Analysis of flow field characteristics of silicon carbide CMP under ultrasonic action
-
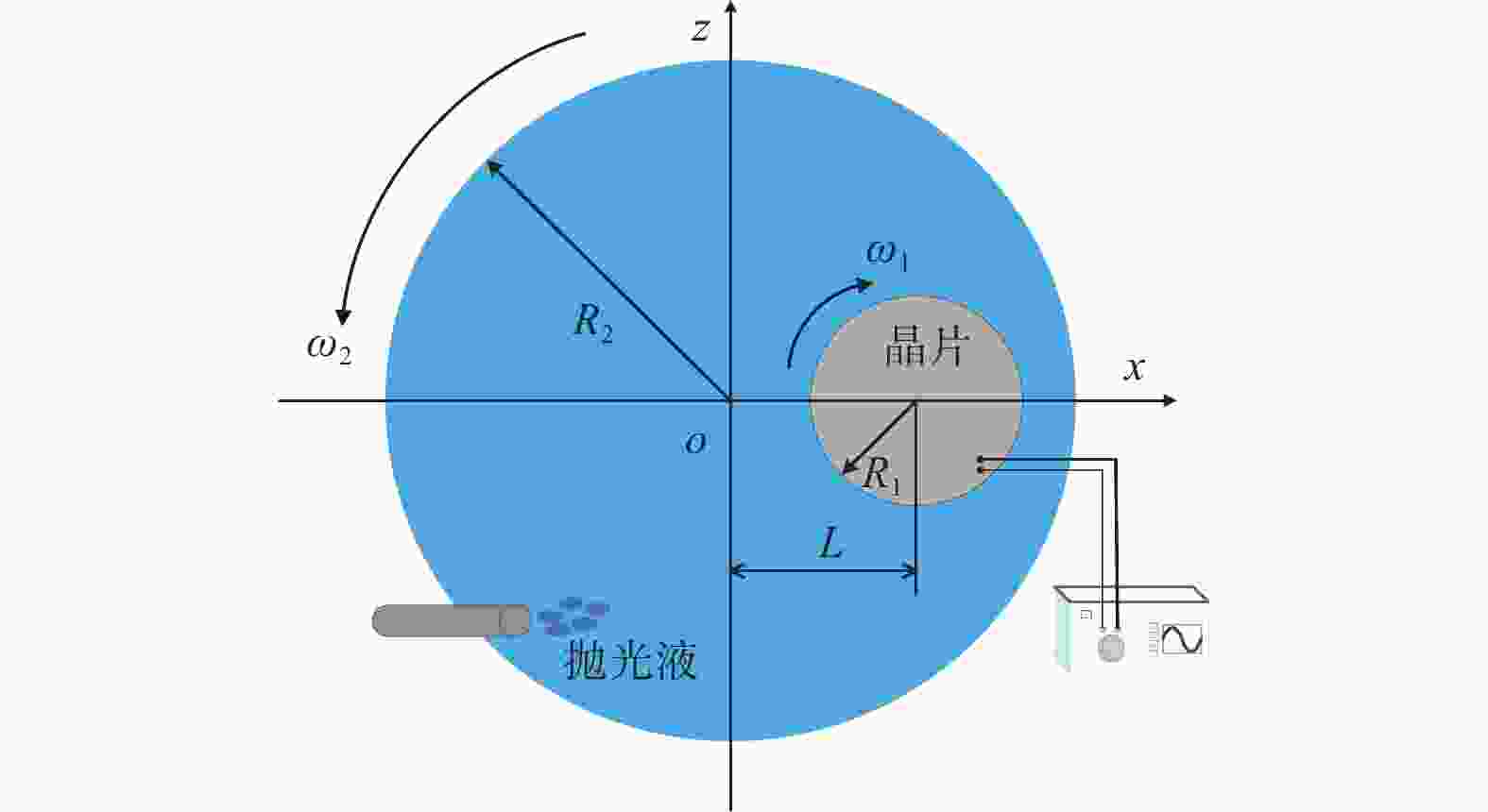
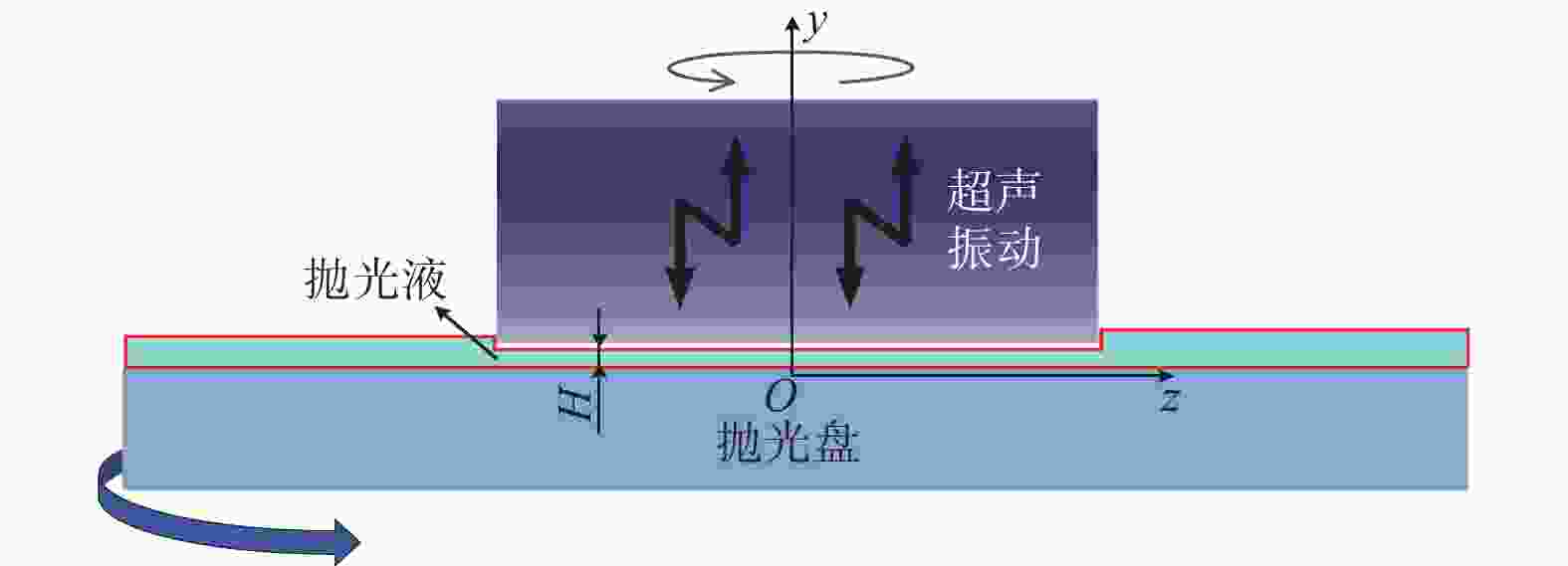
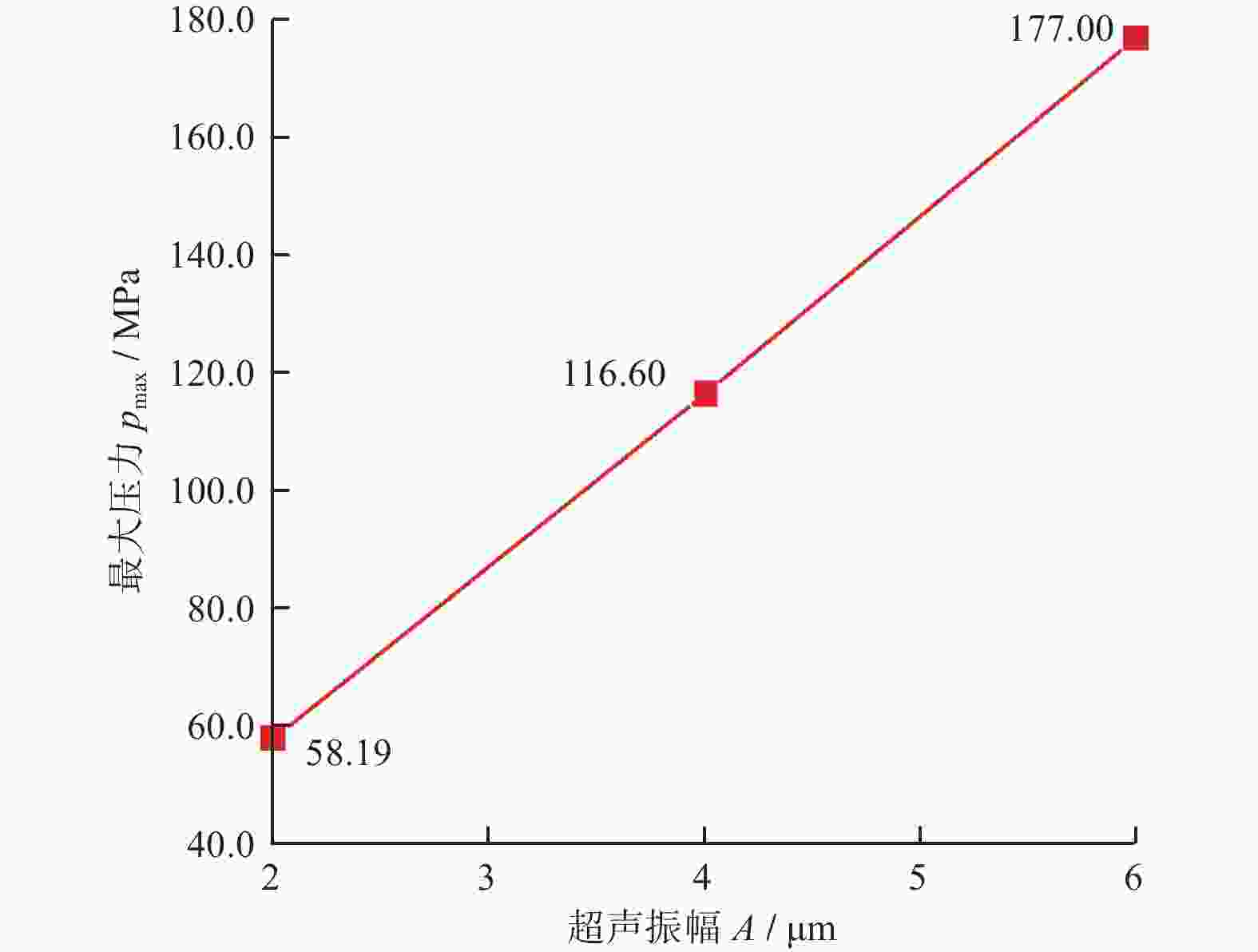
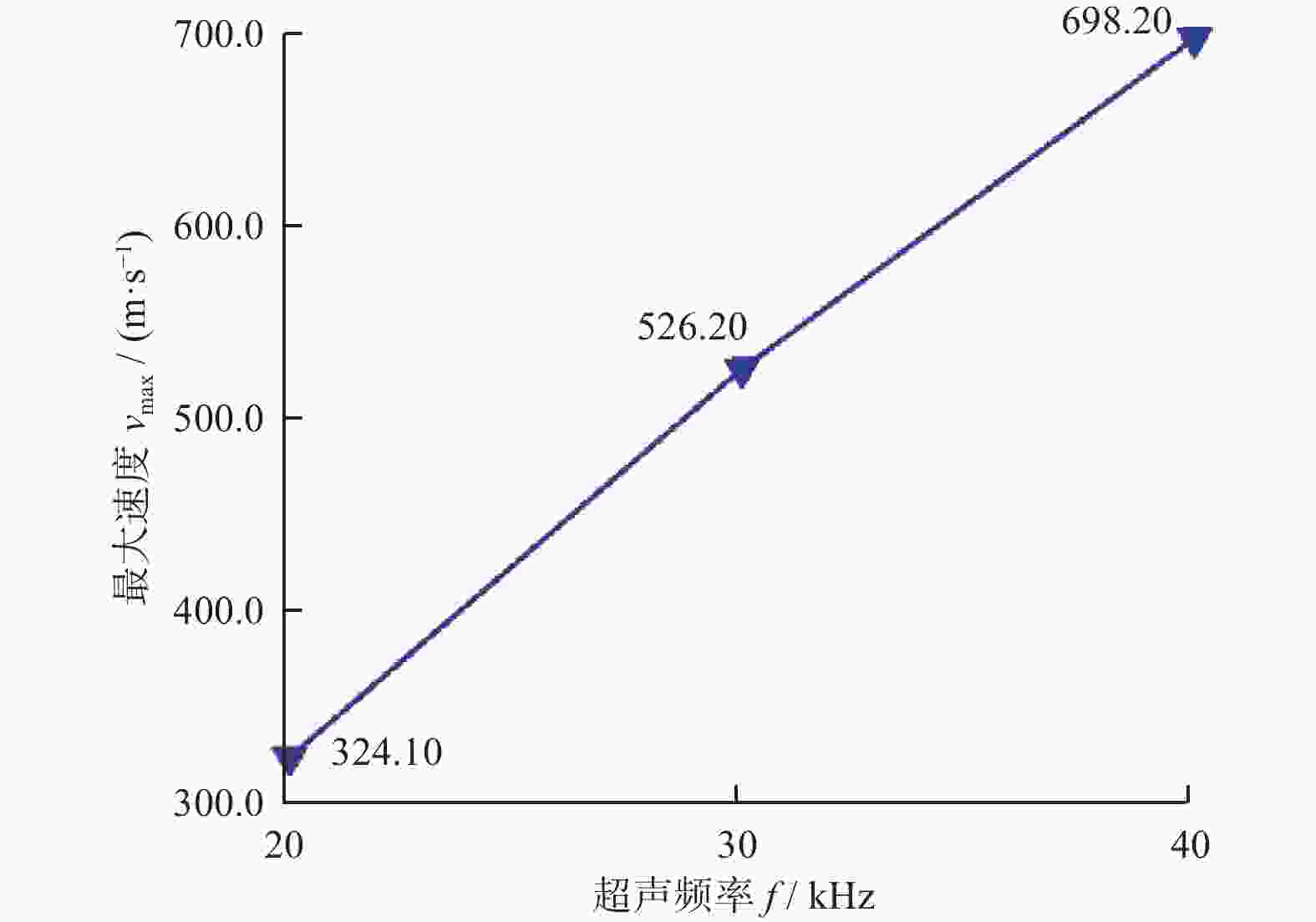
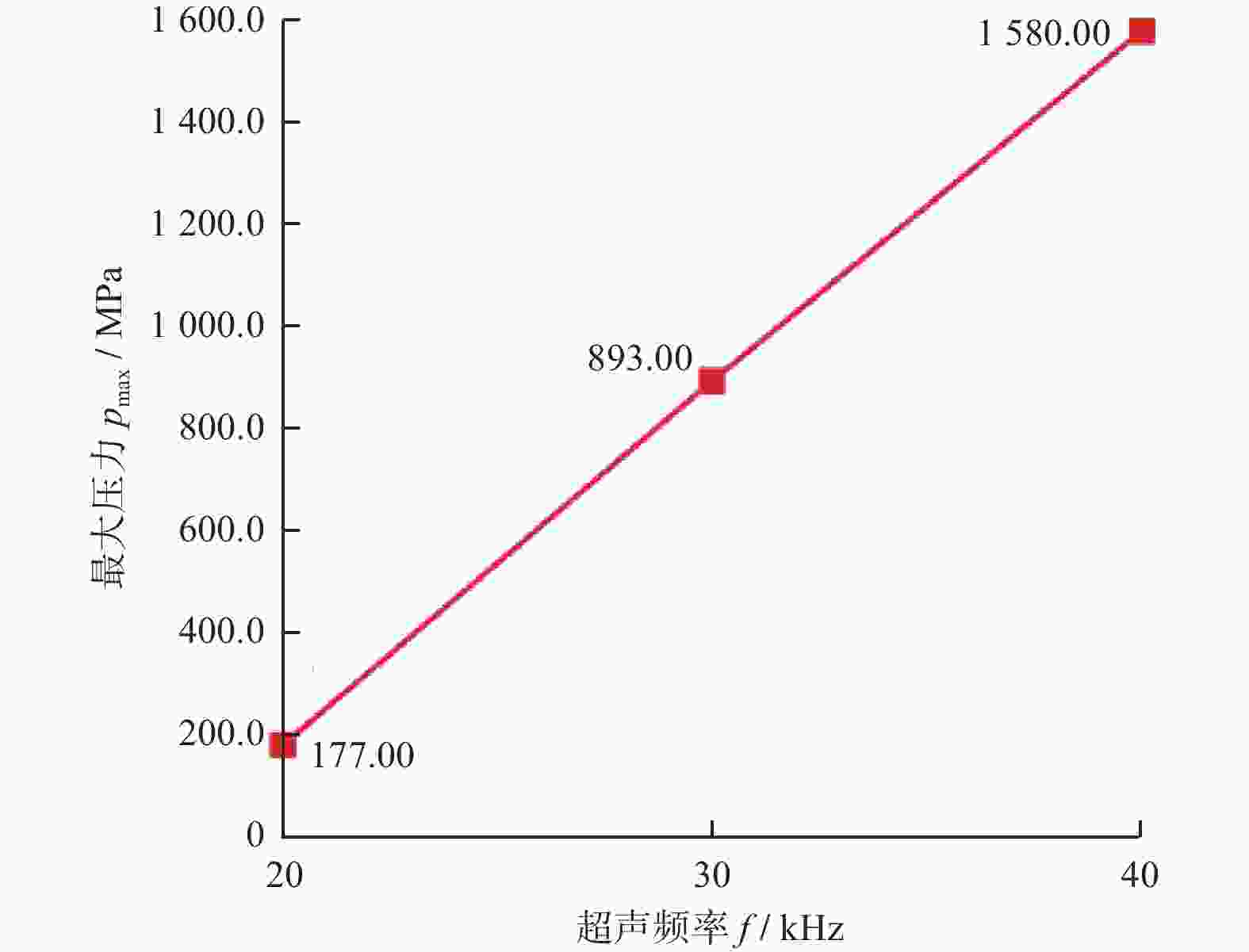
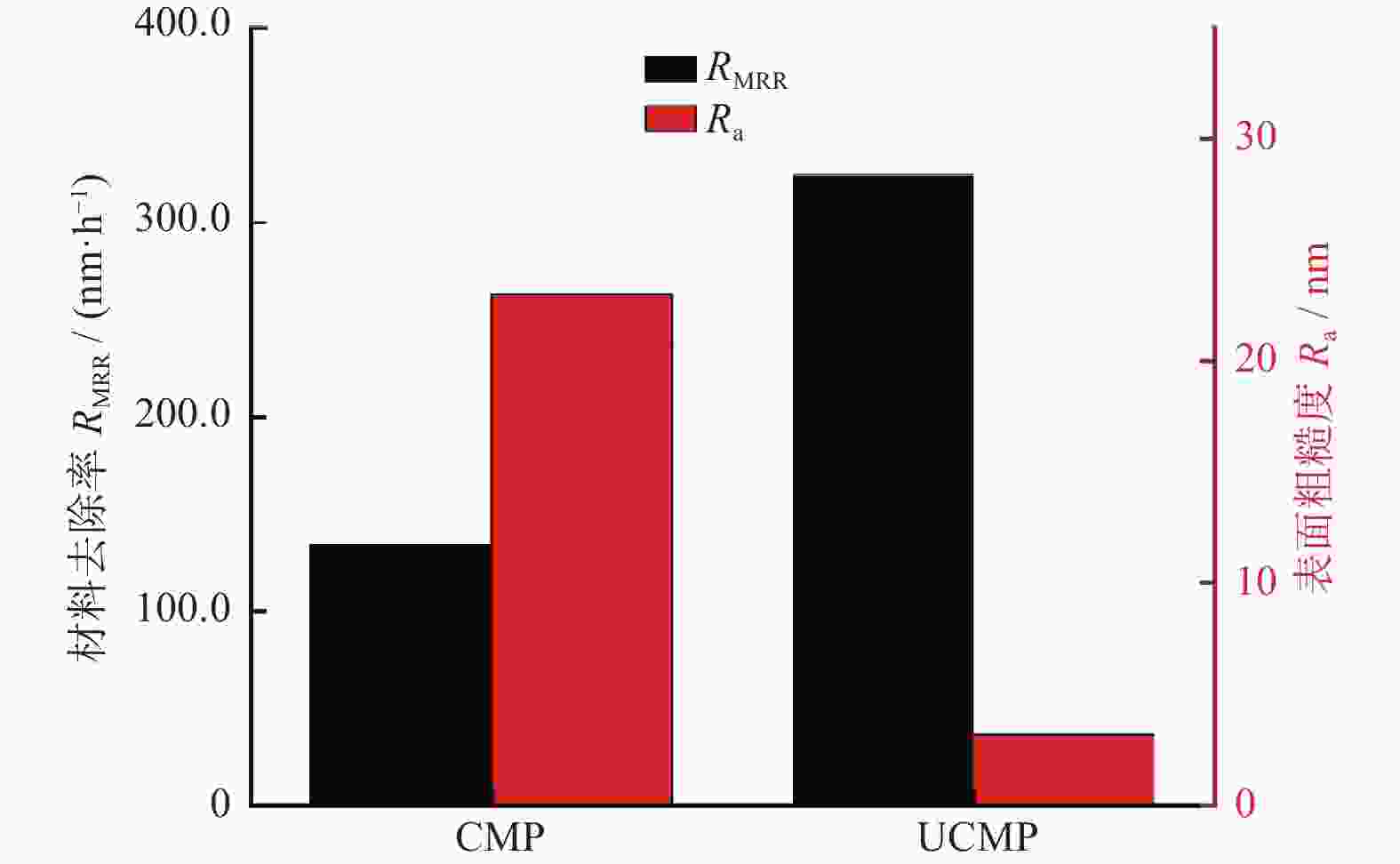
摘要: 针对目前碳化硅抛光效率低、表面质量差等加工难题,采用超声辅助CMP(UCMP)加工工艺对其表面进行光滑无损化抛光。为探究超声辅助对CMP流场的影响,以超声振动下的抛光流场特性为研究对象,基于可实现k−ε模型对超声作用下的抛光流场特性进行分析,并采用有限元分析方法探究不同超声频率、超声振幅、液膜厚度对抛光流场内速度、压力的影响,且开展CMP和UCMP对照试验。结果表明:超声频率对抛光液流场有明显地促进作用,随着超声频率从20 kHz增大到40 kHz,流场最大速度从324.10 m/s增大到698.20 m/s,最大压力从177.00 MPa增大到1 580.00 MPa;与CMP相比,UCMP后碳化硅晶片可获得更好的抛光质量与更高的材料去除率,其表面粗糙度Ra、材料去除率RMRR分别为3.2 nm和324.23 nm/h。Abstract:
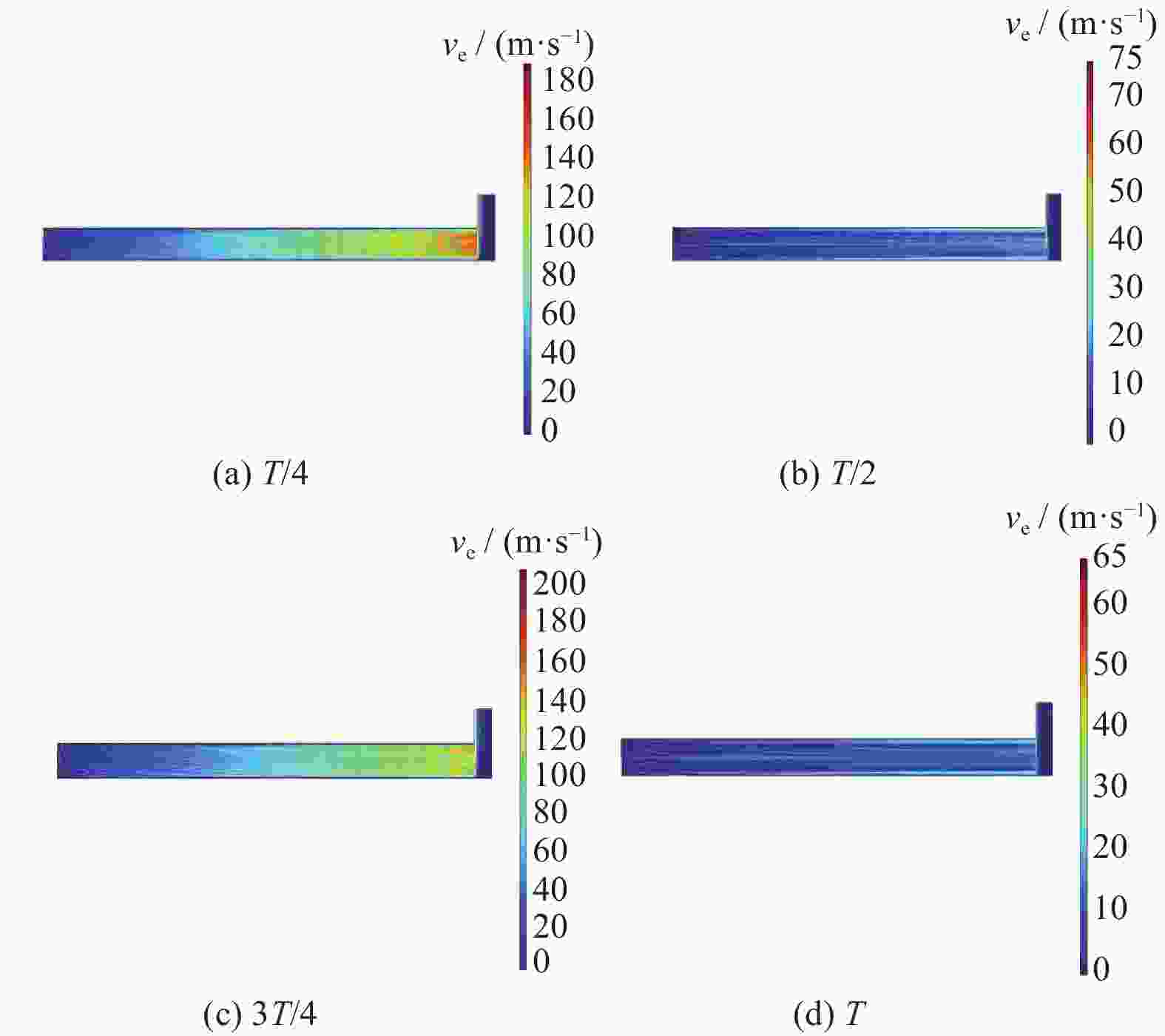
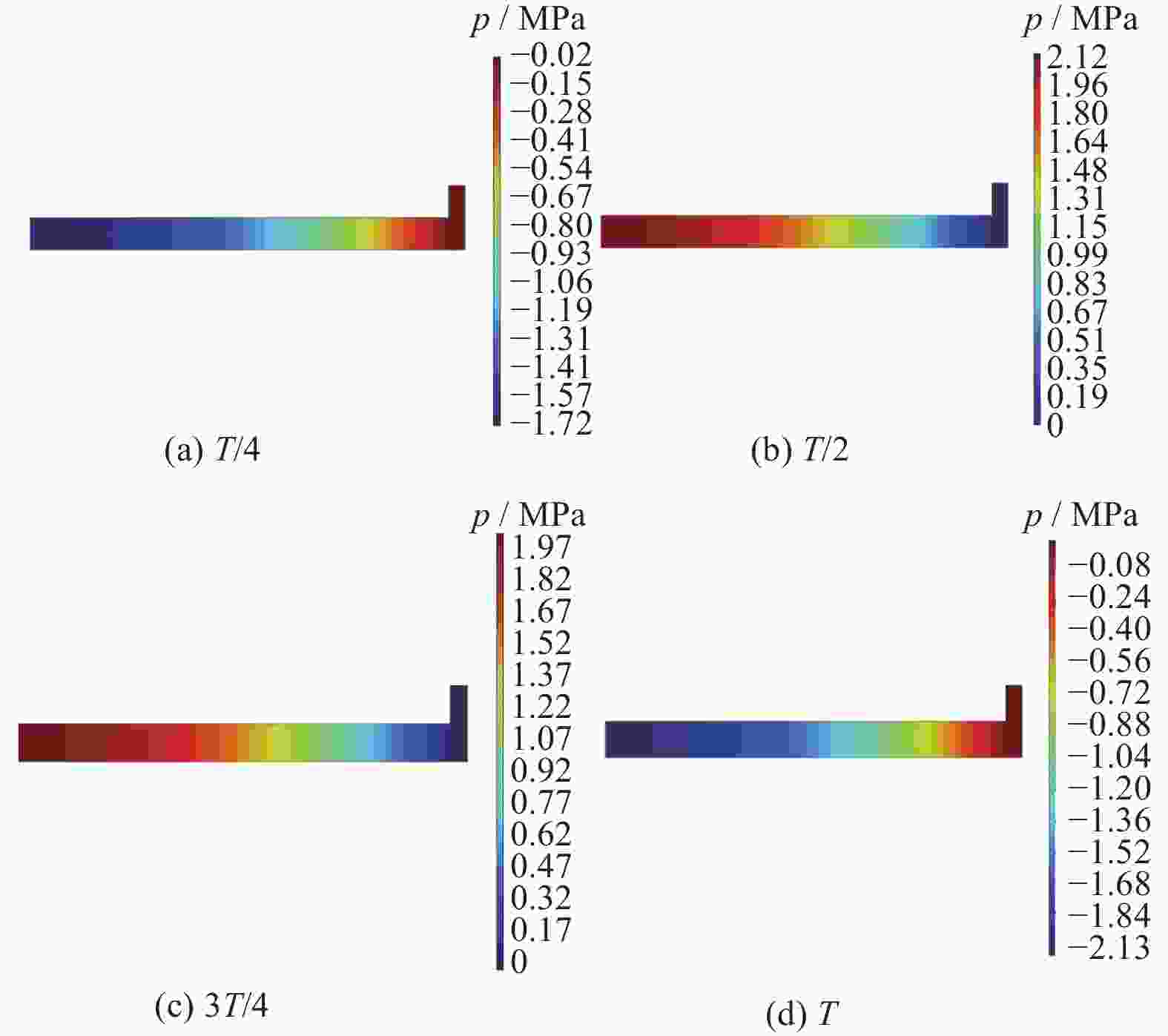
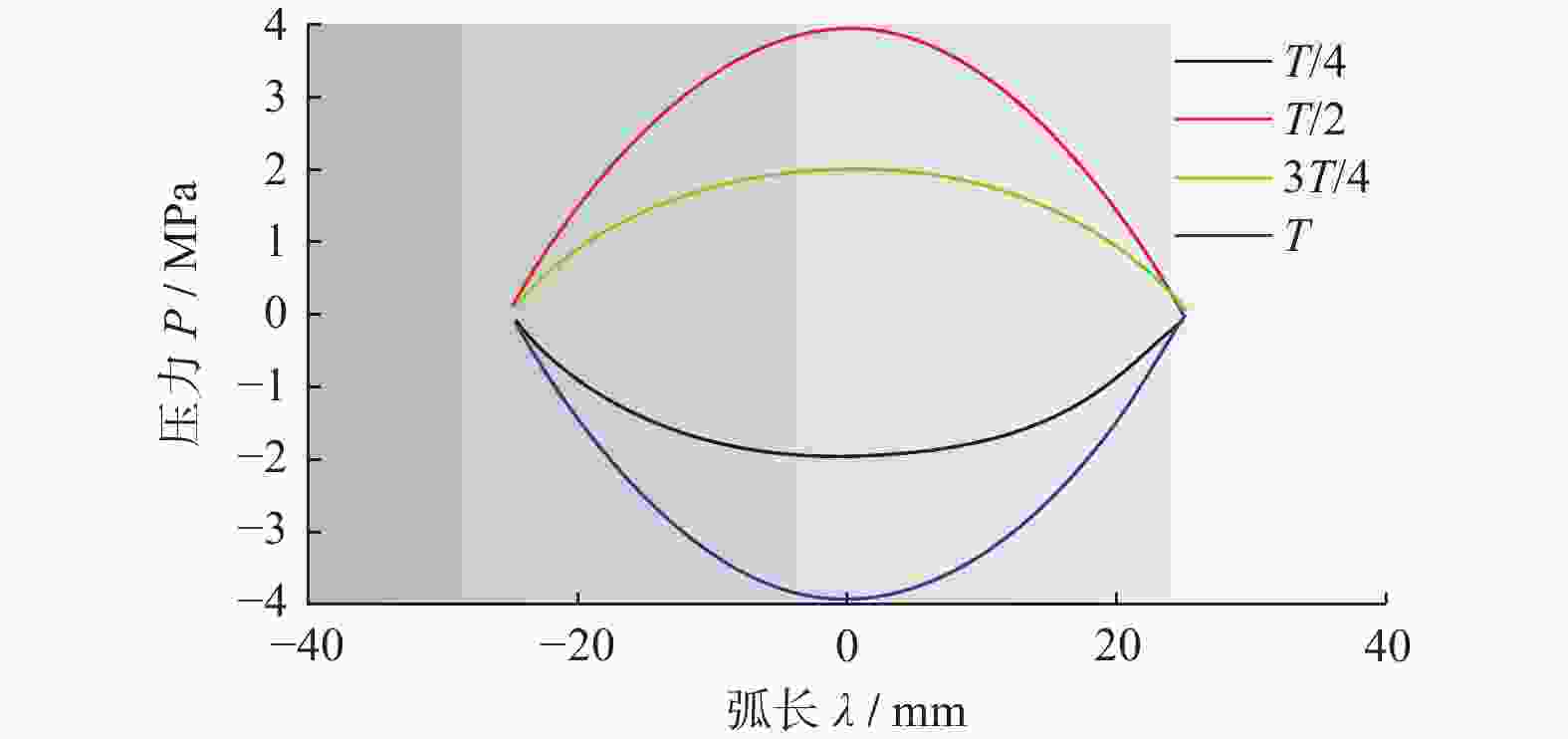
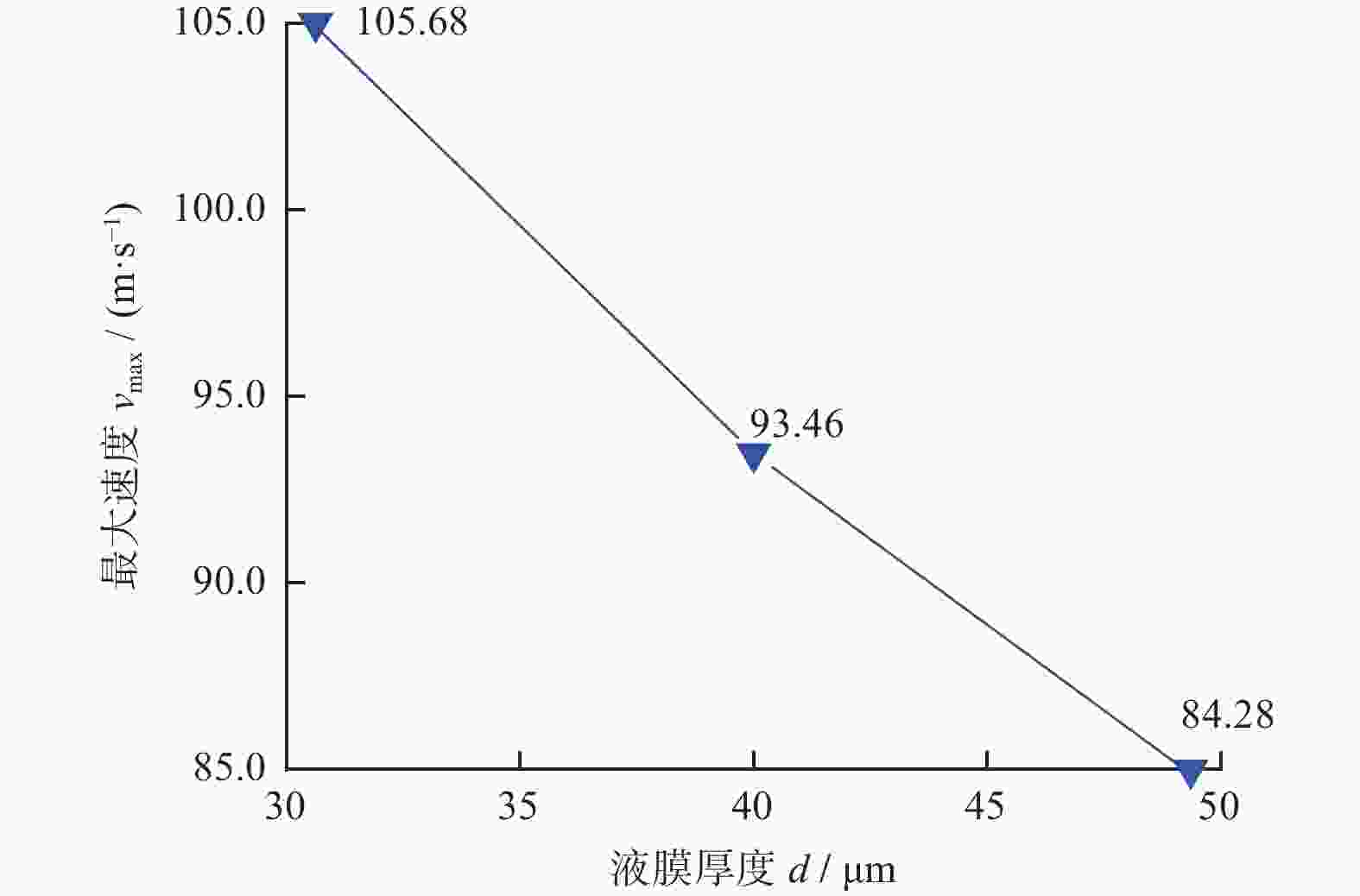
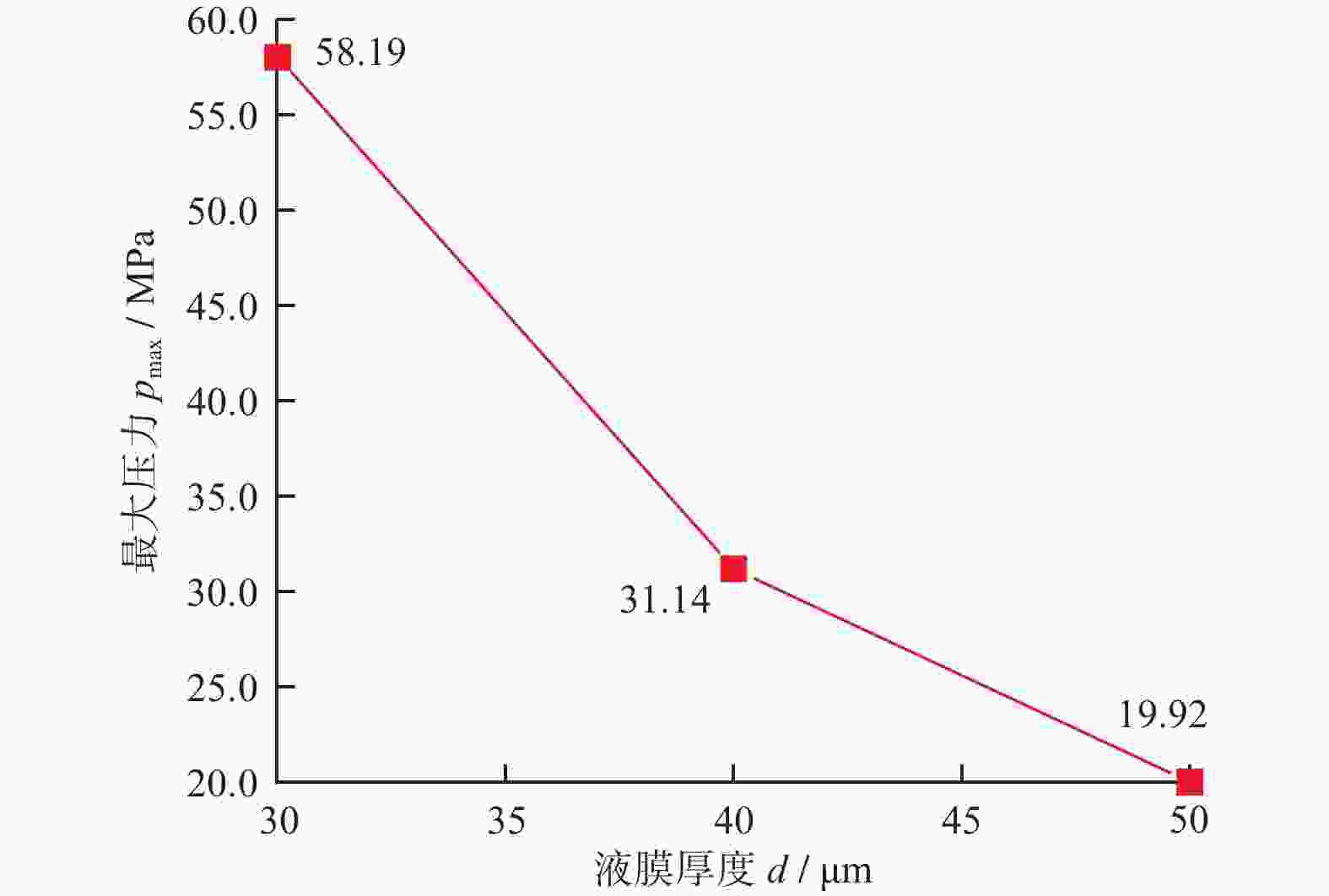
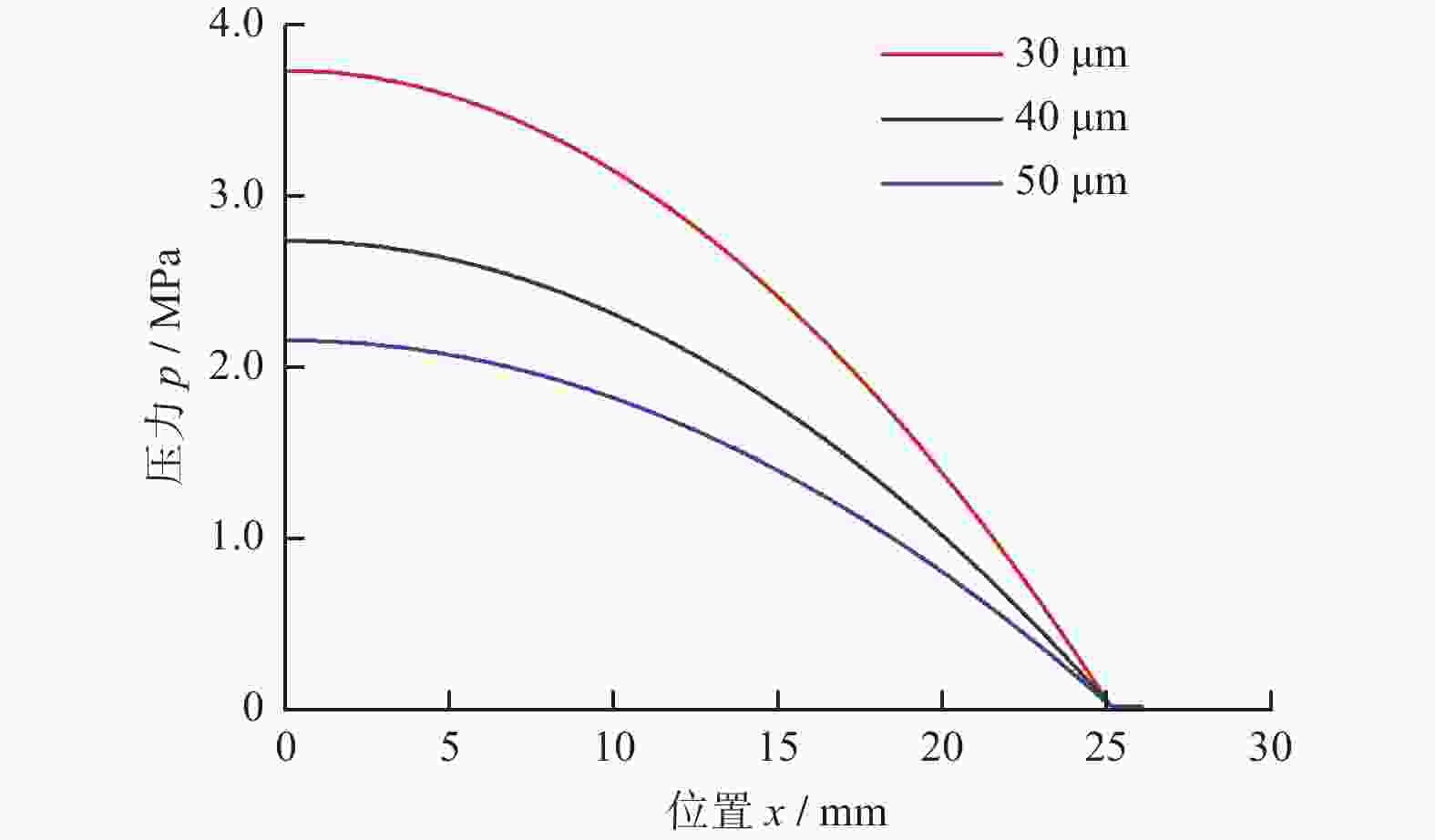
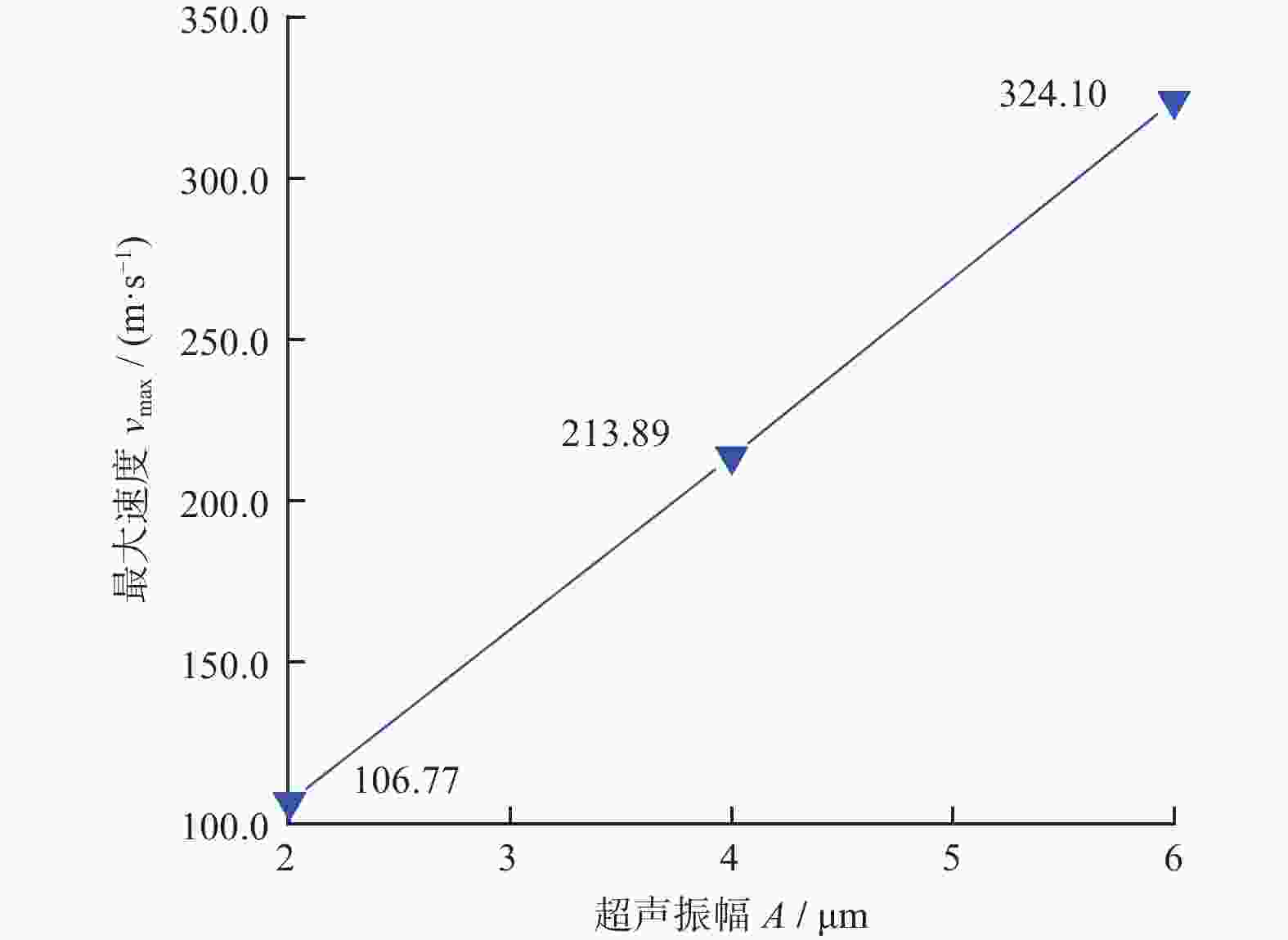
Objectives Silicon carbide faces challenges such as low polishing efficiency and poor surface quality during processing. The ultrasonic-assisted CMP (UCMP) processing technology is used to smooth and non-destructive polishing the SiC surface, and the influence of ultrasonic assistance on the CMP flow field is deeply investigated in order to improve the polishing effect of SiC. Methods (1) COMSOL Multiphysics is used to conduct CFD simulation on the polishing flow field of the silicon carbide UCMP process, aiming to explore the influences of factors such as ultrasonic