Effect of TiH2 addition on grinding performance of Cu3Sn intermetalliccompound diamond wheels
-
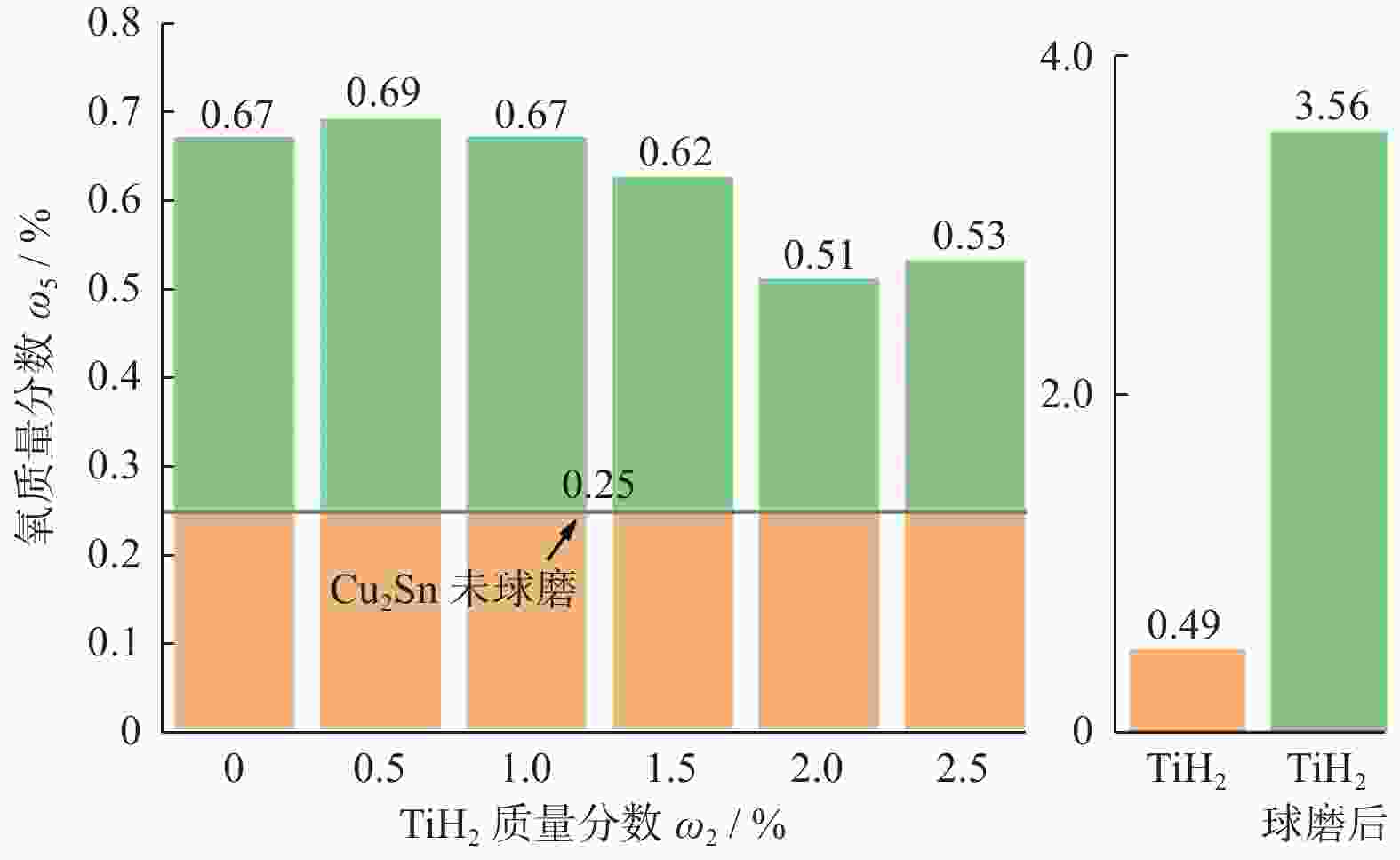
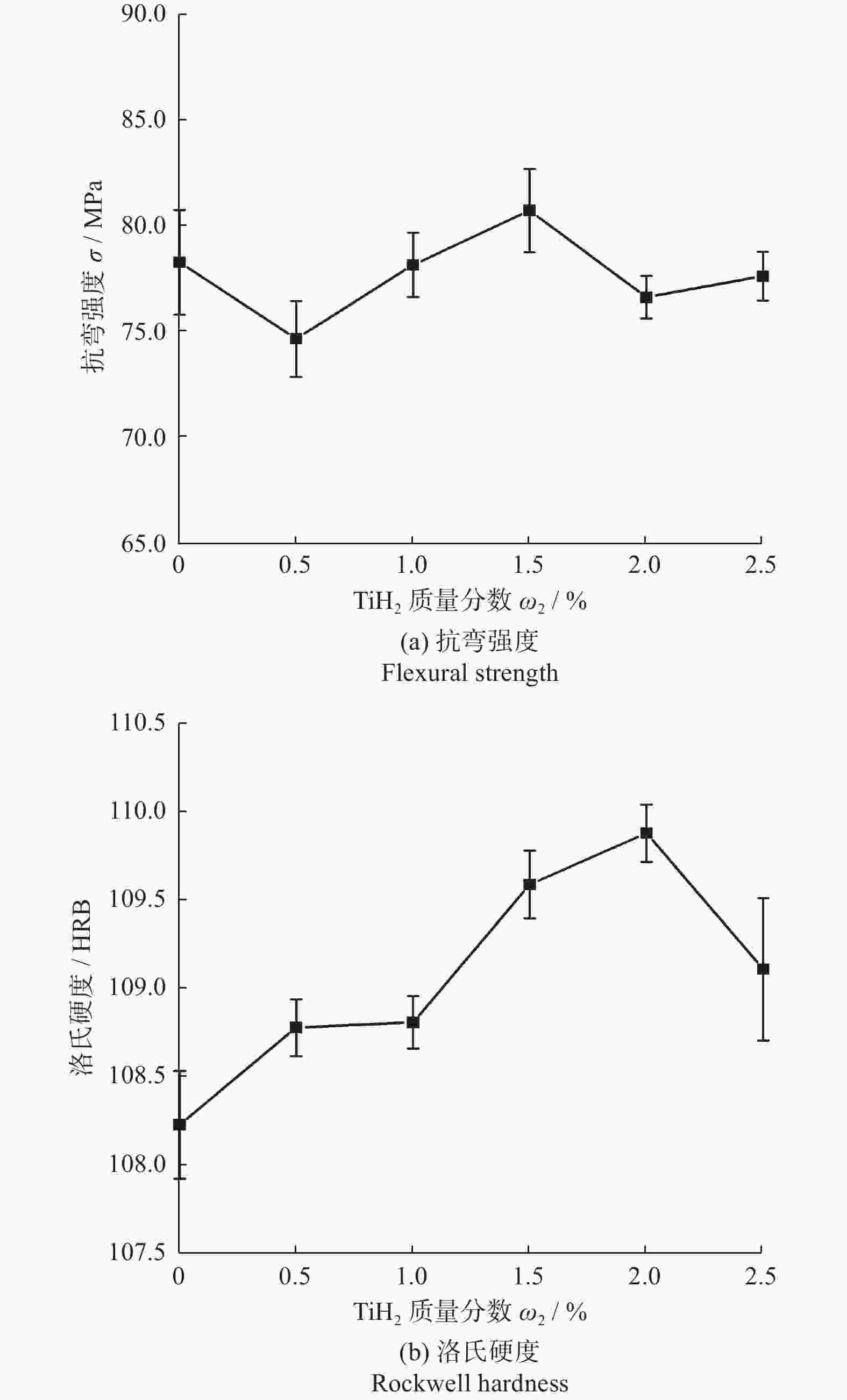
摘要: 为进一步提升Cu3Sn金属间化合物金刚石砂轮的锋利度和保形性,制备不同TiH2加入量的Cu3Sn金属间化合物球磨粉末、金刚石磨块及砂轮。通过对微观形貌、氧含量、物相组成、热效应、力学性能等进行测试和分析,探究TiH2对Cu3Sn金属间化合物金刚石砂轮磨削性能的影响。研究结果表明:TiH2对Cu3Sn球磨粉末有抑制增氧的作用,促进粉末烧结。当TiH2的质量分数为2.0%时,氧质量分数从0.67%降低到最小值0.51%。TiH2能够提高胎体对金刚石的把持力,可提高试样的抗弯强度和硬度:当TiH2的质量分数为1.5%时,抗弯强度达到最大值80.74 MPa;当TiH2的质量分数为2.0%时,洛氏硬度达到最大值109.88 HRB;当TiH2的加入量继续增大时,抗弯强度和硬度反而下降。TiH2可提升砂轮的磨削性能,磨削YG8硬质合金时,加入质量分数为2.0%的TiH2使金刚石砂轮最快进给速率从0.020 mm / 次提升到0.035 mm / 次,磨削比从51.09提升到最大值172.03。Abstract:
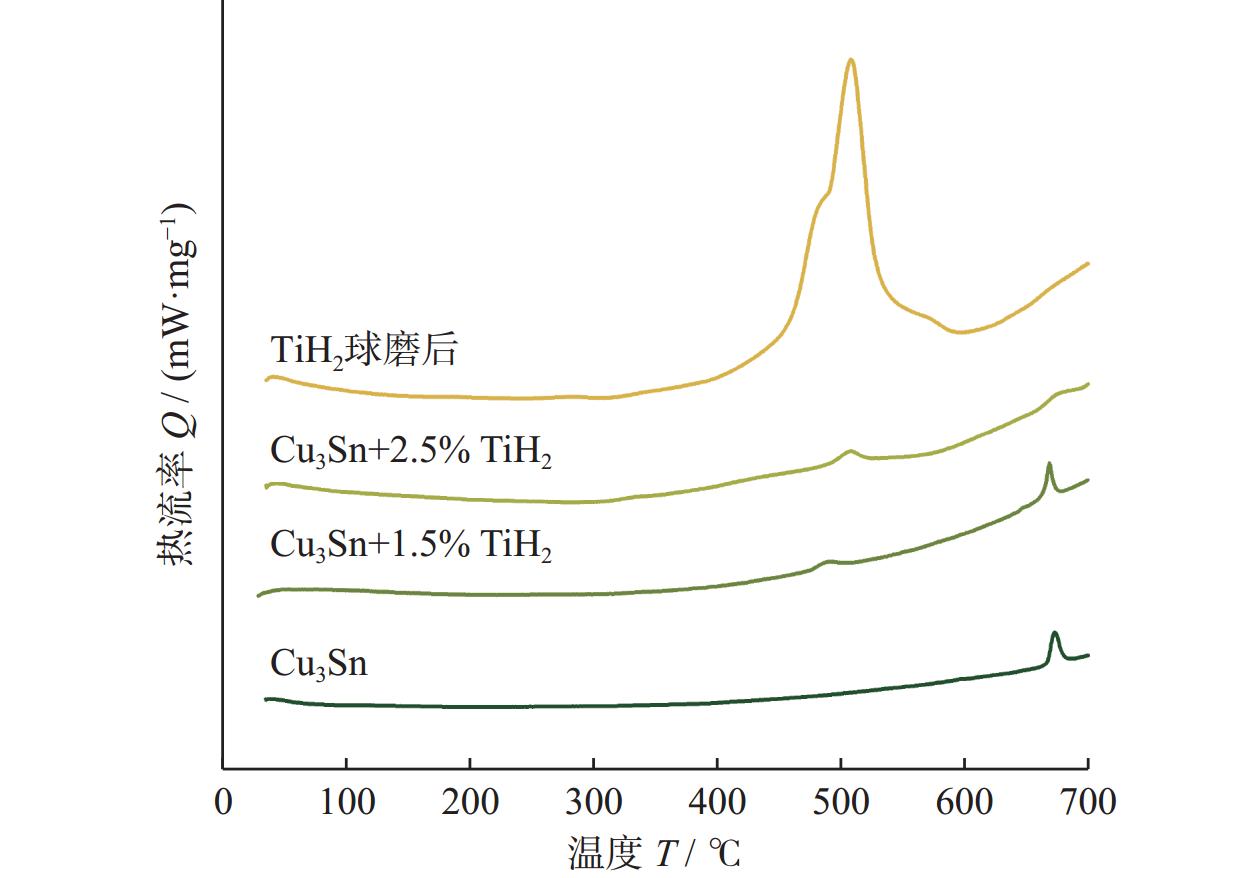
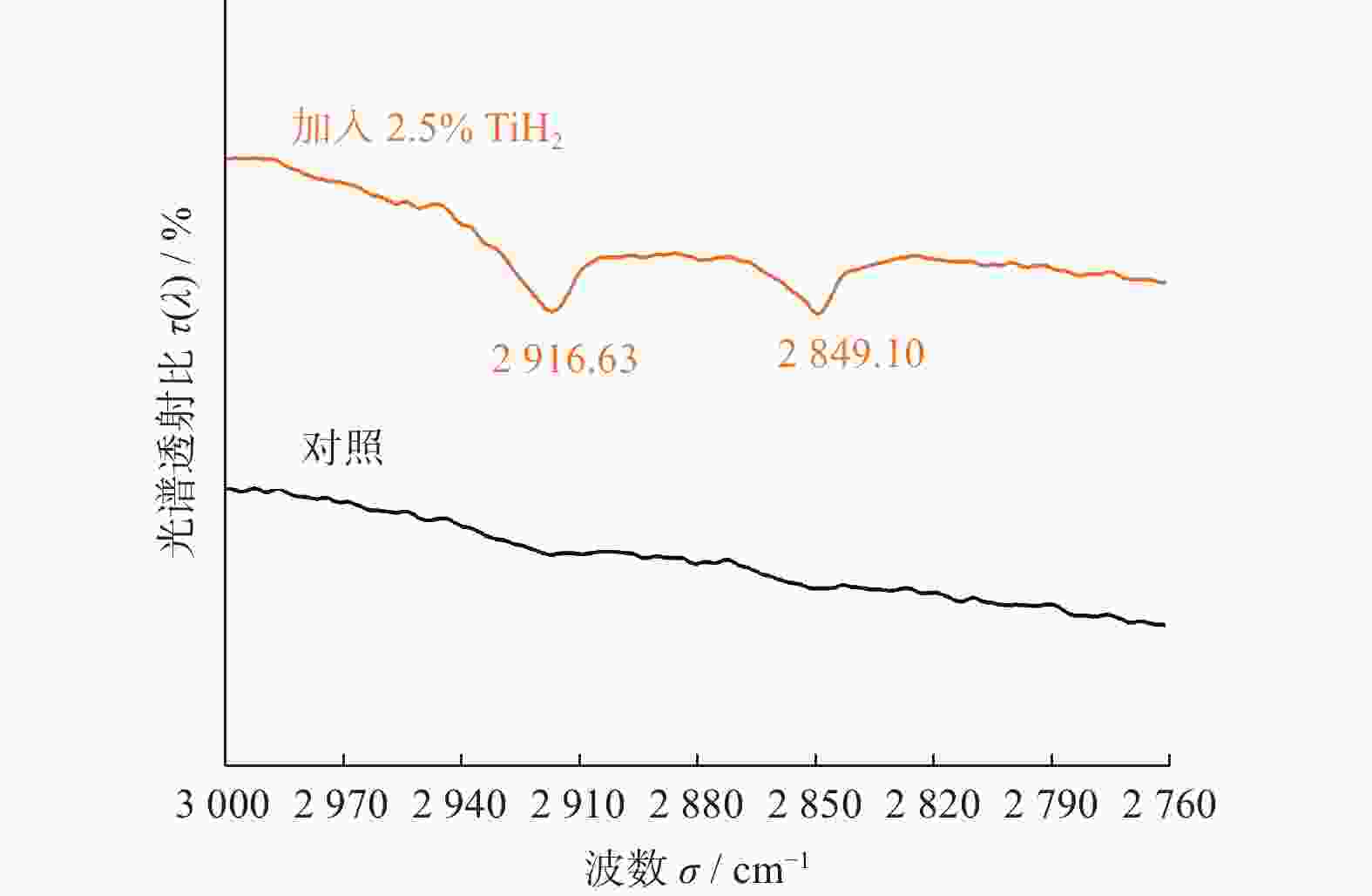
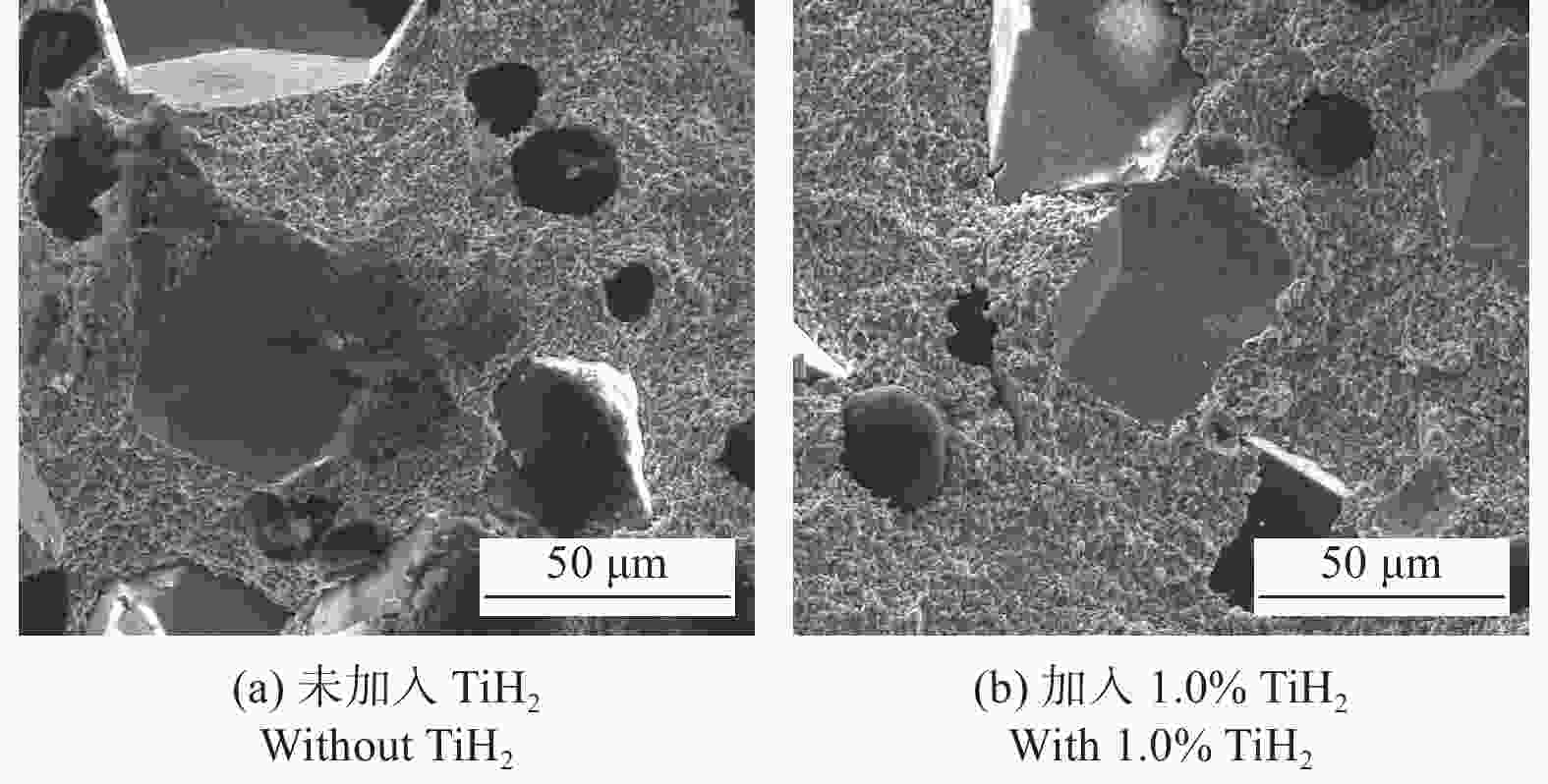
Objectives With the development of the modern manufacturing industry, the requirements for material machining accuracy and surface quality are increases continuously. For the precision grinding of high hardness and high wear-resistant materials, superhard material grinding wheels are required to possess high processing efficiency and durability. Intermetallic compound bond diamond grinding wheels have the wear resistance of metal grinding wheels and the self-sharpness of ceramic grinding wheels simultaneously, but they still lacks of sharpness or shape retention when machining hard and brittle materials at high loads and high speeds. To improve the sharpness and shape retention of Cu3Sn intermetallic compound diamond grinding wheels, this study investigates the addition of TiH2. Cu3Sn ball-milling