Functional surfaces of medical devices based on laser processing: a review
-
摘要: 制备功能性表面是提升医疗器械治疗性能和安全性的重要方法之一。当前,基于激光加工的功能性表面微纳结构制造技术在优化医疗器械表面性能方面应用广泛。综述了医疗植入器械和手术器械表面激光加工功能性微纳结构在细胞功能调控、抗菌性、耐蚀性、摩擦特性、抗黏附性等方面的研究现状,剖析了当前医疗器械功能性表面激光加工的优势和局限,展望了医疗器械功能性表面激光加工技术的发展前景。Abstract: The preparation of functional surfaces is one of the important methods to enhance the therapeutic performance and safety of medical devices. Currently, the fabrication of functional surface microstructures based on laser processing is widely used in the optimizing medical device surface properties. This paper reviews the current research status of functional microstructures for laser processing of medical implantable and surgical devices in terms of cell function regulation, antimicrobial properties, corrosion resistance, frictional properties, and anti-adhesion, etc. It analyzes the advantages and limitations of laser processing of functional surfaces for medical devices and outlines the development prospects of laser processing technology for functional surfaces for medical devices.
-
表 1 部分医疗植入器械和手术器械的分类与所需功能
Table 1. Classification and required functions of some medical implants and surgical instruments
分类 器械 应用 所需功能 植入器械 接骨板 + 骨螺钉 连接固定,维持骨头的位置 高耐磨性;促进骨细胞生长 人工骨 替代人体骨协助修复骨组织缺损 具有良好的生物相容性;促进骨组织、细胞生长和黏附 血管支架 支撑狭窄闭塞段血管,保持管腔血流通畅 表面具有良好的减阻、抗黏附作用,防止发生再狭窄 手术器械 手术刀 用于切开皮肤和肌肉 切割时形成低摩擦,减少阻力保证切口平整 手术钳、血管夹 夹持韧致密组织、离断的组织残端 形成稳定的夹持,具有强大的湿摩擦能力防止滑脱 高频电刀 实现对肌体组织的分离和凝固,起到切割和
止血的目的具有优秀的抗黏附性,减少因表面高温黏附的
生物组织表 2 激光加工医疗器械功能性表面的研究现状
Table 2. Research status of laser processing of functional surfaces of medical devices
器械类别 材料 激光参数 结构参数 主要结论 文献 性能 波长 脉宽 形状 尺寸 植入器械 骨科植入物 Ti6Al4V — — 微槽 宽度10,30 μm
深度10 μm微槽表面呈亲水性,表面粗糙度增加,成骨细胞增殖和分化能力提高 [22] 细胞功能
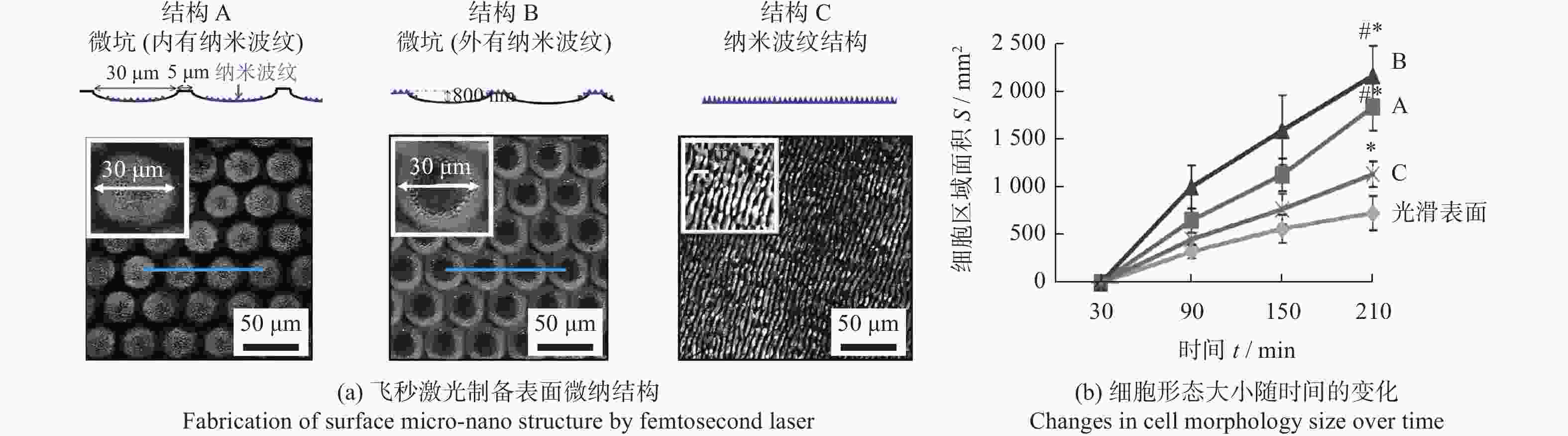
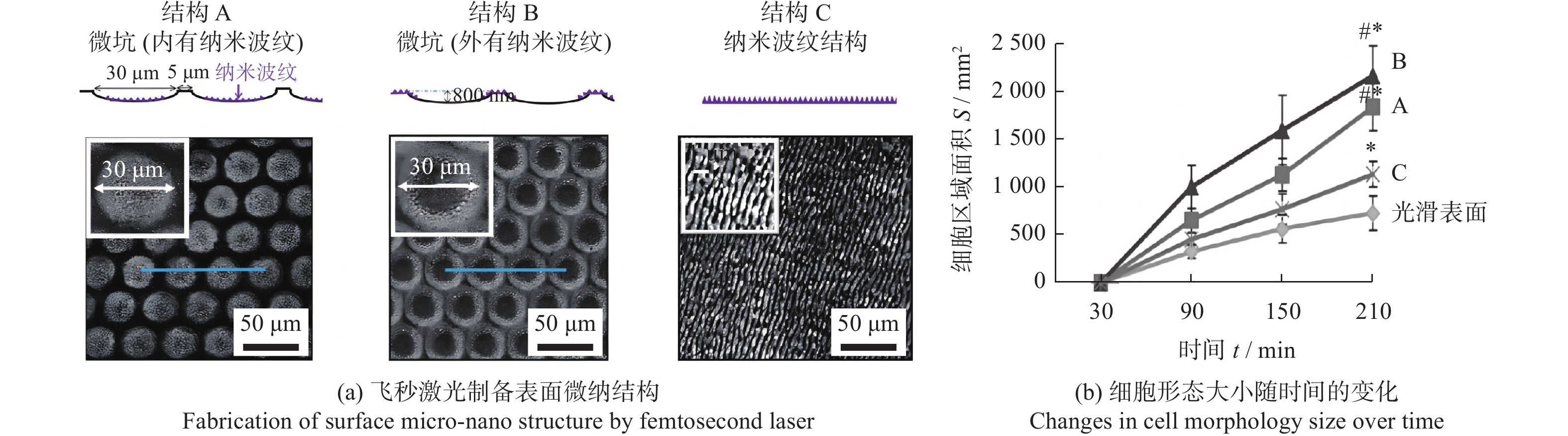
调控骨科植入物 Ti6Al4V 800 nm 120 fs 微坑 + 纳米波纹 微坑深度800 nm,
直径30 μm
纳米波纹深度约200 nm微坑与纳米波纹的结合提高了成骨细胞的分化能力 [23] 牙科、骨
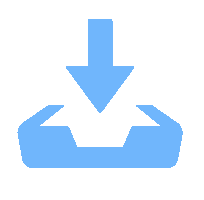
科植入物Ti6Al4V 1070 nm 500 μs 仿生六边形 边长150~300 μm 提高表面亲水性,能够促进成骨细胞的黏附和增殖 [24] 骨科植入物 氧化铝增韧氧化锆陶瓷 1030 nm 560 fs 微槽 + 纳米波纹 微槽宽度10 μm
纳米波纹周期300~400 nm细胞黏着面积、增殖数增加,表面结构可以调节细胞的排列和引导增殖 [26] 牙科、骨科
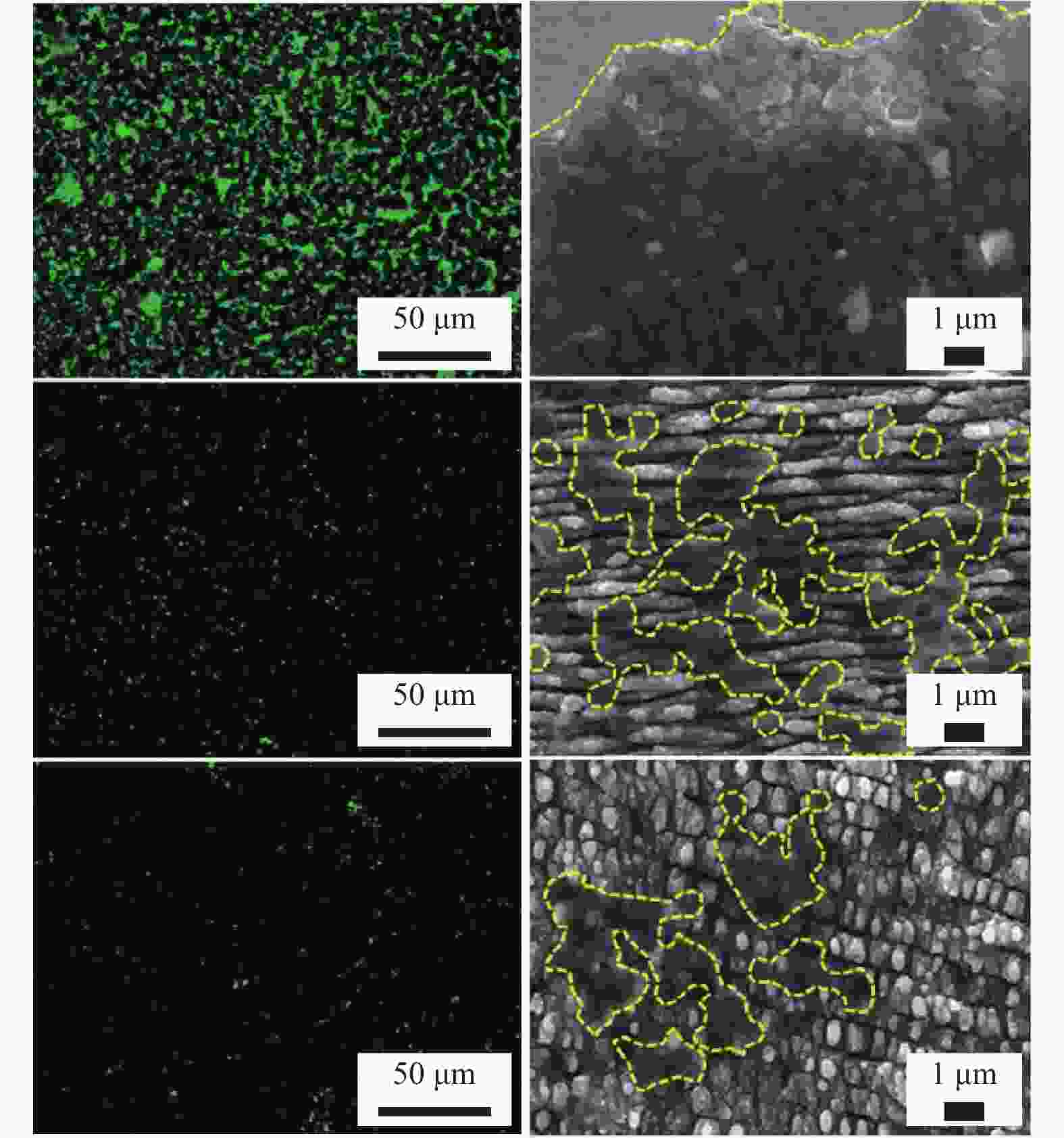
植入物钛合金板(TA2) 1030 nm 500 fs LIPSS、纳米柱 周期(710 ± 60)nm、(750 ±
130)nm结构表面细菌覆盖率远小于光滑表面,抑制细菌生物膜的形成 [34] 抗菌性 植入物 AISI 316L 1030 nm 8 ps 周期性亚微米
结构周期850 nm
深度500 nm大肠杆菌黏附率降低了99.8%,金黄色葡萄球菌降低了70.6% [35] 种植体 Ti6Al4V 1064 nm — 微坑 深度3 μm
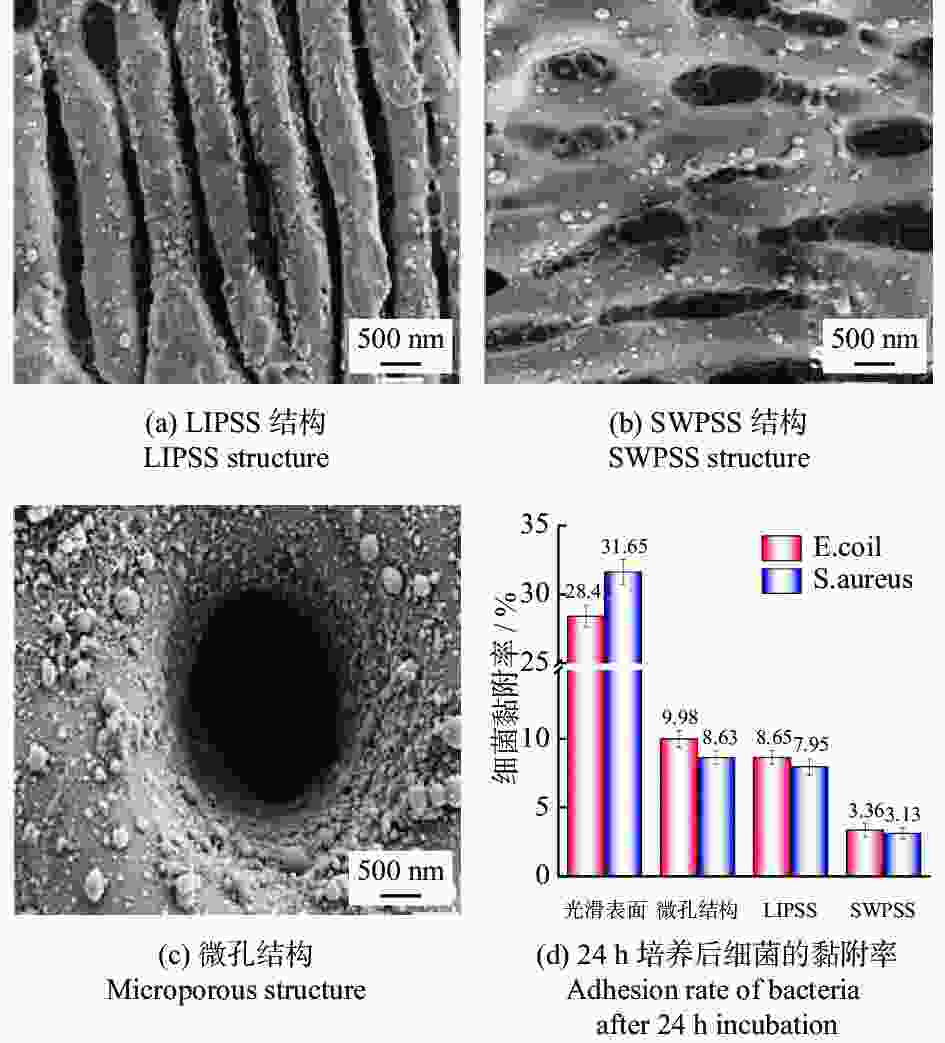
直径20 μm结构表面形成氧化钛结晶层,金黄色葡萄球菌的黏附率降低约85%。 [36] 植入器械 牙科、骨科植入物 Zr非晶合金 1030 nm 300 fs LIPSS、SWPSS、微孔结构 LIPSS周期830 nm
SWPSS周期 2950 nm
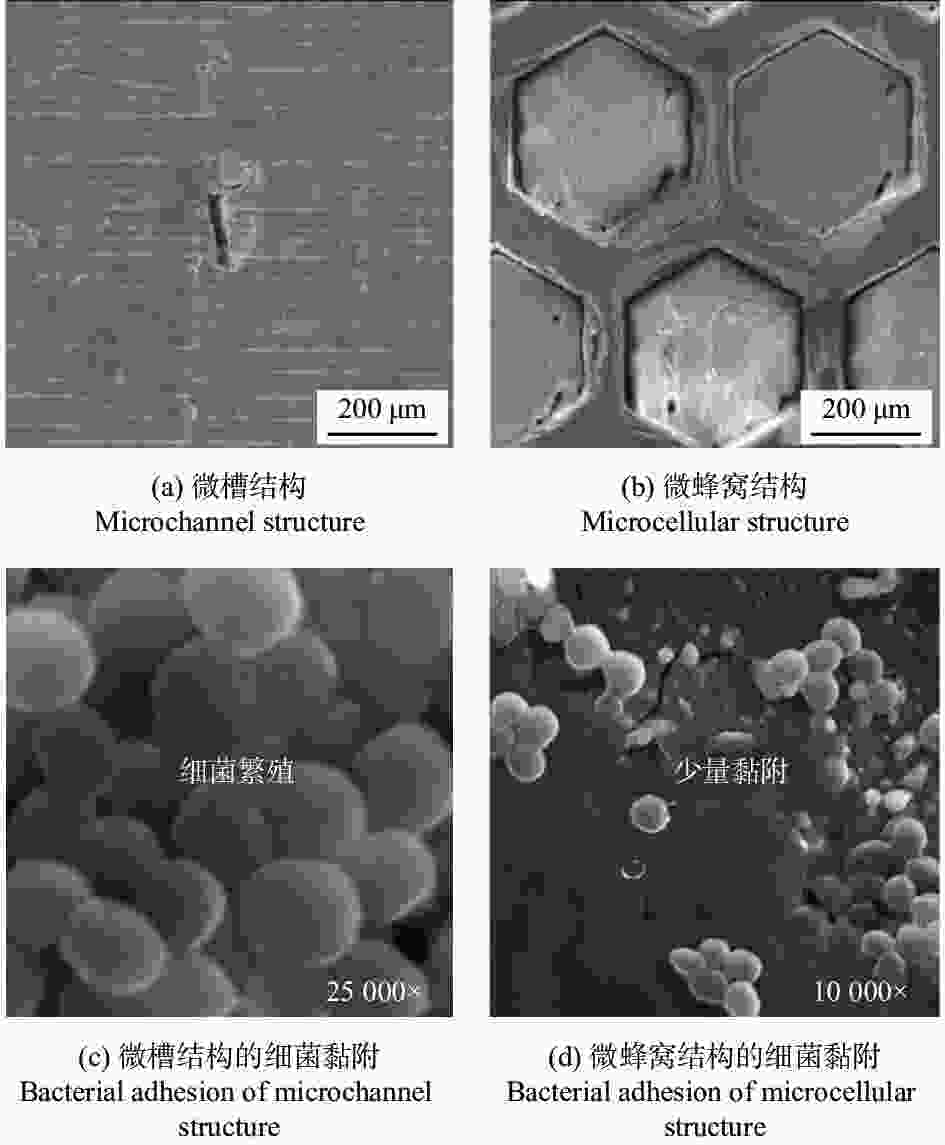
微孔结构周期10.24 µm、直径2.5 µm3种结构均有抑菌效果,SWPSS最好,结构尺寸略小于细菌时,抑制效果最优 [38] 植入物 AISI 316L 1064 nm 104 ns 微坑、微槽 深度3.7~6.2 µm 深度最大的微坑减少98%的细菌黏附,结构深度对细菌黏附行为有显著影响 [40] 牙科种植体 3Y-TZP氧化锆陶瓷 355 nm — 仿生蜂窝结构 边长200 µm
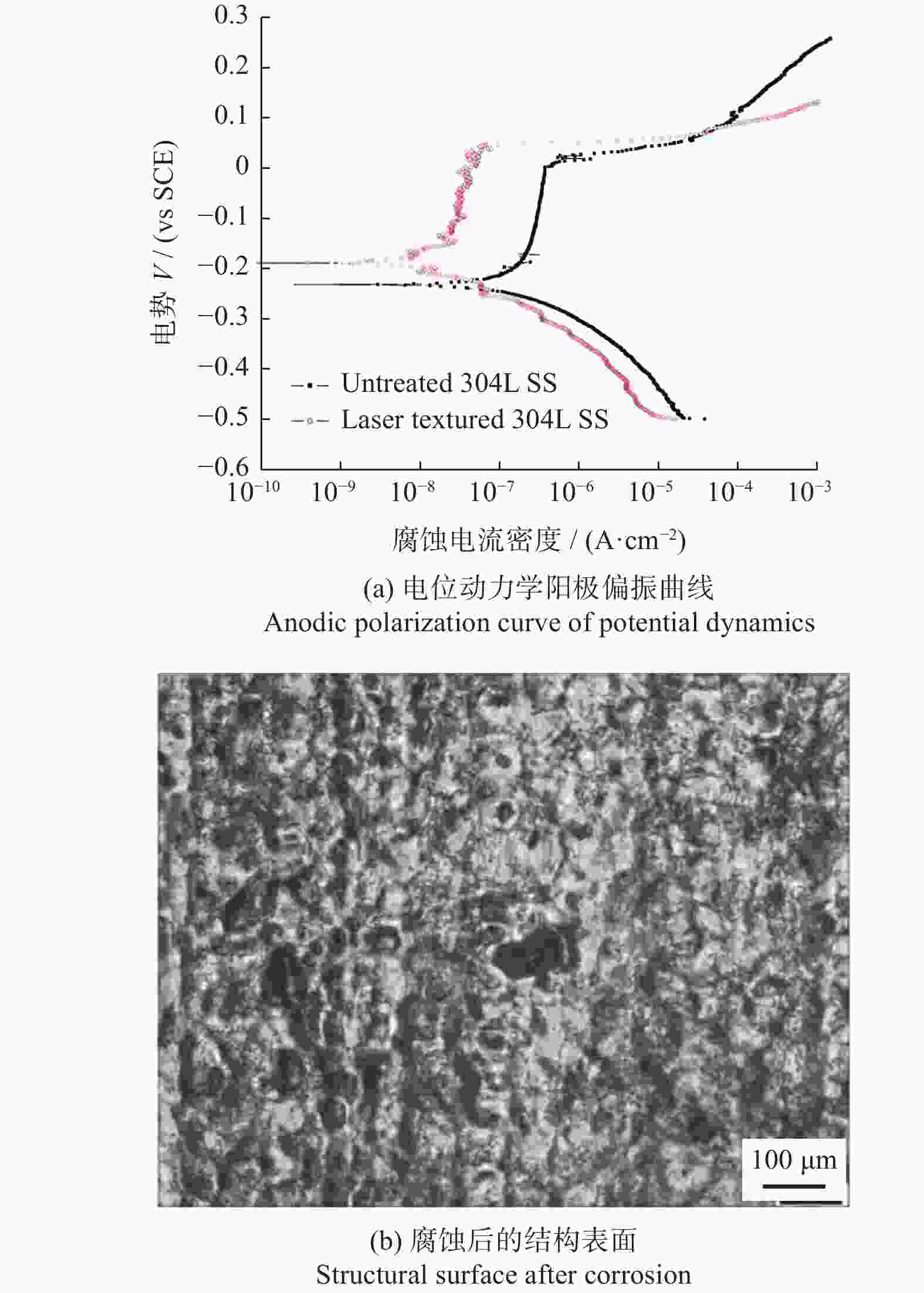
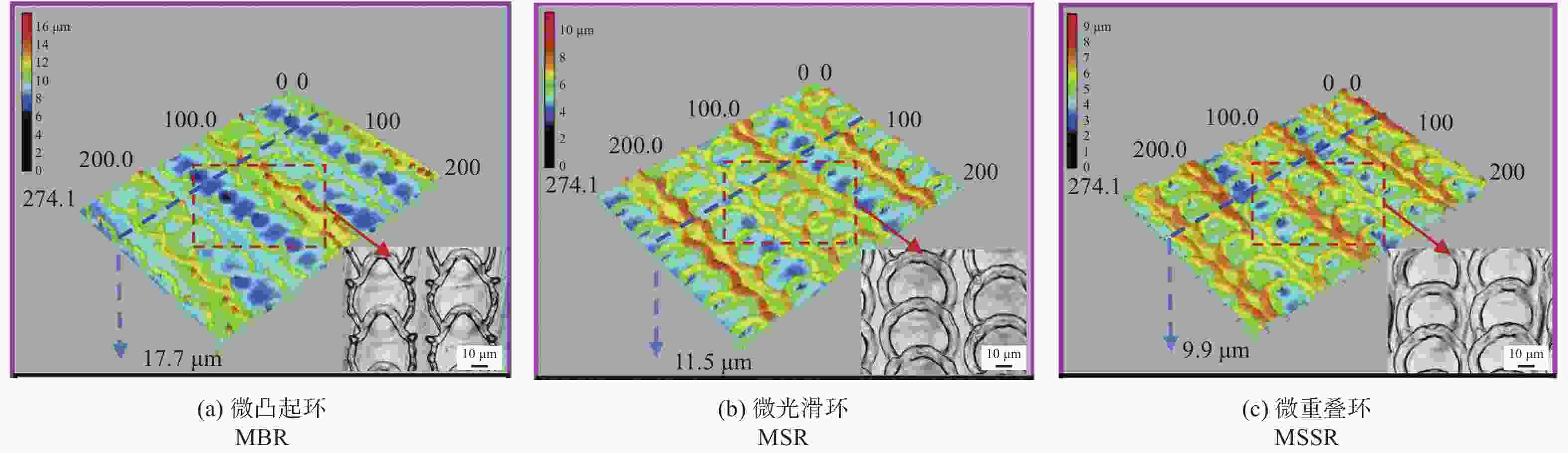
间距50 µm结构表面呈现疏水性,金黄色葡萄球菌约30% [41] 植入物 AISI 304L 1064 nm 100 ns 波纹状 — 提高耐蚀性和抗菌性,腐蚀过后结构表面有凹坑形成 [47] 耐蚀性 植入物 AISI 316L 355 nm 15 ns 微裂纹 — 激光改性后的表面耐蚀性提高了98.61% [48] 血管支架 AISI 316L 1064 nm 10 ps LIPSS 周期220 nm LIPSS减少了接触面积,耐腐蚀性比无结构表面提高约50倍 [50] 骨螺钉 Ti6Al4V 1064 nm 100 ns 微凸起环、
微光滑环、
微重叠环直径50 µm
深度5 µm耐蚀性分别提高97.02%、96.11%和97.97% [51] 手术器械 医用穿刺针 AISI 304L 532 nm 8 ps 微槽 槽宽50 µm