frequency, ultrasonic amplitude, and liquid film thickness on the polishing flow field. A model is constructed to study the polishing flow field characteristics under ultrasonic vibration, based on an achievable k−ε model to analyze the polishing flow field characteristics under ultrasonic action. (2) The influences of ultrasonic frequency, ultrasonic amplitude, and liquid film thickness on velocity and pressure in the polishing flow field are studied by the finite element method. (3) The CMP and UCMP comparative experiments are conducted to compare the polishing effects of SiC wafers under the two processes. Results The ultrasonic frequency has a significant impact on the flow field of the polishing solution, and it has a significant promoting effect on the flow field of the polishing solution. As the ultrasound frequency increases from 20 kHz to 40 kHz, the maximum velocity of the flow field increases from 324.10 m/s to 698.20 m/s, and the maximum pressure increases from 177.00 MPa to 1580 .00 MPa. Compared with CMP, the polishing quality of the SiC wafer after UCMP is better, with a minimum surface roughness Ra of 3.2 nm and a higher material removal rate of 324.23 nm/h.Conclusions The UCMP process is used to process the SiC surface, and the positive effect of ultrasound-assisted polishing flow field is verified through theoretical analysis and experimental verification. The relationship between the ultrasonic frequency and the polishing flow field characteristics has been clarified, providing data support for further optimizing UCMP process parameters. The