The experimental study on structured topological fish scale surface by micro-abrasive jet machining
-
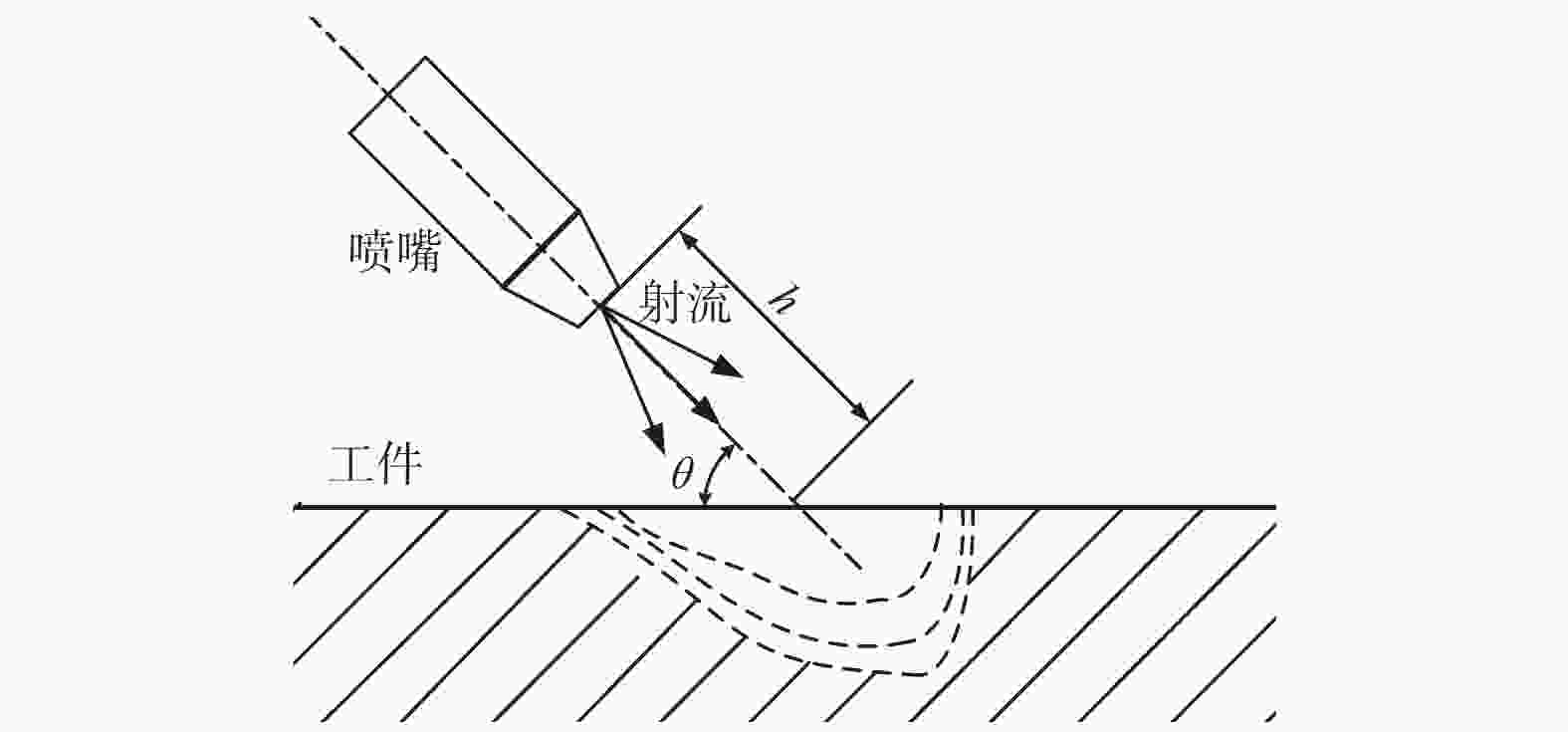
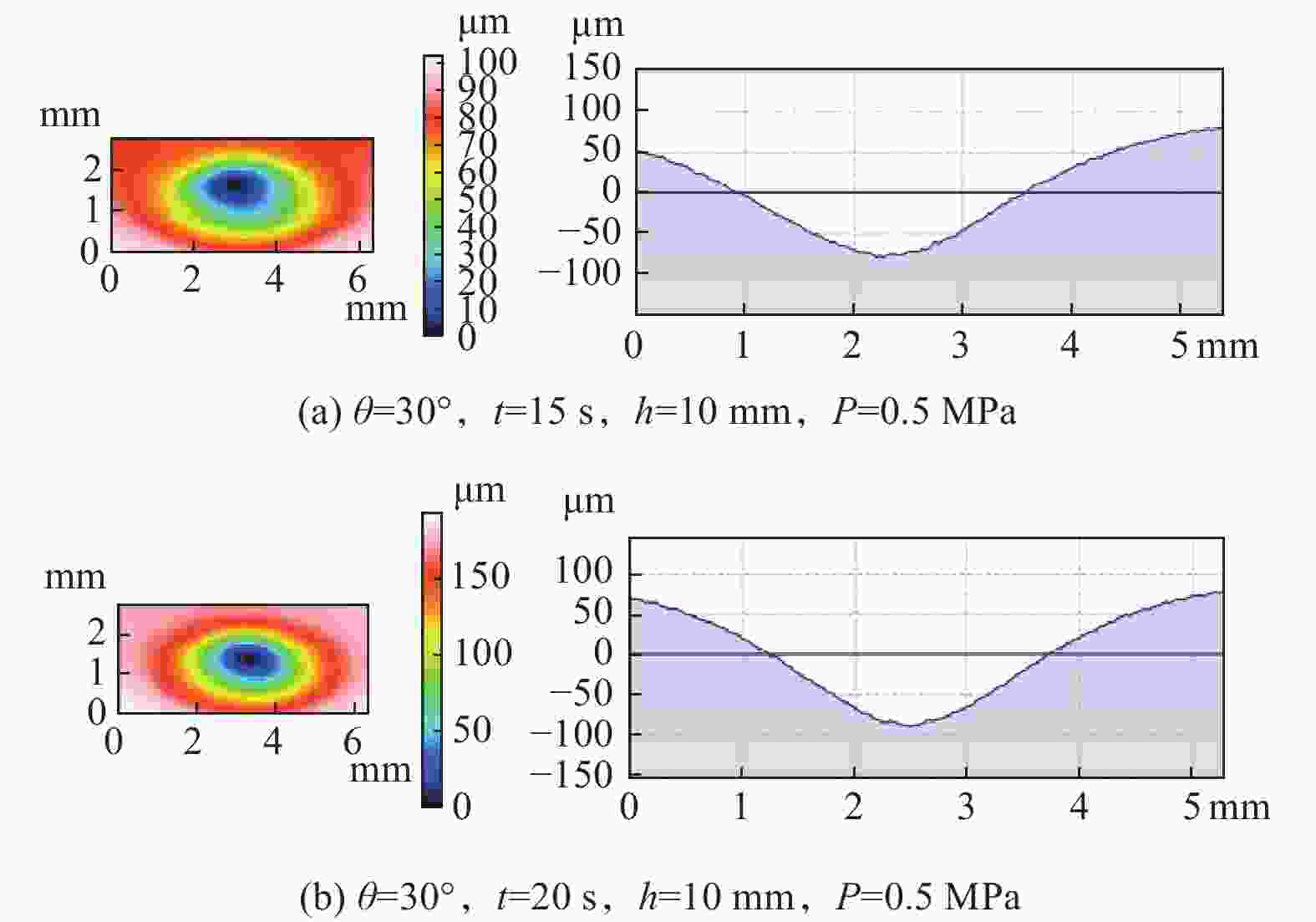
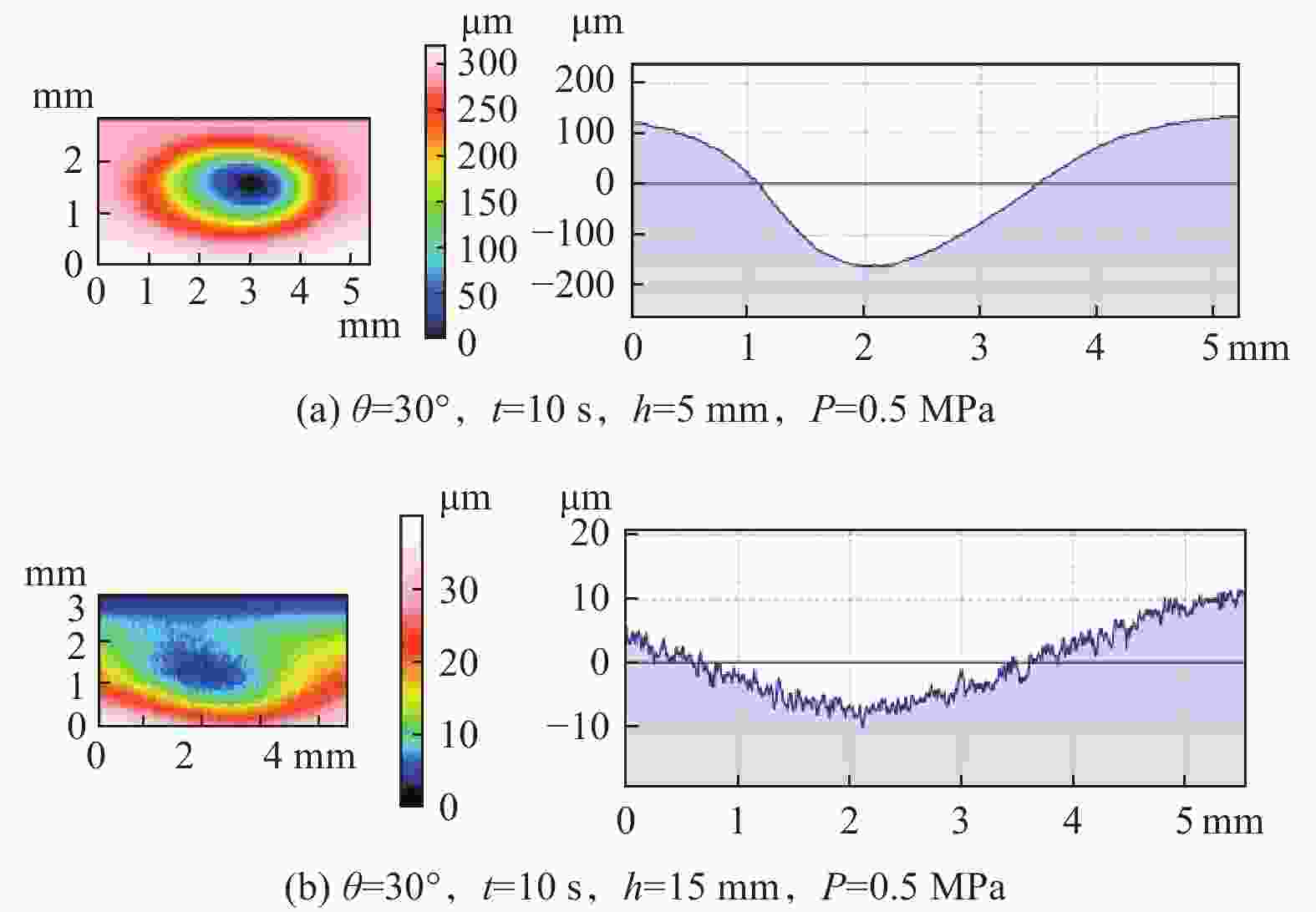
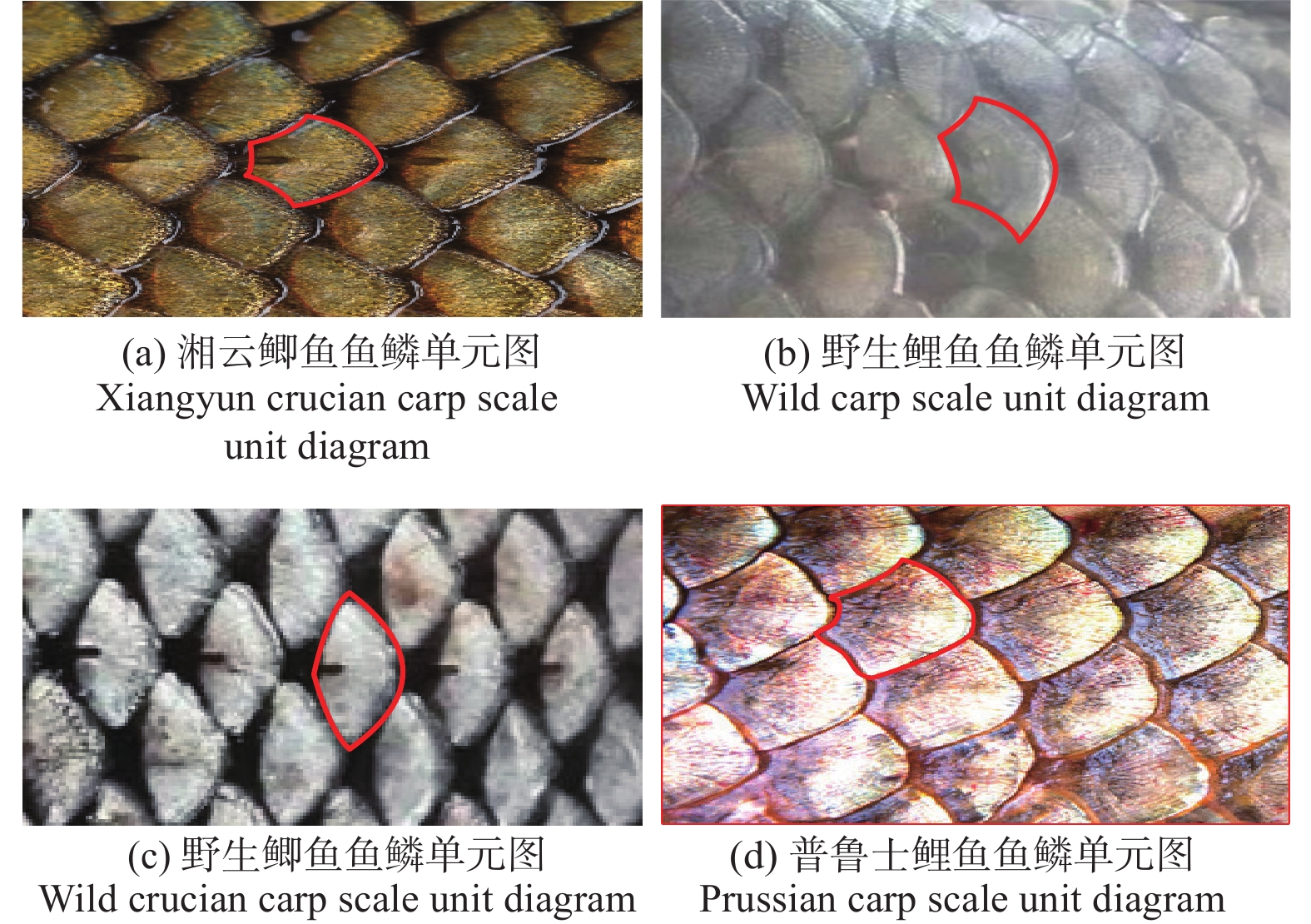
摘要: 为了在脆性难加工材料上制备结构化鱼鳞表面,首先提取了鱼鳞表面的拓扑特征,建立了鱼鳞单元的表面模型,并基于鱼鳞模型进行搭接,得到结构化鱼鳞表面;然后根据微磨料气射流加工原理,分析了气射流加工拓扑鱼鳞实验的可行性与影响结构化鱼鳞表面形貌的重要工艺参数;最后采用单因素实验法对重要加工参数进行实验分析,得到了较好的拓扑鱼鳞表面单元,并以此进行排布得到结构化表面。