Effect of lubricants on microstructure and properties of metal abrasive tools via wet molding
-
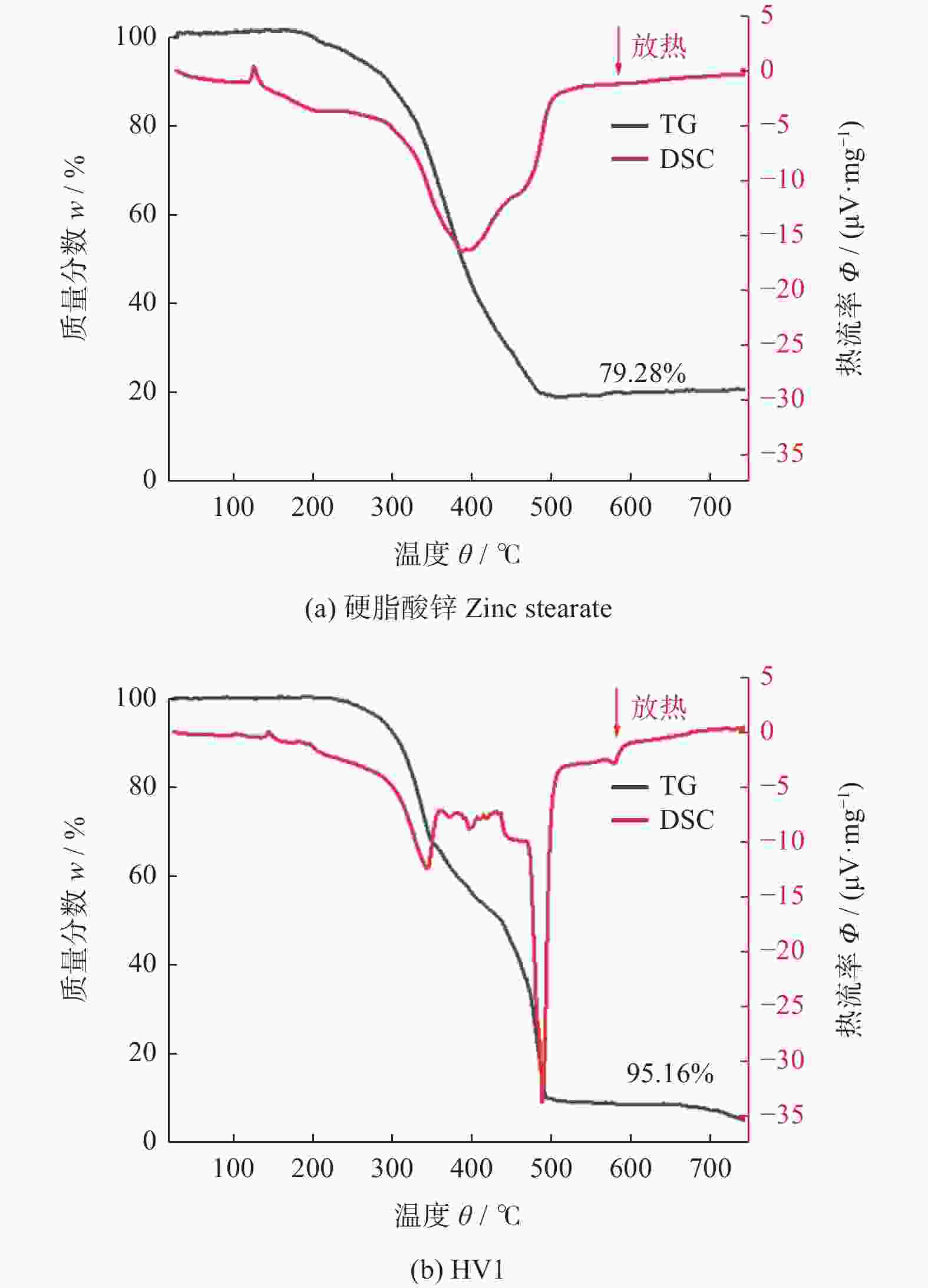
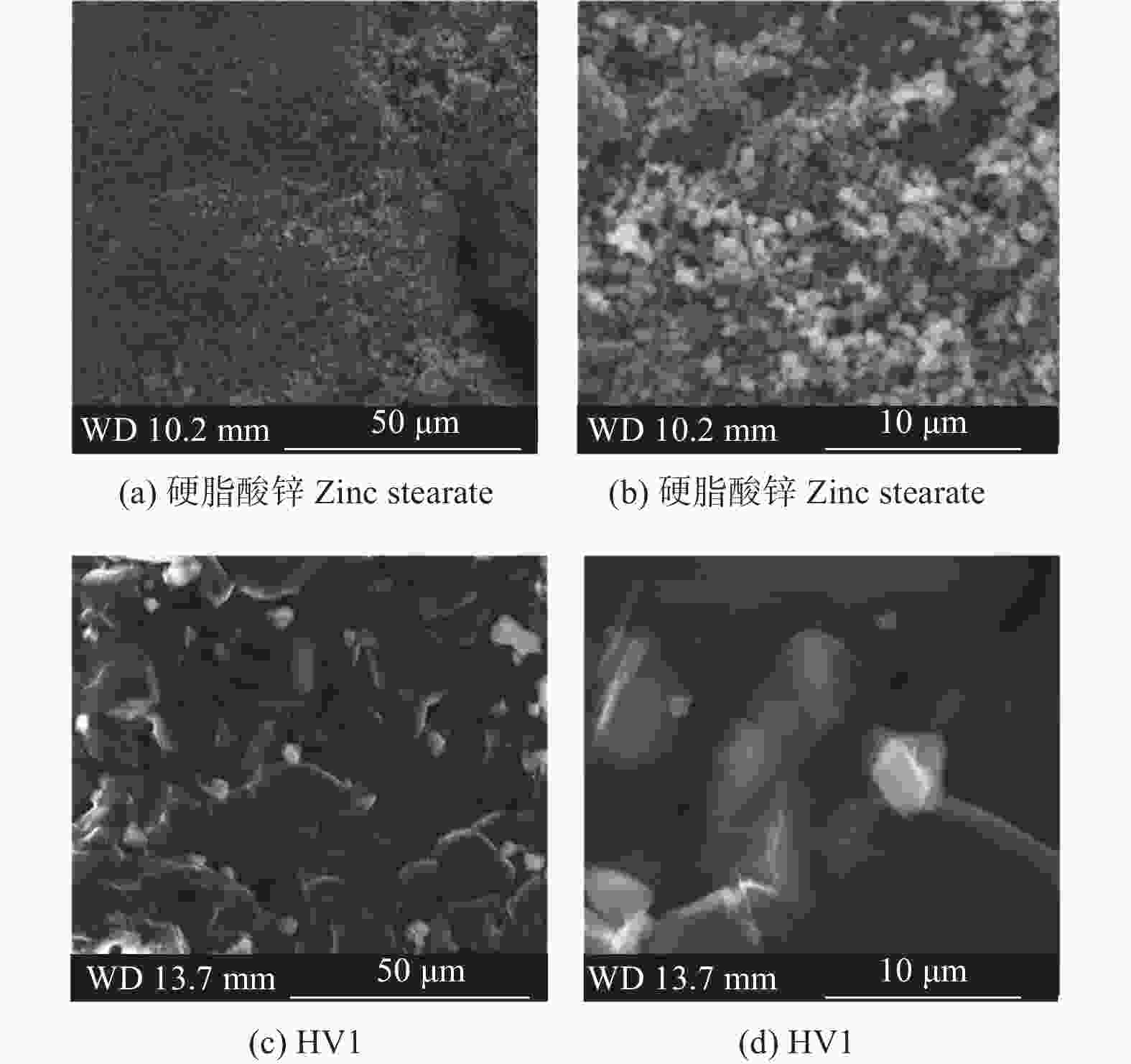
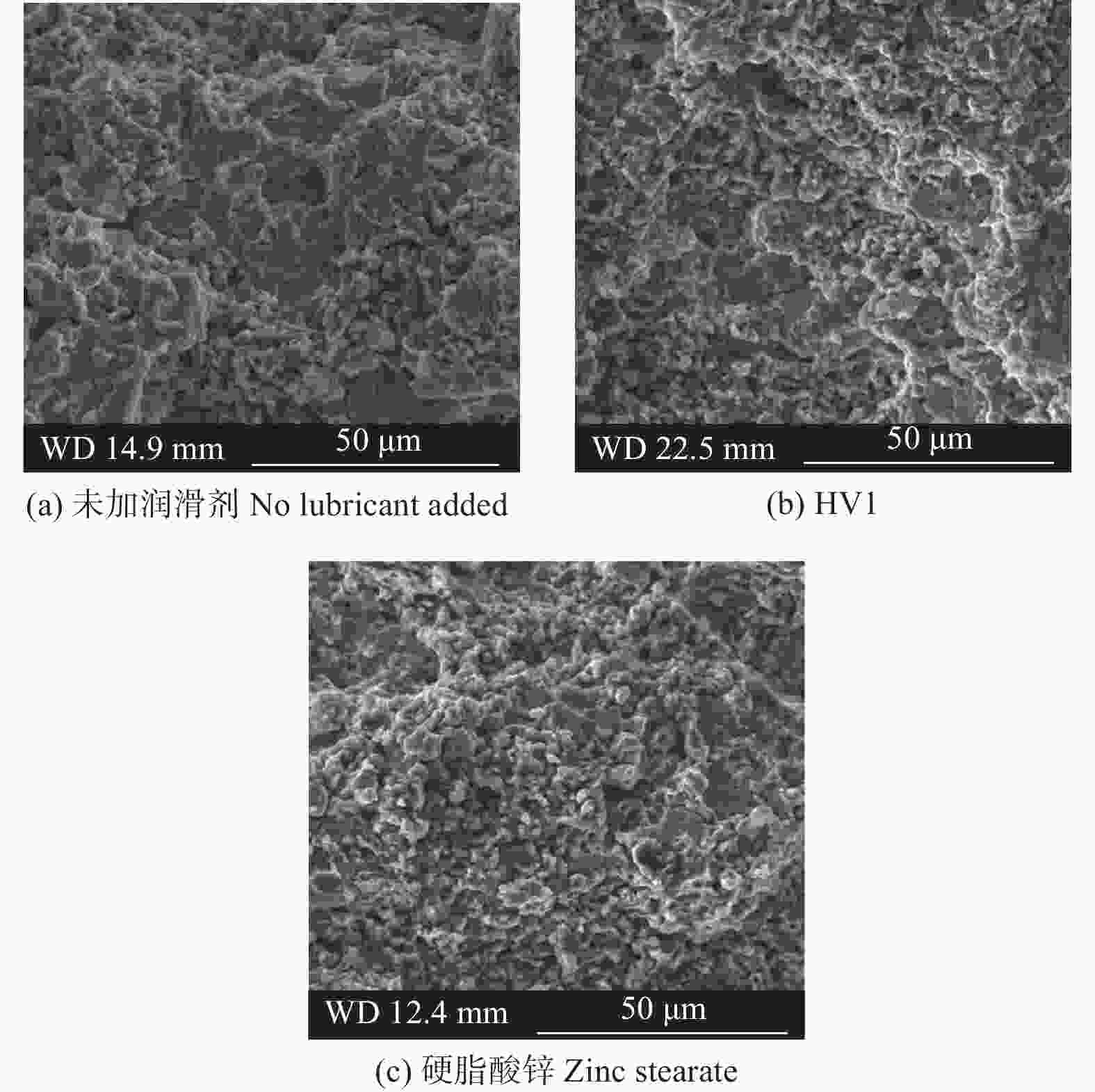
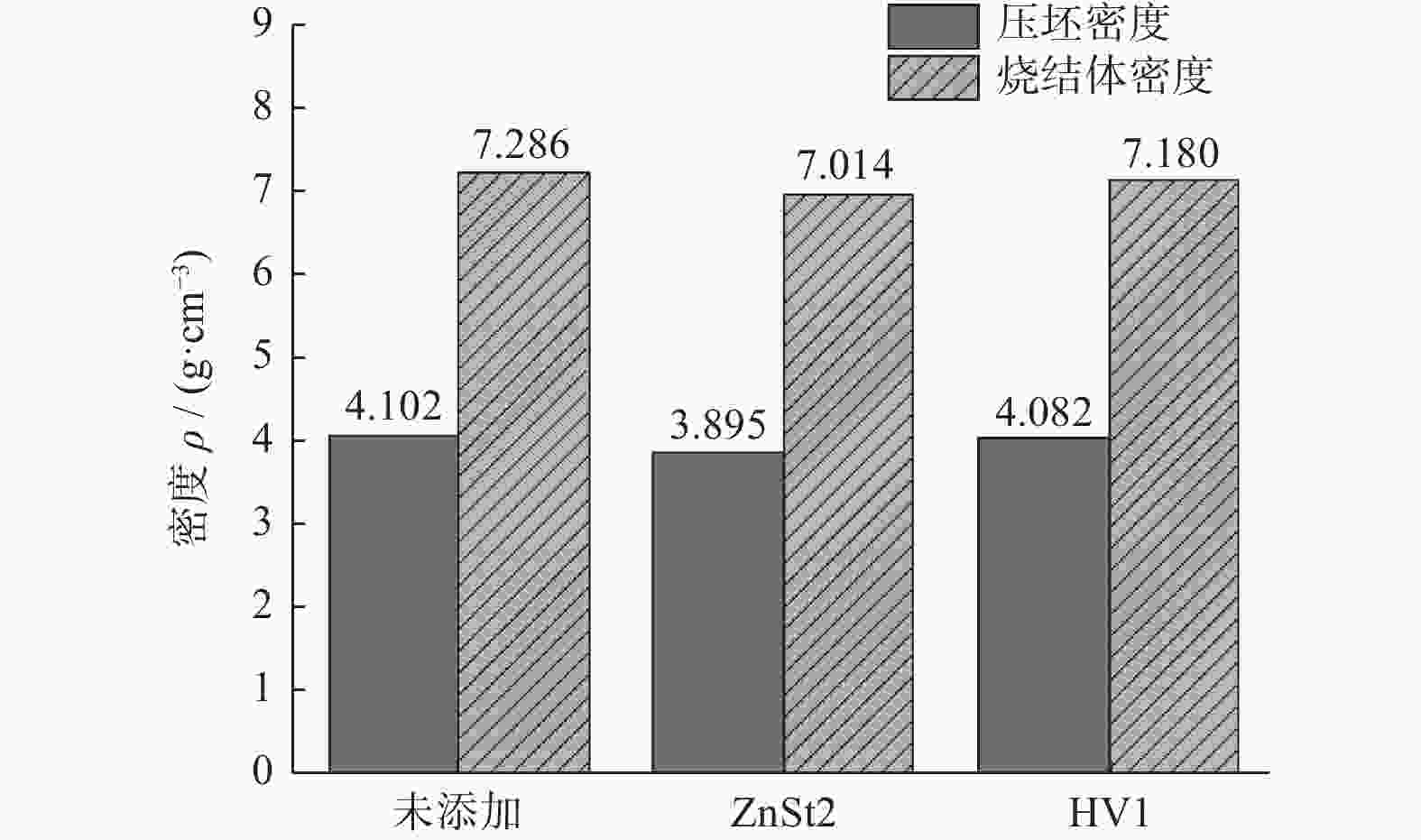
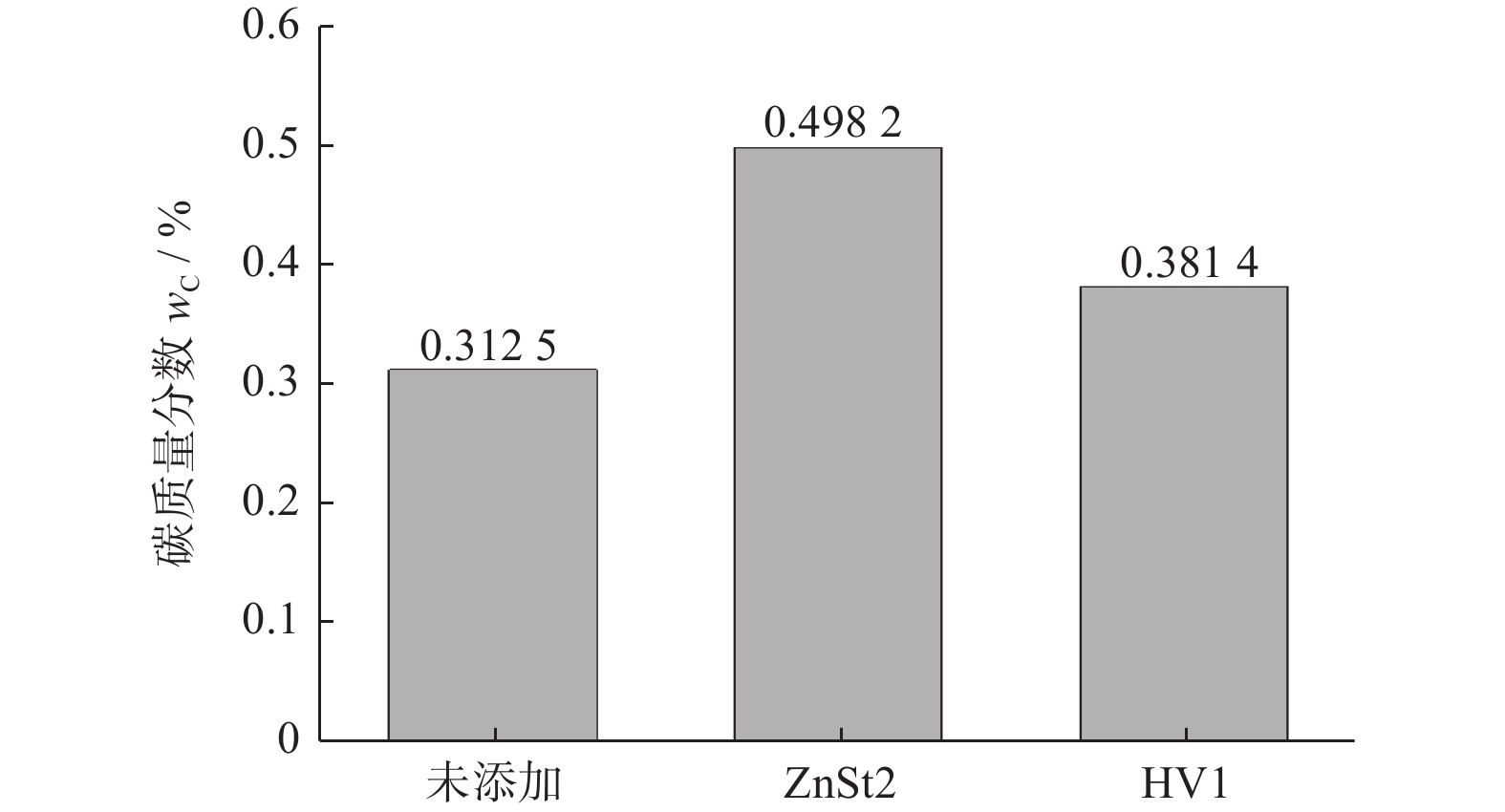
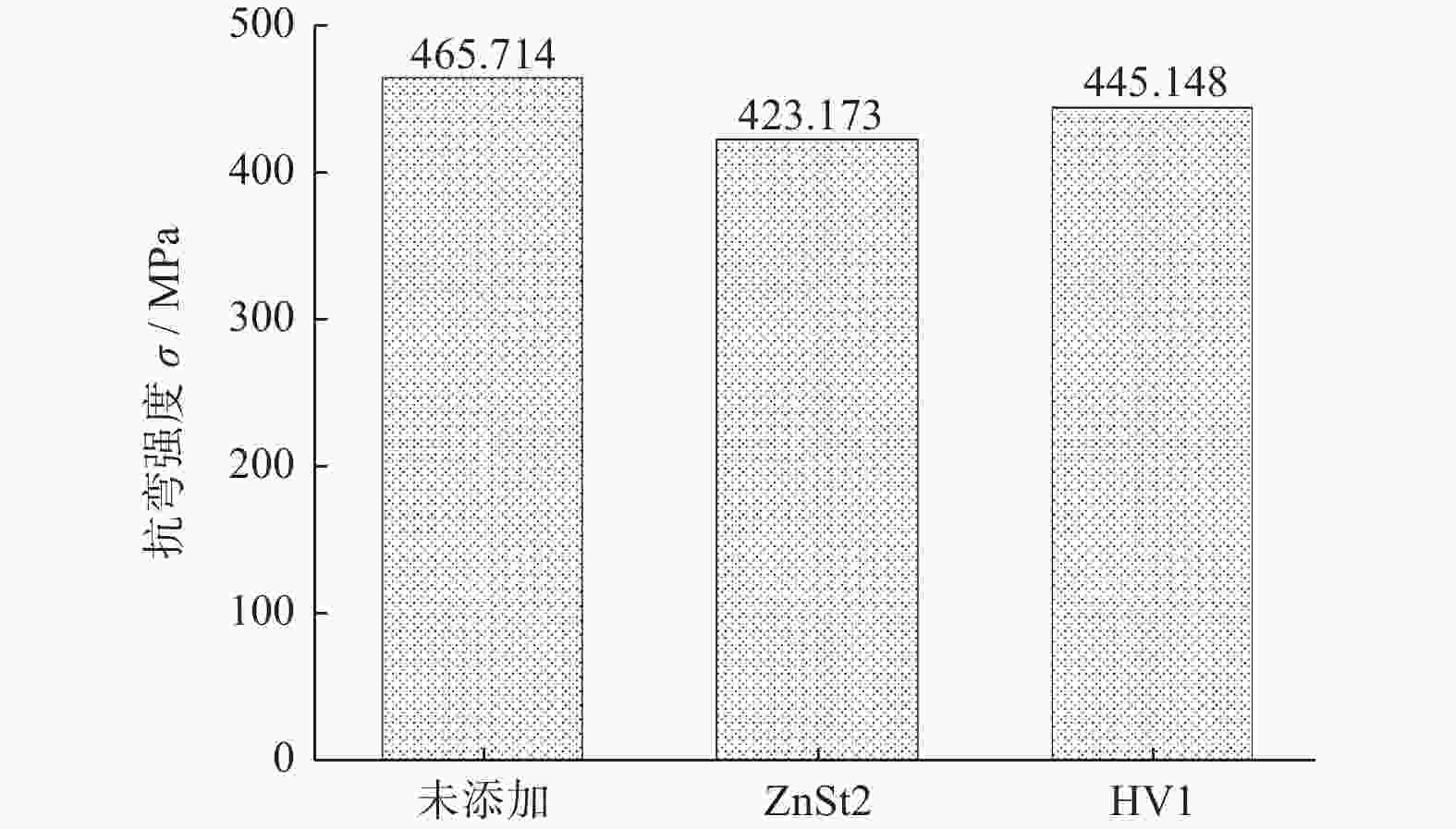
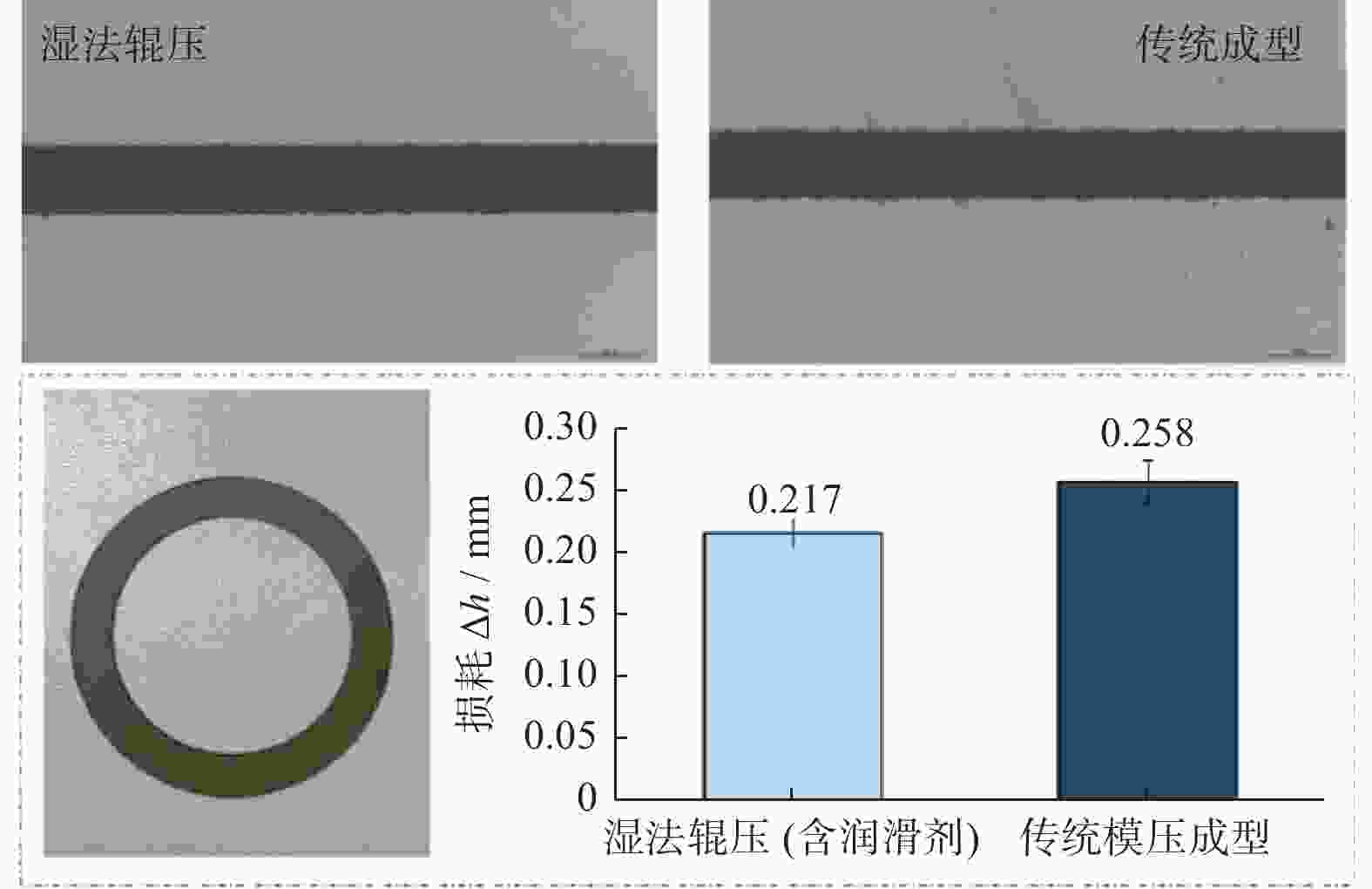
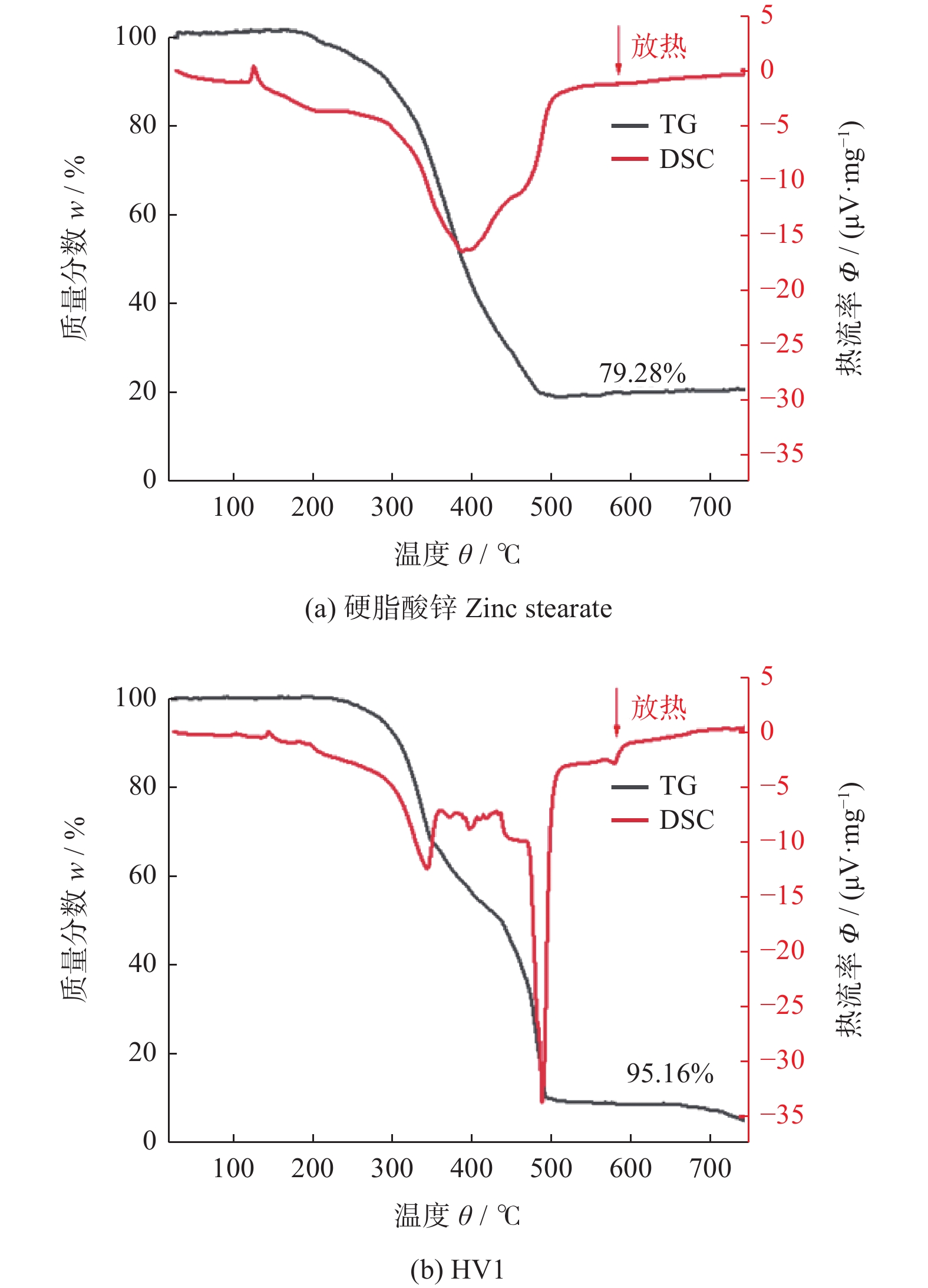
摘要: 为研究不同润滑剂的微观结构和热力学性能及其对湿法成形毛坯或烧结组织的结构和力学性能的影响,在金属磨具中添加不同的润滑脱模剂并以湿法轧制成形和脱脂烧结,使用同步热分析仪、扫描电子显微镜和X射线衍射仪等设备分析试样的性能。结果表明:硬脂酸锌的脱脂残留量(质量分数,下同)约为20.00%,残渣为纳米级颗粒的团聚体,HV1润滑剂的残留量仅为3.00%,残渣为尺寸约10 μm的互锁型无规则颗粒;HV1和硬脂酸锌润滑剂均对湿法成形有较好的脱模效果,但添加HV1和硬脂酸锌润滑剂的压坯密度分别降低0.5%和5.0%,烧结样品的密度分别降低1.5%和3.4%,抗弯强度分别降低4.4%和9.1%。相比于硬脂酸锌润滑剂,HV1对压坯和样品性能的影响较小,同时具有较好的脱模效果,更适用于金属磨具各类湿法成形的应用。Abstract: To study the microstructure and the thermodynamic properties of lubricants, as well as their effects on the structure and mechanical property of wet-forming or sintered materials, different lubrication release agents are added into