UCMP process has significant advantages in improving the polishing quality and material removal rate of SiC, and is expected to be widely applied in the field of silicon carbide material processing. Further research can be conducted on the influence of other factors on the UCMP process effect to achieve more ideal processing results. -
表 1 参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting
参数 取值 超声频率 f / kHz 20,30,40 液膜厚度 d / μm 30,40,50 超声振幅 A / μm 2,4,6 表 2 碳化硅的CMP工艺参数
Table 2. CMP process parameters of SiC
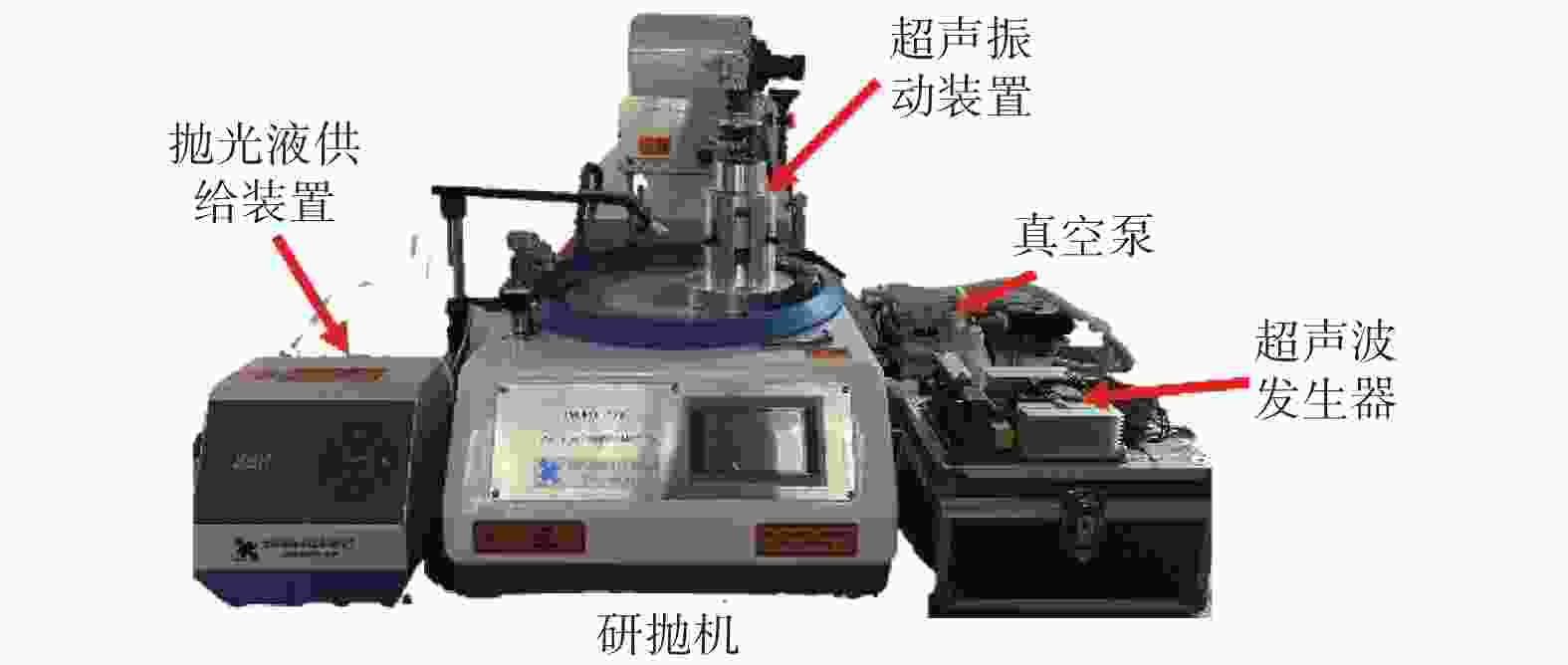
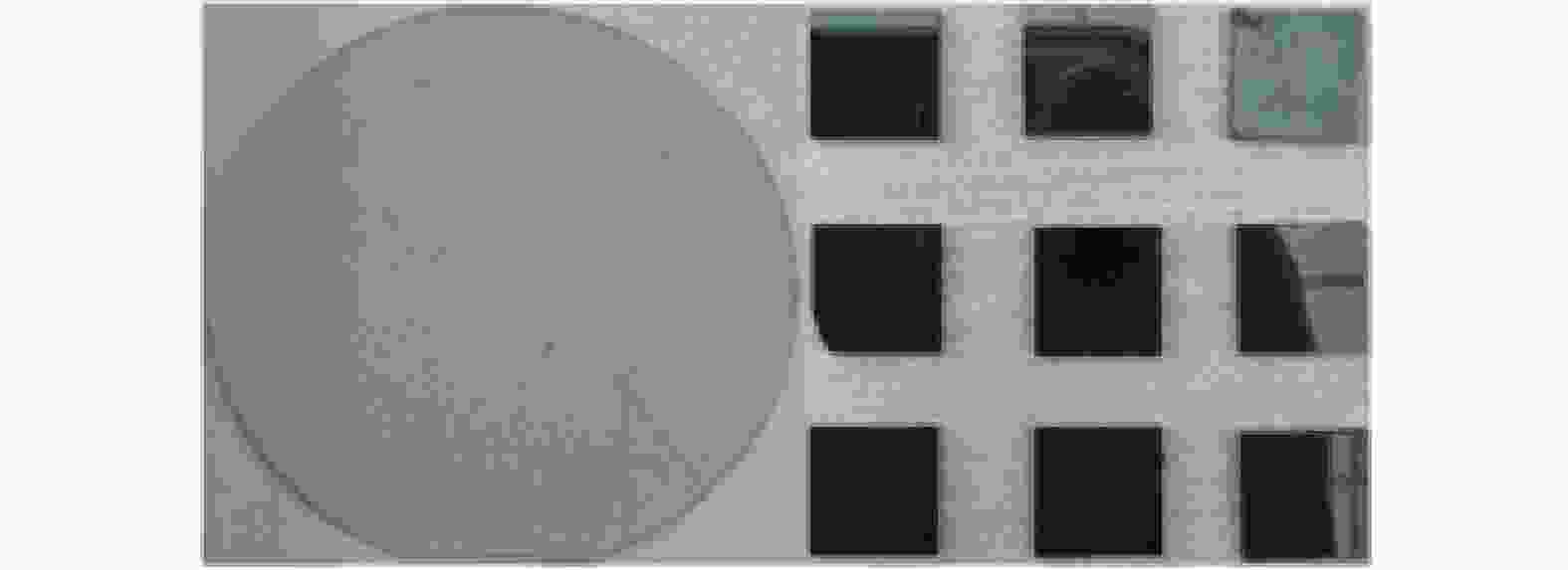
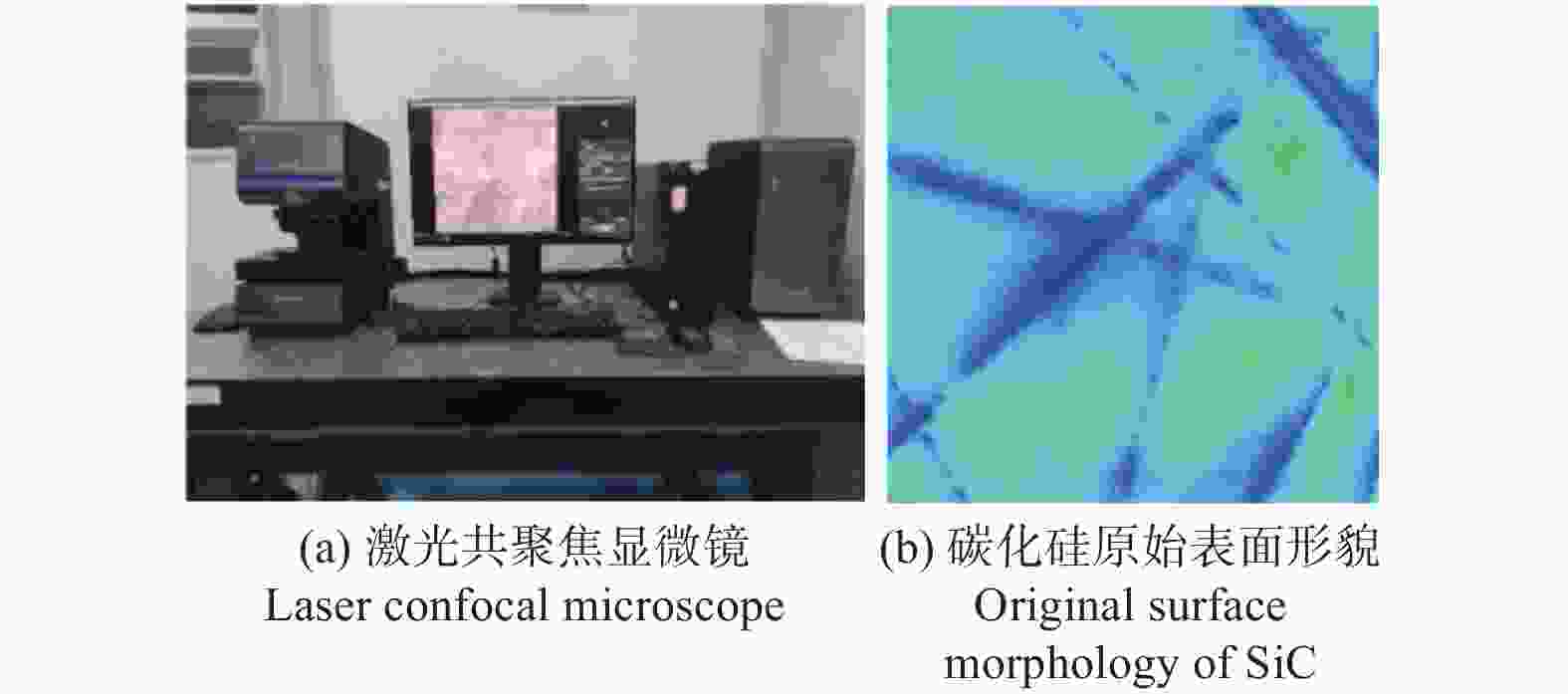
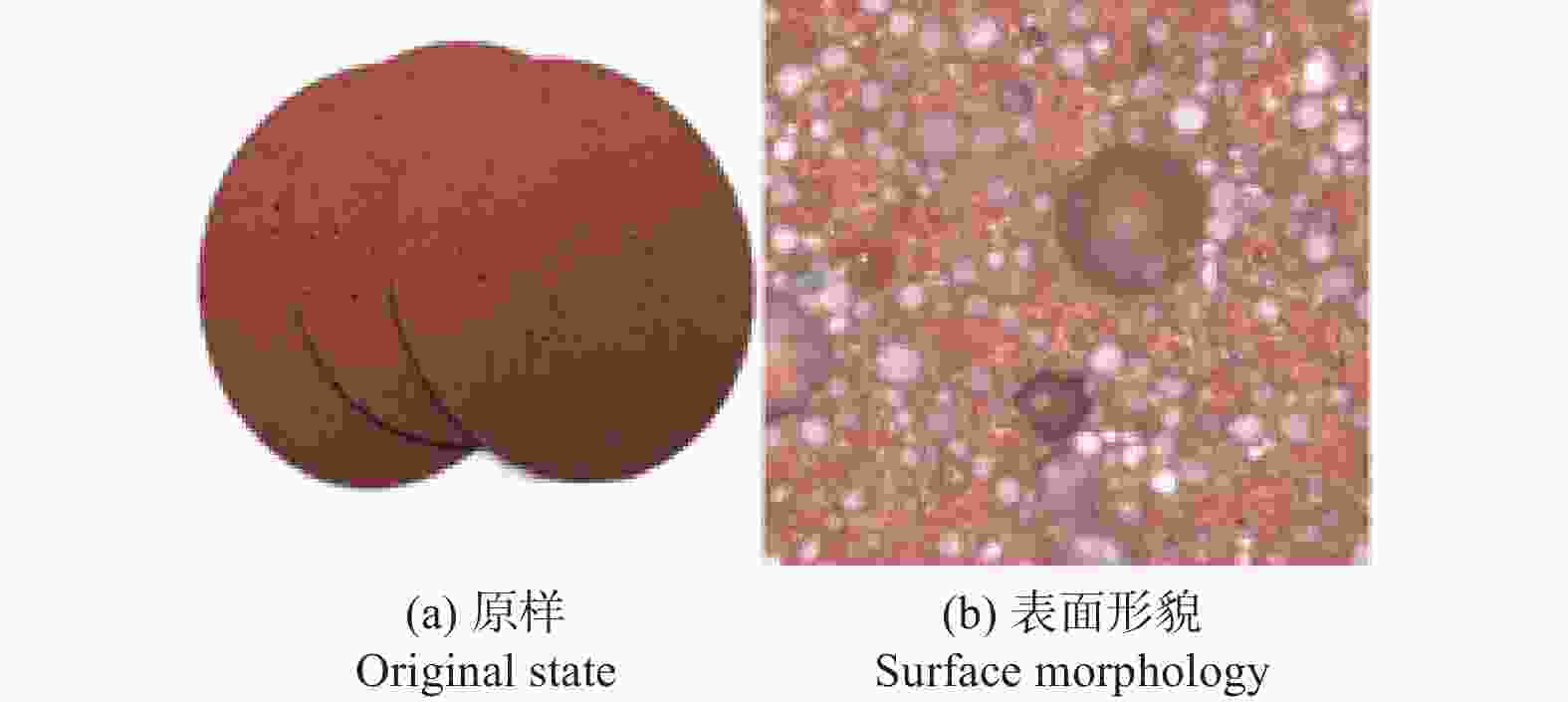
工艺参数 规格或取值 SiC试样尺寸 10 mm × 10 mm × 1 mm 抛光机 UNIPOL-1203 抛光垫 聚氨酯抛光垫 抛光压力 p1 / N 11.76 抛光盘转速 n / ( r·min-1) 180 抛光液流量 qv / (mL·min-1) 10 抛光液 SiO2悬浮抛光液 表 3 碳化硅的材料特性参数
Table 3. Material characteristic parameters of SiC
材料特性 取值 密度 ρ / (kg·m−3) 3215 弹性模量 E / GPa 196 泊松比 ε 0.21 洛氏硬度 / HR 92 断裂韧性 KIc / (MPa·m1/2) 4.5 导热系数 Κ / (W·m−1·K−1) 110 抗弯强度 σb / MPa 400 -
[1] 邓家云. 单晶SiC电芬顿化学机械抛光机理研究 [D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2022.DENG Jiayun. Study on the mechanism of electro-fenton chemical mechanical polishing of single crystal SiC [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2022. [2] ZHANG X, LIU X, WANG Y, et al. Optimizing the flatness of 4H-silicon carbide wafers by tuning the sequence of lapping [J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology,2023,38(3):034001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/acb1ce [3] XIE W, ZHANG Z, LIAO