研究结果表明,微磨料气射流加工结构化拓扑鱼鳞表面较为合理的工艺参数组合是加工时间为10 s、气射流加工压力为0.5 MPa、靶距离为10 mm以及射流角度为30°,在此工艺条件下,鱼鳞表面的形态和尺寸可能会受到一定的影响,但鱼鳞表面的拓扑属性保持不变。Abstract: To prepare structured fish scale surfaces on brittle and difficult-to-process materials, the topological features of fish scale surfaces are first extracted, and a surface model of fish scale units is established. This fish scale model is then used to construct the structured fish scale surface. Next, based on the principle of micro-abrasive air jet processing, the feasibility of air jet processing for topological fish scale experiments and the important process parameters affecting the morphology of the structured fish scale surface are analyzed. Finally, using the single-factor experimental method, the important processing parameters are experimentally analyzed to obtain a better topological fish scale surface unit, and the structured surface is arranged accordingly. The research results show that a reasonable combination of process parameters for micro-abrasive jet machining of structured topological fish scale surfaces includes a machining time of 10s, a machining pressure of 0.5 MPa, a stand-off distance of 10 mm, and a jet angle of 30°. Despite the potential for certain effects on the morphology and size of the fish scale surface, the topological properties of the fish scale surface remain unchanged using the proposed machining method.