metal abrasive tools which are fabricated with wet forming and degreasing sintering process. Synchronous thermal analyzer, scanning electron microscope and X-ray diffractometer are used to analyze the performance of the samples. The results indicate that the the residual degreasing amount of zinc stearate is about 20.00% while that of HV1 lubricant is only 3.00%. The residue of zinc stearate is the aggregate of nanometer particles and the counterpart of HV1 is ~10 μm interlocking irregular particles. Both HV1 and zinc stearate lubricant have better release effect on wet molding. However, adding HV1 or zinc stearate lubricant reduces the density of the compact by 0.5% or 5%, the density of sintered samples by 1.5% or 3.4%, and the bending strength by 4.4% or 9.1%, respectively. Compared with zinc stearate lubricant, HV1 has good demoulding effect and less influence on the properties of the compact and the sample, which is more suitable for metal abrasives of wet forming applications.
-
Key words:
- lubricant /
- metal abrasives /
- microstructure and properties /
- wet molding
-
表 1 湿法辊压成形参数设置
Table 1. Setting of rolling parameters
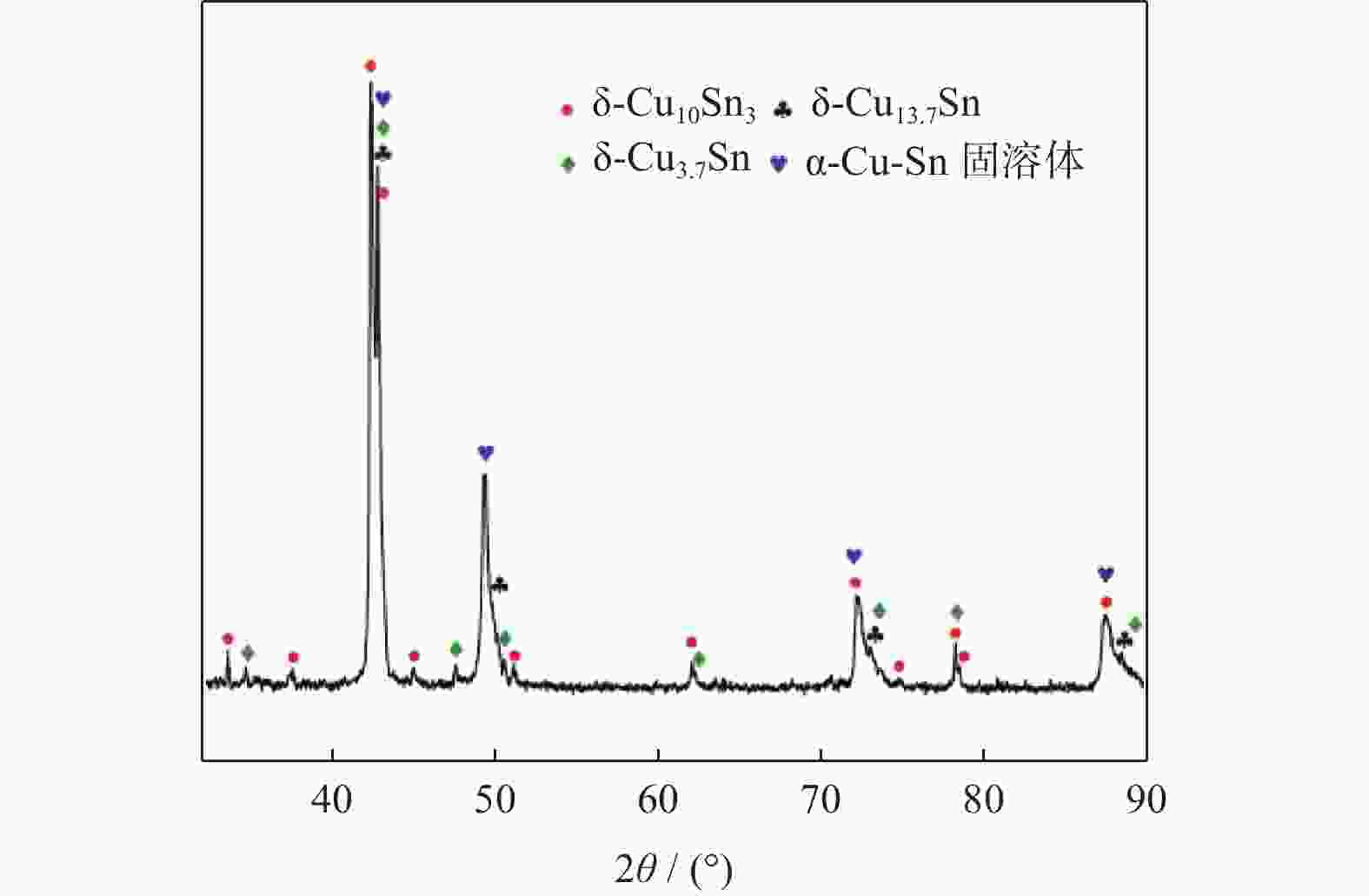
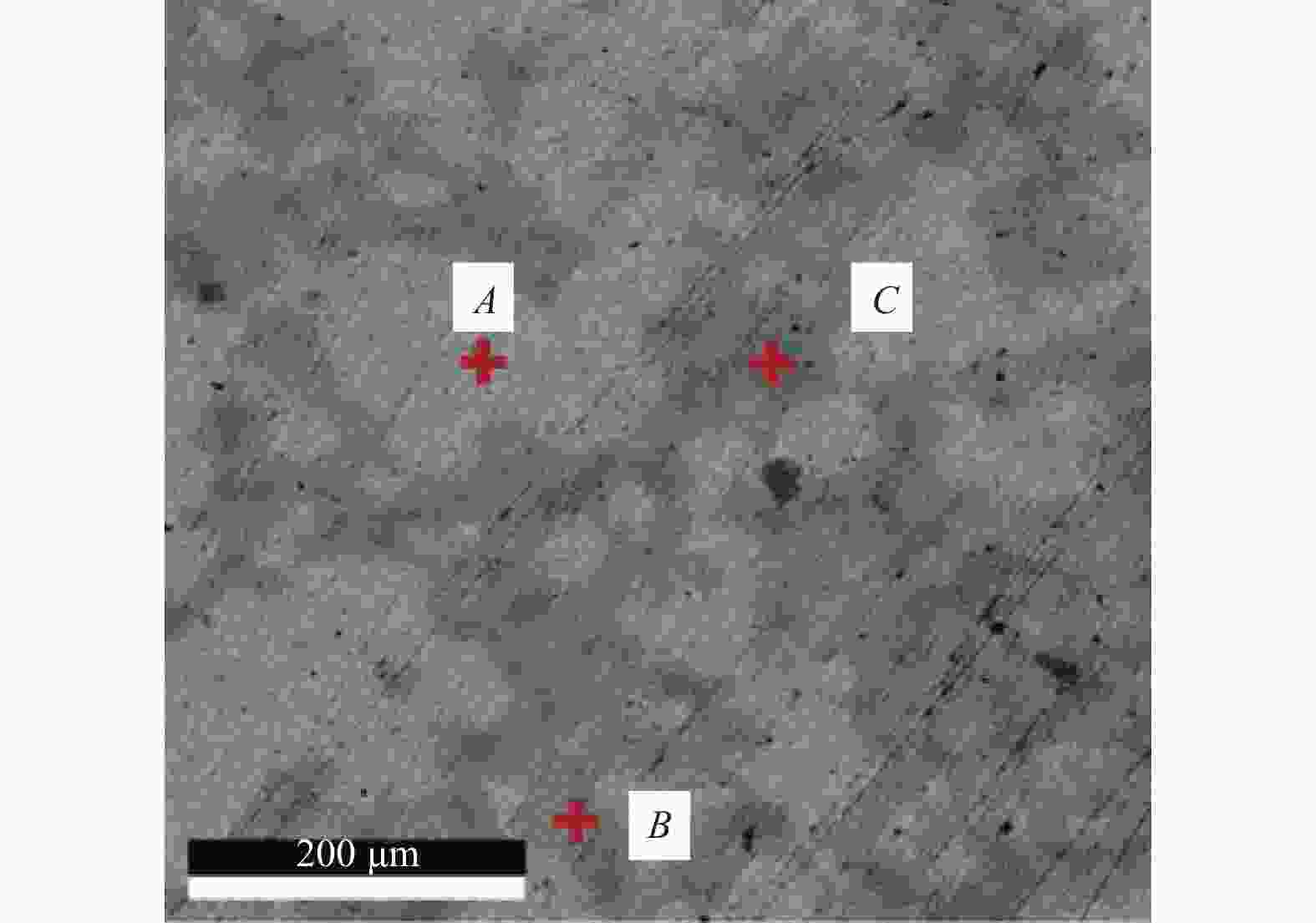
参数名称 参数值 辊压机转速 n / (r/min) 160 单次间隙下降 Δd / mm 0.2 辊缝间隙 d / mm 0.6 辊压压力 F / kN 30 工作温度 θ / ℃ 25 表 2 图4各点的成分分析
Table 2. Component analysis of each point in Figure 4
位置 Cu质量分数
wCu / %Sn质量分数
wSn / %A 77.79 22.21 B 87.38 12.62 C 100.00 / -
[1] 周志德. 金属粉末轧制 [J]. 粉末冶金工业,2001(1):36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2001.01.007ZHOU Zhide. Metal powder rolling [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2001(1):36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2001.01.007 [2] 黄培云. 粉末冶金原理 [M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1982.HUANG Peiyun. Principles of powder metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1982. [3] 王东玺. 粉末轧制成型技术的研究 [J]. 