powders, diamond grinding blocks, and grinding wheels with different TiH2 additions are prepared. Methods The effects of TiH2 addition on the grinding performance of Cu3Sn intermetallic diamond grinding wheels are investigated using testing and analyzing the micro-morphology, oxygen content, physical phase composition, thermal effect, and mechanical properties. Results (1) TiH2 was added to the Cu3Sn intermetallic compound bond, and the mixture is ball milled together. TiH2 inhibits the increase in oxygen content, which improves the properties of the ball-milled bond powder and facilitated the sintering process. When TiH2 is added with a mass fraction of 2.0%, the oxygen content is reduced from 0.67% to a minimum value of 0.51%. (2) TiH2 decomposes into Ti and H2 during the sintering process, and Ti could react with the C atoms on the surface of the diamond to form a Ti—C bond. This chemical bonding between the metal bond and diamonds could increased the bonding strength. TiH2 could improve the mechanical properties of diamond grinding blocks, but a larger amount of TiH2 increased the pores in the metal bond, which reduced its strength. When TiH2 mass fraction is 1.5%, the flexural strength reaches the maximum value of 80.74 MPa, and the addition of 2.0% TiH2 increased the Rockwell hardness to reaches a maximum value of 109.88 HRB. (3) Adding of an appropriate amount of TiH2 forms a chemical metallurgical bond between diamonds and the bonding agent, which strengthens the holding force of the bonding agent to the diamonds, increases the protrusion height