-
表 1 单因素实验设计表
Table 1. Single factor experimental design table
编号 射流角度/(°) 加工时间/s 靶距离/mm 加工压力/MPa 1 30 10 10 0.5 2 45 10 10 0.5 3 60 10 10 0.5 4 30 15 10 0.5 5 30 20 10 0.5 6 30 10 5 0.5 7 30 10 15 0.5 8 30 10 10 0.4 9 30 10 10 0.6 -
[1] 段婷婷, 郑威, 黄玉松. 鱼鳞的结构及其仿生材料 [J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2017,38(4):288-292.DUAN Tingting, ZHENG Wei, HUANG Yusong. Research progress of the structure and biomimetic materials of scales [J]. Journal of Jinan University(Natural Science & Medicine Edition),2017,38(4):288-292. [2] 陶国灿. 超声振动辅助铣削鱼鳞状表面成形机理及表面性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016.TAO Guocan. Study on the forming mechanism and surface properties of ultrasonic vibration assisted milling for squamous surfaces[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. [3] WANG Y H, ZHAN Z B, XU J K, et al. One-step method using laser for large-scale preparation of bionic superhydrophobic & drag-reducing fish-scale surface [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2021(409):1-15. [4] 白利娟, 张建华, 陶国灿, 等. 振动辅助铣削加工仿生表面研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2016, 27(9): 1229-1233, 1242.BAI Lijuan, ZHANG Jianhua, TAO Guocan, et al. Vibration assisted milling for bionic surface manufacturing[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 27(9): 1229-1233, 1242. [5] 张德远, 李元月, 韩鑫, 等. 高精度复合减阻鲨鱼皮复制成形研究 [J]. 科学通报,2010,55(32):3122-3127. doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-32-3122ZHANG Deyuan, LI Yuanyue, HAN Xin, et al. Study on shark skin reproduction with high precision composite drag reduction [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(32):3122-3127. doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-32-3122 [6] 韩鑫, 张德远, 李翔, 等. 大面积鲨鱼皮复制制备仿生减阻表面研究 [J]. 科学通报,2008,53(7):838-842. doi: 10.1360/csb2008-53-7-838HAN Xin, ZHANG Deyuan, LI Xiang, et al. Study on reproduction of large area shark skin to produce biomimetic drag reducing surface [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2008,53(7):838-842. doi: 10.1360/csb2008-53-7-838 [7] LIU Y, ZHANG H, DAI S, et al. Designing a bioinspired scaly textured surface for improving the tribological behaviors of starved lubrication [J]. Tribology International,2022(173):1-7. [8] 李进金, 李克典, 林寿. 基础拓扑学导引[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.LI Jinjin, LI Kedian, LIN Shou. Introduction to fundamental topology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. [9] 樊晶明, 王成勇, 王军. 微磨料空气射流加工技术的发展 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2005(1):25-30,35.FAN Jingming, WANG Chengyong, WANG Jun. Development of micro abrasive jet machining technology [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2005(1):25-30,35. [10] SHIPWAY P H, HUTCHINGS I M. Influence of nozzle roughness on conditions in a gas-blast erosion rig [J]. Wear,1993(162/163/164):148-158. [11] SHELDON G L, KANHERE A. An investigation of impingement erosion usingsingle particles [J]. Wear,1972(21):195-209. [12] OKA Y I, OKAMURA K, YOSHIDA T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact, Part 1: Effects of impact parameterson a predictive equation [J]. Wear,2005(259):95-101. [13] 陈蒙, 赵洋洋, 卢文壮. 磨料气射流预处理的射流模拟与分析 [J]. 机械制造与自动化,2021,50(2):110-112,116.CHEN Meng, ZHAO Yangyang, LU Wenzhuang. Simulation of jet-flow of surface pretreatment by abrasive air jet machining [J]. Machine Building & Automation,2021,50(2):110-112,116. [14] 樊晶明, 王成勇, 王军, 等. 微磨料空气射流加工特性研究 [J]. 中国机械工程,2008(5):584-589.FAN Jingming, WANG Chengyong, WANG Jun, et al. Study on the machining performance of micro abrasive jet machining [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2008(5):584-589. [15] 樊晶明, 樊昶明, 王军. 微磨料水射流加工脆性玻璃的冲蚀机理研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2010,30(3):1-5.FAN Jingming, FAN Changming, WANG Jun. Erosion mechanism of brittle glass by micro-abrasive water jet [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2010,30(3):1-5. [16] 许刘宛, 吕玉山, 李兴山, 等. 结构化砂轮拓扑磨削鱼鳞表面原理及仿真分析 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2021,(9):153-156,161.XU Liuwan, LYU Yushan, LI Xingshan, et al. Principle and simulation analysis of topological grinding of fish scale surface by structured grinding wheel [J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique,2021,(9):153-156,161. -





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