黑龙江科技信息,2011(19):64.WANG Dongxi. Research on powder rolling technology [J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information,2011(19):64. [4] ST-LAURENT S, THOMAS Y, AZZI L. High performance lubricants for demanding PM applications [J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology,2006,32(3):226-234. [5] ADACHI K, MIZUNO Y, ZENG R, et al. Development of internally added lubricant for high-density compaction [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2015(2):70-73. [6] 果世驹, 杨霞, 陈邦峰, 等. 316L不锈钢粉末温压与模壁润滑的高密度成形 [J]. 粉末冶金技术,2005(6):403-408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2005.06.001GUO Shiju, YANG Xia, CHEN Bangfeng, et al. High density compaction of stainless steel 316L powders through warm compaction and die wall lubrication [J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology,2005(6):403-408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2005.06.001 [7] 李达人, 陶麒鹦, 韩胜利. 添加剂对钨铜粉末温轧成形生坯致密化影响的规律研究 [J]. 中国钨业,2017,32(3):58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0622.2017.03.010LI Daren, TAO Qiying, HAN Shengli. Study on the influence of additives on the densification of tungsten copper powder warm-rolled compacts [J]. China Tungsten Industry,2017,32(3):58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0622.2017.03.010 [8] 叶倡华, 黄钧声, 李强, 等. 润滑剂对温压FeSiAl磁粉芯性能的影响 [J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2016,21(5):783-788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.05.018YE Changhua, HUANG Junsheng, LI Qiang, et al. Effects of lubricants on the properties of FeSiAl magnetic powder cores made by warm compaction [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy,2016,21(5):783-788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.05.018 [9] 韩凤麟. 粉末冶金零件生产用润滑剂的性能改进与选择 [J]. 粉末冶金工业,2015,25(2):1-7. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20130116HAN Fenglin. The performance improvement and selection of lubricant for production of PM components [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2015,25(2):1-7. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20130116 [10] 毕岗, 马少波, 王峰, 等. 