Analysis and optimization of traveling wave vibration of large diamond thin-wall drill bits
-
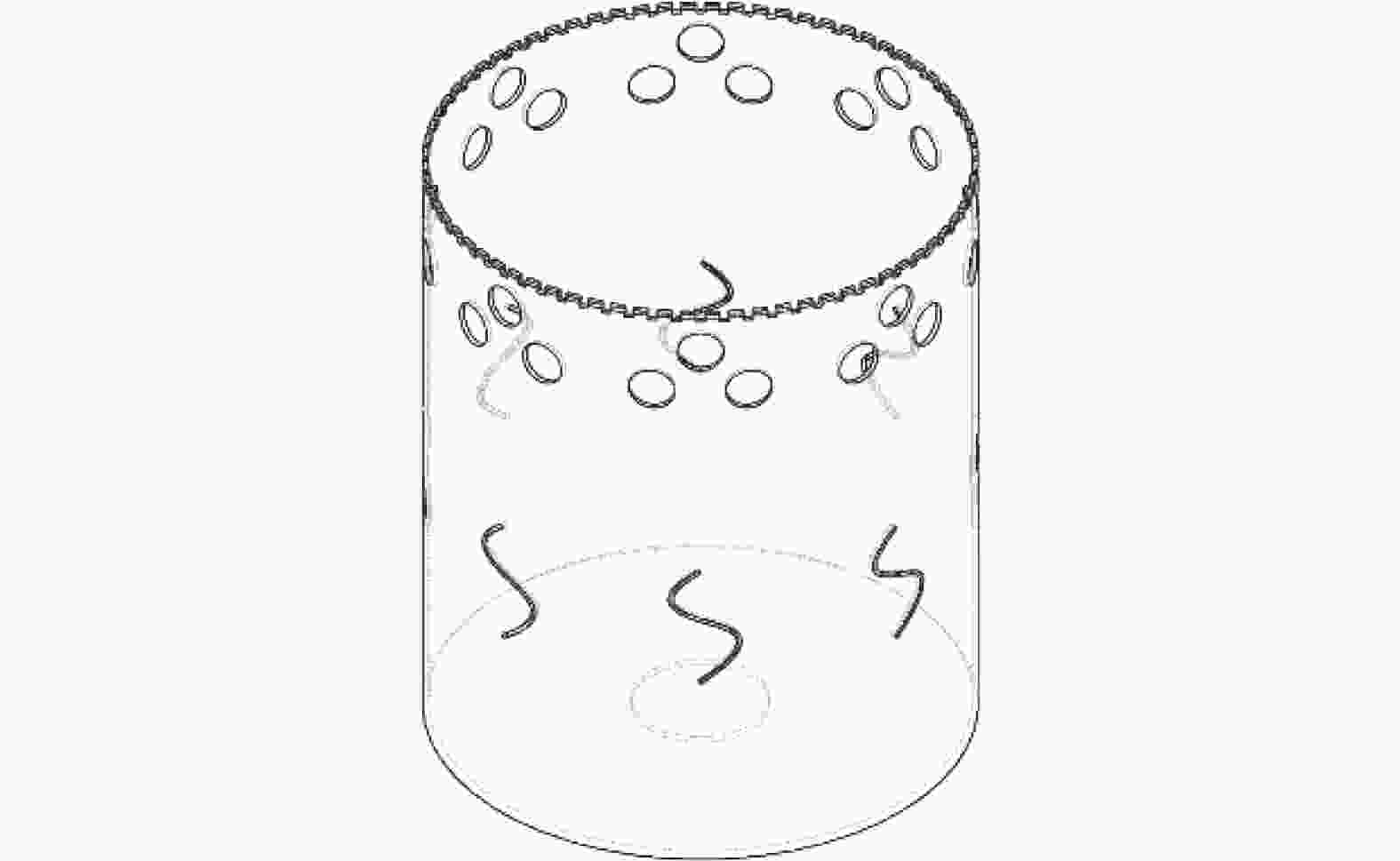
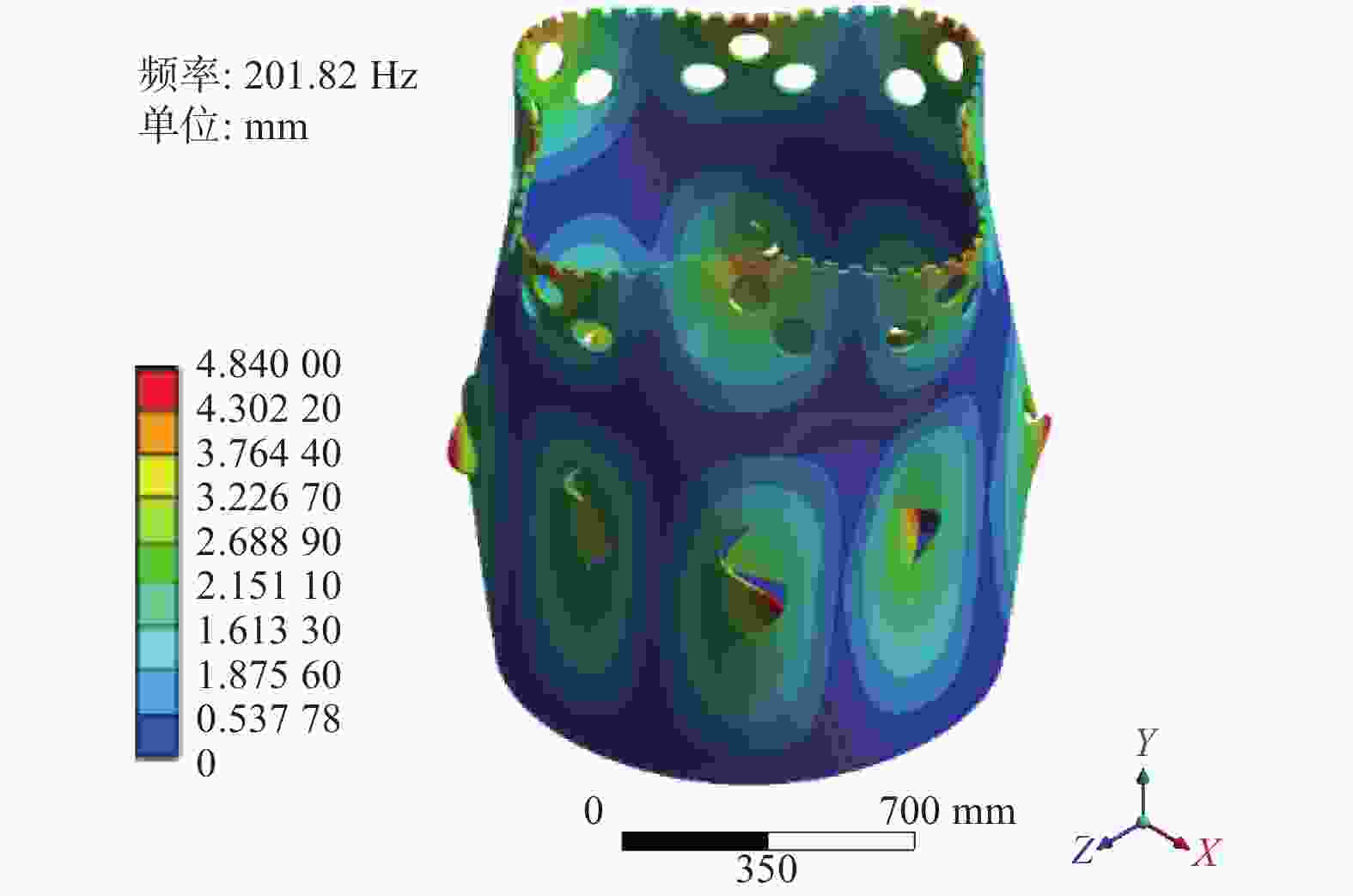
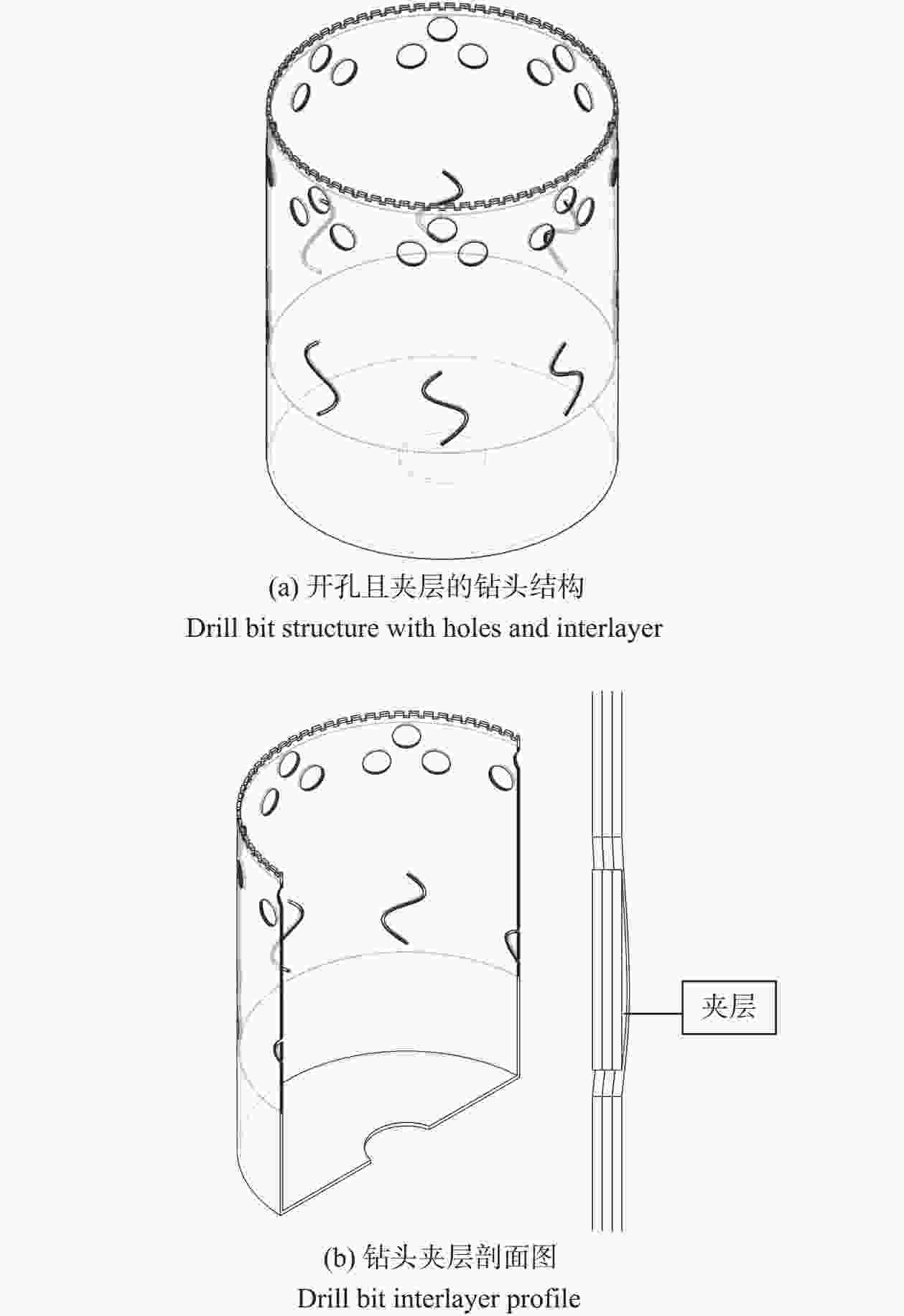
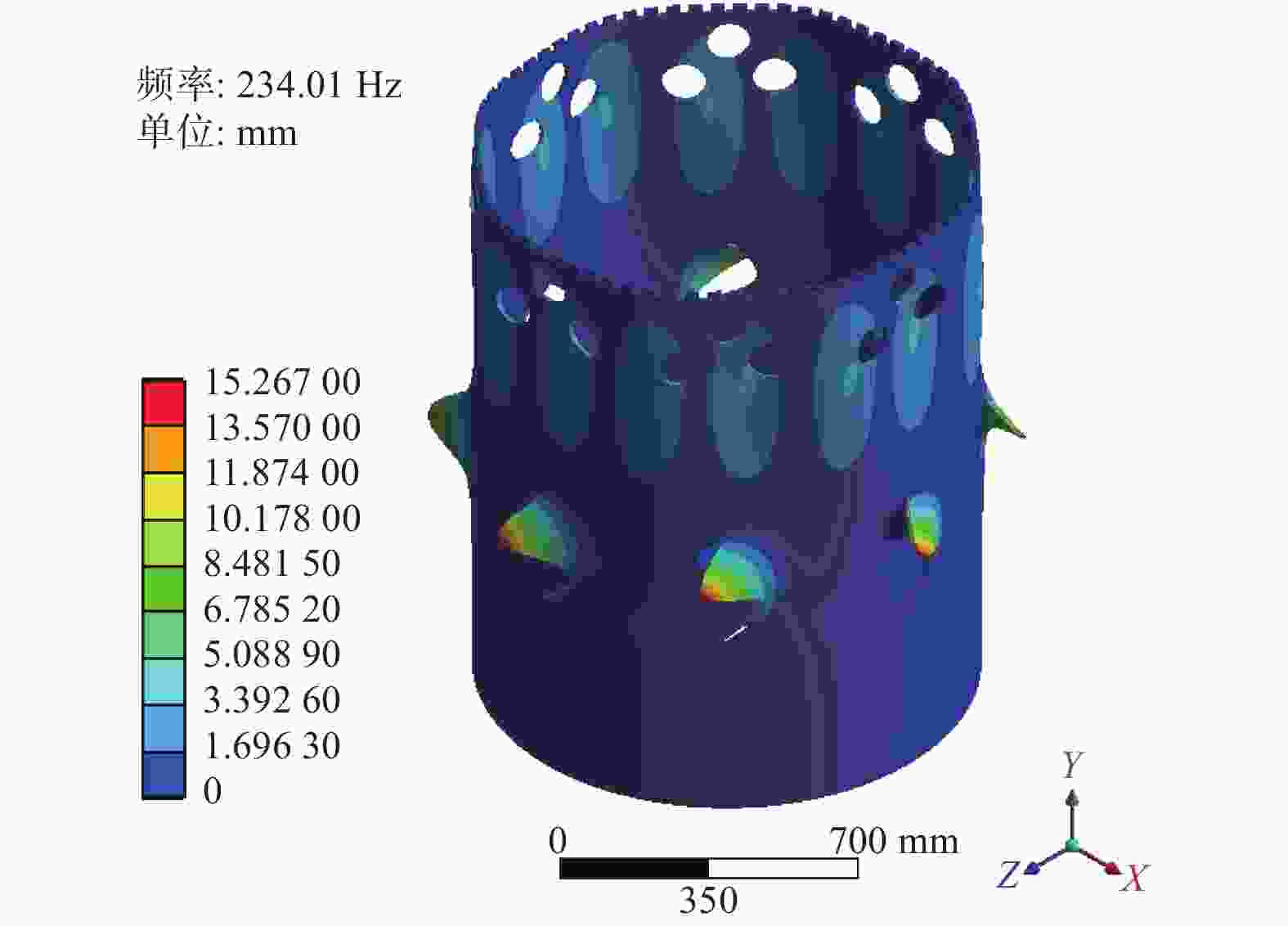
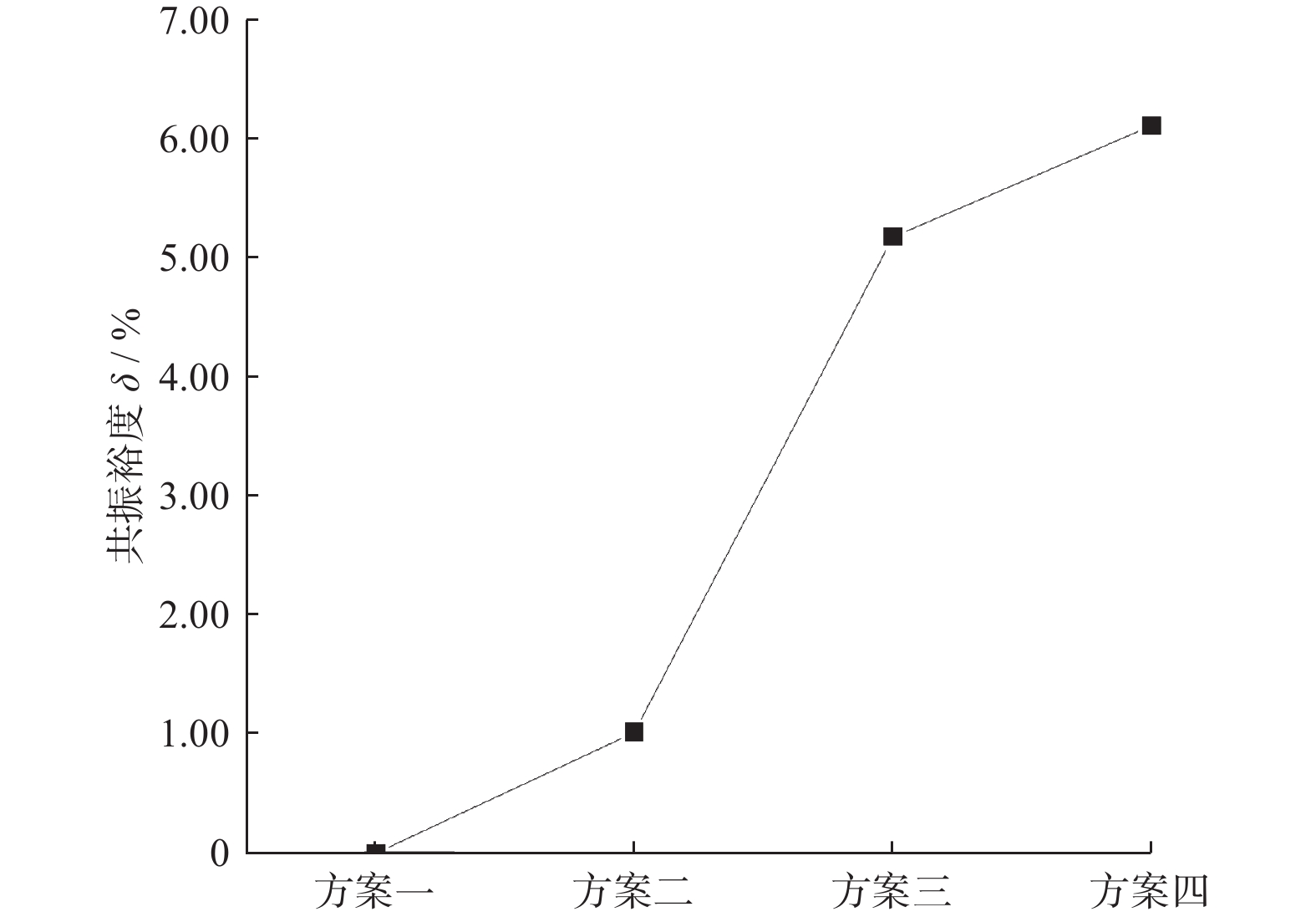
摘要: 针对大型金刚石薄壁钻头在钻切中出现的振动和噪声问题,用Ansys Workbench有限元软件对无开孔、开孔、开孔且夹层和安装定位轮的薄壁钻头进行模态分析,进一步用行波振动理论计算薄壁钻头共振裕度δ,分析避开行波共振的效果,研究开孔、夹层对行波振动的影响。结果表明:钻切转速为187.32 r/min时,无开孔薄壁钻头的共振裕度δ为0,出现后行波共振;在无开孔薄壁钻头出现后行波共振固有模态变形大的区域开8组圆孔(每组3个)和8个S形孔,薄壁钻头的共振裕度δ为5.18%,避开行波共振效果良好;开孔且夹层的薄壁钻头的共振裕度δ为6.11%,避开行波共振效果最好。为提高孔的加工精度,在薄壁钻头周围安装定位轮,分析定位轮数对行波振动的影响,发现安装6个和12个定位轮的薄壁钻头的共振裕度δ分别为4.59%和4.79%,避开行波共振效果好。比较2~12个定位轮薄壁钻头的共振裕度δ,而且考虑安装方便,最后确定最佳安装定位轮数为6个。Abstract: Objectives: To reduce the vibration and noise generated by thin-walled drill bits during the drilling and cutting process, various designs of thin-walled drill bits were studied, including conventional thin-walled drill bits, open-hole thin-walled drill bits, open-hole and interlayer thin-walled drill bits, and thin-walled drill bits with positioning wheel. The reasons for vibration and noise reduction of thin-walled drill bits in different