Diamond grown on KTN substrate and its photocatalytic performance
-
摘要:
采用微波等离子体化学气相沉积技术,以钽铌酸钾(KTa1-xNbxO3,简称KTN)作为衬底,生长高质量金刚石薄膜。用X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜和拉曼光谱仪观察并分析金刚石薄膜的表面形貌和微观结构,并研究样品的光催化性能。结果表明:金刚石生长过程中形成了碳化钽过渡层;随着生长时间延长金刚石质量不断提高;所有样品均表现出良好的降解罗丹明B的能力,其中生长时间为12 h的样品对罗丹明B的降解效率提高了0.29倍,与生长时间为3 h的样品相比其降解效率提高了1.6倍。本研究为生长多晶金刚石提供新型衬底,并探索金刚石在光催化方面的应用。
-
关键词:
- 金刚石 /
- 铌酸钽钾 /
- 光催化 /
- 微波等离子体化学气相沉积(MPCVD)
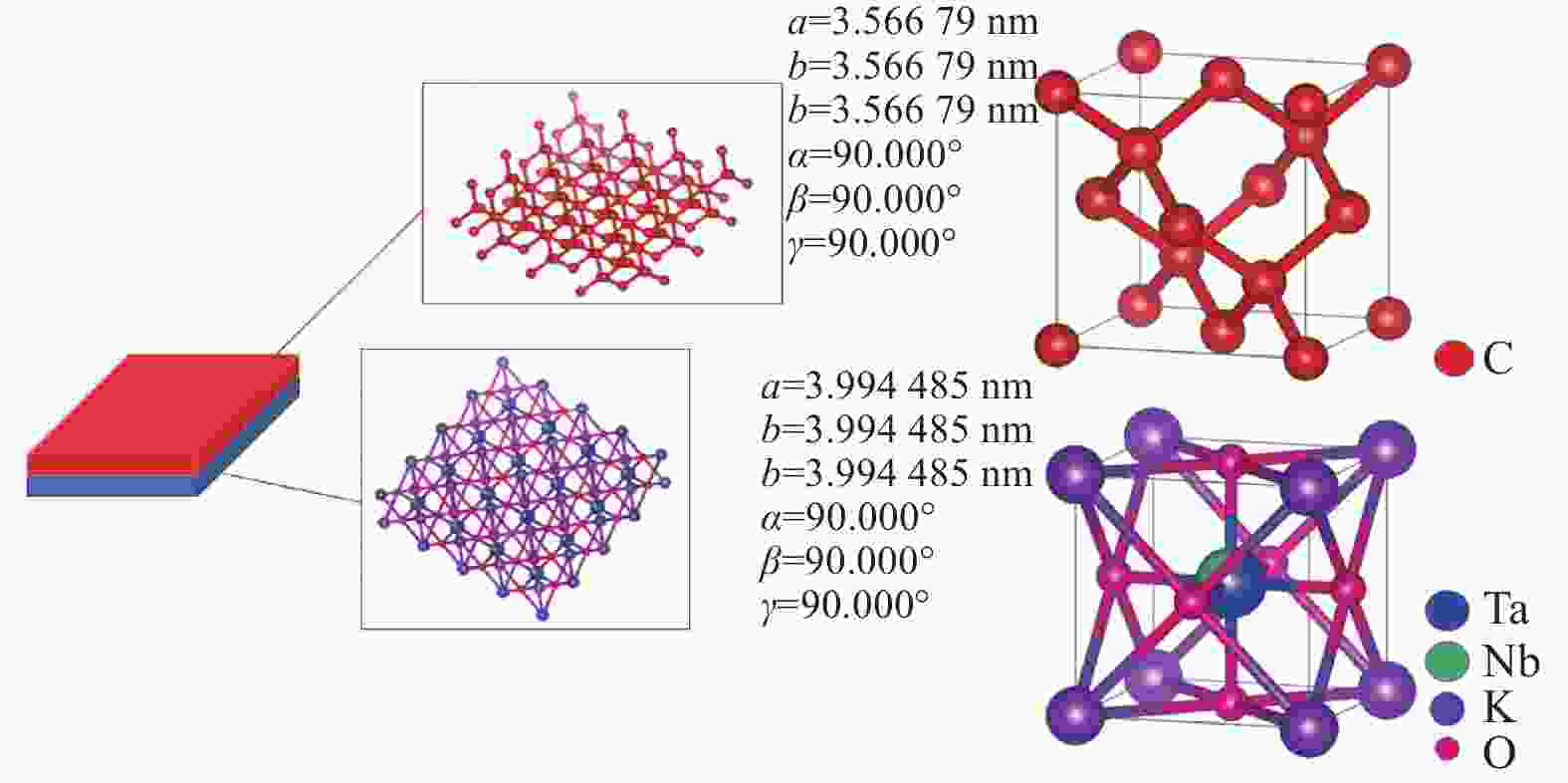
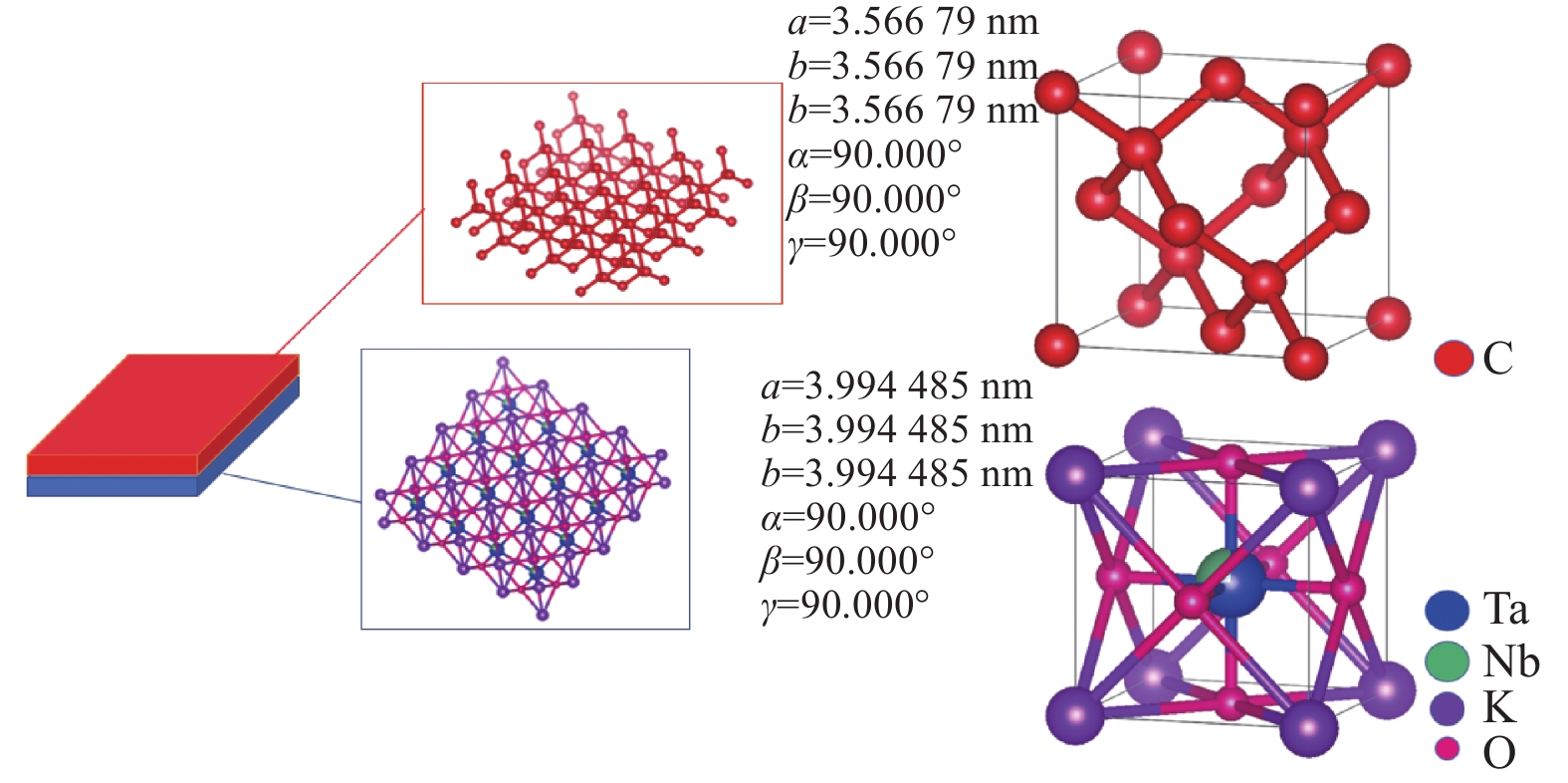
Abstract:[Objectives] Diamond, with advantages of high melting point, good insulation, stable chemical properties, and high thermal conductivity, is a promising semiconductor material for high-power devices, sensors, and quantum computing. The best method for producing high-quality single crystal diamonds through microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) is