Development of multilayer brazed diamond grinding wheel for ceramic precision grinding
-
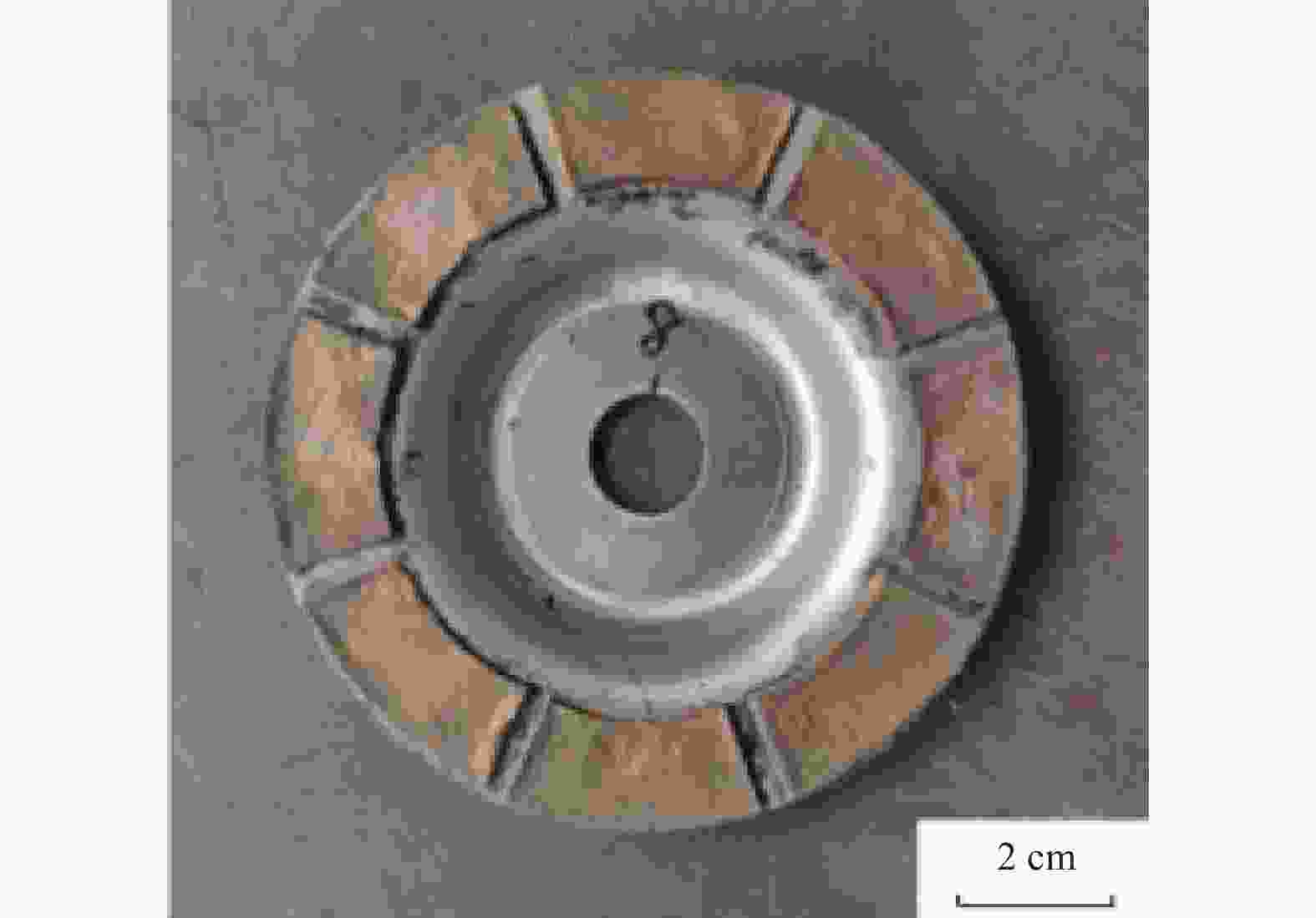
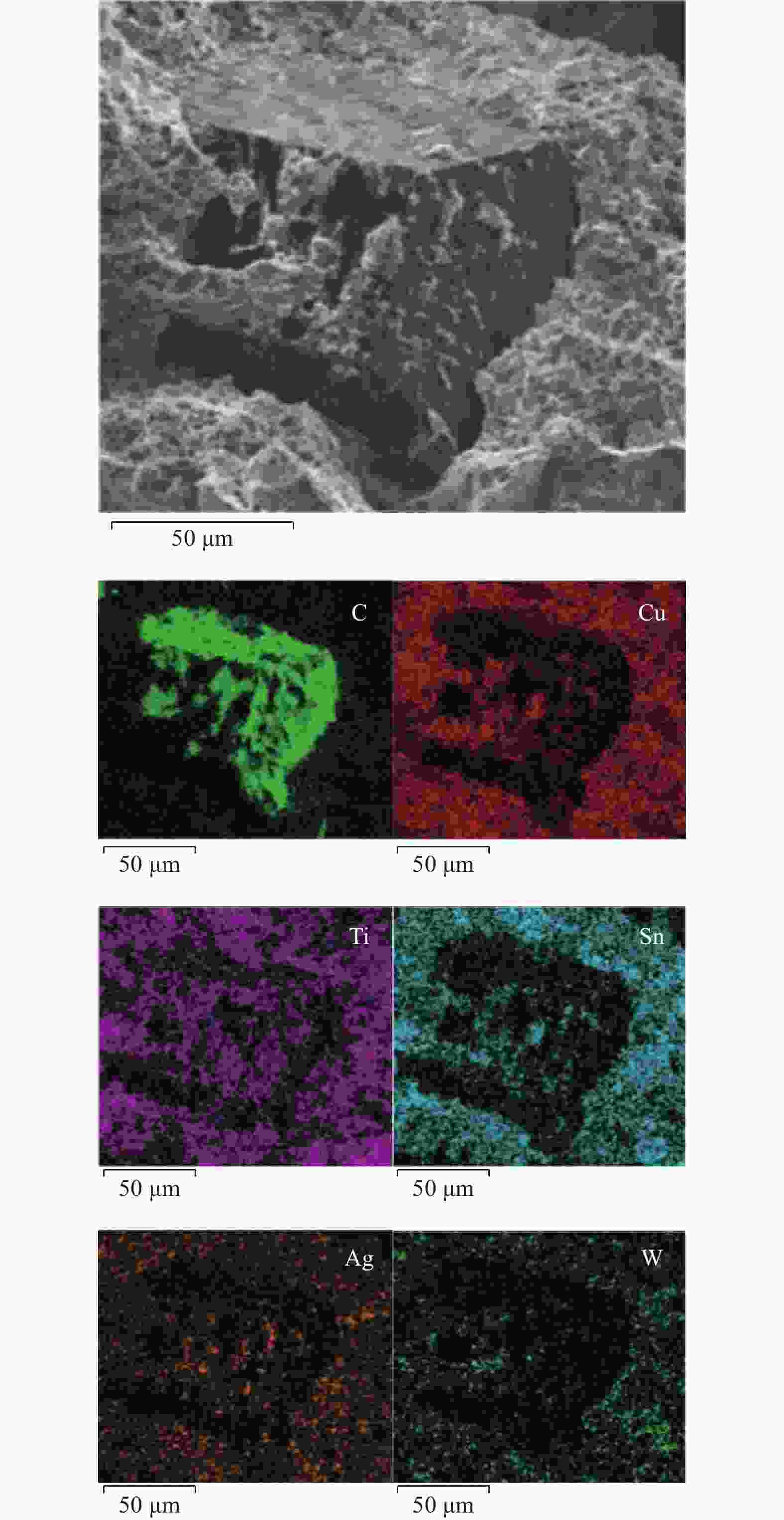
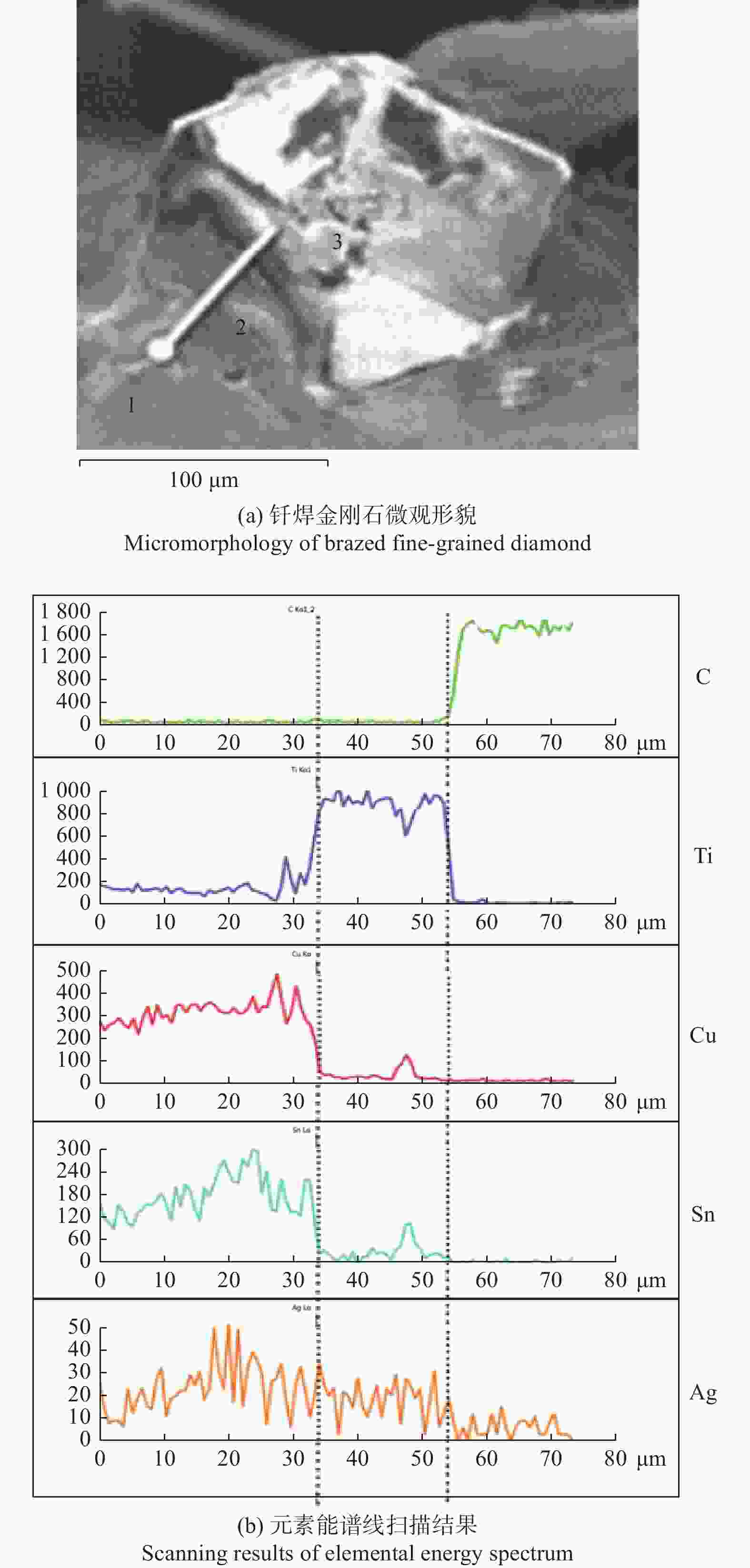
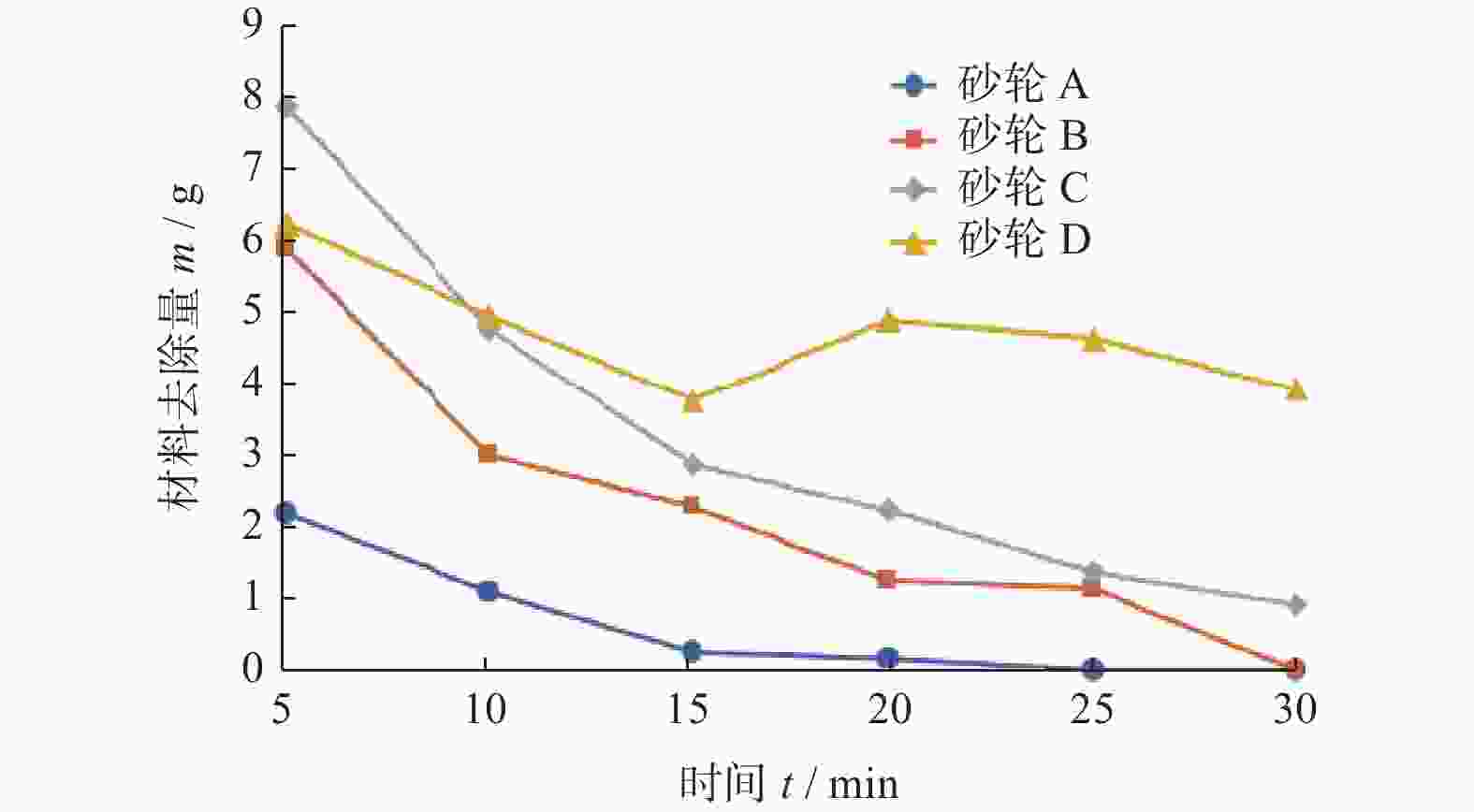
摘要: 为解决传统树脂、电镀金刚石砂轮磨削陶瓷材料时存在的磨削寿命短、砂轮易堵塞烧伤等问题,分析利用钎焊金刚石技术制备陶瓷磨削用多层钎焊金刚石砂轮的可行性。结合钎料组分优选,制备具有开槽结构的多层钎焊金刚石砂轮,并对99.9%高纯度的Al2O3陶瓷进行磨削性能试验。结果表明:树脂、电镀金刚石砂轮分别存在磨削效率低和磨削寿命不足的问题,单层钎焊金刚石砂轮磨削效率较高但磨削寿命有限,多层钎焊金刚石在保持高磨削效率的同时磨削寿命优势明显,较单层钎焊金刚石磨轮提升约60%。