schemes were analyzed at a theoretical level. A new scheme for thin-walled drill bits was proposed, which exhibited good vibration reduction effects, protected the hearing of thin-walled drill bit operators, and complied with China's environmental indicators for workers. Methods: Modal analysis and traveling wave vibration analysis of thin-walled drill bits were performed using Workbench software to study the effects of different thin-walled drill bit designs on traveling wave vibration. First, a solid work model of the thin-walled drill bit was imported into Workbench software and meshed. The inner hole of the thin-walled drill bit was constrained (cantilever type), and the first 30-order modes of the thin-walled drill bit were calculated under standard earth gravity. Using traveling wave vibration theory, the δ value of the resonance margin of the thin-walled drill bit in different schemes was calculated to determine the effectiveness of avoiding traveling wave resonance. Results: At a drilling speed of 187.32 r/min, the conventional thin-walled drill bit had a δ value of 0, leading to rear traveling wave resonance. The opening of 8 groups of round holes and 8 S-hole thin-walled drill bits had a δ value of 5.18%, which was the best opening design scheme. Further interlayering the thin-walled drill bit resulted in a δ value of 6.11%, showing the best effect in avoiding traveling wave resonance. In the δ where 2 to 12 positioning wheels thin-walled drill bits were installed, the δ of 2, 3 and 11 positioning wheels thin-walled drill bits was less than 1.00%, effectively avoiding traveling wave resonance. Conclusions: Thin-walled drill bits with traveling wave resonance will produce strong vibration and noise. Reducing the deformation of the thin-walled drill bit increases the δ value, leading to better vibration and noise reduction. To ensure the precision of the drilled hole, the positioning theory was applied to the thin-walled drill bit. When comparing δ values for drill bits with 2 to 12 positioning wheels, the designs with 6 and 12 positioning wheels had larger δ values and better vibration damping effects. Considering installation convenience, 6 positioning wheels were determined to be the optimal number, providing a theoretical basis for reasonable determination of the number of positioning wheels.
