Research progress of point cloud registration technology based on industrial 3D inspection
-
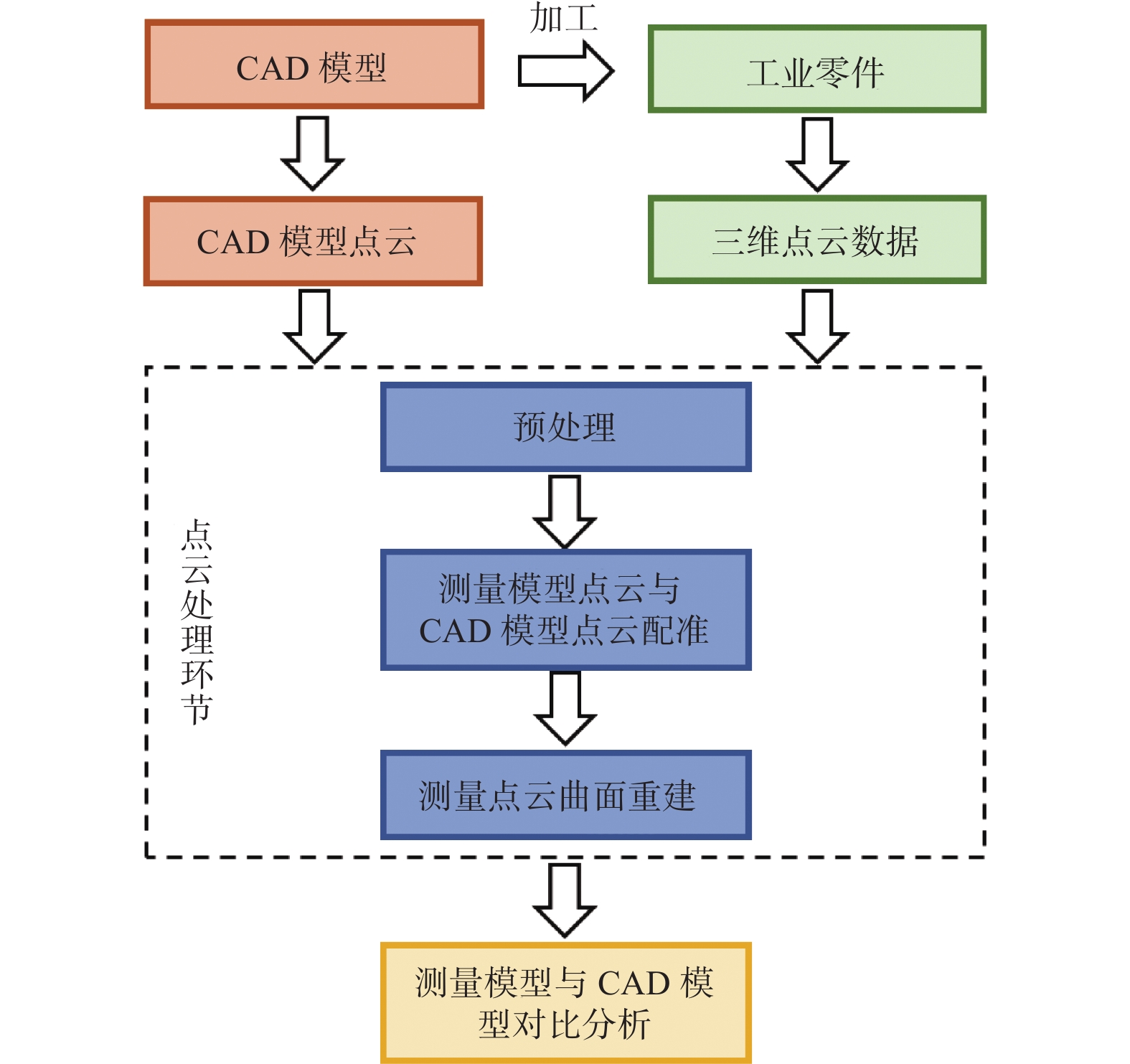
摘要: 随着制造业的发展,所需零件逐渐向大尺寸、复杂形状、表面加工质量高等方向发展,且在加工过程中对零件质量进行检测是必不可少的环节。为提高质量检测的精度、速率以及自动化程度等,基于模型分析的三维检测取代了传统的手工检测和二维检测,成了工业检测领域的重要手段。点云配准作为三维检测中的关键环节,其精度直接影响检测结果的准确性。因此,对国内外学者在点云配准技术方面的主要研究成果进行综述,从算法原理出发,将目前的配准方法归纳为传统配准方法、基于仿生群智能优化算法的配准方法和基于深度学习的配准方法。详细介绍了各类方法的特点、优缺点、典型算法及其变体,总结了点云配准的技术难点并对未来的发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: With the development of the manufacturing industry, the required parts are gradually moving towards larger sizes, complex shapes, and high surface processing quality. Moreover, detecting the quality of parts during the processing is an essential step. In order to improve the accuracy, the speed and the automation of quality inspection, the 3D inspection based on model analysis has replaced the traditional manual inspection and the 2D inspection, and becomes an important means in the field of industrial inspection. The accuracy of point cloud registration, as a key part of 3D inspection, directly affects the accuracy of detection results. Therefore, the main research achievements of scholars at home and abroad in point cloud registration technology are summarized. Based on algorithm principles, the current registration methods are summarized into traditional registration methods, registration methods based on affine swarm intelligent optimization algorithms, and registration methods based on deep learning. The characteristics, the advantages and the disadvantages, the typical algorithms and their variants of each method are introduced in detail. The technical difficulties of point cloud registration are summarized and the future development trend is prospected.