and chip space on the working surface, and improves the sharpness of the grinding wheel. At the same time, it can avoid the premature shedding of diamonds, reducing the consumption of the working layer and improving the shape retention of the grinding wheel. The grinding wheels prepared by adding a certain amount of TiH2 prior to the ball milling treatment of Cu3Sn bond powder exhibited better grinding performance. Both sharpness and shape retention are enhanced. When grinding YG8 cemented carbide, the addition of 2.0% TiH2 enhanced the fastest feed rate of the grinding wheel from 0.020 mm/feed to 0.035 mm/feed. Meanwhile, the grinding ratio of the wheel reached a maximum value of 172.03, which is enhanced by 237% compared with the specimen without TiH2 addition. Conclusions In this paper, TiH2 is added to Cu3Sn intermetallic compounds by ball milling, and the oxygen content of the bond powder is reduced. At the same time, the carbide-formation element Ti reacts with the diamond to form a chemical metallurgical bond, which improves the bonding strength between the diamond and the bonding agent. This results in improved grinding performance of the diamond wheel and provides a reference for the design and development of diamond grinding wheels with high sharpness and high conformal retention. -
Key words:
- TiH2 /
- intermetallic compounds /
- mechanical properties /
- grinding ratio
-
表 1 实验试剂
Table 1. Experimental reagents
试剂 纯度 /
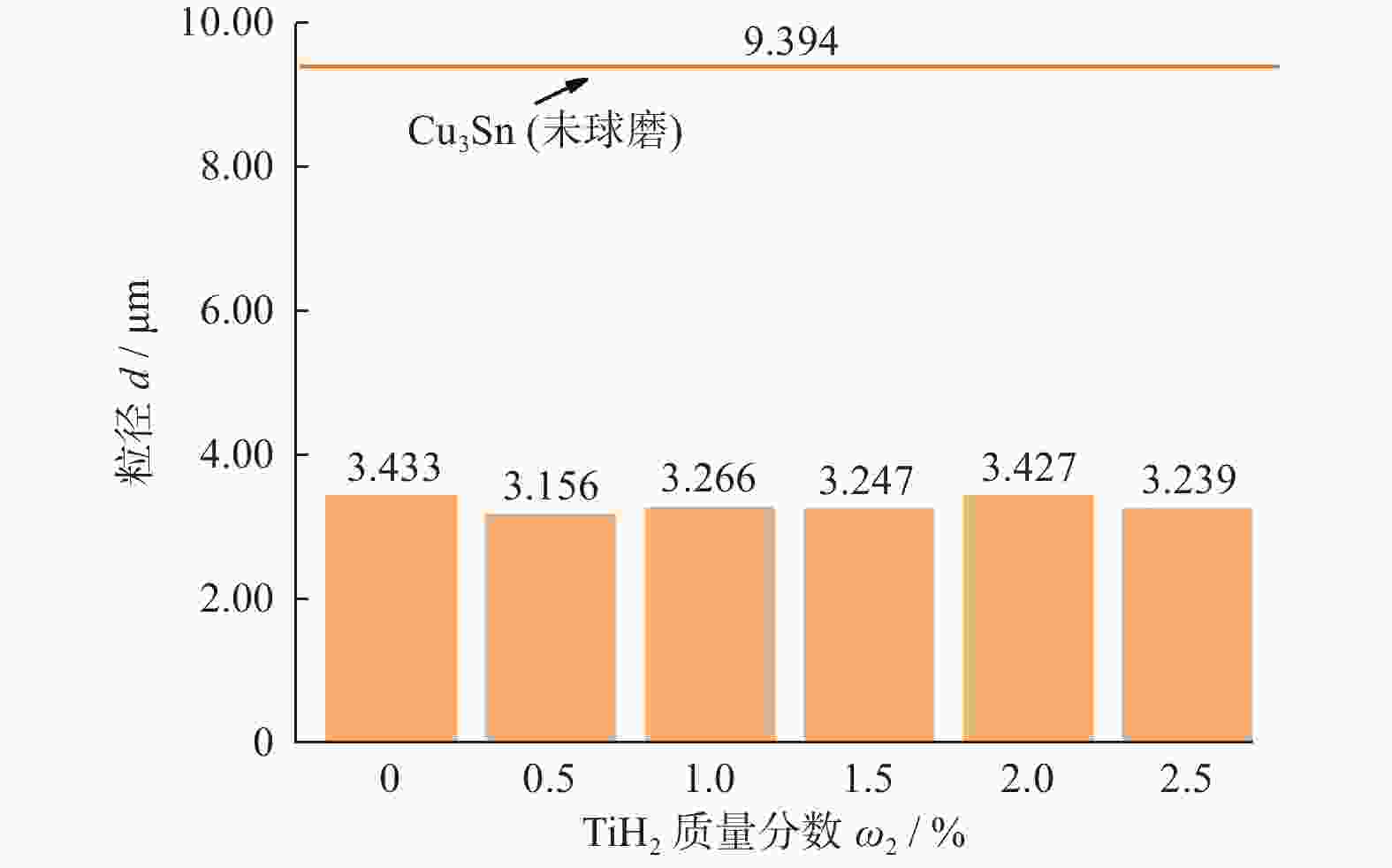
质量分数粒度 生产商 Cu3Sn >99.9% 9.394 μm