-
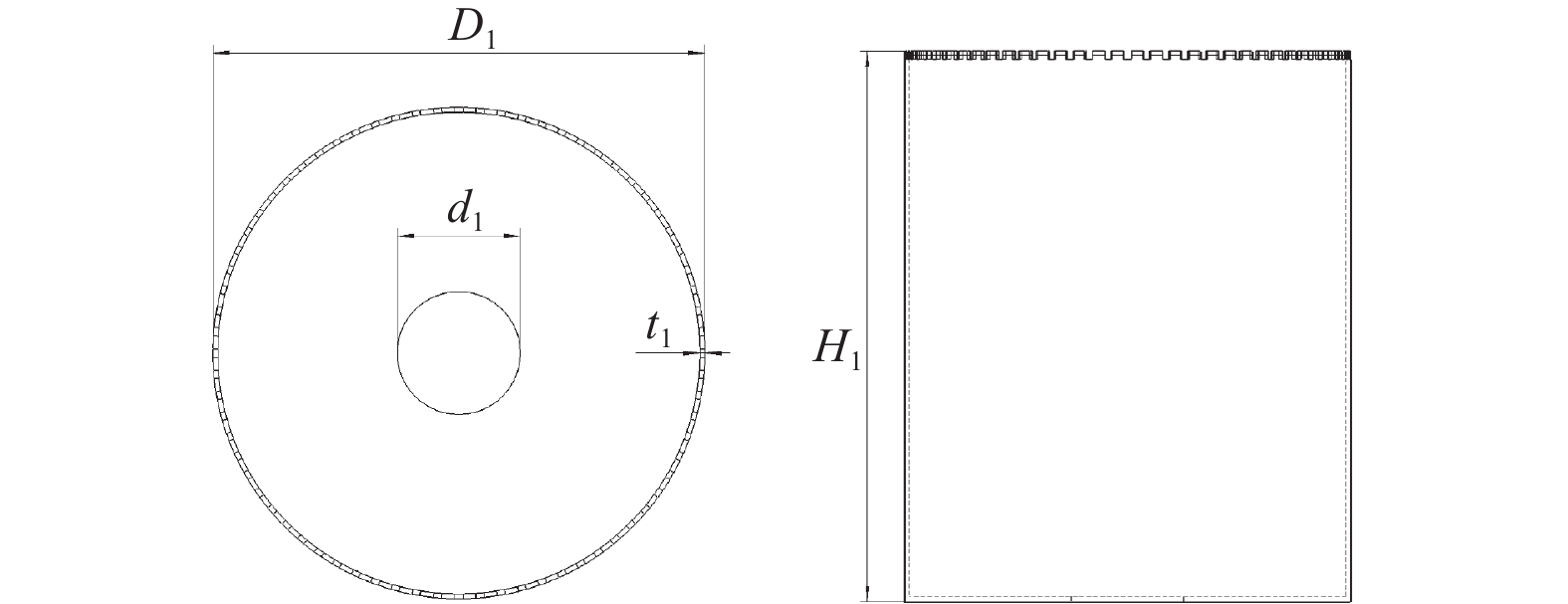
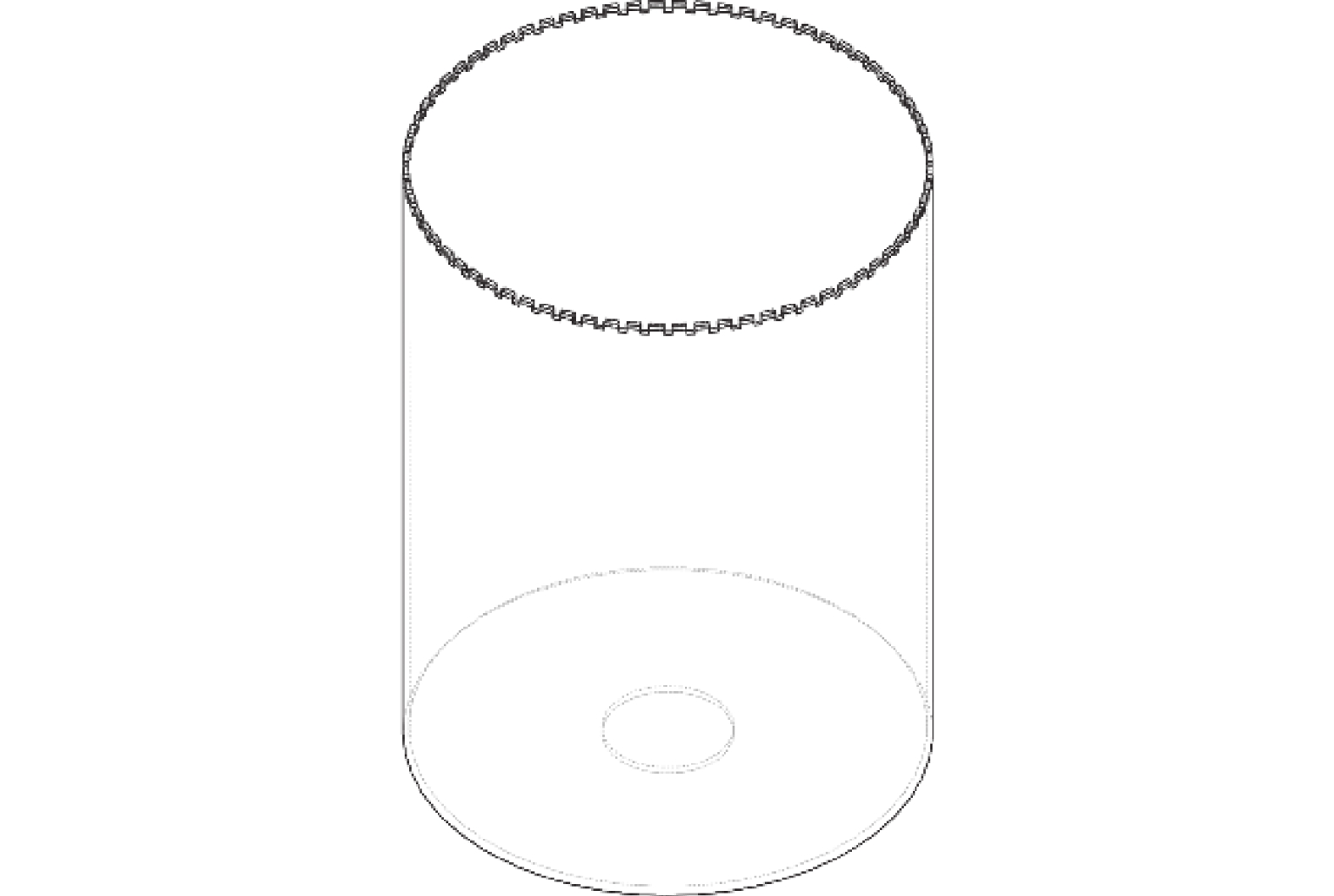
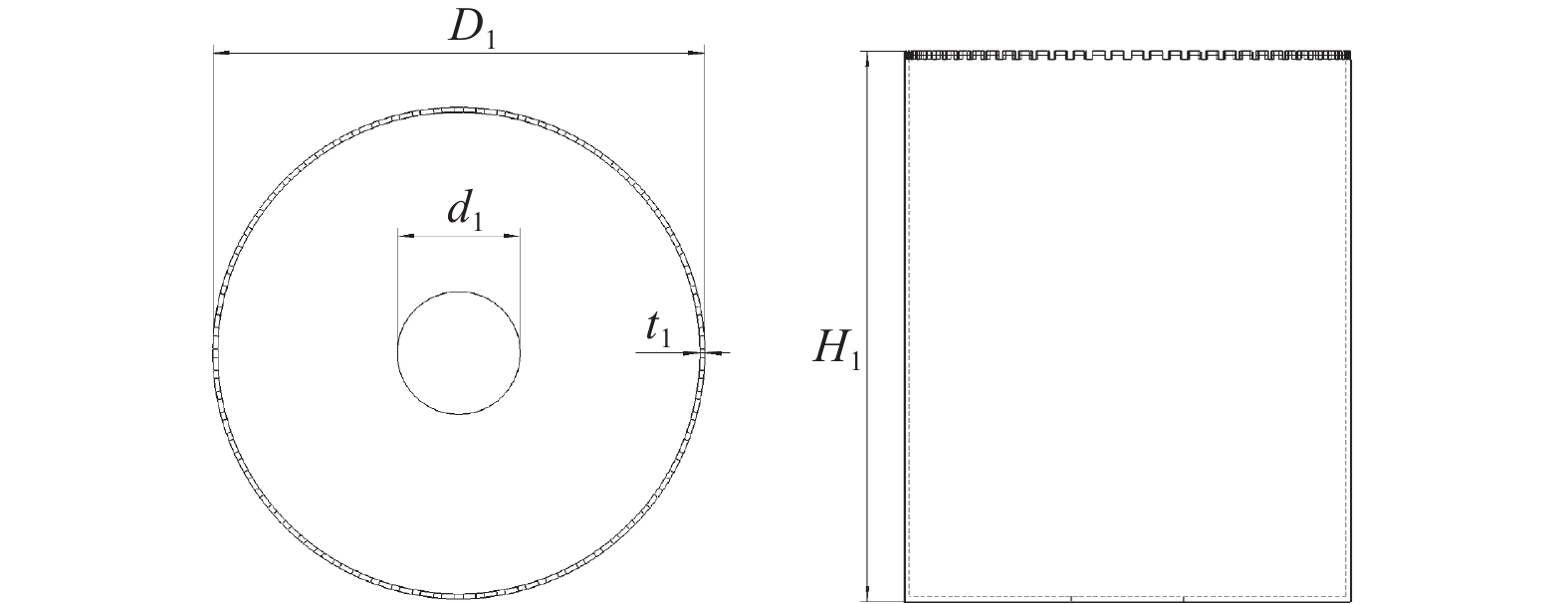
表 1 钻头基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of thin-wall drill bit
参数 数值 外径 $ D_1/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ 1200 内径 $ {d}_{1}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ 300 厚度 $ {t}_{1}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ 12 齿数 $ Z\ /\mathrm{个} $ 72 高度 $ {H}_{1}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ 1500 基体弹性模量 $ E_1/\ \mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ 2.1 × 1011 基体泊松比 $ {\varepsilon }_{1} $ 0.30 密度 $ \rho_{1\ }/\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{m}^{-3}\right) $ 7800 表 2 方案一钻头前30阶固有频率
Table 2. First 30 natural frequencies of Scheme 1 drill bit
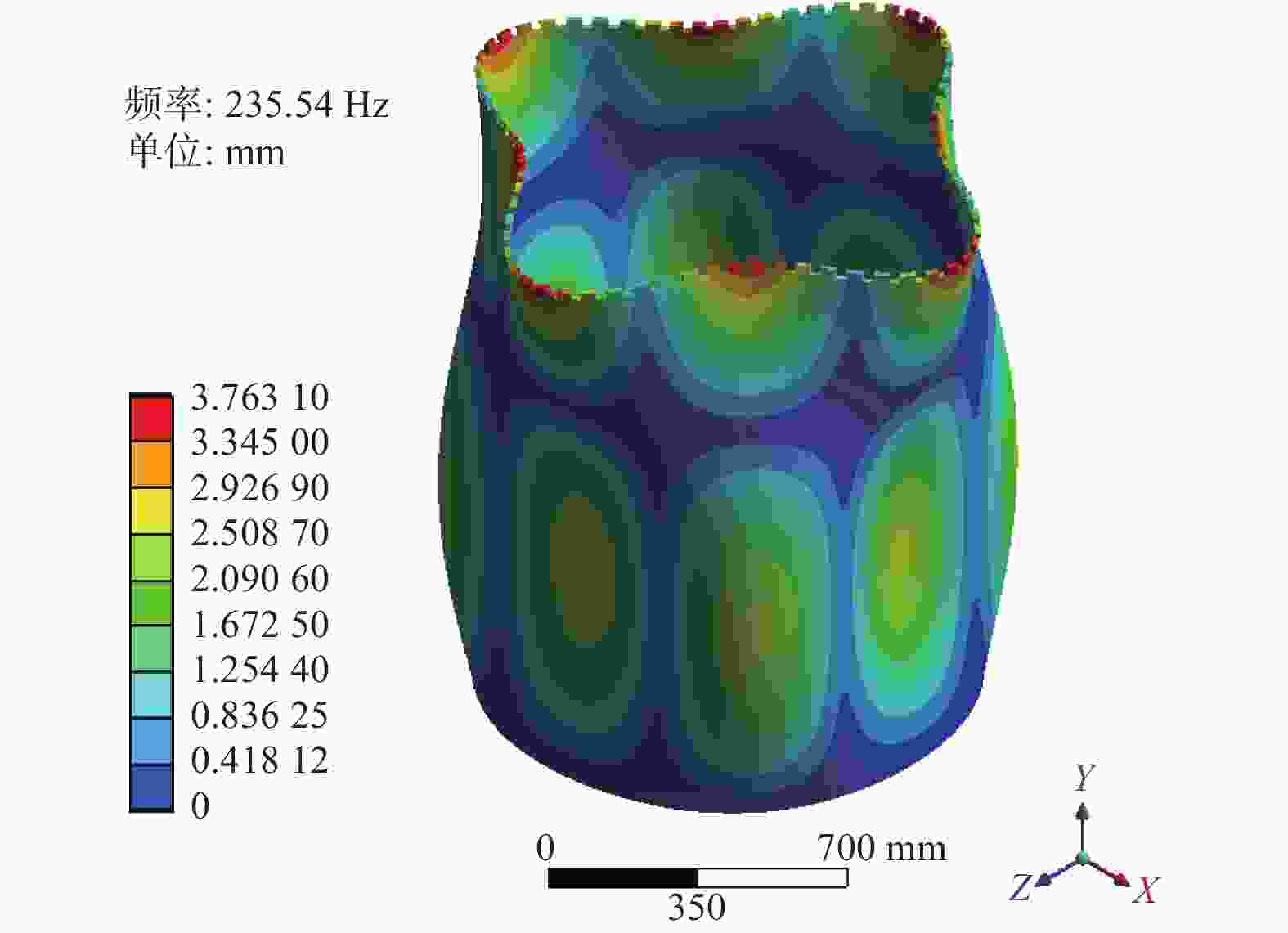
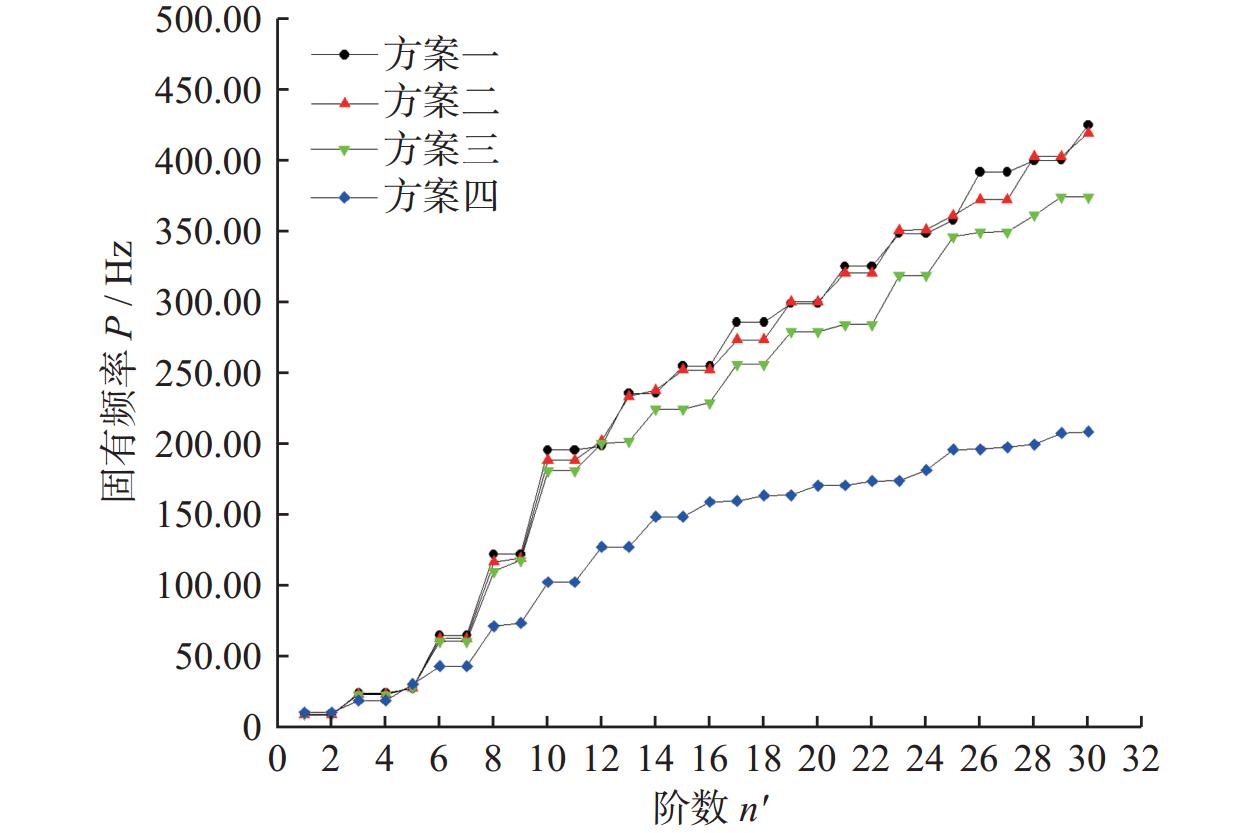
阶数 固有频率 $ P_{ }\left(\mathrm{\mathit{m}},\mathrm{\mathit{n}}\right)/\ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{z} $ 阶数 固有频率 $ P_{ }\left(\mathrm{\mathit{m}},\mathrm{\mathit{n}}\right)\ /\mathrm{\ H}\mathrm{z} $ 1 8.73 16 254.88 2 8.73 17 285.60 3 24.19 18 285.63 4 24.19 19 298.96 5 27.25 20 298.96 6 64.88 21 325.28 7 64.89 22 325.31 8 122.11 23 348.30 9 122.11 24 348.31 10 195.72 25 357.71 11 195.74 26 391.60 12 198.41 27 391.67 13 235.54 28 400.03 14 235.54 29 400.06 15 254.87 30 424.89 表 3 方案四钻头夹层材料基本参数