L, et al. Green chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafers using a novel slurry [J]. Nanoscale,2020,12(44):22518-22526. doi: 10.1039/D0NR04705H [4] LIAO L, ZHANG Z, MENG F, et al. A novel slurry for chemical mechanical polishing of single crystal diamond [J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,564:150431. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150431 [5] ZHANG Z, CUI J, ZHANG J, et al. Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper [J]. Applied Surface Science,2019(467/468):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.133 [6] ZHANG Z, LIAO L, WANG X, et al. Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy [J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,506:144670. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144670 [7] ZHANG Z, SHI Z, DU Y, et al. A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry [J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,427:409-415. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.064 [8] CUI X, ZHANG Z, SHI C, et al. A novel green chemical mechanical polishing for potassium dihydrogen phosphate using corn oil slurry [J]. Materials Today Sustainability,2022,20:100257. doi: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100257 [9] AIDA H, DOI T, TAKEDA H, et al. Ultraprecision CMP for sapphire, GaN, and SiC for advanced optoelectronics materials [J]. Current Applied Physics,2012,12:S41-S46. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2012.02.016 [10] ZHAI W, GAO B, CHANG J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted polishing SiC through CFD simulation [J]. Nanomanufacturing and Metrology,2019,2(1):36-44. doi: 10.1007/s41871-018-0033-8 [11] ZHOU M, ZHONG M, XU W. Novel model of material removal rate on ultrasonic-assisted chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire [J]. Friction,2023,11(11):2073-2090. doi: 10.1007/s40544-022-0713-7 [12] LIU T, LEI H. Nd3 + -doped colloidal SiO2 composite abrasives: Synthesis and the effects on chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) performances of sapphire wafers [J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,413:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.270 [13] SU J, DU J, LIU H, et al. Research on material removal rate of CMP 6H-SiC crystal substrate (0001) Si surface based on abrasive alumina(Al2O3) [J]. Procedia Engineering,2011,24:441-446. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2673 [14] 梁庆瑞, 胡小波, 陈秀芳, 等. 4H-SiC的强氧化液化学机械抛光(英文) [J]. 人工晶体学报,2015,44(7):1741-1747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2015.07.005LIANG Qingrui, HU Xiaobo, CHEN Xiufang, el al. Chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC with strong oxidizing slurry [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals(in English),2015,44(7):1741-1747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2015.07.005 [15] 陈国美, 倪自丰, 钱善华, 等. SiC晶片不同晶面的CMP抛光效果对比研究 [J]. 