007,202:261-267. [24] YANG S M, HE Z T, LI Q T, et al. Diamond films with preferred <110> texture by hot filament CVD at low pressure [J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2008,17:2075-2079. [25] KOPF A, FEISTRITZER S, UDIER K. Diamond coated cutting tools for machining of non-ferrous metals and fibre reinforced polymers [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials,2006,24:354-359. [26] ZOU Y M. The effect of various dopants on diamond growth: A combined experimental & theoretical approach [D]. Acta University Upsaliensis, 2016. [27] MORTET V, ZIVCOVA Z V, TAYLOR A, et al. Insight into boron-doped diamond Raman spectra characteristic features [J]. Carbon,2017,115:279-284. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.022 [28] 李春燕. 掺硼金刚石膜的制备及其电学性能研究 [D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2006.LI Chunyan. Preparation and electrical properties of boron-doped diamond films [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006. [29] LU X R, DING M H, ZHANG C, et al. Investigation on microstructure evolution and failure mechanism of boron doped diamond coated titanium electrode during accelerated life test [J]. Thin Solid Films,2018,660:306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.06.039 [30] LI C Y, LI B, LV X Y, et al. Superconductivity in heavily boron-doped diamond films prepared by electron assisted chemical vapour deposition method [J]. Chinese Physics Letters,2006,23:2856-2863. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/23/10/063 [31] MARSELLI B, GARCIA-GOMEZ J, MICHAUD P A, et al. Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society,2003,150(3):D79-D83. doi: 10.1149/1.1553790 [32] MCCRORY C C L, JUNG S, PETERS J C, et al. Benchmarking heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Journal of The American Chemical Society 2013, 135(45): 16977-16987. [33] CHEN Y H, GAO X L, LIU G S, et al. Correlation of the role of boron concentration on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of diamond electrodes [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,1(1):197-204. [34] CHEN W P, LI W, LIU F M, et al. Microstructure of boron doped diamond electrodes and studies on its basic electrochemical characteristics and applicability of dye degradation [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8:104348. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104348 [35] SCHWARZOVA-PECKOVA K, VOSAHLOVA J, BAREK J, et al. Influence of boron content on the morphological, spectral, and electroanalytical characteristics of anodically oxidized boron-doped diamond electrodes [J]. Electrochimica Acta,2017,243:170-182. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.05.006 -



 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