Table 3. Basic parameters of Scheme 4 drill bit interlayer material
参数 数值 外径 $ {D}_{2} $ / mm 1192 厚度 $ {t}_{2} $/ mm 4 高度 $ {H}_{2} $/ mm 933 弹性模量 $ {E}_{2} $/ $ \mathrm{P}\mathrm{a} $ $ 7.86\times {10}^{6} $ 泊松比 $ {\varepsilon }_{2} $ 0.47 密度 $ {\rho }_{2} $ / ($ \mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-3} $) 1300 表 4 钻头行波振动计算结果
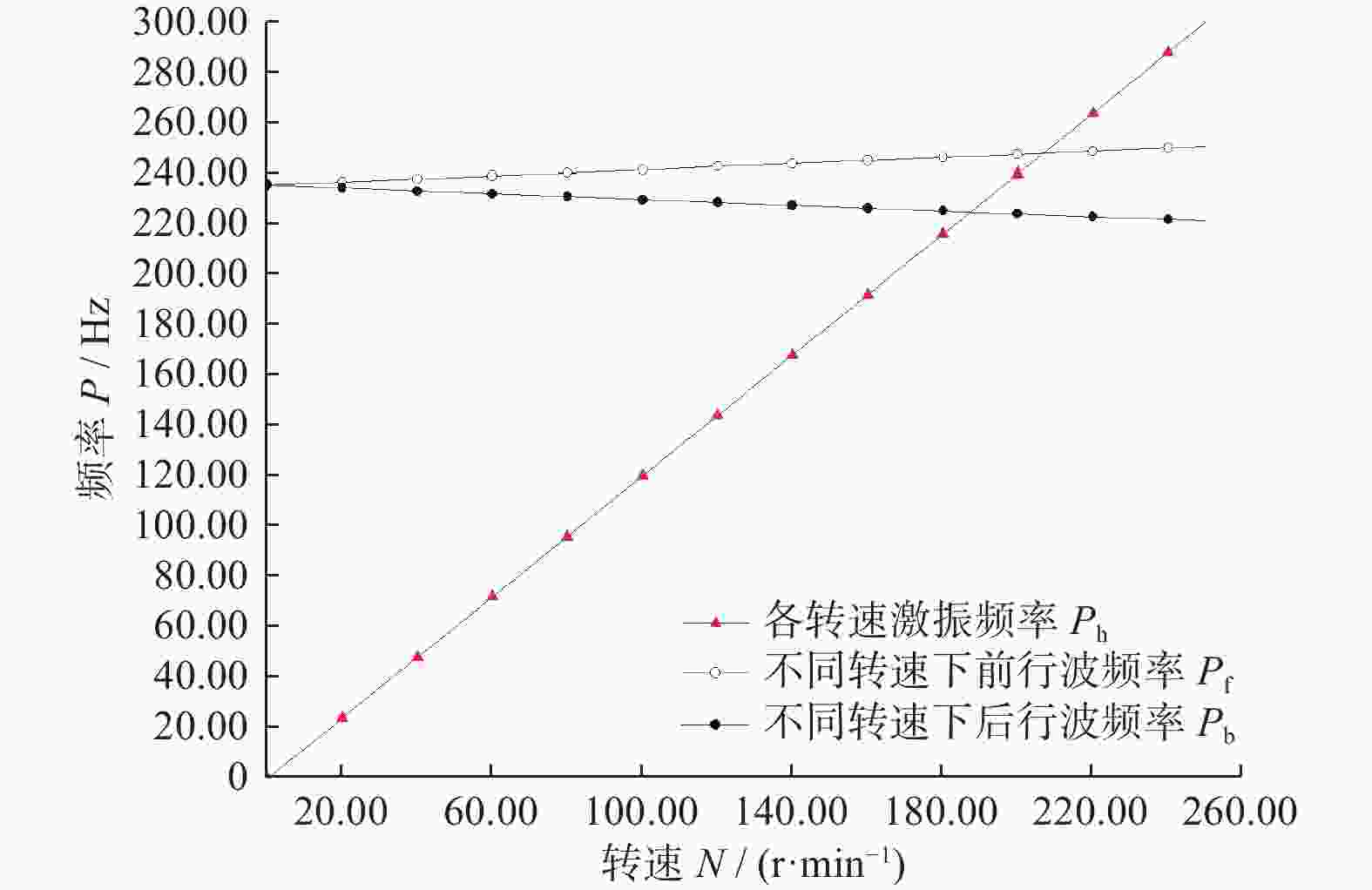
Table 4. Calculation results of drill bits traveling wave vibration
方案 前行波频率
$ \mathrm{\mathit{P}}_{\mathrm{f}}\ /\ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{z} $后行波频率
$ \mathrm{\mathit{P}}_{\mathrm{b}}\ /\mathrm{\ H}\mathrm{z} $$ \mathit{\Delta}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}}\ /\mathrm{\ H}\mathrm{z} $ 共振裕度
$ \mathrm{\delta }/\mathrm{\%} $一 246.82 224.78 0 0 二 244.53 222.49 2.29 1.03 三 213.14 191.10 11.64 5.18 四 259.50 211.05 13.73 6.11 表 5 前30阶固有频率
Table 5. First 30 natural frequencies
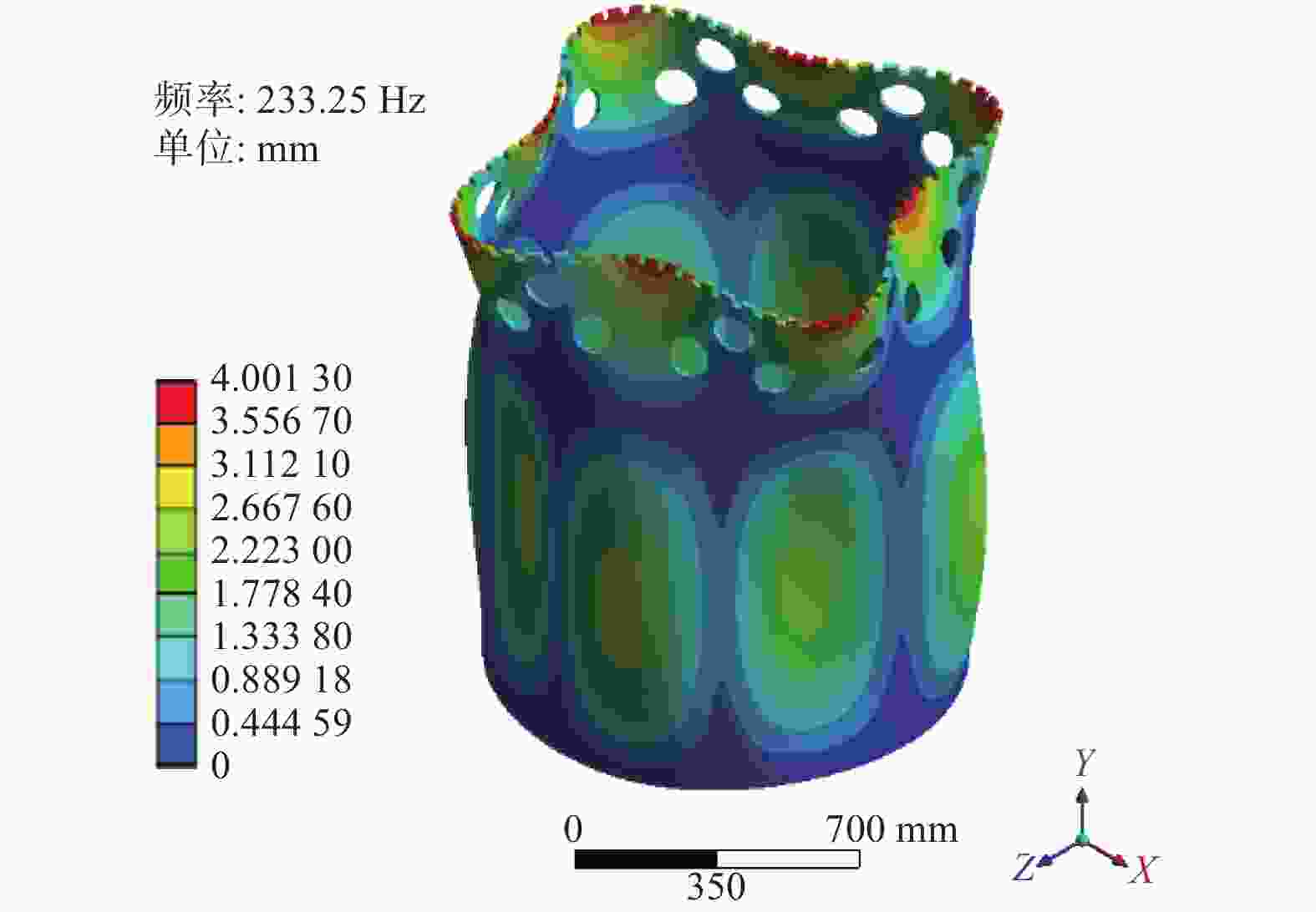
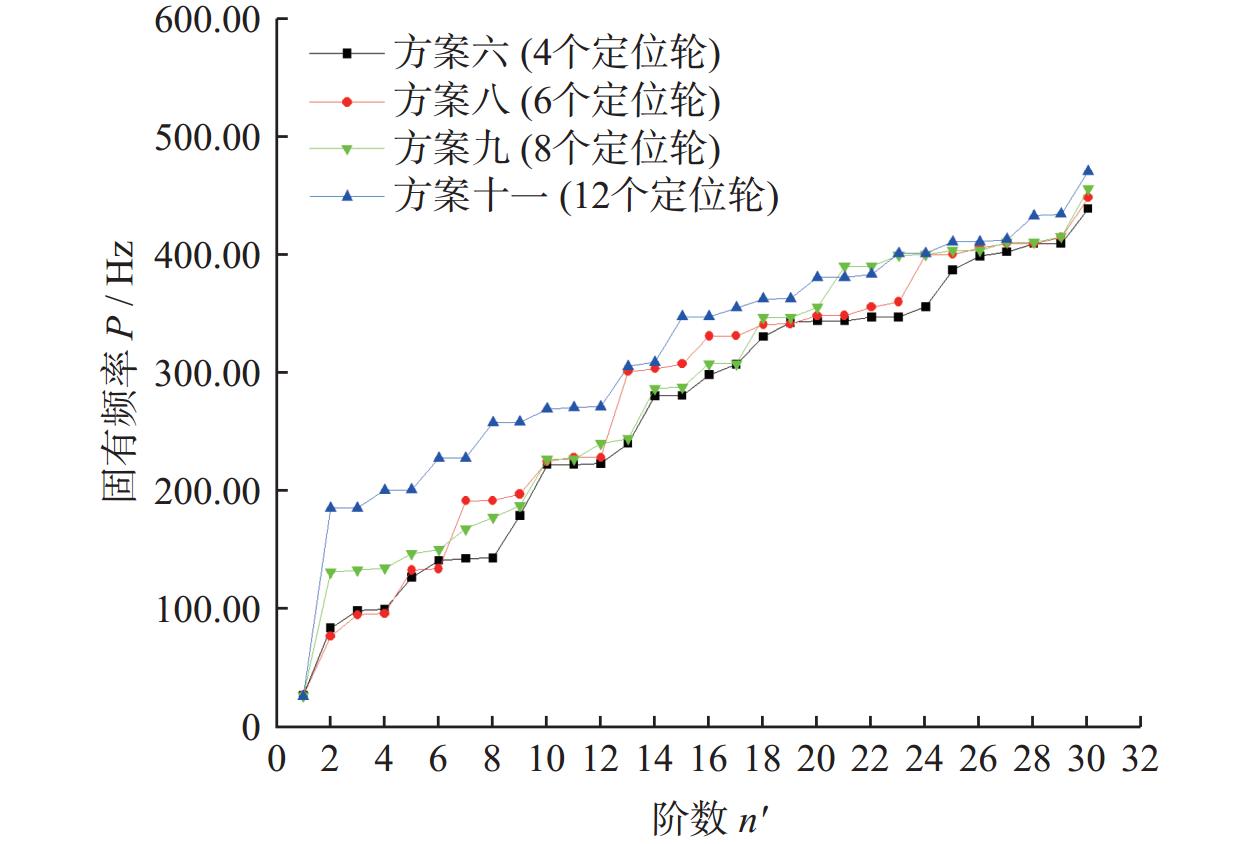
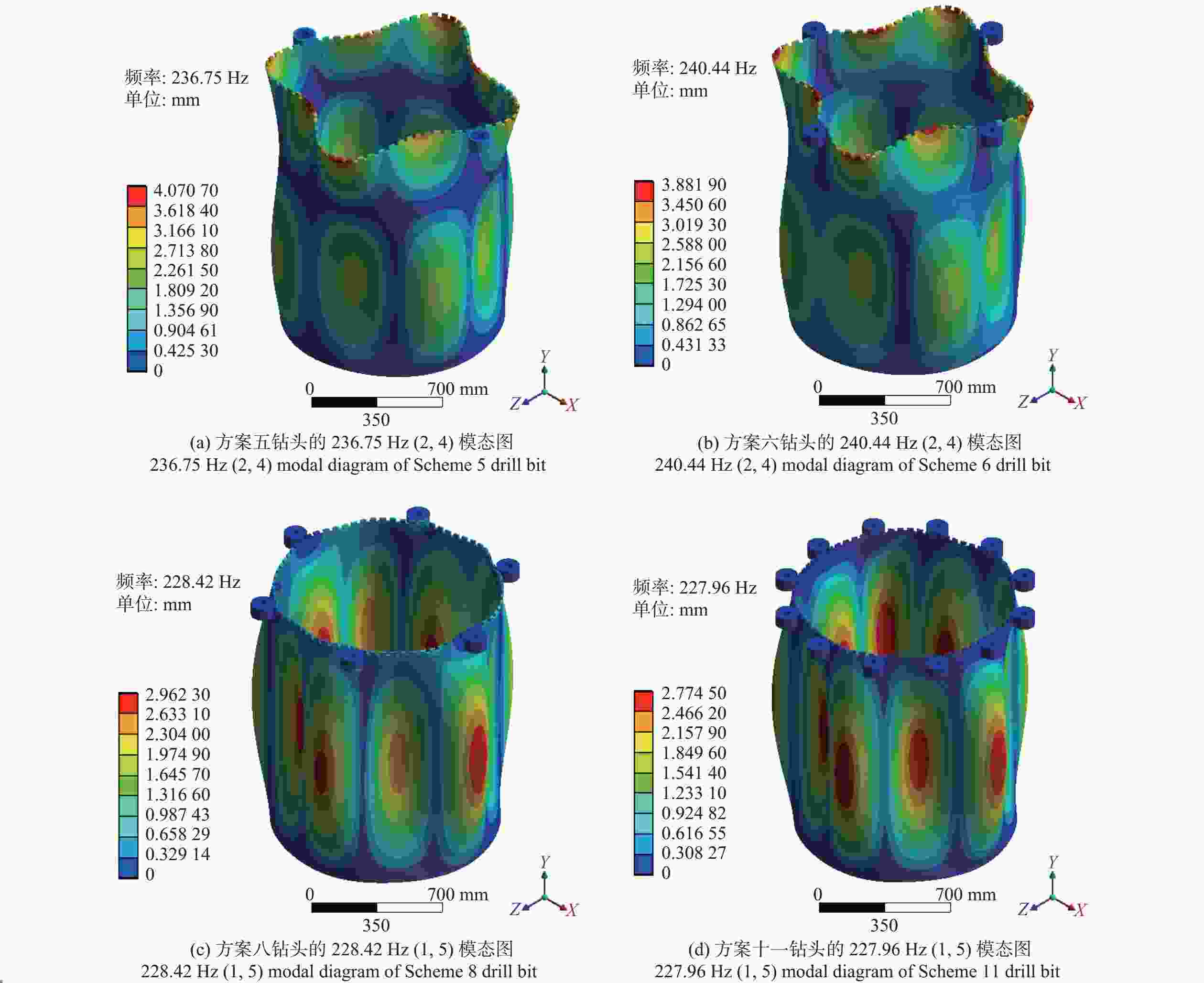
阶数 固有频率P(m, n)/Hz 方案六 方案八 方案九 方案十一 1 26.65 26.41 26.17 25.72 2 83.71 76.77 131.21 185.39 4 99.56 95.88 134.39 200.55 6 141.06 134.03 150.19 227.90 8 143.00 191.79 177.82 258.09 10 222.42 225.04 226.95 269.46 12 223.23 228.42 240.42 