(D50)有研新材料股份有限公司 TiH2 >99.7% <38 μm 成都国衡科技有限公司 无水乙醇 AR,>99.7% 湖南汇虹试剂有限公司 球形石墨 >99.0% 20~30 μm 中钢碳素化学股份有限公司 金刚石 >98.0% 53 / 45 μm 郑州金开新材料科技
有限公司硬脂酸 AR 天津市科密欧化学试剂
有限公司浓盐酸 AR,36.0%~38.0% 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 浓硝酸 AR,65.0%~68.0% 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 表 2 实验仪器
Table 2. Experimental instruments
仪器 型号 制造商 行星式球磨机 XQM-2 长沙天创粉末技术
有限公司电热恒温烘箱 101-3 兴化市金虎电热电器
有限公司三维混料机 Turbula T2C Willy A. Bachofen AG
Maschinenfabrik四柱液压机 YQ32-400 山东滕州泰力数控机床
有限公司箱式电阻炉 SX-12-10 长沙市长城电炉厂 场发射扫描电子显微镜 Quanta FEG 250 FEI Company, Inc. 激光粒度分布仪 BT-9300H 丹东百特仪器有限公司 X射线衍射仪 Empyrean PANalytical B.V. 氧氮氢分析仪 TCH600 LECO Corporation 同步热分析仪 STA 449F3 NETZSCH 微机控制电子
万能试验机LD25.504 深圳市兰博三思材料检测
有限公司数显洛氏硬度计 200HRS-150 莱州华银试验仪器
有限公司傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 Nicolet™ iS50 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. 三维超景深显微镜 VHX- 5000 KEYENCE Corporation 卧轴矩台平面磨床 SG2550AHD 上海启哲实业有限公司 表 3 金刚石磨块及砂轮的配方设计
Table 3. Formulation of diamond grinding blocks and wheels
样品 Cu3Sn质量
分数 ω1 / %TiH2质量
分数 ω2 / %石墨质量
分数 ω3 / %金刚石质量
分数 ω4 / %对照 88.5 0 1.5 10 1 88.0 0.5 1.5 10 2 87.5 1.0 1.5 10 3 87.0 1.5 1.5 10 4 86.5 2.0 1.5 10 5 86.0 2.5 1.5 10 表 4 Cu3Sn / TiH2金刚石砂轮磨削YG8硬质合金的实验数据
Table 4. Experimental data of Cu3Sn / TiH2 diamond grinding wheel grinding YG8 cemented carbide
TiH2质量分数
ω2 / %最快进给速率
v / (mm / 次)硬质合金体积变化值
V1 / mm3砂轮体积变化值
V2 / mm3磨削比
G磨耗比
Φ表面粗糙度
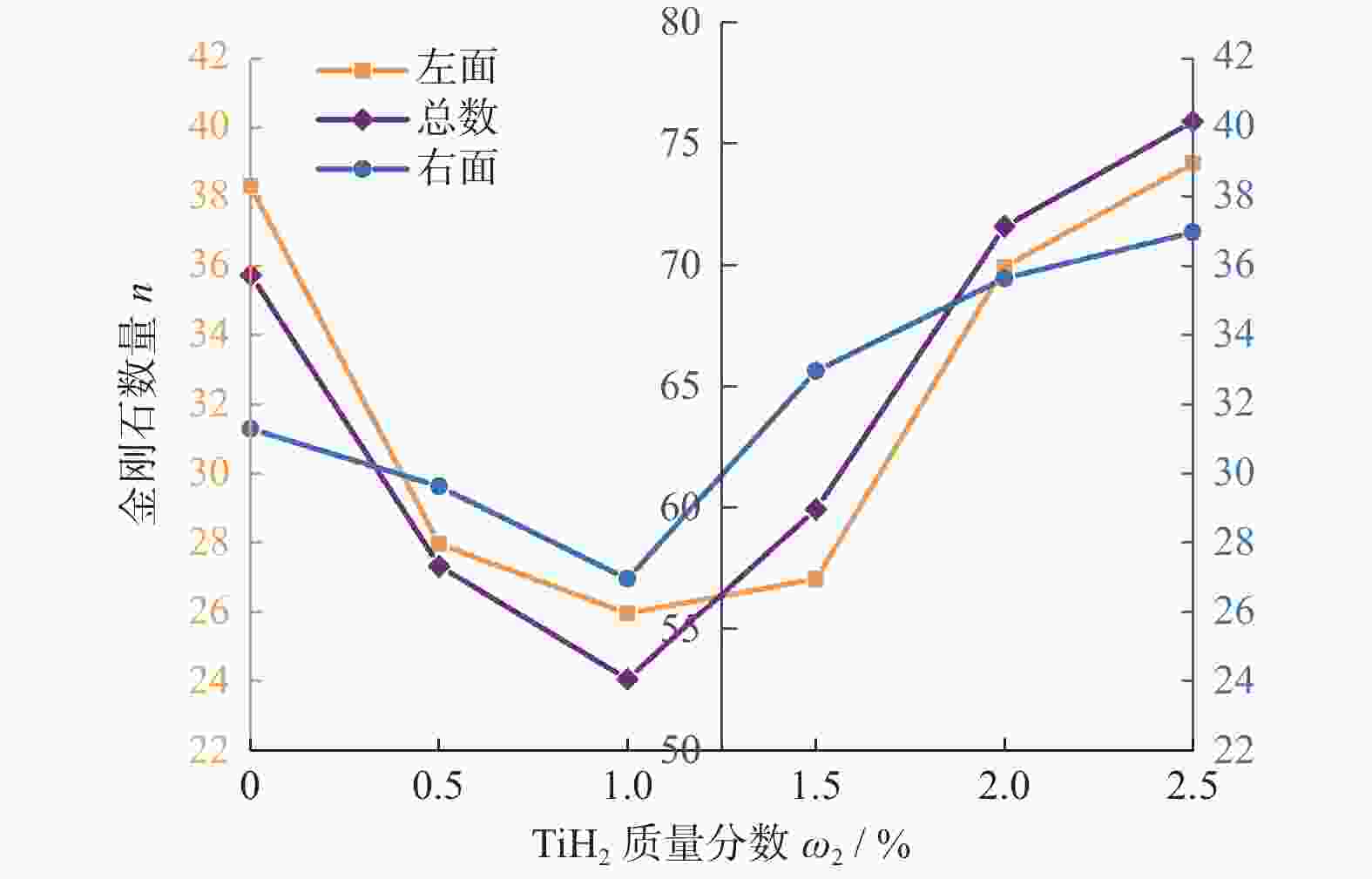
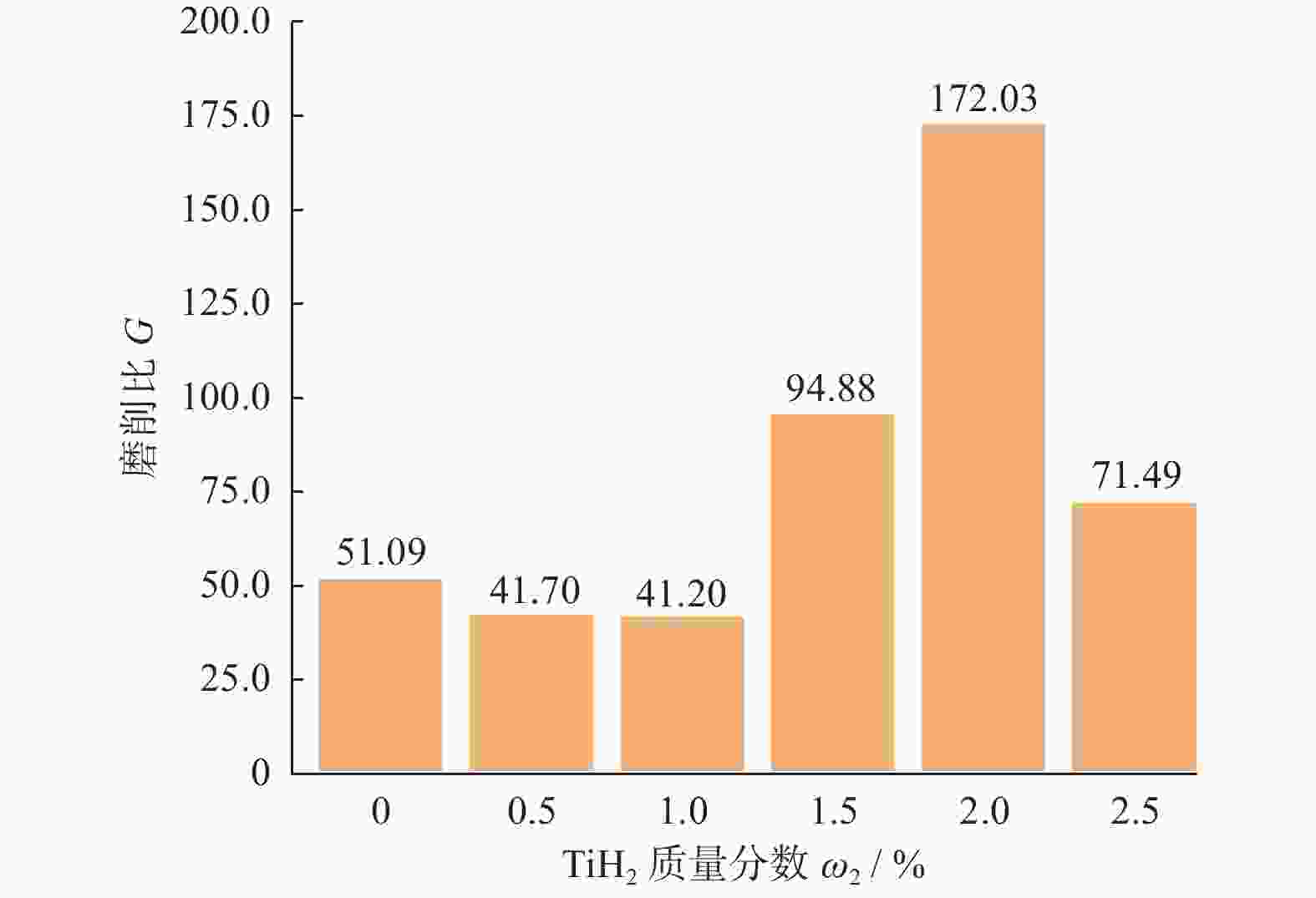