-
Key words:
- 3D inspection /
- point cloud registration /
- bionic swarm intelligence /
- deep learning
-
表 1 各类算法的归纳表
Table 1. Summary table of various algorithms
分类 算法
类型代表算法 优势 劣势 适用范围 传统配准
方法全局搜索 ICP、4PCS等 精度高、运算简单 耗时、初始位姿要求高,
容易陷入局部最优精度要求较高,模型数据量较少,点云重叠率较高 局部特征
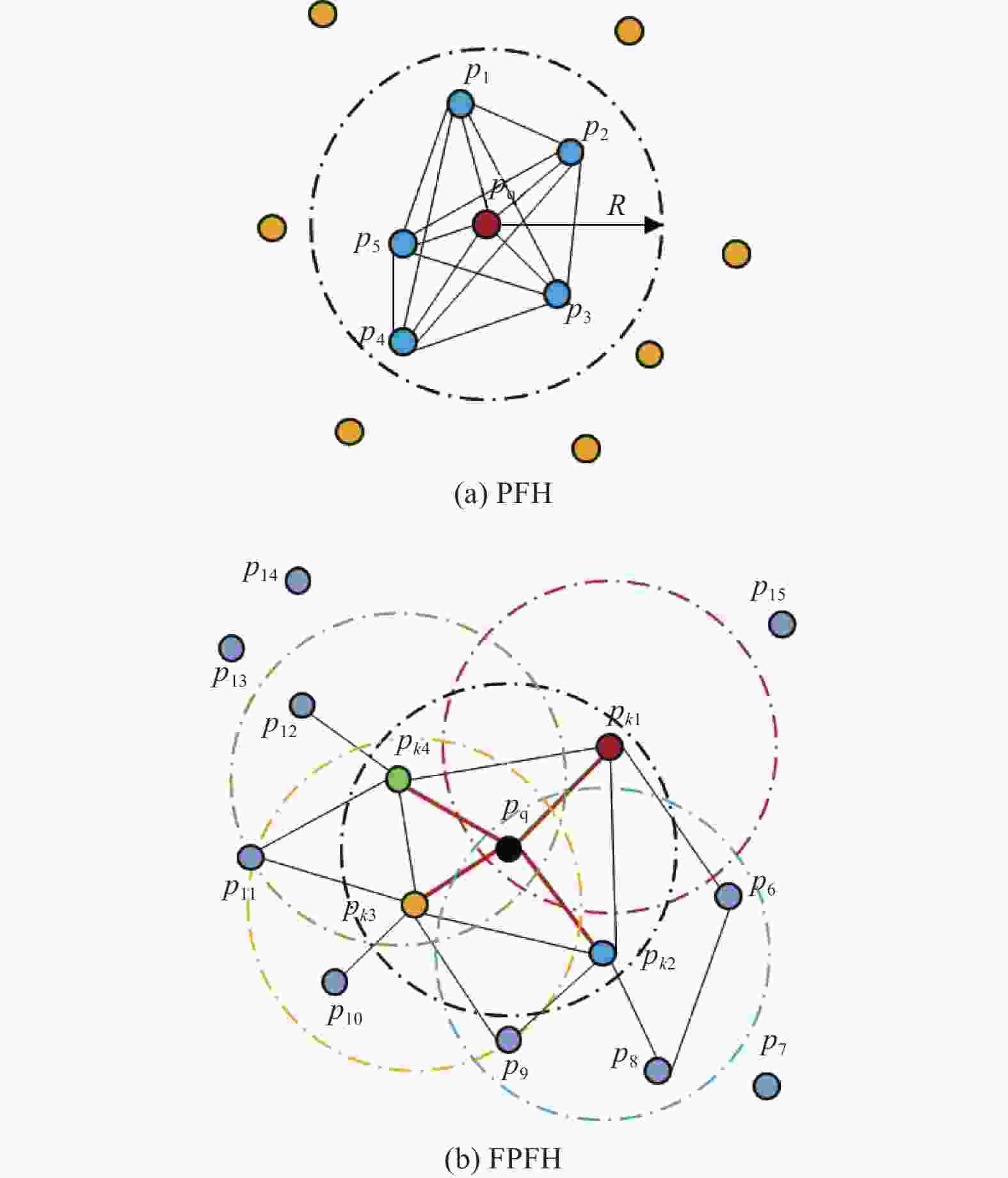
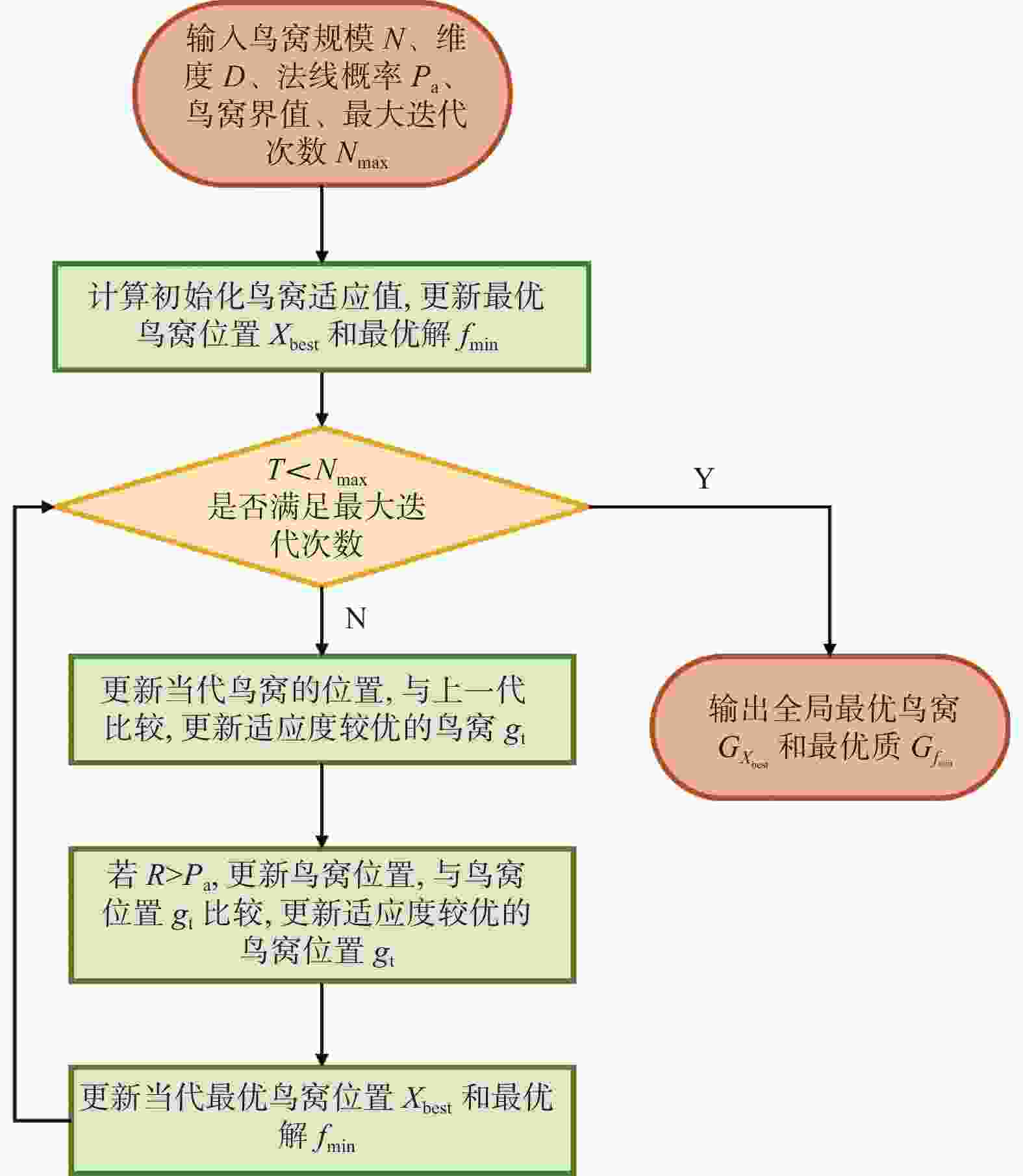
描述PFH、FPFH、3DSC等 精度高、抗噪性强 运算复杂、耗时 点云局部特征明显,效率要求较低,也可应用于存在点云遮挡的模型的配准 概率学统计 NDT、CPD等 抗噪性强、效率高 容易陷入局部最优 数据量庞大且配准精度要求较高 仿生群智能优化算法 布谷鸟搜索算法 CSA、MACSA、ICSA等 参数少、模型简单、效率高、全局搜索能力强 搜索方式具有盲目性,无法兼具全局搜索和局部寻优
能力简洁、快速、高精度的配准,也可应用于点云缺失、部分重合、点云遮挡的模型的配
准人工蜂群
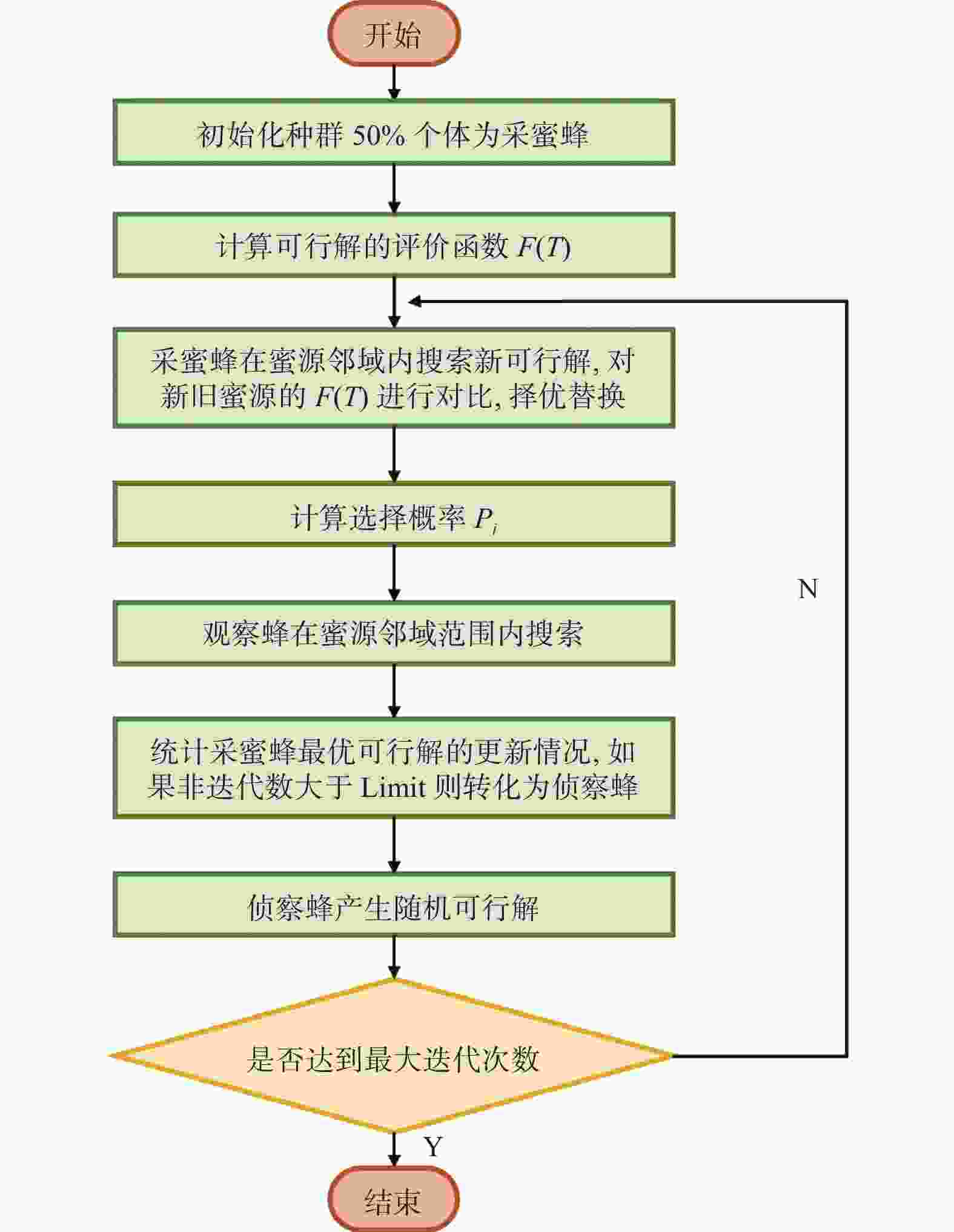
算法ABC、SAABC、SAABC等 算法灵活性强、全局搜索能力强、搜索性能好 搜索速度不均匀,表现为早熟收敛 深度学习
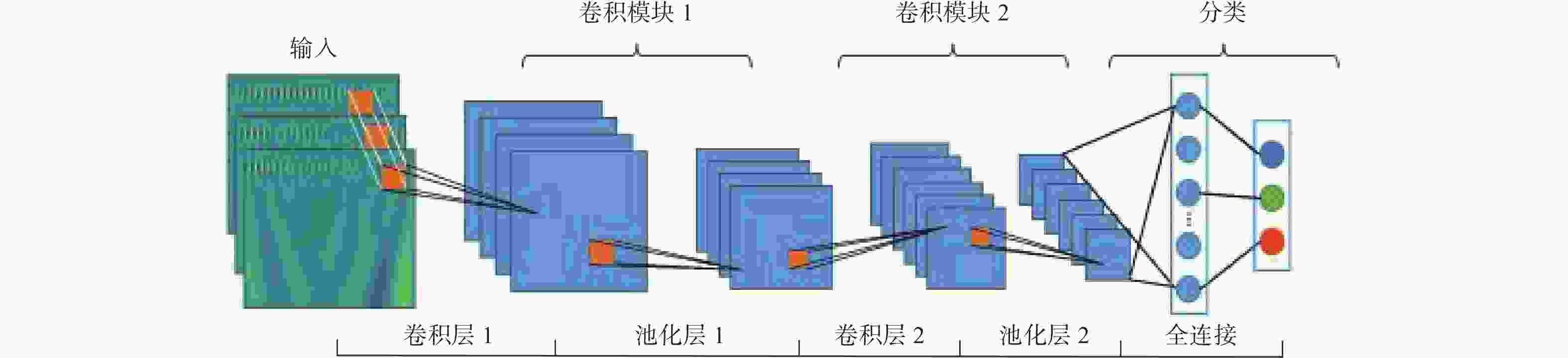
方法端到端 PointNet、CNN、DeepVCP等 效率高、精度高、智能化程度高 对噪声和密度差敏感 配准精度要求很高,结构复杂,形状多样 部分学习 PointNetLk、PCRNet、语义辅助正态分布变换等 灵活性强、收敛速度快、鲁棒性强 运算复杂 -
[1] 李文辉, 温学杰, 李秀红, 等. 航空发动机叶片再制造技术的应用及其发展趋势 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2021,41(4):8-18.LI Wenhui, WEN Xuejie, LI Xiuhong, et al. Application and development trend of aero-engine blade remanufacturing technology [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2021,41(4):8-18. [2] 石广丰, 王雪, 王淑坤, 等. 基于机器视觉的金刚石原石检测系统 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2019(6):7-12.SHI Guangfeng, WANG Xue, WANG Shukun, et al. Diamond raw detection system based on machine vision [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2019(6):7-12. [3] 李雷辉. 基于3D视觉传感器的工业零件表面质量检测关键技术研究 [D]. 天津: 天津理工大学, 2021.LI Leihui. Research o key techniques of the industrial parts, surface inspection based on 3d vision [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Technology, 2021. [4] 肖明, 鲍永亮, 颜仲新. 基于点特征的图像配准方法综述 [J]. 兵工学报,2015,36(S2):326-340.XIAO Ming, BAO Yongliang, YAN Zhongxin. Point feature-based image registration: A survey [J]. Acta Armamentarii,2015,36(S2):326-340. [5] LAI J Y, UENG W D, YAO C Y. Registration and data merging for multiple sets of scan data [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,1999,15(1):54-63. doi: 10.1007/s001700050039 [6] POMERLEAU F, COLAS F, SIEGWART R. A review of point cloud registration algorithms for mobile robotics [J]. Foundations and Trends in Robotics,2015,4(1):1-104. [7] 张政. 点云数据配准算法研究 [D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2008.ZHANG Zheng. Research on registration algorithm of point cloud data [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2008. [8] CHENG L, CHEN S, LIU X, et al. Registration of laser scanning point clouds: A review [J]. Sensors,2018,18(5):1641. doi: 10.3390/s18051641 [9] 张步. 三维激光点云数据配准研究 [D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2015.ZHANG Bu. Research on 3D laser poing cloud registration [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2015 [10] CHENG X, LI Z, ZHONG K, et al. An automatic and robust point cloud registration framework based on view-invariant local feature descriptors and transformation consistency verification [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,2017,98:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.05.011 [11] YANG J, QUAN S, WANG P, et al. Evaluating local geometric feature representations for 3D rigid data matching [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2019,29:2522-2535. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2959236 [12] BESL P J, MCKAY N D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1992,14(2):239-256. doi: 10.1109/34.121791 [13] CHEN Y, MEDIONI G. Object modeling by registration of multiple range images [J]. Image and Vision Computing,1992,10(3):145-155. doi: 10.1016/0262-8856(92)90066-C [14] RUSINKIEWICZ S. A symmetric objective function for ICP [J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics,2019,38(4):1-7. [15] 王建军, 卢云鹏, 张荠匀, 等. 实现激光点云高效配准的ICP优化及性能验证 [J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(10):309-315.WANG Jianjun, LU Yunpeng, ZHANG Jiyun, et al. Optimization and performance verification of high efficiency ICP registration for laser point clouds [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering,2021,50(10):309-315. [16] LIU Y. Automatic registration of overlapping 3D point clouds using closest points [J]. Image and Vision Computing,2006,24(7):762-781. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2006.01.009 [17] LIU Y. Constraints for closest point finding [J]. Pattern Recognition Letters,2008,29(7):841-851. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2007.12.004 [18] GELFAND N, IKEMOTO L, RUSINKIEWICZ S, et al. Geometrically stable sampling for the ICP algorithm: Fourth international conference on 3-D digital imaging and modeling [C]. Banff: IEEE, 2003: 260-267. [19] WEIK S. Registration of 3-D partial surface models using luminance and depth information: International conference on recent advances in 3-D digital imaging and modeling [C]. Ottawa: IEEE, 1997: 93-100. [20] 任伟建, 高梦宇, 高铭泽, 等. 基于混合算法的点云配准方法研究 [J]. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版),2019,37(4):408-416.REN Weijian, GAO Mengyu, GAO Mingze, et al. Research on point cloud registration method based on hybrid algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition),2019,37(4):408-416. [21] 代许松, 花向红, 田朋举, 等. 一种基于轴向偏离比的点云配准方法 [J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(12):98-105.DAI Xusong, HUA Xianghong, TIAN Pengju, et al. A point cloud registration method based on axial deviation ratio [J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(12):98-105. [22] CHETVERIKOV D, STEPANOV D, KRSEK P. Robust euclidean alignment of 3D point sets: The trimmed iterative closest point algorithm [J]. Image and Vision Computing,2005,23(3):299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2004.05.007 [23] HAN B, WU W, WANG Y, et al. The semi-dense ICP algorithm based on the sift feature points neighborhood [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1631: 12-58 [24] AIGER D, MITRA N J, COHEN-OR D. 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration [J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics,2008,27(3):1-10. [25] MELLADO N, AIGER D, MITRA N J. Super 4PCS fast global pointcloud registration via smart indexing [J]. Eurographics,2014,33(5):205-215. [26] 鲁铁定, 袁志聪, 郑坤. 结合尺度不变特征的Super 4PCS点云配准方法 [J]. 