271.27 13 240.44 301.30 244.29 305.67 14 280.72 303.58 286.92 308.94 16 298.43 331.48 307.79 347.72 18 330.93 341.22 347.05 362.87 20 344.19 348.57 355.73 380.93 22 347.35 355.93 390.73 383.65 24 356.13 400.48 400.47 401.33 26 399.07 406.26 404.10 411.16 28 409.79 409.80 411.10 433.30 30 439.46 448.67 456.11 471.20 表 6 行波振动计算结果
Table 6. Calculation results of traveling wave vibration
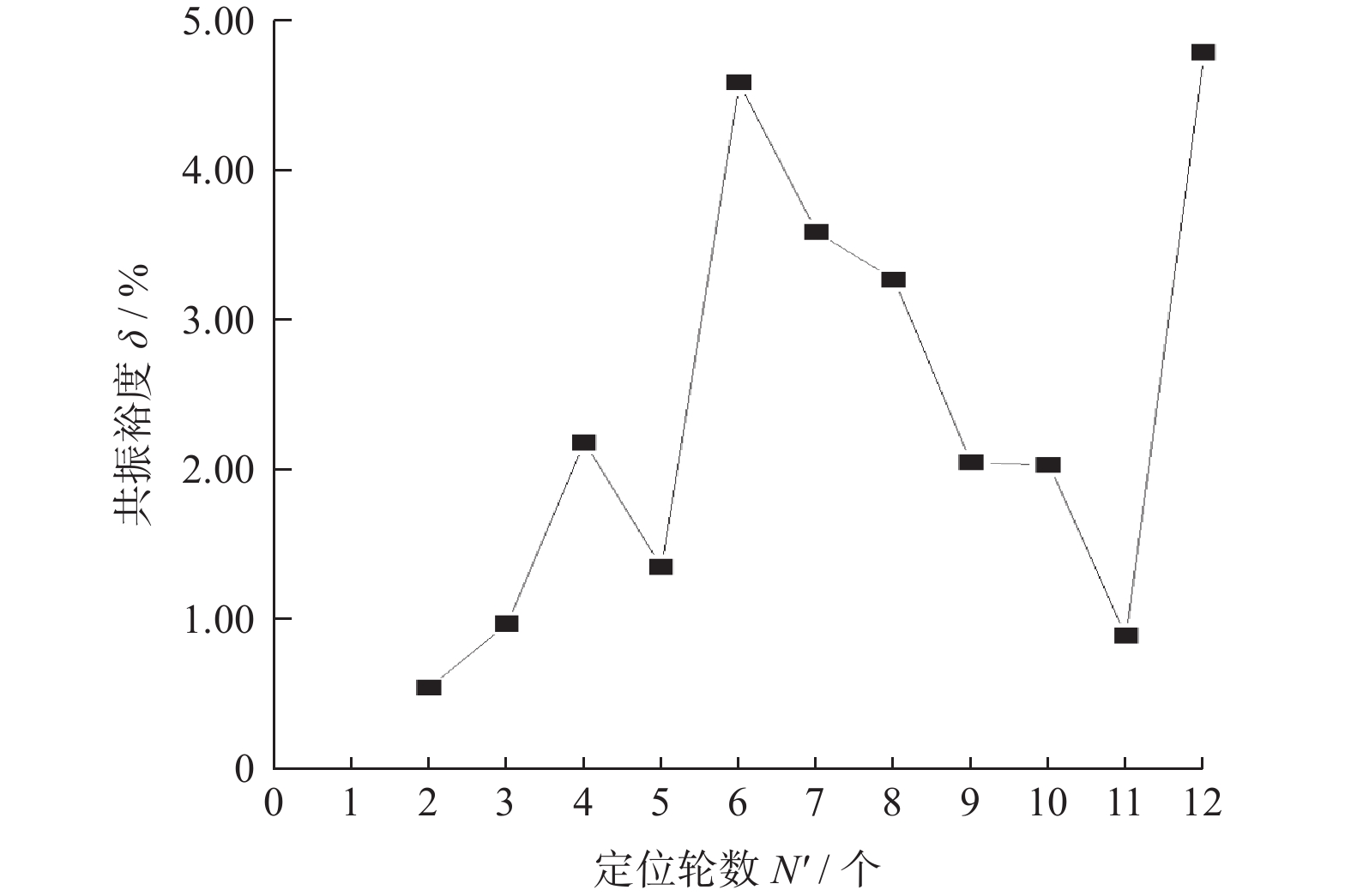
方案 定位轮
数N' / 个前行波
频率
$ P_{\mathrm{f}}\ /\ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{z} $后行波
频率
$ P_{\mathrm{b}}\ /\mathrm{\ H}\mathrm{z} $$ \mathit{\Delta}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}}\ /\mathrm{\ H}\mathrm{z} $ 共振
裕度
$ \delta\ /\ \mathrm{\%} $五 2 248.03 225.99 1.21 0.54 六 4 251.71 229.67 4.89 2.18 七 5 250.57 221.75 3.03 1.35 八 6 243.28 214.46 10.32 4.59 九 8 265.84 217.43 7.35 3.27 十 10 290.55 229.35 4.57 2.03 十一 12 242.82 214.01 10.77 4.79 -
[1] 张所邦, 周玉龙. 金刚石薄壁钻技术的发展与展望[J]. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程), 2003(S1): 187-189.ZHANG Suobang, ZHOU Yulong. Development and prospect of diamond thin wall drilling technology [J]. Exploration Engineering (Geotechnical Drilling Engineering), 2003 (S1): 187-189. [2] 田永军, 孙爽, 张翔宇,等. 金刚石圆锯片振动与噪声机理及其减振降噪技术研究综述 [J]. 机械设计,2020,37(3):1-13. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2020.03.001TIAN Yongjun, SUN Shuang, ZHANG Xiangyu, et al. Overview of research on vibration and noise mechanism of diamond circular saw blade and its vibration and noise reduction technology [J]. Mechanical Design,2020,37(3):1-13. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2020.03.001 [3] 王婷. 夹层阻尼圆锯片减振降噪研究[D]. 天津:河北工业大学, 2013.WANG Ting. Research on vibration and noise reduction of sandwich damping circular saw blade [D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2013. [4] 赵雷, 张德臣, 闫春宝, 等. 金刚石圆锯片行波共振分析及优化 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2022,42(2):240-247. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.0112ZHAO Lei, ZHANG Dechen, YAN Chunbao, et al. Traveling wave resonance analysis and optimization of diamond circular saw blade [J]. Diamond & Abrasive Engineering,2022,42(2):240-247. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.0112 [5] 鞠军伟, 张进生, 黄波,等. 基于FEM/IBEM的金刚石圆锯片振动噪声及其频谱分析 [J]. 工具技术,2015,49(9):28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2015.09.006JU Junwei, ZHANG Jinsheng, HUANG Bo, et al. Vibration noise and its spectrum analysis of diamond circular saw blade based on FEM/IBEM [J]. Tool Technology,2015,49(9):28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2015.09.006 [6] 王宇, 夏鑫, 杨志宏,等. 高转速硬涂层阻尼薄壁圆柱壳的行波共振特性研究 [J]. 振动与冲击,2021,40(13):73-81. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.13.010WANG Yu, XIA Xin, YANG Zhihong, et al. Study on traveling wave resonance characteristics of high speed hard coated damping thin-wall cylindrical shells [J]. Vibration and Shock,2021,40(13):73-81. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.13.010 [7] 王宇, 谷月, 李昌,等. 黏弹性层合悬臂薄壁圆柱壳的模态特性研究 [J]. 力学与实践,2015,37(3):344-349. doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-14-371WANG Yu, GU Yue, LI Chang, et al. Study on modal characteristics of viscoelastic laminated cantilever thin-wall cylindrical shells [J]. Mechanics and Practice,2015,37(3):344-349. doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-14-371 [8] 孙传涛, 张德臣, 代爽. 圆孔锯锯片的模态分析 [J]. 辽宁科技大学学报,2015(5):358-362.SUN Chuantao, ZHANG Dechen, DAI Shuang. Modal analysis of circular saw blade [J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Science and Technology,2015(5):358-362. [9] SAITO T, INOUE M, ENDO M. Vibration analysis of rotating general axisymmetric shells [J] .Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1993,52 (5): 1343-1349. [10] SAITO T, ENDO M. Vibration of rotating cylindrical shells [J]. Bulletin of Jsme, 1986, 52 (2): 718-723. [11] ROBERT BOSCH GMBH. Cylindrical drilling body for hole sawing: CN201410087831.7 [P]. 2014-09-17. -



 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