人工晶体学报,2019,48(1):155-159,172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.01.026CHEN Guomei, NI Zifeng, QIAN Shanhua, el al. Influence of different crystallographic planes on CMP performance of SiC wafer [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2019,48(1):155-159,172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.01.026 [16] YIN L, VANCOILLE E Y J, RAMESH K, et al. Surface characterization of 6H-SiC(0001) substrates in indentation and abrasive machining [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2004,44(6):607-615. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2003.12.006 [17] TAM H Y, CHENG H B, WANG Y W. Removal rate and surface roughness in the lapping and polishing of RB-SiC optical components [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2007(192/193):276-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.091 [18] LIANG C, LIU W, ZHENG Y, et al. Fractal nature of non-spherical silica particles via facile synthesis for the abrasive particles in chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2016,500:146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.04.031 [19] LIANG C, LIU W, LI S, et al. A nano-scale mirror-like surface of Ti–6Al–4V attained by chemical mechanical polishing [J]. Chinese Physics B,2016,25(5):058301. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/5/058301 [20] MUHAMMAD S N F A, MOHD Y M H, SENG O B, et al. Ultrafiltration based on various polymeric membranes for recovery of spent tungsten slurry for reuse in chemical mechanical polishing process [J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2018,548:232-238. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.034 [21] KHANNA A J, GUPTA S, KUMAR P, et al. Study of agglomeration behavior of chemical mechanical polishing slurry under controlled shear environments [J]. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology,2018,7(5):P238-P242. doi: 10.1149/2.0091805jss [22] CHAVOSHI S Z, LUO X. Hybrid micro-machining processes: A review [J]. Precision Engineering,2015,41:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.03.001 [23] YU T, ZHANG T, YU X, et al. Study on optimization of ultrasonic-vibration-assisted polishing process parameters [J]. Measurement,2019,135:651-660. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.008 [24] KANG J W, HU Y S, MA J Y, et al. Effect of different air content on cavitation with ultrasonic treatment [J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013(655/657):43-47. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.655-657.43 [25] ZHAO Q, SUN Z, GUO B. Material removal mechanism in ultrasonic vibration assisted polishing of micro cylindrical surface on SiC [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2016,103:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.01.003 [26] ZHOU M, ZHONG M, XU W. Effects of ultrasonic amplitude on sapphire ultrasonic vibration assisted chemical mechanical polishing by experimental and CFD method [J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures,2022,29(28):7086-7103. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2021.1992691 [27] CHEN X, LIANG Y, CUI Z, et al. Study on material removal mechanism in ultrasonic chemical assisted polishing of silicon carbide [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,84:1463-1477. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.11.014 [28] YU T, ZHANG T, YANG T, et al. CFD simulation and experimental studies of suspension flow field in ultrasonic polishing [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2019,266:715-725. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.11.034 [29] MCTAVISH S, FESZTY D, NITZSCHE F. Evaluating Reynolds number effects in small-scale wind turbine experiments [J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2013,120:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2013.07.006 [30] SHAHEED R, MOHAMMADIAN A, KHEIRKHAH G H. A comparison of standard k–ε and realizable k–ε turbulence models in curved and confluent channels [J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics,2019,19(2):543-568. doi: 10.1007/s10652-018-9637-1 [31] SAHU S, BHATTACHARYAY R. Validation of COMSOL code for analyzing liquid metal magnetohydrodynamic flow [J]. Fusion Engineering and Design,2018,127:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.01.009 [32] IVORRA B. Application of the laminar navier–stokes equations for solving 2D and 3D pathfinding problems with static and dynamic spatial constraints: Implementation and validation in comsol multiphysics [J]. Journal of Scientific Computing,2018,74(2):1163-1187. doi: 10.1007/s10915-017-0489-5 [33] RAHAEIFARD M, KARIMZADEH A. A size-dependent axisymmetric plate element: Application to MEMS [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics,2024,94(3):667-681. doi: 10.1007/s00419-024-02544-2 -




 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