润滑剂添加量对铁基混合粉末工艺性能的影响 [J]. 粉末冶金工业,2018,28(3):19-23.BI Gang, MA Shaobo, WANG Feng, et al. The effect of the addition of lubricant on process performance of iron-based mixed powder [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2018,28(3):19-23. [11] 闫志巧, 陈峰, 蔡一湘. 润滑剂含量对钛粉高速压制性能的影响 [J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2011(1):54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.009YAN Zhiqiao, CHEN Feng, CAI Yixiang. Effect of lubricant content on properties of Ti powder compact in high velocity compaction [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy,2011(1):54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.009 [12] 谭援强, 黄伟九. 润滑剂作用能力的分子轨道指数判据—润滑剂分子极性基团与金属表面之间的相互作用 [J]. 摩擦学学报,2000,20(4):280-283. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0595.2000.04.011TAN Yuanqiang, Huang Weijiu. The molecular orbital index criterion of the action ability of lubricants-The interaction between the polar groups of lubricant molecules and the metal surface [J]. Tribology,2000,20(4):280-283. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0595.2000.04.011 [13] 项品峰, 李元元, 龙雁, 等. 聚合物加入方式对粉末冶金温压成形的影响 [J]. 机械工程材料,2001,25(3):23-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2001.03.007XIANG Pinfeng, LI Yuanyuan, LONG Yan, et al. Effects of polymeric lubricant adding method on the warm compaction of powder metallurgy [J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering,2001,25(3):23-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2001.03.007 [14] LUK S H. Advances in binder-treatment technology statistical data on ancorbond plus [J]. Advances in Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials,2000,1(1/2/3):163-167. [15] AHLIN A, AHLQVIST A, LITSTRM O. Newly developed lubricants for high performance metal powder mixes: Proceedings of the euro international powder metallurgy congress and exhibition [C]. Mannheim: Euro Powder Metallurgy, 2008. [16] 于奇, 马佳, 钟素娟, 等. 铜锡预合金粉热压性能研究 [J]. 粉末冶金工业,2019,29(1):13-17. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20170106YU Qi, MA Jia, ZHONG Sujuan, et al. Study on hot pressing properties of Cu-Sn pre-alloyed powder [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2019,29(1):13-17. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20170106 [17] 于奇, 马佳, 龙伟民, 等. 金刚石工具用适配型CuSnZnNi预合金粉末的研制 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(2):23-27. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.2.0004YU Qi, MA Jia, LONG Weimin, et al. Development of suitable CuSnZnNi pre-alloyed powder for diamond tools [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(2):23-27. doi: 10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2021.2.0004 [18] 韩凤麟. 烧结青铜零件显微组织的控制 [J]. 粉末冶金工业,2005(6):4-10. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.2005.06.001HAN Fenglin. Control of microstructure of sintered bronze parts [J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2005(6):4-10. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.2005.06.001 -



 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