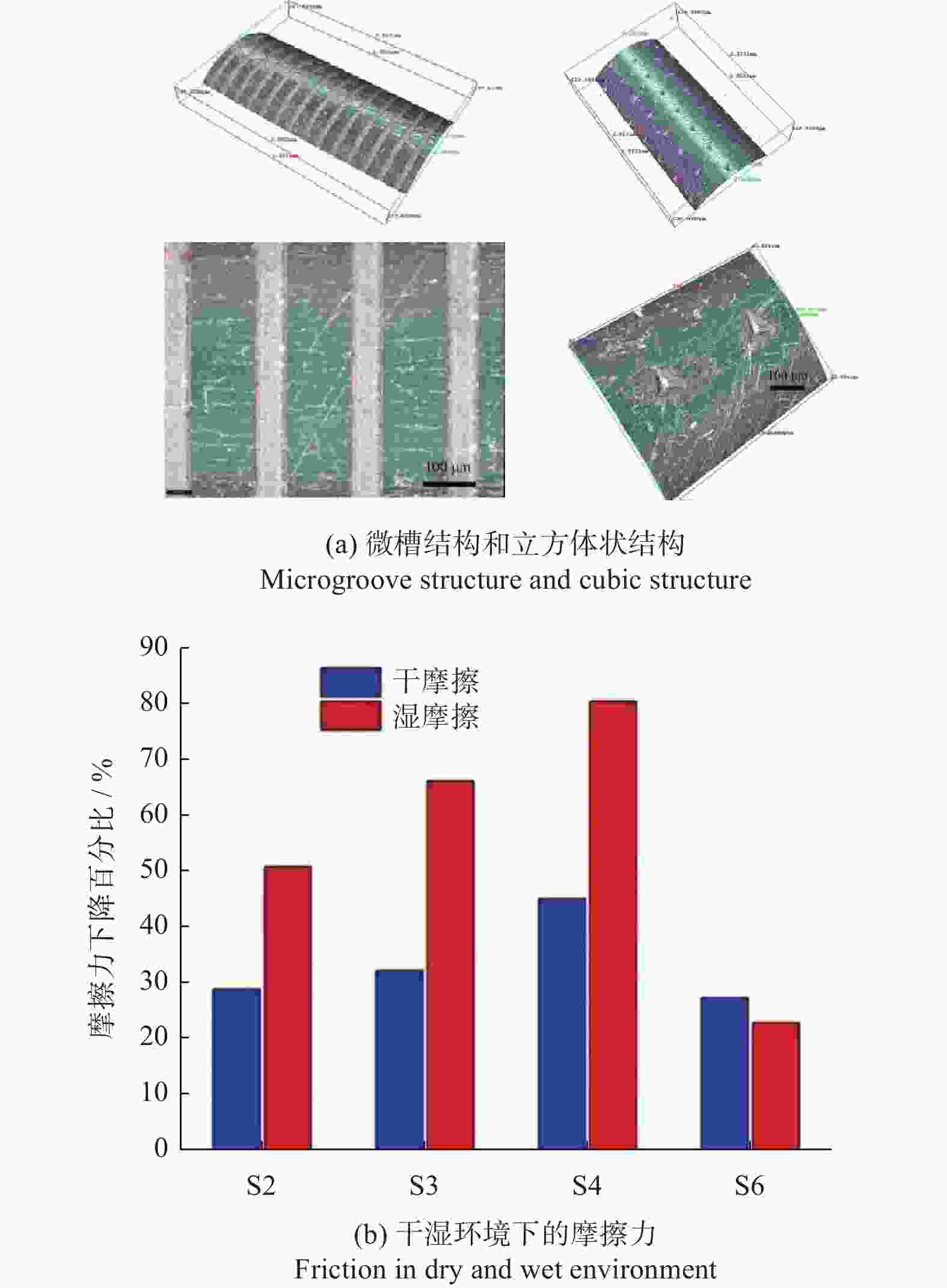
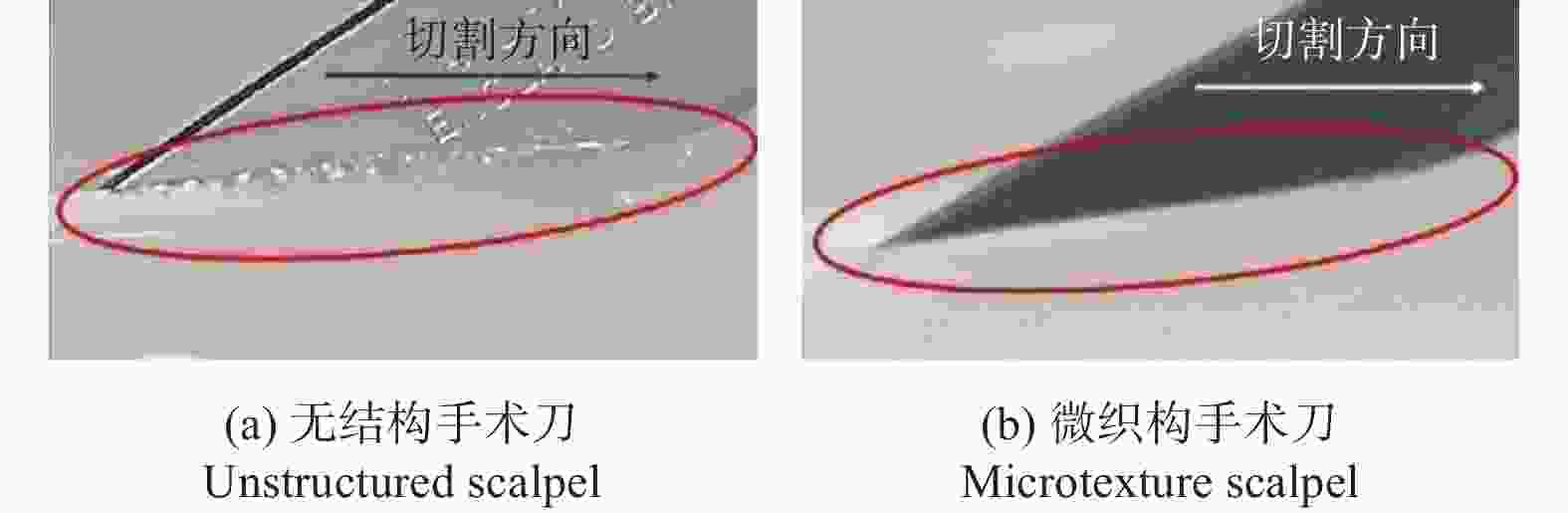
间距200 µm结构能减少接触面积,减摩效果超过80% [59] 摩擦特性 手术刀 AISI 316L 1053 nm 12 ns 微槽 槽宽100~500 µm
槽深5~15 µm切割时摩擦力降低33.2%,微织构表面切口更加平整 [62] 手术刀 AISI 316L 532 nm 8 ps 微凹坑 直径110 μm
深度30 μm
间距250 μm切割组织时摩擦力降低48% [63] 血管夹 Ti6Al4V 355 nm — 微槽、微坑 直径30~54 µm
间距40~100 µm
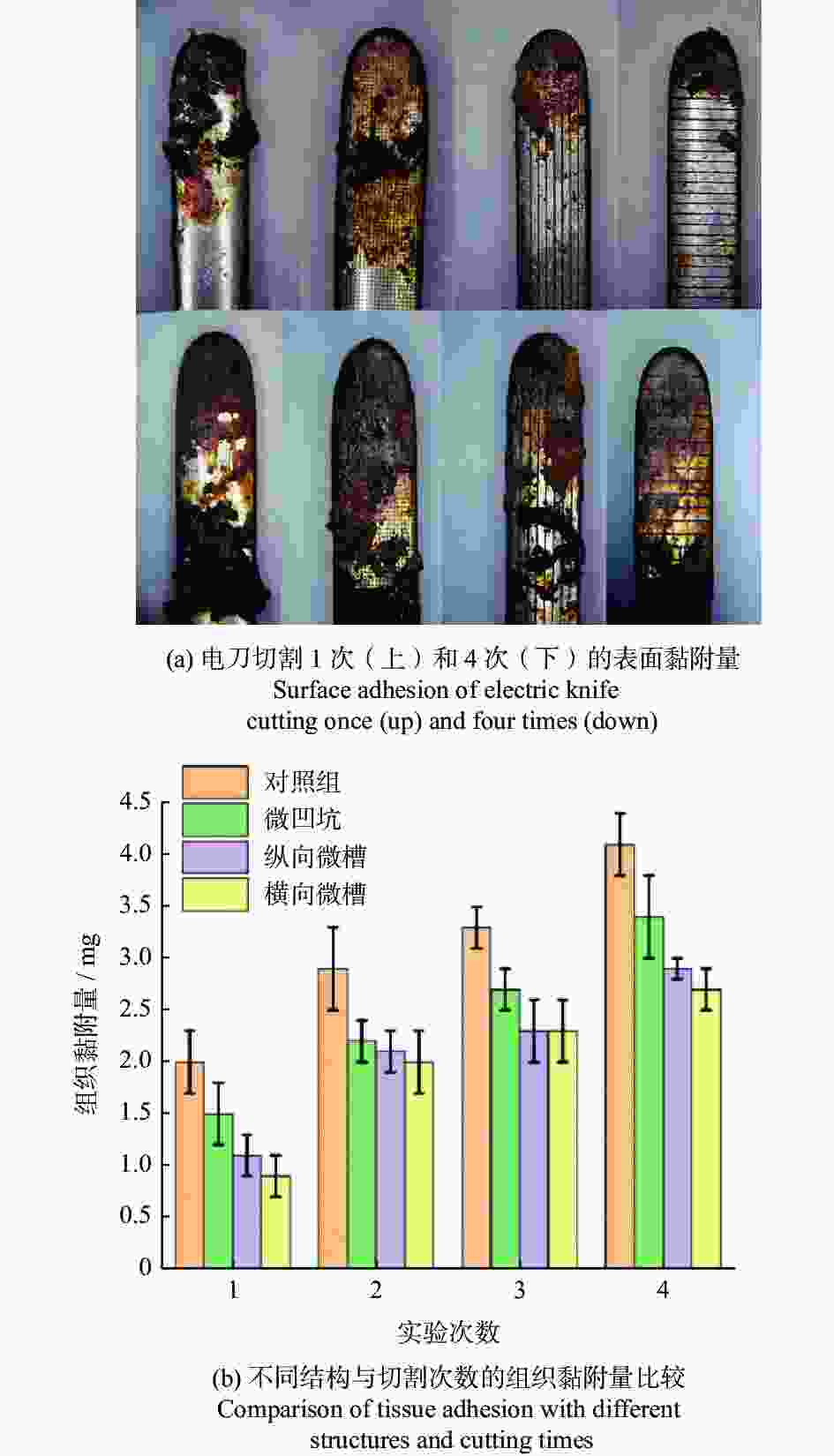
槽宽30~50 µm微槽宽度30 µm、间距40 µm的摩擦系数最高,摩擦力与接触面积成正比 [64] 电刀 AISI 316L 1070 nm 500 µs 仿生鳞片 高度0.5 µm 切割过程中,摩擦系数降低约15% [65] 电刀 AISI 304 532 nm 10 ps 微坑、微槽 微坑直径50 µm
槽宽25~100 µm
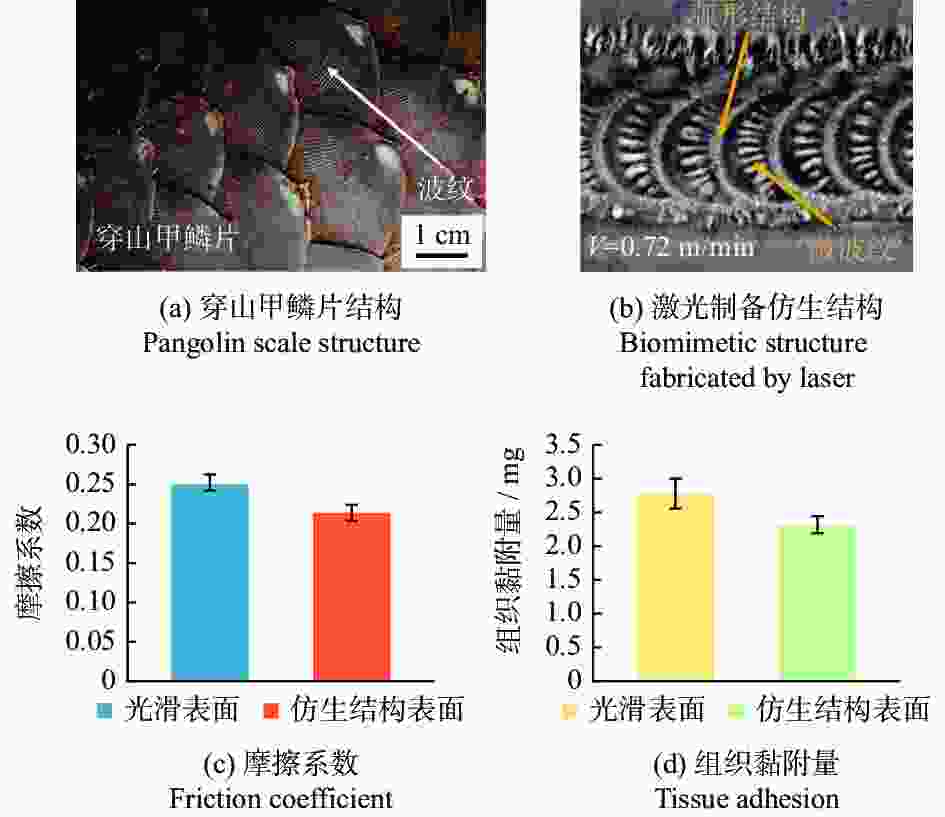
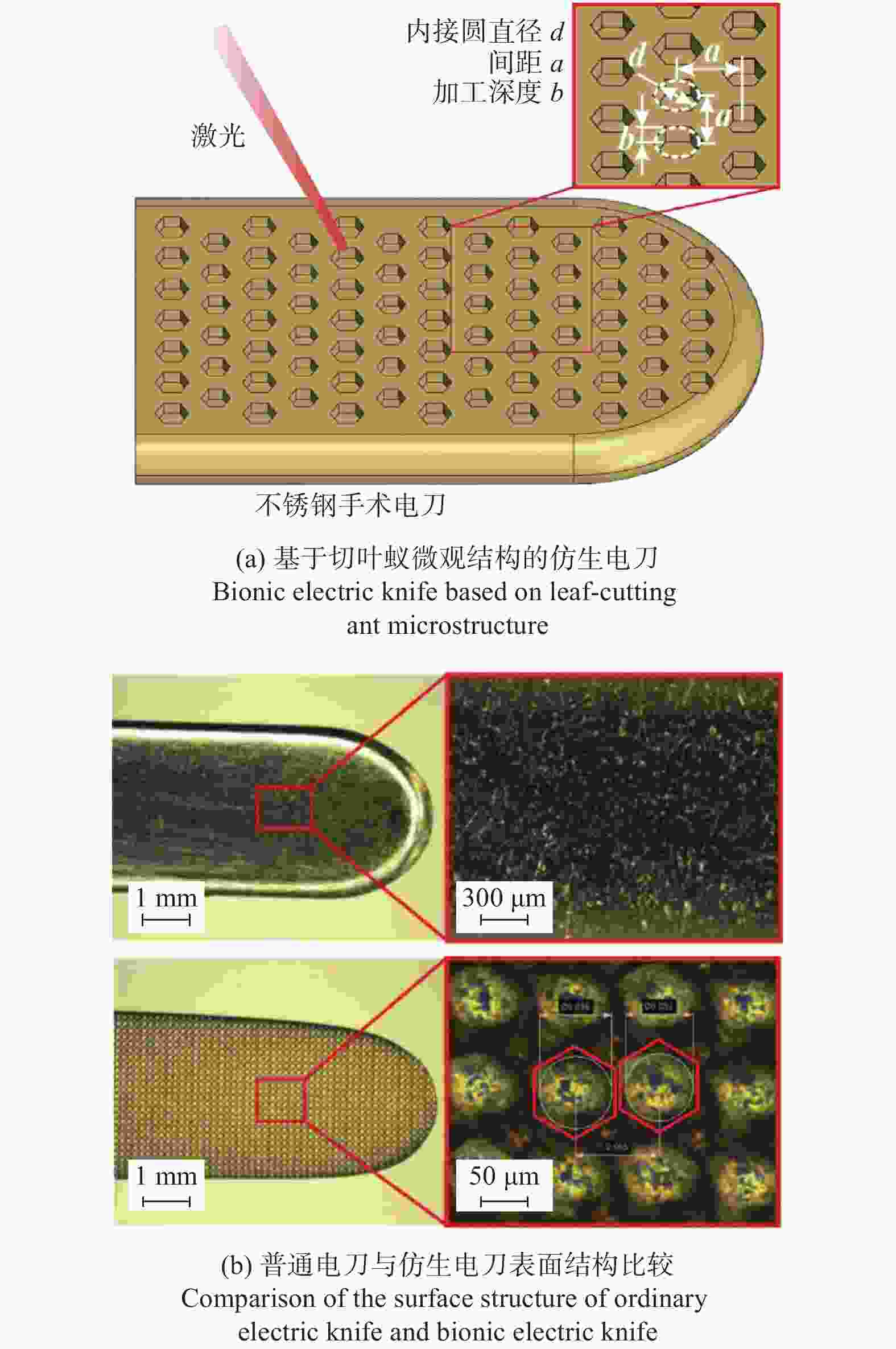
深度12 µm横向微槽的抗黏附效果最好,面积密度增加,黏附量减小 [72] 抗黏附性 电刀 AISI 304 1030 nm 300 fs 仿生六边形 内接圆直径20 μm 结构间距40 μm 加工深度6 μm 仿生结构的黏附力与其疏水性呈正相关,平均组织黏附量减少约36%。 [75] 手术刀 AISI 316L 1064 nm 100 ns 微凸圆 直径30~90 µm
间距30~90 µm结构表面呈疏水性,对血清溶液具有强大抗黏附效果 [76] 手术刀 AISI 316L 1064 nm 100 ns 激光烧蚀多孔 宽度4~6 μm
长度10~15 μm结构表面可以减少血清的黏附量,其性能与疏水性呈正相关 [77] -
[1] AHMMED K, COLIN G, ANNE-MARIE K. Fabrication of micro/nano structures on metals by femtosecond laser micromachining [J]. Micromachines,2014,5(4):1219-1253. doi: 10.3390/mi5041219 [2] KIETZIG A M, HATZIKIRIAKOS S G, ENGLEZOS P. Ice friction: The effects of surface roughness, structure, and hydrophobicity [J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2009,106(2):97. doi: 10.1063/1.3173346 [3] ZORBA V, STRATAKIS E, BARBEROGLOU M, et al. Biomimetic artificial surfaces quantitatively reproduce the water repellency of a lotus leaf [J]. Advanced Materials,2008,20(21):4049-4054. doi: 10.1002/adma.200800651 [4] VOROBYEV A Y, GUO C. Metal pumps liquid uphill [J]. Applied Physics Letters,2009,94(22):224102. doi: 10.1063/1.3117237 [5] CUI Z, LU L , GUAN Y , et al. Enhancing SERS detection on biocompatable metallic substrate for diabetes diagnosing [J]. Optics Letters,2021,46(15):3801-3804. doi: 10.1364/OL.430044 [6] ZUPANCIC M, MOZE M, GREGORCICP, et al. Evaluation of enhanced nucleate boiling performance through wall-temperature distributions on PDMS-silica coated and non-coated laser textured stainless steel surfaces [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2017,111:419-428. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.03.128 [7] LEI S, DEVARAJAN S, CHANG Z. A study of micropool lubricated cutting tool in machining of mild steel [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech,2009,209(3):1612-1620. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.024 [8] KUMAR B A, BABU P D, MARIMUTHU P, et al. Effect of laser surface texturing on tribological behaviour of grey cast iron [J]. International Journal of Surface Science and Engineering,2019,13(2/3):220. doi: 10.1504/IJSURFSE.2019.102381 [9] 张群英, 严玉蓉. 复合材料在医疗器械中的应用 [J]. 中国医疗器械信息,2012,18(2):13-17. doi: 10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2012.02.018ZHANG Qunying, YAN Yurong. The application of composite materials in the medical instrument [J]. China Medical Device Information,2012,18(2):13-17. doi: 10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2012.02.018 [10] 卢立斌, 王海鹏, 管迎春, 等. 激光微加工技术制备生物医用器械的现状与进展 [J]. 中国激光,2017,44(1):65-79. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0102005LU Libin, WANG Haipeng, GUAN Yingchun, et al. Laser microfabrication of biomedical devices [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2017,44(1):65-79. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0102005 [11] LIU W, LIU S, WANG L. Surface modification of biomedical titanium alloy: micromorphology, microstructure evolution and biomedical applications [J]. Coatings,2019,9(4):249. doi: 10.3390/coatings9040249 [12] 王艳颖,宫苹,张健. 不同种植体表面性质对雪旺细胞生物学行为影响的研究 [J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2021,39(3):279-285. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.03.006WANG Yanying, GONG Ping, ZHANG Jian. Effects of different implant surface properties on the biological behavior of Schwann cells [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology,2021,39(3):279-285. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.03.006 [13] ZAFFORA A, FRANCO F D, VIRTÙ D, et al. Tuning of the Mg alloy AZ31 anodizing process for iodegradable implants [J]. Applied Materials and Interfaces,2021,13(11):12866-12876. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c22933 [14] 张一, 方均, 王茜, 等. 医用钽类植入物抗菌性能研究进展 [J]. 河北医科大学学报,2021,42(1):116-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2021.01.025ZHANG Yi, FANG Jun, WANG Qian, et al. Research progress on antibacterial properties of medical tantalum implants [J]. Journal of Hebei Medical University,2021,42(1):116-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2021.01.025 [15] 张力文, 陈华伟, 王炎,等. 基于树蛙脚掌湿黏附的仿生手术夹钳表面研究 [J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(17):14-20. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.17.014ZHANG Liwen, CHEN Huawei, WANG Yan, et al. Bioinspired surgical grasper based on the strong wet attachment of tree frog's toe pads [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2018,54(17):14-20. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.17.014 [16] 江汪彪, 胡亚辉, 郑清春, 等. 基于微织构刀具的皮质骨钻削温度研究 [J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(11):207-211. doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2016.11.045JIANG Wangbiao, HU Yahui, ZHENG Qingchun, et al. Study of drilling temperature on cortical bone based on micro-texture tool [J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2016,37(11):207-211. doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2016.11.045 [17] 蔡彦坤, 祁星颖, 隋磊. 种植材料表面纳米级形貌对细胞成骨效应的影响 [J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2019,35(6):891-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2019.06.028CAI Yankun, QI Xingying, SUI Lei. The influence of nanoscale morphology on the surface of implant materials on the osteogenic effect of cells [J]. Journal of Practical Stomatology,2019,35(6):891-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2019.06.028 [18] CHANG H S, JEONG H, FURUKAWA K S, et al. The switching of focal adhesion maturation sites and actin filament activation for MSCs by topography of well-defined micropatterned surfaces [J]. Biomaterials,2013,34(7):1764-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.11.031 [19] HUANG Q, ELKHOOLY T A, LIU X, et al. Effects of hierarchical micro/nano-topographies on the morphology, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2016,145:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.04.031 [20] HOHMANN J K, FREYMANN G V. Influence of direct laser written 3D topographies on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells: towards improved implant surfaces [J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2014,24(42):6573-6580. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201401390 [21] HU Y, DUAN J, YANG X, et al. Wettability and biological responses of titanium surface's biomimetic hexagonal microstructure [J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications,2022,37(6):1112-1123. doi: 10.1177/08853282221121883 [22] ZHENG Q, MAO L, SHI Y, et al. Biocompatibility of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy implants with laser microgrooved surfaces [J]. Materials Technology,2020,37(12):2039-2048. doi: 10.1080/10667857.2020.1816011 [23] DUMAS V, GUIGNANDON A, VICO L, et al. Femtosecond laser nano/micro patterning of titanium influences mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and commitment [J]. Biomedical Materials,2015,10(5):055002. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/10/5/055002 [24] LI C, YANG L, LIU N, et al. Bioinspired surface hierarchical microstructures of Ti6Al4V alloy with a positive effect on osteoconduction [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2020,388:125594. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125594 [25] XU Y, LIU W, ZHANG G, et al. Friction stability and cellular behaviors on laser textured Ti–6Al–4V alloy implants with bioinspired micro-overlapping structures [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2020:103823. [26] CARVALHO A, CANGUEarvalho, Liliana, et al. Femtosecond laser microstructured Alumina toughened Zirconia: A new strategy to improve osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs [J]. Applied Surface Science: A Journal Devoted to the Properties of Interfaces in Relation to the Synthesis and Behaviour of Materials,2018,435:1237-1245. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.206 [27] YU Z, YANG G, ZHANG W, et al. Investigating the effect of picosecond laser texturing on microstructure and biofunctionalization of titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2018,255:129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.12.009 [28] WANG Y, YU Z, LI K, et al. Study on the effect of surface characteristics of short-pulse laser patterned titanium alloy on cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2021,128:112349. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112349 [29] VEERACHAMY S, YARLAGADDA T, MANIVASAGAM G, et al. Bacterial adherence and biofilm formation on medical implants: A review. [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part H Journal of Engineering in Medicine,2014,228(10):1083-99. doi: 10.1177/0954411914556137 [30] 贾曼, 金文姬, 李娜, 等. 骨科患者手术植入物感染的相关因素分析与预防 [J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(23):5391-5394. doi: 10.11816/cn.ni.2017-171610JIA Man, JIN Wenji, LI Na, et al. Related factors analysis and prevention of surgical implant infections in orthopedic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology,2017,27(23):5391-5394. doi: 10.11816/cn.ni.2017-171610 [31] FERRARIS S, SPRIANO S. Antibacterial titanium surfaces for medical implants [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2016,61:965-978. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.062 [32] JENKINS J, MANTELL J, NEAL C, et al. Antibacterial effects of nanopillar surfaces are mediated by cell impedance, penetration and induction of oxidative stress [J]. Nature Communications,2020,11:1626. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15471-x [33] JAGGESSAR A, SHAHALI H, MATHEW A, et al. Bio-mimicking nano and micro-structured surface fabrication for antibacterial properties in medical implants [J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology,2017,15(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0306-1 [34] CUNHA A, ELIE A M, PLAWINSKI L, et al. Femtosecond laser surface texturing of titanium as a method to reduce the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and biofilm formation [J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,360:485-493. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.102 [35] PETER A, LUTEY A, FAAS S, et al. Direct laser interference patterning of stainless steel by ultrashort pulses for antibacterial surfaces [J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2019,123:105954. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105954 [36] VADAKKUMPURATH S, VENUGOPAL A N, ULLATTIL S. Influence of micro-textures on antibacterial behaviour of titanium-based implant surfaces: In vitro studies [J]. Biosurface and Biotribology,2019,5(1):20-23. doi: 10.1049/bsbt.2018.0023 [37] 王芳, 程翔, 刘桂英, 等. 牙科用微弧氧化后锆基非晶合金的组织相容性研究 [J]. 口腔医学,2016,36(9):784-787, 800. doi: 10.13591/j.cnki.kqyx.2016.09.004WANG Fang, CHENG Xiang, LIU Guiying, et al. Histocompatibility evaluation of Zr-based bulk metallic glass with micro-arc oxidation for dental restoration [J]. Stomatology,2016,36(9):784-787, 800. doi: 10.13591/j.cnki.kqyx.2016.09.004 [38] HUANG H, ZHANG P, YU Z, et al. Effects of periodic surface structures induced by femtosecond laser irradiation on the antibacterial properties of Zr-based amorphous material [J]. International Journal for Light and Electron Optics,2022,268:169760. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169760 [39] LUO X, YAO S, ZHANG H, et al. Biocompatible nano-ripples structured surfaces induced by femtosecond laser to rebel bacterial colonization and biofilm formation [J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2020,124:105973. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105973 [40] ROMOLI L, LAZZINI G, LUTEY A, et al. Influence of ns laser texturing of AISI 316L surfaces for reducing bacterial adhesion [J]. CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology,2020,69(1):529-532. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2020.04.003 [41] XU J, JI M, LI L, et al. Improving wettability, antibacterial and tribological behaviors of zirconia ceramics through surface texturing [J]. Ceramics International,2022,48(3):3702-3710. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.152 [42] SHAIKH S, KEDIA S, SINGH D, et al. Surface texturing of Ti6Al4V alloy using femtosecond laser for superior antibacterial performance [J]. Journal of Laser Applications,2019,31(1):022011. doi: 10.2351/1.5081106 [43] 王鲁宁, 刘丽君, 岩雨, 等. 