遥感信息,2019,34(5):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.05.005LU Tieding, YUAN Zhicong, ZHENG Kun. Super 4PCS point cloud registration algorithm combining scale invariant features [J]. Remote Sensing Information,2019,34(5):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.05.005 [27] 陆军, 范哲君, 王婉佳. 点邻域信息加权的点云快速拼接算法 [J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2019,31(7):1238-1246.LU Jun, FAN Zhejun, WANG Wanjia. Fast point cloud splicing algorithm based on weighted neighborhood information of points [J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics,2019,31(7):1238-1246. [28] XU Z, XU E, ZHANG Z, et al. Multiscale sparse features embedded 4-points congruent sets for global registration of TLS point clouds [J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,2018,16(2):286-290. [29] 刘世光, 王海荣, 刘锦. 快速四点一致性点云粗配准算法 [J]. 山东大学学报(工学版),2019,49(2):1-7.LIU Shiguang, WANG Hairong, LIU Jin. Fast 4-points congruent sets for coarse registration of 3D point cloud [J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science),2019,49(2):1-7. [30] 汪霞, 赵银娣, 王坚. 一种低重叠率激光点云的配准方法 [J]. 测绘科学,2018,43(12):130-136.WANG Xia, ZHAO Yindi, WANG Jian. A registration method of laser point cloud with low overlap [J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2018,43(12):130-136. [31] HUANG J, KWOK T H, ZHOU C. V4PCS: Volumetric 4PCS algorithm for global registration [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2017, 139(11): 4037477. [32] DA SILVA J P, BORGES D L, DE BARROS VIDAL F. A dynamic approach for approximate pairwise alignment based on 4-points congruence sets of 3D points: 18th IEEE international conference on image processing [C]. Brussels: IEEE, 2011: 889-892. [33] BELONGIE S, MALIK J, PUZICHA J. Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2002,24(4):509-522. doi: 10.1109/34.993558 [34] RUSU R B, BLODOW N, MARTON Z C. Aligning point cloud views using persistent feature histograms: 2008 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems [C]. Nice: IEEE, 2008: 3384-3391. [35] FROME A, HUBER D, KOLLURI R, et al. Recognizing objects in range data using regional point descriptors [J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2004,3023(1):224-237. [36] 范莹, 白瑞林, 王秀平, 等. 改进型形状上下文的工件立体匹配方法 [J]. 激光技术,2016,40(6):814-819.FAN Ying, BAI Ruilin, WANG Xiuping, et al. Stereo matching algorithm of workpiece images based on improved shape context [J]. Laser Technology,2016,40(6):814-819. [37] 化春键, 熊雪梅, 陈莹. 基于形状上下文的工件边缘轮廓点匹配 [J]. 光电子·激光,2018,29(6):634-638.HUA Chunjian, XIONG Xuemei, CHEN Ying. Shape matching of workpiece edge based on shape context [J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser,2018,29(6):634-638. [38] 郑丹晨, 韩敏. 基于改进典型形状上下文特征的形状识别方法 [J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2013,25(2):215-220.ZHENG Danchen, HAN Min. Improved shape recognition method based on representative shape context [J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics,2013,25(2):215-220. [39] 吴晓雨, 何彦, 杨磊, 等. 基于改进形状上下文特征的二值图像检索 [J]. 光学精密工程,2015,23(1):302-309. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152301.0302WU Xiaoyu, HE Yan, YANG Lei, et al. Binary image retrieval based on improved shape context algorithm [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering,2015,23(1):302-309. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152301.0302 [40] 赵键, 孙即祥, 李智勇, 等. 基于相对形状上下文和谱匹配方法的点模式匹配算法 [J]. 电子与信息学报,2010,32(10):2287-2293.ZHAO Jian, SUN Jixiang, LI Zhiyong, et al. Point pattern matching algorithm based on relative shape context and spectral matching method [J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology,2010,32(10):2287-2293. [41] WEI E B, LIU S B, WANG Z Z, et al. Emissivity measurements of foam-covered water surface at l-band for low water temperatures [J]. Remote Sensing,2014,6(11):10913-10930. doi: 10.3390/rs61110913 [42] SCHEELER R, POPOVIC Z. A 1.4 GHz MMIC active cold noise source: 2013 IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium [C]. Monterey: IEEE, 2013: 13-16. [43] TOMBARI F, SALTI S, DI S L. Unique shape context for 3D data description: The ACM workshop on 3D object retrieval [C]. Firenze: ACM, 2010: 57-62. [44] RUSU R B, BLODOW N, BEETZ M. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation [C]. Kobe: IEEE, 2009: 3212-3217. [45] 朱琛琛. 基于ICP算法的点云配准研究 [D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2019.ZHU Chenchen. Point cloud registration based on ICP algorithm research [D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2019. [46] 陆军, 彭仲涛. 基于快速点特征直方图的特征点云迭代插值配准算法 [J]. 国防科技大学学报,2014,36(6):12-17.LU Jun, PENG Zhongtao. Iterative interpolation point cloud registration algorithm based on fast point feature histograms [J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology,2014,36(6):12-17. [47] WU L, WANG G, HU Y. Iterave closest point registration for fast point feature histogram features of a volume density optimization algorithm [J]. Measurement and Control,2020,53(1/2):29-39. doi: 10.1177/0020294019878869 [48] 吴飞, 赵新灿, 展鹏磊, 等. 自适应邻域选择的FPFH特征提取算法 [J]. 计算机科学,2019,46(2):266-270. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.02.041WU Fei, ZHAO Xincan, ZHAN Penglei, et al. FPFH feature extraction algorithm based on adaptive neighborhood selection [J]. Computer Science,2019,46(2):266-270. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.02.041 [49] 赵明富, 曹利波, 宋涛, 等. 三维点云配准中FPFH邻域半径自主选取算法 [J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(6):123-131.ZHAO Mingfu, CAO Libo, SONG Tao, et al. Independent method for selecting radius of FPFH neighborhood in 3d point cloud registration [J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2021,58(6):123-131. [50] LIU Y, KONG D, ZHAO D, et al. A point cloud registration algorithm based on feature extraction and matching [J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018: 1-9. [51] 刘剑, 白迪. 基于特征匹配的三维点云配准算法 [J]. 光学学报,2018,38(12):240-247.LIU Jian, BAI Di. 3D point cloud registration algorithm based on feature matching [J]. Acta Optica Sinica,2018,38(12):240-247. [52] 庄祉昀, 张军, 孙广富. 用于三维点云表示的扩展点特征直方图算法 [J]. 国防科技大学学报,2016,38(6):124-129. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201606020ZHUANG Zhiyun, ZHANG Jun, SUN Guangfu. Extended point feature histograms for 3D point cloud representation [J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology,2016,38(6):124-129. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201606020 [53] BIBER P, STRASSER W. The normal distributions transform: A new approach to laser scan matching: 2003 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems [C]. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2003: 2743-2748. [54] MAGNUSSON M, LILIENTHAL A, DUCKETT T. Scan registration for autonomous mining vehicles using 3D-NDT [J]. Journal of Field Robotics,2007,24(10):803-827. doi: 10.1002/rob.20204 [55] 赵凯, 朱愿, 王任栋. 基于改进NDT算法的城市场景三维点云配准 [J]. 军事交通学院学报,2019,21(3):80-84.ZHAO Kai, ZHU Yuan, WANG Rendong. Urban scene 3D point cloud registration based on improved NDT algorithm [J]. Journal of Academy of Military Transportation,2019,21(3):80-84. [56] DAS A, WASLANDER S L. Scan registration with multi-scale k-means normal distributions transform: 2012 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems [C]. Vilamoura-Algarve: IEEE, 2012. [57] DAS A, WASLANDER S L. Scan registration using segmented region growing NDT [J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research,2014,33(13):1645-1663. doi: 10.1177/0278364914539404 [58] MYRONENKO A, SONG X. Point set registration: Coherent point drift [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2010,32(12):2262-2275. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.46 [59] YANG X S, DEB S. Cuckoo search via levy flights: 2009 world congress on nature & biologically inspired computing [C]. Coimbatore: IEEE, 2009: 210-214. [60] ZHANG Y, WANG L, WU Q. Modified adaptive cuckoo search (MACS) algorithm and formal description for global optimisation [J]. International Journal of Computer Application in Technology,2012,44(2):73-79. doi: 10.1504/IJCAT.2012.048675 [61] 张永韡, 汪镭, 吴启迪. 动态适应布谷鸟搜索算法 [J]. 控制与决策,2014,29(4):617-622.ZHANG Yongwei, WANG Lei, WU Qidi. Dynamic adaptation cuckoo search algorithm [J]. Control and Decision,2014,29(4):617-622. [62] 王李进, 尹义龙, 钟一文. 逐维改进的布谷鸟搜索算法 [J]. 软件学报,2013,24(11):2687-2698.WANG Lijin, YIN Yilong, ZHONG Yiwen. Cuckoo search algorithm with dimension by dimension improvement [J]. Journal of Software,2013,24(11):2687-2698. [63] 林要华, 王维. 基于逐维策略的布谷鸟搜索增强算法 [J]. 计算机工程与科学,2017,39(1):165-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2017.01.023LIN Yaohua, WANG Wei. An enhanced cuckoo search algorithm based on dimension by dimension strategy [J]. Computer Engineering & Science,2017,39(1):165-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2017.01.023 [64] GHODRATI A, LOTFI S. A hybrid CS/PSO algorithm for global optimization [J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2012,7198(1):89-98. [65] WANG F, LUO L, HE X, et al. Hybrid optimization algorithm of PSO and cuckoo search: 2011 2nd international conference on artificial intelligence, management science and electronic commerce(AIMSEC) [C]. Dengleng: IEEE, 2011: 1172-1175. [66] VALIAN E, MOHANNA S, TAVAKOLI S. Improved cuckoo search algorithm for global optimization [J]. International Journal of Communications and Information Technology,2011,1(1):31-44. [67] WALTON