Ra / μm0 0.020 10 276.08 201.140 0 51.09 0.019 6 0.07 ~ 0.11 0.5 0.030 10 074.87 241.623 0 41.70 0.024 0 0.05 ~ 0.09 1.0 0.040 10 200.30 247.557 6 41.20 0.024 3 1.5 0.030 10 390.62 109.513 1 94.88 0.015 0 2.0 0.035 10 436.30 60.648 8 172.03 0.005 8 2.5 0.040 10 362.18 144.938 5 71.49 0.014 0 -
[1] 胡妙. 利用激光熔覆在钢铁表面制备WC-Co耐磨涂层的工艺及机理研究 [D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020.HU Miao. Study on the process and mechanism of WC-Co wear-resistant coating on the surface of steel by laser cladding [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020. [2] UPADHYAYA G S. Materials science of cemented carbides: An overview [J]. Materials & Design,2001,22(6):483-489. doi: 10.1016/S0261-3069(01)00007-3 [3] 谭兴龙, 易茂中, 罗崇玲. 球形钴粉的制备及其在超细晶粒硬质合金中的应用 [J]. 中国有色金属学报,2008,18(2):209-214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.02.003TAN Xinglong, YI Maozhong, LUO Chongling. Preparation of spherical cobalt powder and its application in ultra-fine cemented carbides [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2008,18(2):209-214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.02.003 [4] HE M, WANG J Y, HE R G, et al. Effect of cobalt content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of coarse grained WC-Co cemented carbides fabricated from chemically coated composite powder [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,766:556-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.366 [5] 李志远, 李益民, 何浩, 等. 磨削硬质合金用金属结合剂金刚石砂轮的性能影响因素 [J]. 有色金属科学与工程,2016,7(6):77-82. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2016.06.013LI Zhiyuan, LI Yimin, HE Hao, et al. Metallic bond diamond grinding wheel for grinding cemented carbide [J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering,2016,7(6):77-82. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2016.06.013 [6] 范红伟, 袁巨龙, 吕冰海, 等. 金属结合剂砂轮的研究与发展 [J]. 航空精密制造技术,2010,46(4):38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2010.04.010FAN Hongwei, YUAN Julong, LV Binghai, et al. Progress and prospects of metal bonded grinding wheel [J]. Aviation Precision Manufacturing Technology,2010,46(4):38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2010.04.010 [7] 何聪华, 袁慧. 精密金刚石砂轮的制造、修整及其磨削机理研究进展 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2008,20(4):30-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2008.04.009HE Conghua, YUAN Hui. Development of research on the manufacturing, dressing and grinding mechanism of diamond grinding wheel [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2008,20(4):30-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2008.04.009 [8] 杨佳乐, 尹育航, 刘震, 等. 稀土元素及其化合物在超硬磨具中的应用 [J]. 中国稀土学报,2021,39(6):871-880. doi: 10.11785/S1000-4343.20210605YANG Jiale, YIN Yuhang, LIU Zhen, et al. Application of rare earth elements and their compounds in superhard abrasive tools [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths,2021,39(6):871-880. doi: 10.11785/S1000-4343.20210605 [9] CHEN S P, KANG X Y, HE Y H. Study on the preparation of NiAl intermetallic-bonded diamond grinding block and grinding performance for sapphire [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022,130:109490. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109490 [10] 唐洲, 贺跃辉, 陈帅鹏. 