蛋白质吸附对医用金属材料体外腐蚀行为的影响 [J]. 金属学报,2021,57(1):1-15. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00198WANG Luning, LIU Lijun, YAN Yu, et al. Influences of protein adsorption on the in vitro corrosion of biomedical metals [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica,2021,57(1):1-15. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00198 [44] TALHA M, MA Y, KUMAR P, et al. Role of protein adsorption in the bio corrosion of metallic implants – A review [J]. Colloids and surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2019,176:494-506. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.038 [45] WANG C, ZHANG G, LI Z, et al . Tribological behavior of Ti-6Al-4V against cortical bone in different biolubricants [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2019,90:460-471. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.10.031 [46] 王俊鸿. 骨科植入物的抗腐蚀性能 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1676-1679. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2012.09.035WANG Junhong. Corrosion resistance of orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2012,16(9):1676-1679. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2012.09.035 [47] GUPTA R K, ANANDKUMAR B, CHOUBEY A, et al. Antibacterial and corrosion studies on nanosecond pulse laser textured 304L stainless steel surfaces [J]. Lasers in Manufacturing & Materials Processing,2019,6(3):332-343. [48] LU Y, GUAN Y C, LI Y, et al. Nanosecond laser fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on 316L stainless steel and corrosion protection application [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,604:125259. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125259 [49] ANDRZEJ GRABOWSKI, M SOZAŃSKA, ADAMIAK M. Laser surface texturing of Ti6Al4V alloy, stainless steel and aluminium silicon alloy [J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,417:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.060 [50] MUHAMMAD S, NATALIA B, RICCARDO P, et al. Tailoring surface properties, biocompatibility and corrosion behavior of stainless steel by laser induced periodic surface treatment towards developing biomimetic stents [J]. Surfaces and Interfaces,2022,34:102365. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102365 [51] XU Y, LI Z, ZHANG G, et al. Electrochemical corrosion and anisotropic tribological properties of bioinspired hierarchical morphologies on Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by laser texturing [J]. Tribology International,2019,134:352-364. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2019.01.040 [52] KUCZYNSKA-ZEMLA D, SOTNICZUK A, PISAREK M, et al. Corrosion behavior of titanium modified by direct laser interference lithography [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2021,418:127219. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127219 [53] WANG C, TIAN P, CAO H, et al. Enhanced biotribological and anticorrosion properties and bioactivity of Ti6Al4V alloys with laser texturing [J]. ACS Omega,2022,7(35):31081-31097. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03166 [54] HAN P, CHE D, PALLAV K, et al. Models of the cutting edge geometry of medical needles with applications to needle design [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2012,65(1):157-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2012.09.014 [55] TSAI P H, LI T H, HSU K T, et al. Effect of coating thickness on the cutting sharpness and durability of Zr-based metallic glass thin film coated surgical blades [J]. Thin Solid Films,2016,618:36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2016.05.020 [56] NISHIZAKA C, NISHIKAWA M, YATA T, et al. Inhibition of surgical trauma-enhanced peritoneal dissemination of tumor cells by human catalase derivatives in mice [J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2011,51(3):773-779. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.025 [57] SADJADI H, HASHTRUDI-ZAAD K, FICHTINGER G. Needle deflection estimation: Prostate brachytherapy phantom experiments [J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery,2014,9(6):921-929. doi: 10.1007/s11548-014-0985-0 [58] SAFAVI-ABBASI S, MORON F, SUN H, et al. Techniques and long-term outcomes of cotton-clipping and cotton-augmentation strategies for management of cerebral aneurysms [J]. Journal of Neurosurgery,2016,125(3):720-729. doi: 10.3171/2015.7.JNS151165 [59] WANG X, HAN P, KAG M, et al. Surface-blended texturing of medical needles for friction reduction using a picosecond laser [J]. Applied Physics A,2016,122(4):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s00339-016-9892-2 [60] WANG X, GIOVANNINI M, XING Y, et al. Fabrication and tribological behaviors of corner-cube-like dimple arrays produced by laser surface texturing on medical needles [J]. Tribology International,2015,92:553-558. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2015.07.042 [61] PAN C, XU C, HUANG Z, et al. Antifriction effect of 316L stainless steel textured surface with superhydrophilic properties in brain tissue insertion [J]. Materials Research Express,2021,8(10):105401. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac2a61 [62] BUTLER-SMITH P, SEE T L, HUMPHREY E, et al. A comparison of the tactile friction and cutting performance of textured scalpel blades modified by direct laser writing and direct laser interference patterning processes [J]. Procedia CIRP,2022,111:657-661. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2022.08.005 [63] VELASQUEZ T, HAN P, CAO J, et al. Feasibility of laser surface texturing for friction reduction in surgical blades [C]// ASME 2013 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference Collocated with the 41st North American Manufacturing Research Conference, June 10-14, 2013, Madison, Wisconsin. New York: ASME, c2013: MSEC2013-1193, V001T01A009 [64] ITTA I, TSUKIYAMA Y, NOMURA S, et al. Frictional characteristics of clamp surfaces of aneurysm clips finished by laser processing [J]. Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing,2016,10(2):JAMDSM0026. doi: 10.1299/jamdsm.2016jamdsm0026 [65] LI C, YANG Y, YANG L, et al. Biomimetic anti-adhesive surface microstructures on electrosurgical blade fabricated by long-pulse laser inspired by pangolin scales [J]. Micromachines,2019,10(12):816. doi: 10.3390/mi10120816 [66] LI C, YANG L J, YANG C C, et al. Biomimetic anti-adhesive surface micro-structures of electrosurgical knife fabricated by fibre laser [J]. Journal of Laser Micro Nanoengineering,2018,13(3):309-313. doi: 10.2961/jlmn.2018.03.0028 [67] LU J, WANG X, HUANG Y, et al. Fabrication and cutting performance of bionic micro-serrated scalpels based on the miscanthus leaves [J]. Tribology International,2020,145:106162. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106162 [68] MEAKIN L B, MURRELL J C, DORAN I C P, et al. Electrosurgery reduces blood loss and immediate postoperative inflammation compared to cold instruments for midline celiotomy in dogs: A randomized controlled trial [J]. Veterinary Surgery,2017,46(4):515-519. doi: 10.1111/vsu.12641 [69] ZHENG L, WAN J, LONG Y, et al. Effect of high-frequency electric field on the tissue sticking of minimally invasive electrosurgical devices [J]. Royal Society Open Science,2018,5(7):180125. doi: 10.1098/rsos.180125 [70] SUTTON P A, AWAD S, PERKINS A C, et al. Comparison of lateral thermal spread using monopolar and bipolar diathermy, the Harmonic Scalpel™ and the Ligasure™ [J]. British Journal of Surgery,2010,97(3):428-433. doi: 10.1002/bjs.6901 [71] TESLER A B, KIM P, KOLLE S, et al. Extremely durable biofouling-resistant metallic surfaces based on electrodeposited nanoporous tungstite films on steel [J]. Nature Communications,2015,6(1):8649. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9649 [72] ZHOU C, LU J, WANG X. Adhesion behavior of textured electrosurgical electrode in an electric cutting process [J]. Coatings,2020,10(6):596. doi: 10.3390/coatings10060596 [73] LIN C C, LIN H J, LIN Y H, et al. Micro/nanostructured surface modification using femtosecond laser pulses on minimally invasive electrosurgical devices [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B:Applied Biomaterials,2017,105(4):865-873. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33613 [74] HAN Z, FU J, FENG X, et al. Bionic anti-adhesive electrode coupled with maize leaf microstructures and TiO2 coating [J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(72):45287-45293. doi: 10.1039/C7RA08184G [75] LIU Z, WU F, GU H, et al. Adhesion failure and anti-adhesion bionic structure optimization of surgical electrodes in soft tissue cutting [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2023,89:444-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.01.071 [76] LI K, YAO W, XIE Y, et al. A strongly hydrophobic and serum-repelling surface composed of CrN films deposited on laser-patterned microstructures that was optimized with an orthogonal experiment [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2020,391:125708. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125708 [77] LI K, XIE Y, LIANG L, et al. Wetting behavior investigation of a complex surface prepared by laser processing combined with carbon films coating [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2019,378:124989. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.124989 [78] ZHANG J, LI G, LI D, et al. In vivo blood-repellent performance of a controllable facile-generated superhydrophobic surface [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(24):29021-29033. -



 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