S, HASSAN O, MORGAN K, et al. Modified cuckoo search: A new gradient free optimisation algorithm [J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals,2011,44(9):710-718. [68] KARABOGA D, BASTURK B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm [J]. Journal of Global Optimization,2007,39(3):459-471. doi: 10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x [69] ZHU G, KWONG S. Gbest-guided artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation,2010,217(7):3166-3173. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2010.08.049 [70] BANHARNSAKUN A, ACHALAKUL T, SIRINAOVAKUL B. The best-so-far selection in artificial bee colony algorithm [J]. Applied Soft Computing,2011,11(2):2888-2901. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.11.025 [71] AKAY B, KARABOGA D. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm for real-parameter optimization [J]. Information Sciences,2012,192:120-142. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2010.07.015 [72] BANSAL J C, SHARMA H, ARYA K V, et al. Self-adaptive artificial bee colony [J]. Optimization,2014,63(10):1513-1532. doi: 10.1080/02331934.2014.917302 [73] GAO W, LIU S. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm [J]. Computers & Operations Research,2012,39(3):687-697. [74] GAO W, LIU S. Improved artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization [J]. Information Processing Letters,2011,111(17):871-882. doi: 10.1016/j.ipl.2011.06.002 [75] LI G, NIU P, XIAO X. Development and investigation of efficient artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization [J]. Applied Soft Computing,2012,12(1):320-332. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2011.08.040 [76] XIANG W, MA S, AN M. Habcde: A hybrid evolutionary algorithm based on artificial bee colony algorithm and differential evolution [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation,2014,238:370-386. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2014.03.055 [77] KANG F, LI J, MA Z. Rosenbrock artificial bee colony algorithm for accurate global optimization of numerical functions [J]. Information Sciences,2011,181(16):3508-3531. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2011.04.024 [78] WU B, QIAN C, NI W, et al. Hybrid harmony search and artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization problems [J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications,2012,64(8):2621-2634. [79] QI C R, SU H, MO K, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation: 30th IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition [C]. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 77-85. [80] 李建微, 占家旺. 三维点云配准方法研究进展 [J]. 中国图象图形学报,2022,27(2):349-367.LI Jianwei, ZHAN Jiawang. Review on 3D point cloud registration method [J]. Journal of Image and Graphics,2022,27(2):349-367. [81] QI C R, YI L, SU H, et al. PointNet + + : Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space [J]. Computer Science, 2017: ArXiv 1706.02413. [82] LU W, WAN G, ZHOU Y, et al. DeepVCP: An end-to-end deep neural network for point cloud registration: IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision [C]. Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 12-21. [83] SU H, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 945-953. [84] 舒程珣, 何云涛, 孙庆科. 基于卷积神经网络的点云配准方法 [J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(3):129-137.SHU Chengxun, HE Yuntao, SUN Qingke. Point cloud registration based on convolutional neural network [J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2017,54(3):129-137. [85] WANG Y, SUN Y, LIU Z, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds [J]. Acm Transactions on Graphics,2019,38(5):1-12. [86] THOMAS H, QI C R, DESCHAUD J E, et al. KPConv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds: IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision [C]. Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 6411-6420. [87] XU M, DING R, ZHAO H, et al. PAConv: Position adaptive convolution with dynamic kernel assembling on point clouds: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition [C]. Nashville: IEEE, 2021: 3173-3182. [88] CHOY C, PARK J, KOLTUN V. Fully convolutional geometric features: IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision [C]. Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 8958-8966. [89] WANG Y, SOLOMON J M. Deep closest point: Learning representations for point cloud registration [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019, 2019: 3523-3532. [90] AOKI Y, GOFORTH H, SRIVATSAN R A, et al. PointNetLK: Robust & efficient point cloud registration using pointNet: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition [C]. Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 7163-7172. [91] SARODE V, LI X, GOFORTH H, et al. PcrNet: Point cloud registration network using pointNet encoding [J]. Computer Science, 2019: ArXiv 1908.07906. [92] 易倩, 钟浩宇, 刘龙, 等. 基于ROI-RSICP算法的车轮廓形动态检测 [J]. 中国激光,2020,47(11):154-165.YI Qian, ZHONG Haoyu, LIU Long, et al. Dynamic inspection of profile based on ROI-RSICP algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2020,47(11):154-165. [93] ZAGANIDIS A, SUN L, DUCKETT T, et al. Integrating deep semantic segmentation into 3-D point cloud registration [J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2018,3(4):2942-2949. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2848308 [94] 陈强, 岳东杰, 陈健. 基于特征空间匹配的激光雷达点云配准算法 [J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2020,40(12):1303-1307.CHEN Qiang, YUE Dongjie, CHEN Jian. Laser lidar point registration algorithm based on feature space matching [J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2020,40(12):1303-1307. [95] 李昌华, 史浩, 李智杰. 基于卷积神经网络结合改进Harris-SIFT的点云配准方法 [J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(20):238-247.LI Changhua, SHI Hao, LI Zhijie. Point cloud registration method based on combination of convolutional neural network and improved Harris-SIFT [J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2020,57(20):238-247. -




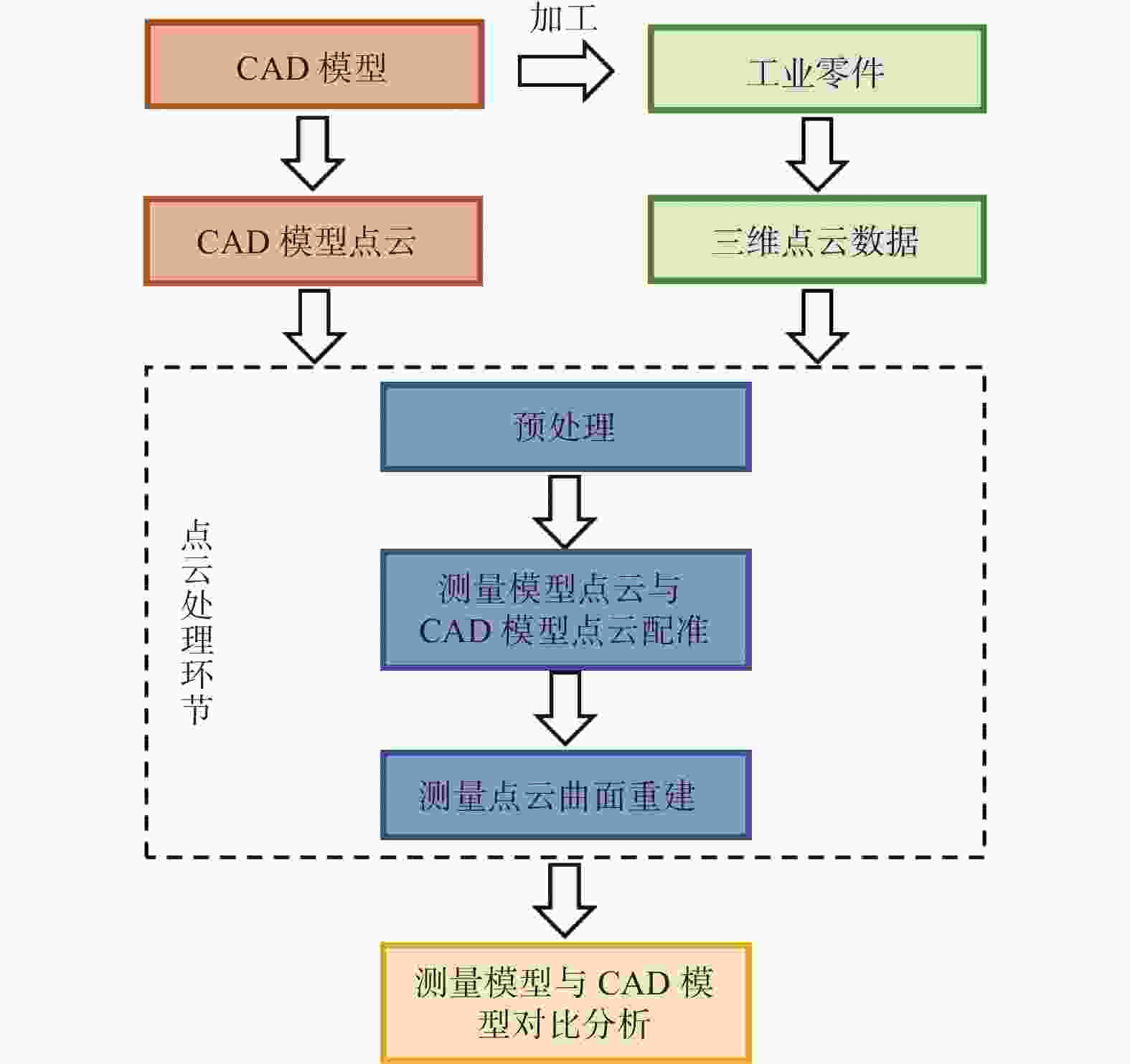
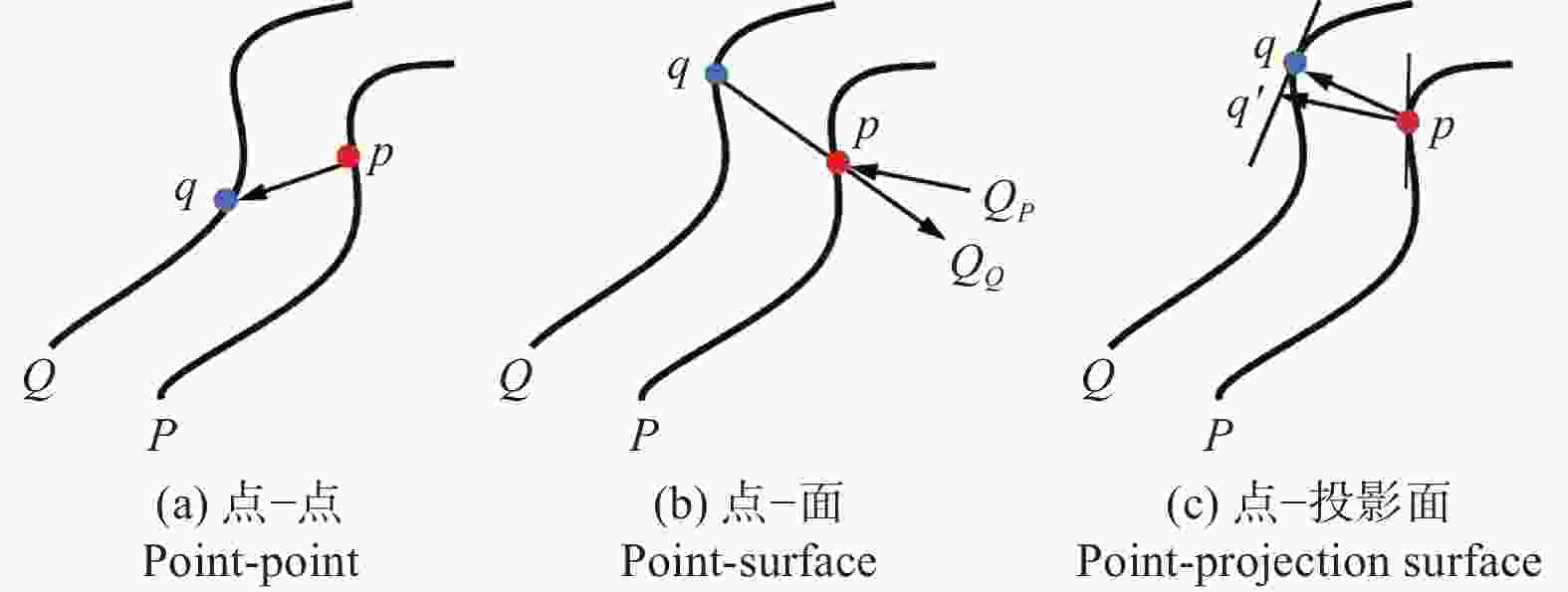
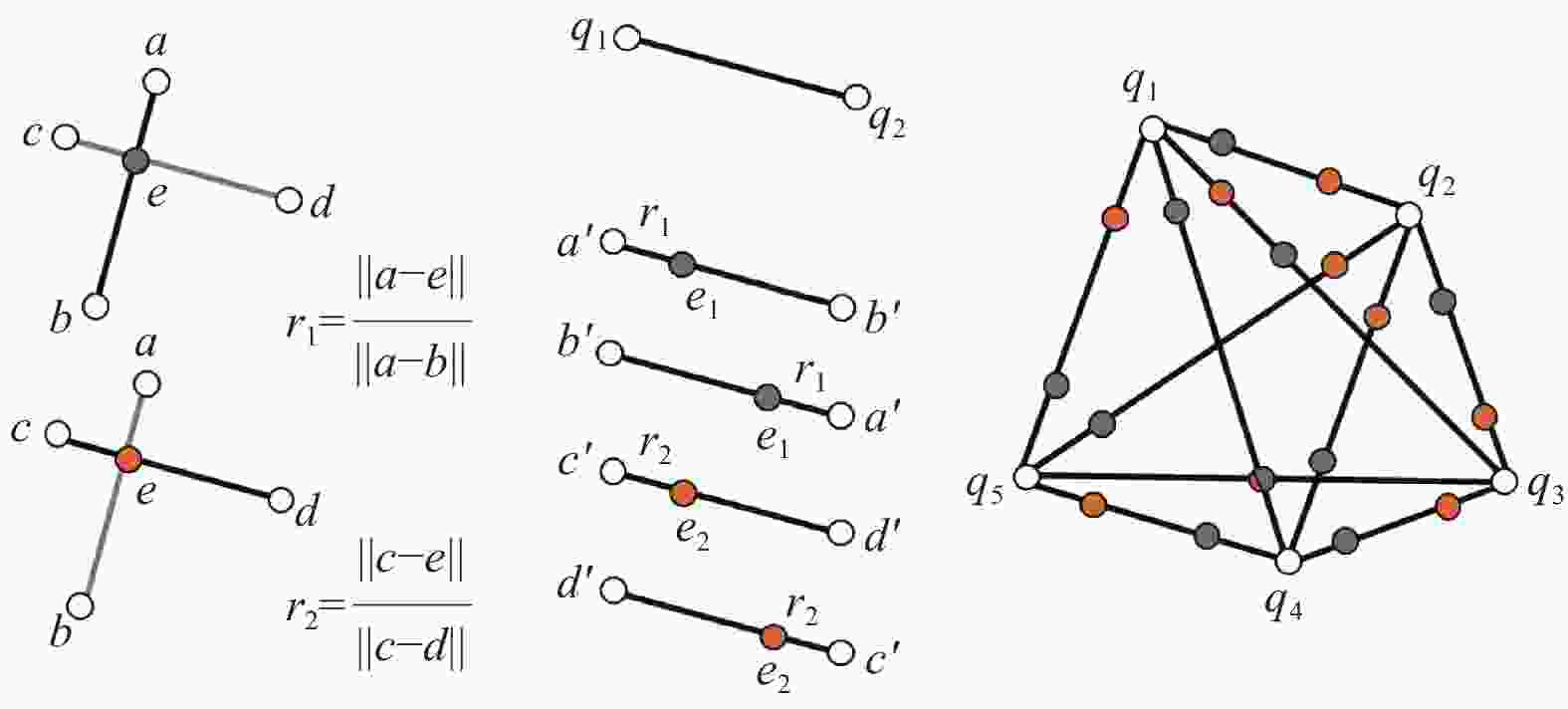
 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