烧结温度对Ti-Al金属间化合物黏结剂金刚石磨块力学性能和磨削性能的影响 [J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2023,28(3):288-295. doi: 10.19976/j.cnki.43-1448/TF.2023032TANG Zhou, HE Yuehui, CHEN Shuaipeng. Effects of sintering temperature on mechanical and grinding properties of Ti-Al intermetallic-bonded diamond grinding block [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy,2023,28(3):288-295. doi: 10.19976/j.cnki.43-1448/TF.2023032 [11] 高洪吾, 刘士魁, 赵彦波, 等. 加热氧化处理对TiH2释氢行为的影响 [J]. 中国有色金属学报,2005,15(3):363-367. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2005.03.007GAO Hongwu, LIU Shikui, ZHAO Yanbo, et al. Effect of heat oxidation treatment on gas release behavior of TiH2 [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2005,15(3):363-367. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2005.03.007 [12] 王俊程. 基于TiH2 + TiB2反应制备原位TiBw / Ti复合材料的组织性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021.WANG Juncheng. Research on microstructure and properties of in-situ TiBw / Ti composites prepared by basing on the reaction between TiH2 and TiB2 powders [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. [13] 刘恒源. 多孔金属结合剂磨具的制备与性能研究 [D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2021.LIU Hengyuan. Study on the process and mechanism of WC-Co wear-resistant coating on the surface of steel by laser cladding [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2021. [14] 王耀奇, 张宁, 任学平, 等. 