homoepitaxial growth, which requires expensive single crystal diamond substrates. Therefore, heteroepitaxial growth on foreign substrates is a compromise approach that has to be adopted, where the selection of a proper substrate becomes a major challenge for growing high-quality diamonds. To enhance the quality of heteroepitaxial growth, potassium tantalum niobate (KTa1-xNbxO3, referred to as KTN) crystals are proposed as the substrate. Their lattice parameter (0.3994 nm) is close to that of diamond (0.3567 nm). The structural similarity between them makes it possible to achieve an ideal result with small lattice mismatch and high crystal quality.
[Methods] Diamond thin films were grown on large-size, high-quality KTN single crystals using MPCVD. The effect of different growth times on diamond quality was explored by varying the duration of diamond growth. The surface morphologies, microstructures, and crystalline quality were analyzed using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy. Diamond samples with different growth times were used to degrade Rhodamine B (RhB) to assess their photocatalytic effect. The absorbance of RhB was measured to evaluate the degradation efficiency of diamond films as catalysts for the pollutant solution.
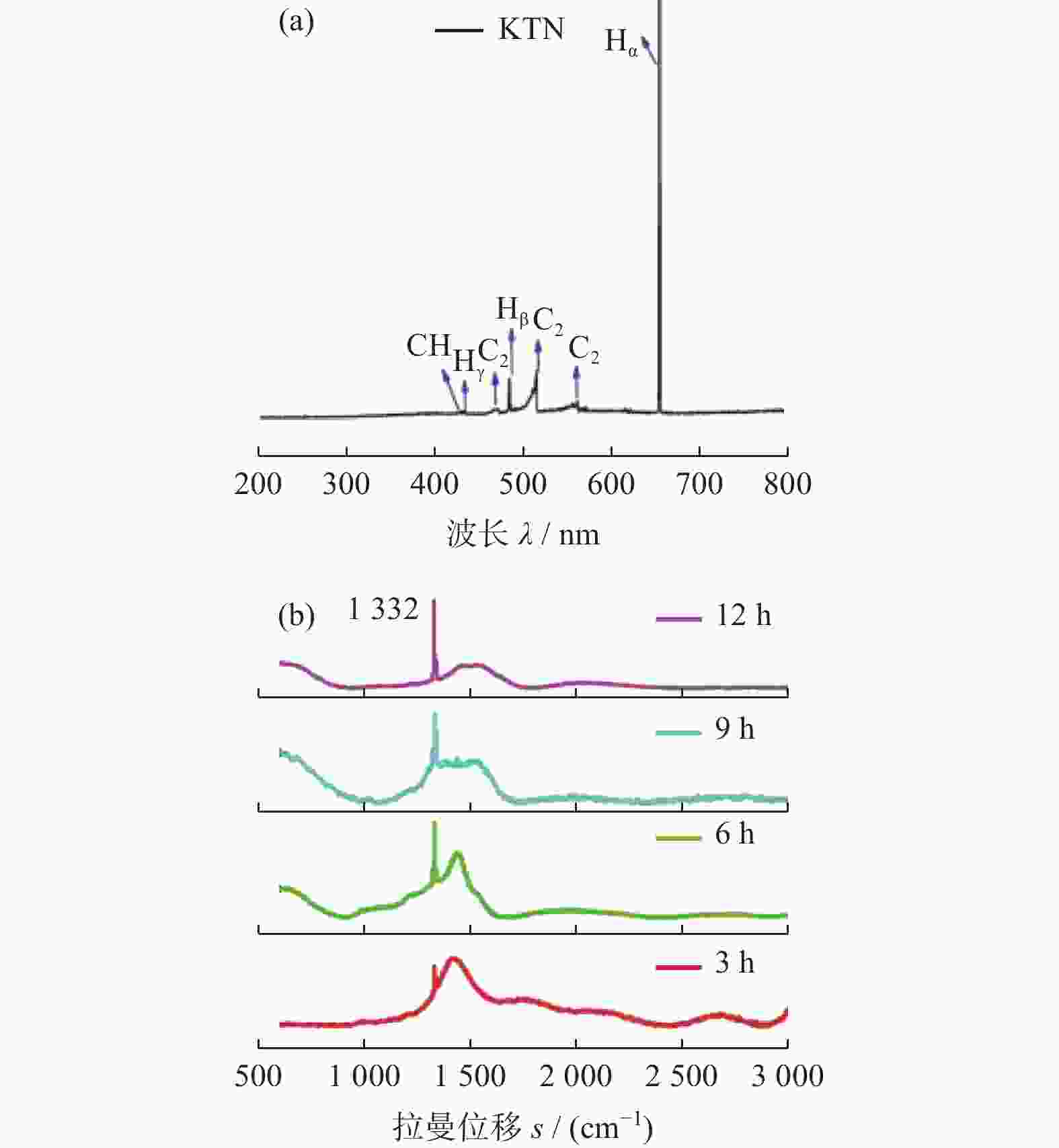
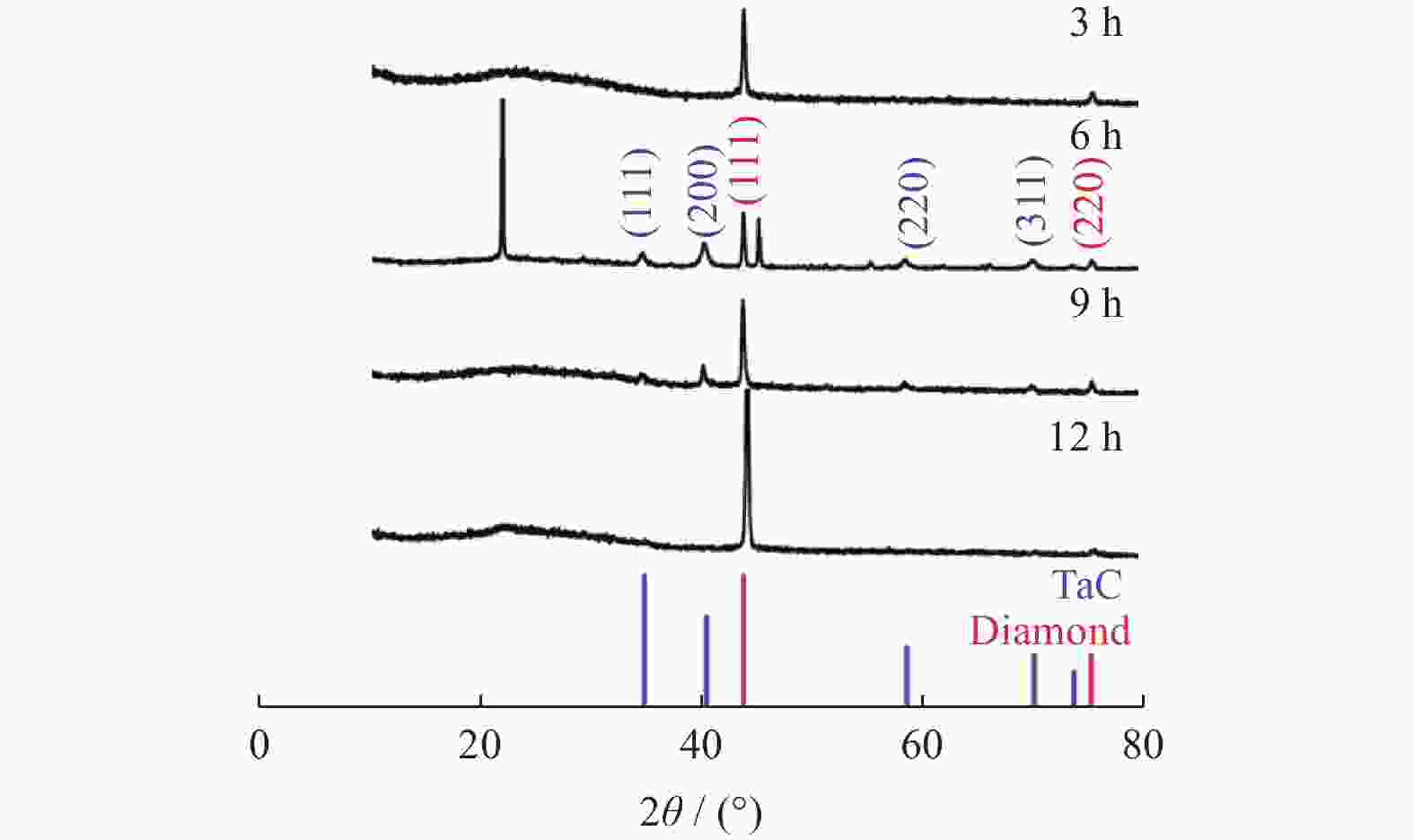
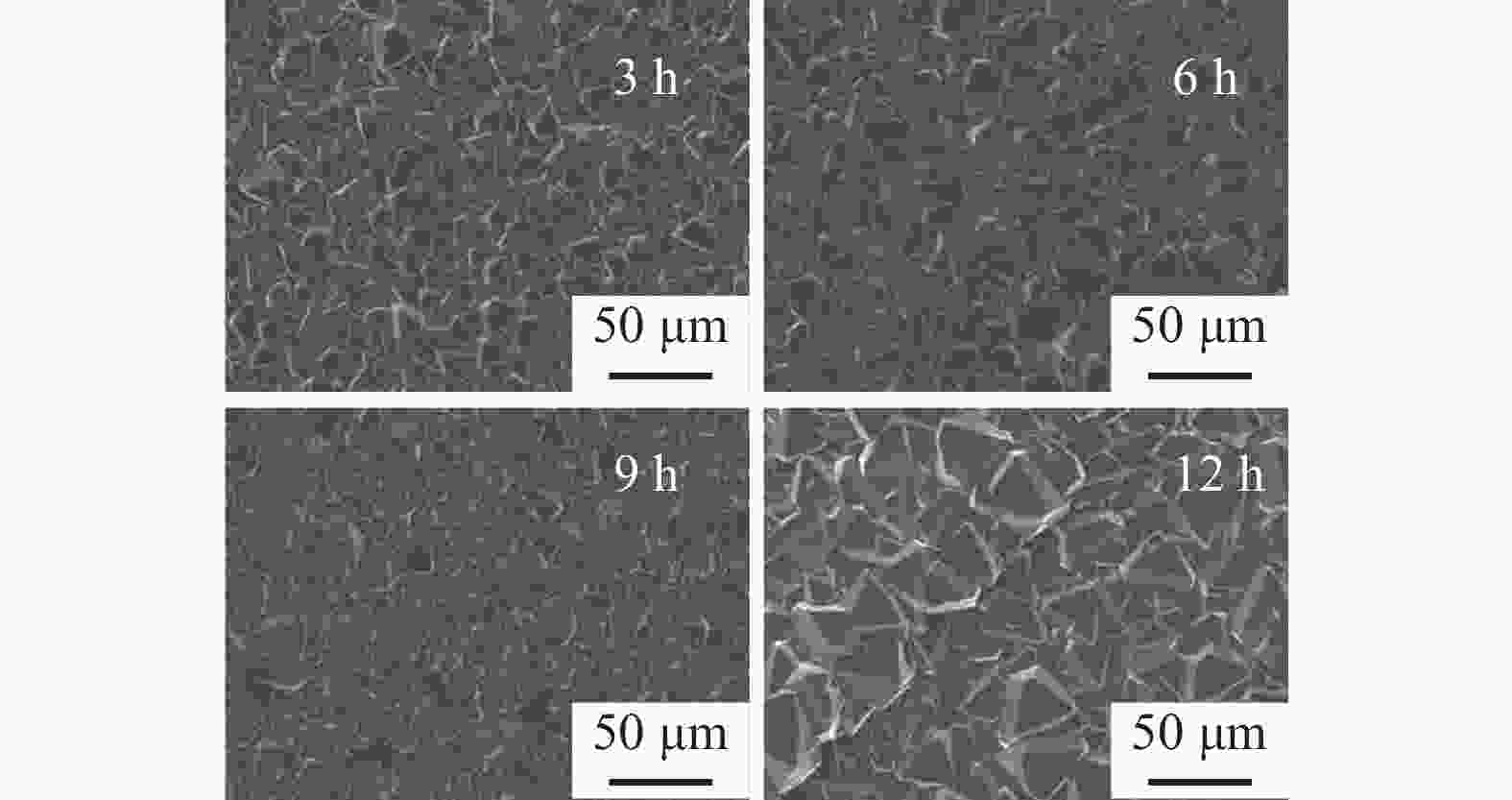
[Results ] Analysis of plasma diagnostic spectra confirmed the presence of H groups and carbon source groups, while CN groups were absent. The H group exhibited the highest spectral line intensity, higher than that of the C2 group. This indicated that the system was well-sealed and provided sufficient reactive groups for