在陶瓷材料磨削过程中,多层钎焊金刚石砂轮磨削效果显著,虽磨粒出露高度有限,但开槽设计的排屑效果显著,砂轮表面不易发生陶瓷粉末黏结、堵塞。Abstract: To address the issues of low grinding efficiency and the tendency of blockage and burning of the grinding wheel when working with ceramic materials using traditional resin and electroplated diamond grinding wheels, the feasibility of using brazed diamond technology to prepare a multilayer brazed diamond grinding wheel for ceramic grinding is analyzed. Combined with the optimization of filler metal composition, a multilayer brazed diamond grinding wheel with a slotted structure is prepared, and the grinding performance of 99.9% high-purity Al2O3 ceramics is tested. The results show that resin and electroplated diamond grinding wheels suffer from low grinding efficiency and insufficient grinding life, respectively. Single-layer brazed diamond grinding wheels exhibit high grinding efficiency but have limited grinding life. Multilayer brazed diamond grinding wheels show obvious advantages in terms of grinding life while maintaining high grinding efficiency, being about 60% higher than that of single-layer brazed diamond grinding wheels. During the ceramic material grinding process, the multilayer brazed diamond grinding wheel demonstrates remarkable grinding effectiveness. Despite the limited exposed height of abrasive particles, the slotting design significantly enhances chip removal, preventing the wheel's surface from bonding and blocking with ceramic powder.