氢化钛的动态分解行为与规律 [J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2011,16(6):795-798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.06.001WANG Yaoqi, ZHANG Ning, REN Xueping, et al. Behavior and rule of titanium hydride dynamic decomposition [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy,2011,16(6):795-798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.06.001 [15] 曹杰义, 肖平安, 雷豹, 等. TiH2粉末的高能行星球磨及超细晶钛烧结 [J]. 中国有色金属学报,2013,23(10):2825-2832. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.10.013CAO Jieyi, XIAO Ping'an, LEI Bao, et al. High-energy planetary milling of TiH2 powders and sintering of titanium alloy with ultrafine grains [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2013,23(10):2825-2832. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.10.013 [16] 王高峰, 松林, 欧志强, 等. MnFeP0.6Si0.25Ge0.15粉末样品的制备及X射线衍射分析 [J]. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版),2007,36(2):156-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8735.2007.02.009WANG Gaofeng, SONG Lin, OU Zhiqiang, et al. Preparation and X-ray diffraction analysis of MnFeP0.6Si0.25Ge0.15 powder [J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2007,36(2):156-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8735.2007.02.009 [17] 丁天然, 龙伟民, 张海燕, 等. 氧含量对金刚石工具胎体力学性能的影响 [J]. 焊接,2013(1):42-44,70-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2013.01.010DING Tianran, LONG Weimin, ZHANG Haiyan, et al. Effect of oxygen content on mechanical properties in diffusion welding Fe-based matrix and diamond tool [J]. Welding & Joining,2013(1):42-44,70-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2013.01.010 -



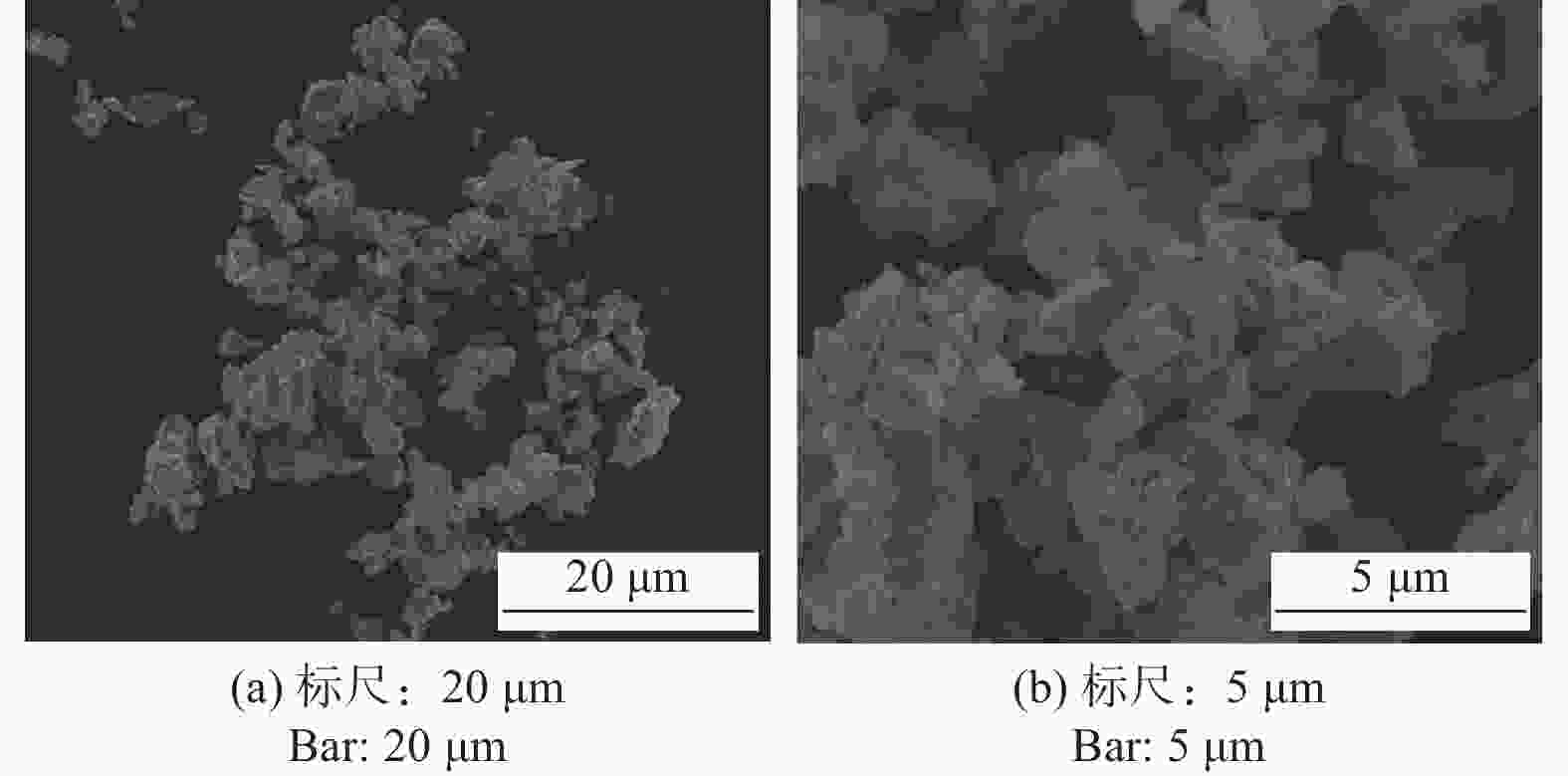
 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