diamond growth. The ratio of peak intensities between Hα and Hβ was high, while the ratio between C2 and Hα was low, both of which were favorable for the deposition of high-quality diamonds. Raman spectroscopy revealed structural changes in diamonds through comparing Isp3/Isp2, the relative intensities of diamond-phase characteristic peaks and non-diamond-phase characteristic peaks. The ratio gradually increased with the extension of growth time, indicating that the quality of diamonds was improving. XRD analysis of diamond films showed characteristic diamond peaks. In the 6h sample, characteristic peaks appeared at 34.8° (111), 40.5° (200), 58.6° (220) and 70.0° (311), consistent with the standard card (JCPDS No. 35-0801) as the characteristic peaks of TaC, indicating the presence of TaC in the 6h sample. However, the TaC characteristic peaks were lower in the 9h sample, and only diamond characteristic peaks were observed in the 12h sample. This indicated that TaC was only a transitional layer formed in the pre-nucleation stage, and TaC was no longer generated with the extension of growth time. From the SEM images of diamond films at different deposition time, it could be seen that the grain size of the 12h sample was much larger and more evenly distributed than those of other samples. The surface of the 12h sample was mostly composed of (100) faceted grains with a high degree of flatness, and the grains growing at the grain boundaries tended to grow significantly larger. Analysis of photocatalytic activity showed that higher diamond purity and lower non-diamond phase proportion led to better photocatalytic activity, more stable photocatalytic performance, and higher reusability.
[Conclusions] A new diamond substrate, potassium tantalum niobate (KTa1-xNbxO3), was successfully used to grow high-quality diamond films using MPCVD technology. The samples were characterized by XRD, SEM and Raman spectroscopy. Results indicate the formation of a TaC transition layer when growing diamond films on the KTN substrate, which is favorable for stable diamond growth. Moreover, with increasing growth time, the diamond grain size increases, the diamond phase content increases, and the sample quality improves. Photocatalytic results show that the sample grown for 12 hours has stronger photocatalytic ability and higher photocatalytic stability, achieving a degradation efficiency of 91.9% for RhB, which is 1.6 times higher than that of the 3h sample. These findings broaden the application of diamond and provide valuable insights for substrate selection in diamond fabrication.