-
Key words:
- ceramic grinding /
- brazed diamond /
- multi-layer grinding wheel /
- grinding efficiency
-
表 1 磨削试验参数
Table 1. Grinding test conditions
试验条件 主要参数 铣床参数 直流电机,最高转速1700 r/min,
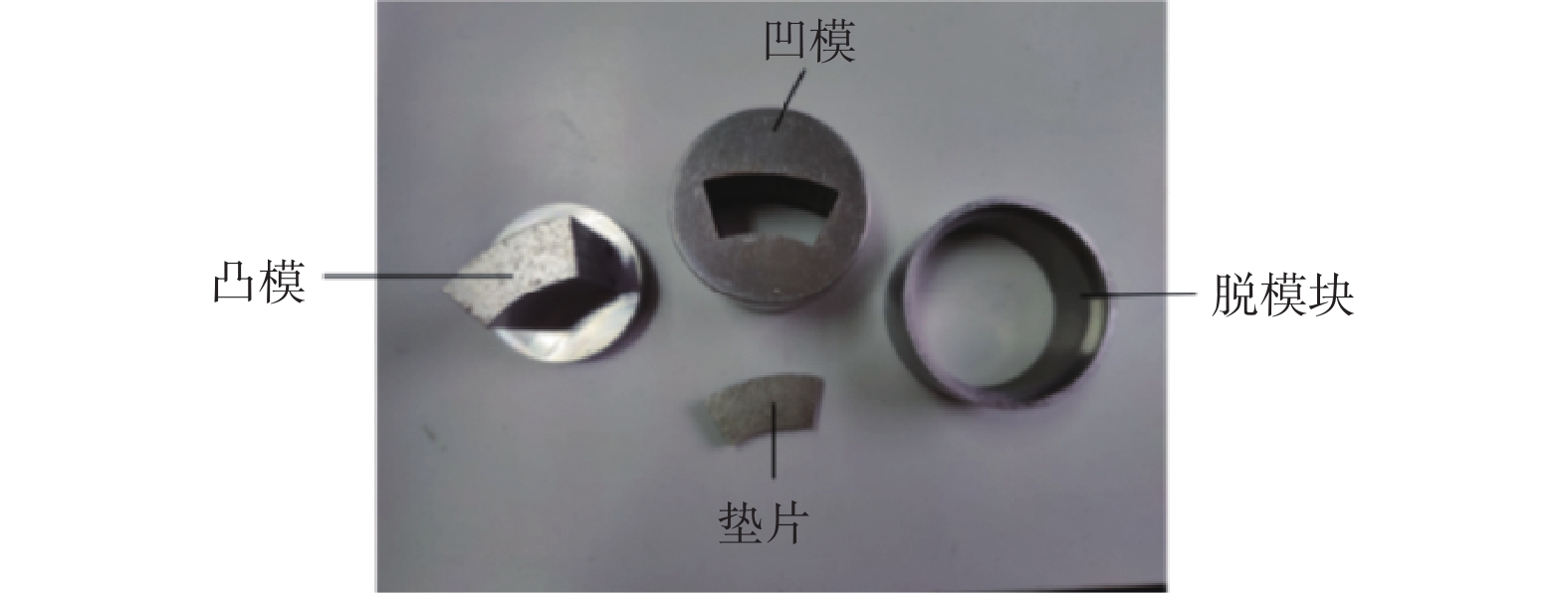
工作台进给速度为0.05~20 m/min砂轮 砂轮直径为100 mm,磨粒粒径为125 μm 磨削方式 切入式磨削 砂轮转速 1700 r/min 进给速度 12 mm/min 冷却方式 5%水基乳化液 加工对象 99.9%高纯度 Al2O3 陶瓷 -
[1] 朱爱菊. 金刚石砂轮平面磨削石英陶瓷的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2005ZHU Aiju. Research on surface grinding of quartz ceramics with diamond wheel [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2005 [2] LOU W C, MAO M M, SONG K Z, et al. Low permittivity cordierite-based microwave dielectric ceramics for 5G/6G telecommunications [J] . Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022 (6): 2820-2826. [3] IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques Special Issue on Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Communication and Sensor Systems [J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2020 (6): c2. [4] 张红轩. 金刚石砂轮磨削蓝宝石晶片加工过程实验研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2020.ZHANG Hongxuan. Experimental study on sapphire wafer grinding process with diamond wheel [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2020. [5] 王会, 高超, 王生, 等. 碳化硅陶瓷钻孔中钎焊金刚石刀具的磨损实验研究 [J]. 机械设计与制造,2018(S2):43-46.WANG Hui, GAO Chao, WANG Sheng, et al. Experimental study on wear of brazed diamond tools in silicon carbide ceramic drilling [J]. Mechanical design and manufacturing,2018(S2):43-46. [6] WANG X L, GAO X D, ZHANG Z H, et al. Advances in modifications and high-temperature applications of silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites in aerospace: A focused review [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021 (9): 4671-4688. [7] 卢金斌 , 徐九华. Ag-Cu-Ti钎料钎焊金刚石的界面微观组织分析 [J]. 焊接学报,2007,8:29-32, 114.LU Jinbin, XU Jiuhua. Interface microstructure analysis of Ag-Cu-Ti brazed diamond [J]. Journal of Welding,2007,8:29-32, 114. [8] 轩庆庆. CuSnTi活性钎料组织性能分析及非晶态钎料钎焊金刚石研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2018.XUAN Qingqing. Microstructure and properties analysis of CuSnTi active filler metal and research on diamond brazing with amorphous filler metal [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2018 [9] 陈世隐. 大直径细粒度钎焊金刚石砂轮的制备及其磨削性能研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2017.CHEN Shiyin. Study on the preparation and grinding performance of large diameter and fine grain brazed diamond grinding wheel [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2017 [10] 刘文锋 , 黄国钦 , 徐西鹏. 细粒度钎焊金刚石砂轮磨削花岗石的磨削力特征分析 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2012(2):39-42.LIU Wenfeng, HUANG Guoqin, XU Xipeng. Analysis of grinding force characteristics of granite grinding with fine-grained brazed diamond wheel [J]. Diamond and abrasive tools engineering,2012(2):39-42. [11] 肖冰 , 徐鸿钧 , 武志斌, 等. Ni-Cr合金真空单层钎焊金刚石砂轮 [J]. 焊接学报,2001(2):3, 23-26.XIAO Bing, XU Hongjun, WU Zhibin, et al. Ni-Cr alloy vacuum single-layer brazed diamond grinding wheel [J]. Journal of Welding,2001(2):3, 23-26. [12] 贺鑫. 钎焊金刚石砂轮高效深磨氧化铝陶瓷的实验研究 [D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2016.HE Xin. Experimental study on high efficiency and deep grinding of alumina ceramics with brazed diamond wheels [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2016 [13] 刘慧男 , 徐学彬. XK5040型数控立式铣床主轴精度的装配调整方法[J]. 机械工程师, 2012(7): 125-126.LIU Huinan, XU Xuebin. Assembly and adjustment method for spindle accuracy of XK5040 CNC vertical milling machine [J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2012 (7): 125-126. [14] HUANG H, LIU Y C. Experimental investigations of machining characteristics and removal mechanisms of advanced ceramics in high speed deep grinding [J] . International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2003 (8): 811-823. [15] SEBASTIAN B, CHRISTIAN L, RALPH S, et al. Microstructure, residual stresses and shear strength of diamond–steel-joints brazed with a Cu–Sn-based active filler alloy [J] . International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2011 (1): 16-24. [16] 丁兰英. 自润滑多层有序钎焊金刚石工具技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.DING Lanying. Research on self-lubricating multilayer ordered brazing diamond tool technology [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