-
图 5 (a)不同生长时间样品的RhB降解曲线;(b)不同生长时间样品对RhB降解速率变化曲线;(c) 12 h样品不同光照时间下降解RhB的紫外−可见吸收光谱;(d) 12 h样品RhB的光降解循环曲线
Figure 5. (a) RhB degradation curves of prepared samples; (b) RhB degradation rate curves of samples at different growth times; (c) RhB absorption spectra of diamond under different illumination times; (d) Photodegradation cycle curve of RhB
表 1 金刚石生长条件
Table 1. The growth conditions of diamond
生长参数 类型或取值 衬底 KTN 气体流量比(CH4∶H2) 5∶200 微波功率 P / W 1000 工作压力 p / kPa 14 温度 T / ℃ 700 -
[1] LIAO M. Progress in semiconductor diamond photod-etectors and MEMS sensors [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,1(1):29-46. doi: 10.1080/26941112.2021.1877019 [2] LIU J, ZHENG Y, LIN L, et al. Surface conductivity enhancement of H-terminated diamond based on the purified epitaxial diamond layer [J]. Journal of Materials Science,2018,53(18):13030-13041. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2579-7 [3] YANG B, ZHANG R, SHEN Q, et al. Study on the lateral growth of the diamond in the substrate holder and the effect of temperature gradient on the large-area diamond surface morphology [J]. Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(36):17072-17080. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-05256-4 [4] BONNAURON M, SAADA S, MER C, et al. Transparent diamond‐on‐glass micro‐electrode arrays for ex‐vivo neuronal study [J]. Physica Status Solidi (A),2008,205(9):2126-2129. doi: 10.1002/pssa.200879733 [5] LI T, HAO J, CAO W, et al. Designing of room temperature diluted ferromagnetic Fe doped diamond semiconductor [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,2(1):80-83. doi: 10.1080/26941112.2022.2098065 [6] CAO W, GAO D, ZHAO H, et al. Epitaxial lateral growth of single-crystal diamond under high pressure by a plate-to-plate MPCVD [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,1(1):143-149. doi: 10.1080/26941112.2021.1947750 [7] SHU G, DAI B, BOLSHAKOV A, et al. Coessential-connection by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition: a common process towards wafer scale single crystal diamond [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,1(1):47-62. doi: 10.1080/26941112.2020.1869511 [8] CHEN J, WANG G, QI C, et al. Morphological and structural evolution on the lateral face of the diamond seed by MPCVD homoepitaxial deposition [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth,2018,484:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2017.12.022 [9] NAD S, GU Y, ASMUSSEN J. Growth strategies for large and high quality single crystal diamond substrates [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2015,60:26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2015.09.018 [10] LLORET F, GUTIERREZ M, ARAUJO D, et al. MPCVD diamond lateral growth through microterraces to reduce threading dislocations density [J]. Physica Status Solidi (A),2017,214(11):1700242. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201700242 [11] 李思佳, 冯曙光, 郭胜惠, 等. MPCVD法制备金刚石膜的工艺 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(6):31-37. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.6.0006LI Sijia, FENG Shuguang, GUO Shenghui, et al. Pre-paration technology of diamond film by MPCVD method [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(6):31-37. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.6.0006 [12] 丁康俊, 马志斌, 宋修曦, 等. 温度对MPCVD法同质外延单晶金刚石缺陷的影响 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2018,38(2):8-11,19. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2018.2.0002DING Kangjun, MA Zhibin, SONG Xiuxi, at al. Effect of temperature on defects in homoepitaxial single crystal diamond by MPCVD [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2018,38(2):8-11,19. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2018.2.0002 [13] MENG Y, YAN C, KRASNICKI S, et al. High optical quality multicarat single crystal diamond produced by chemical vapor deposition [J]. Physica Status Solidi (A),2012,209(1):101-104. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201127417 [14] JIANG X, KLAGES C, ROSLER M, et al. Deposition and characterization of diamond epitaxial thin films on silicon substrates [J]. Applied Physics A,1993,57(6):483-489. doi: 10.1007/BF00331746 [15] FAN Q, PEREIRA E, GRACIO J. Diamond deposition on copper: studies on nucleation, growth, and adhesion behaviours [J]. Journal of Materials Science,1999,34(6):1353-1365. doi: 10.1023/A:1004566502572 [16] FU Y, YAN B, LOH N, et al. Deposition of diamond coating on pure titanium using micro-wave plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition [J]. Journal of Materials Science,1999,34(10):2269-2283. doi: 10.1023/A:1004569406535 [17] SCHRECK M, GSELL S, BRESCIA R, et al. Ion bombardment induced buried lateral growth: the key mechanism for the synthesis of single crystal diamond wafers [J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x [18] BENSALAH H, STENGER I, SAKR G, et al. Mosaicity, dislocations and strain in heteroepitaxial diamond grown on iridium [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2016,66:188-195. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.04.006 [19] WANG Q, WU G, NEWHOURSE-ILLIGE T, et al. Heteroepitaxial diamond film deposition on KTaO3 substrates via single-crystal iridium buffer layers [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2020,110:108117. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108117 [20] 赵中琴, 唐伟忠, 苗晋琦, 等. 含金刚石的复相过渡层及Al2O3衬底上金刚石薄膜的附着力 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2004(1):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2004.01.010ZHAO Zhongqin, TANG Weizhong, MIAO Jinqi, et al. Deposition of a new kind of composite interlayer containing diamond phase and its application in enhancing adhesion of diamond coatings on alumina substrates [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2004(1):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2004.01.010 [21] GUAN Q, HU X, WEI J, et al. Growth, etching, polarization and second harmonic generation of potassium lithium tantalate niobate crystals [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth,1999,197(4):1012-1014. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(98)00889-6 [22] WANG X, LIU B, YANG Y, et al. Anomalous laser deflection phenomenon based on the interaction of electro-optic and graded refractivity effects in Cu-doped KTa1− xNbxO3 crystal [J]. Applied Physics Letters,2014,105(5):051910. doi: 10.1063/1.4892663 [23] TRIEBWASSER S. Study of ferroelectric transitions of solid-solution single crystals of KNbO3-KTaO3 [J]. Physical Review,1959,114(1):63. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.114.63 [24] SUZUKI K, SAKAMOTO W, YOGO T, et al. Processing of oriented K (Ta, Nb) O3 films using chemical solution deposition [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,1999,82(6):1463-1466. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb01942.x [25] WANG X, WANG J, YU Y, et al. Growth of cubic KTa1− xNbxO3 crystal by Czochralski method [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth,2006,293(2):398-403. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.05.021 [26] KNIGHT D S, WHITE W. Characterization of diamond films by Raman spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Materials Research,1989,4(2):385-393. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1989.0385 [27] ISBERG J, HAMMERSBERG J, JOHANSSON E, et al. High carrier mobility in single-crystal plasma-deposited diamond [J]. Science,2002,297(5587):1670-1672. doi: 10.1126/science.1074374 [28] SU L, CAO Y, HAO H, et al. Emerging applications of nanodiamonds in photocatalysis [J]. Functional Diamond,2022,1(1):93-109. doi: 10.1080/26941112.2020.1869431 [29] BAGHERI S, JULKAPLI N. Nano-diamond based p-hotocatalysis for solar hydrogen production [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(56):31538-31554. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.193 [30] DUAN X, AO Z, LI D, et al. Surface-tailored nano-diamonds as excellent metal-free catalysts for organic oxidation [J]. Carbon,2016,103:404-411. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.03.034 [31] NAVALON S, DHAKSHINAMOORTHY A, ALVARO M, et al. Diamond nanoparticles in heterogeneous catalysis [J]. Chemistry of Materials,2020,32(10):4116-4143. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c00204 -




 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
