Optimization of laser sharpening parameters for diamond grinding wheel based on CNN
-
摘要: 采用正交试验法对青铜金刚石砂轮进行激光修锐试验,并对其激光修锐参数进行优化。通过卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)对砂轮表面图片进行像素级的金刚石磨粒识别,提取磨粒面积信息,求出磨粒突出高度,利用统计分布规律得到突出高度得分和最佳区间比率2个激光修锐质量评价指标。利用提出的评价指标对试验得到的砂轮激光修锐图片进行质量评价,并进行极差分析。结果表明:平均功率是影响修锐质量最大的因素。最优的修锐工艺参数为:平均功率,35 W;重复频率,100 kHz;转速,300 r/min;扫描速度,1.0 mm/min。Abstract: To optimize laser sharpening parameters for bronze diamond grinding wheels, the laser sharpening test was carried out on the bronze diamond grinding wheel using the orthogonal test method.The convolutional neural network (CNN) is used to identify the diamond abrasive grains at the pixel level. The protruding height of abrasive grains is obtained by extracting the area information of abrasive grains. Two laser sharpening quality evaluation indicators, the protruding height score and the optimal interval ratio, are obtained by using the statistical distribution law. The quality of the grinding wheel laser sharpening effect obtained by the test is evaluated by the evaluation index proposed and the range method is performed. The results show that the average power is the biggest factor affecting the quality of trimming. The optimal trimming process parameters are as follows: the average power is 35 W; the repetition frequency is 100 kHz; the rotational speed is 300 r/min; the scanning speed is 1.0 mm/min.
-
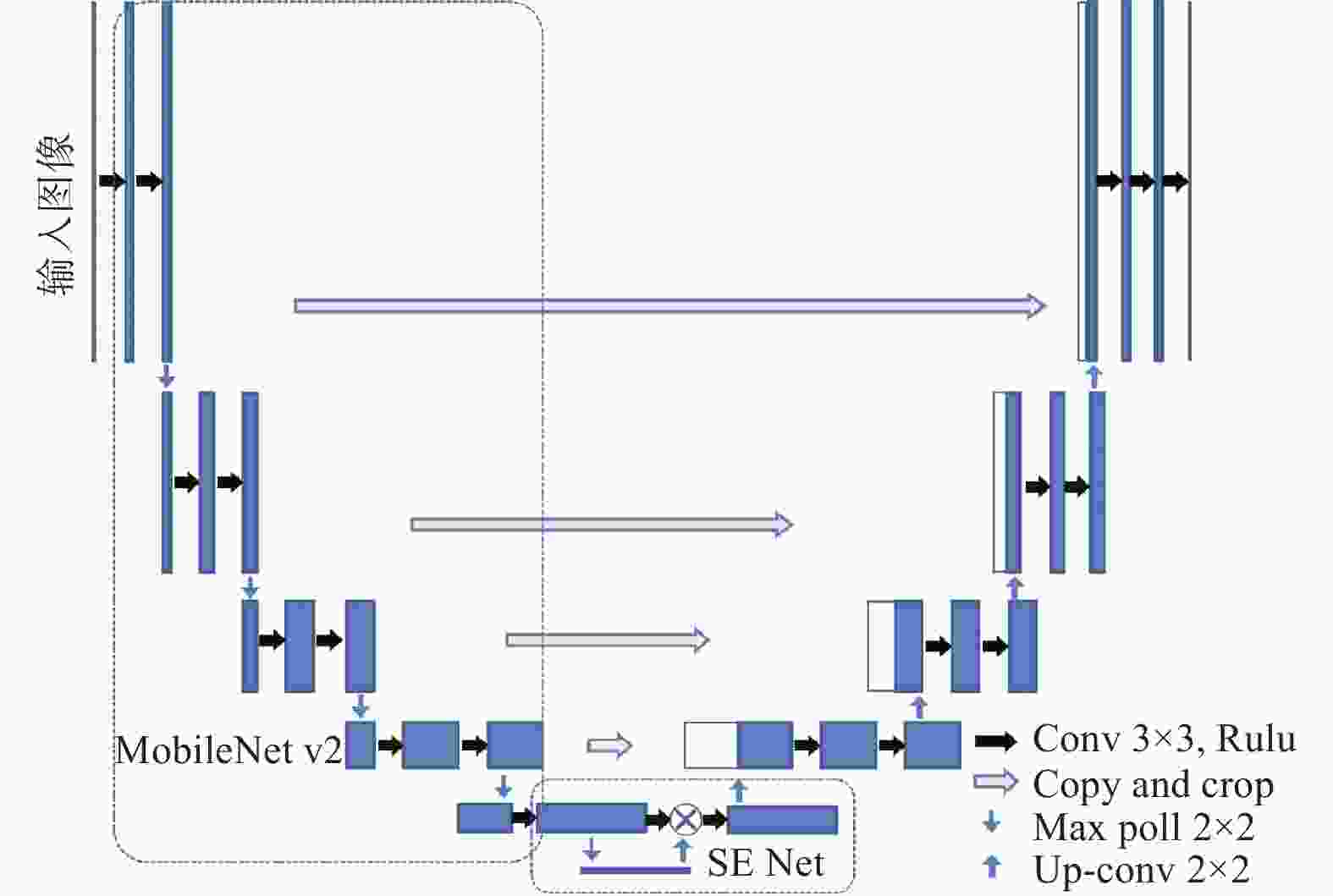
表 1 神经网络评价结果
Table 1. Neural network evaluation results
模型 平均交并比
ζ / %准确率
η / %U-Net 82.97 90.29 MobileNet v2
SE Net + Focal Loss87.53 93.05 表 2 正交试验因素与水平
Table 2. Orthogonal test factors and levels
水平 因素 A
平均功率
Pm / WB
重复频率
f0 / kHzC
转速
vs / (r∙min−1)D
扫描速度
v / (mm∙min−1)1 25 70 150 1.0 2 30 80 200 2.5 3 35 90 250 4.0 4 40 100 300 5.5 表 3 正交试验表
Table 3. Orthogonal test table
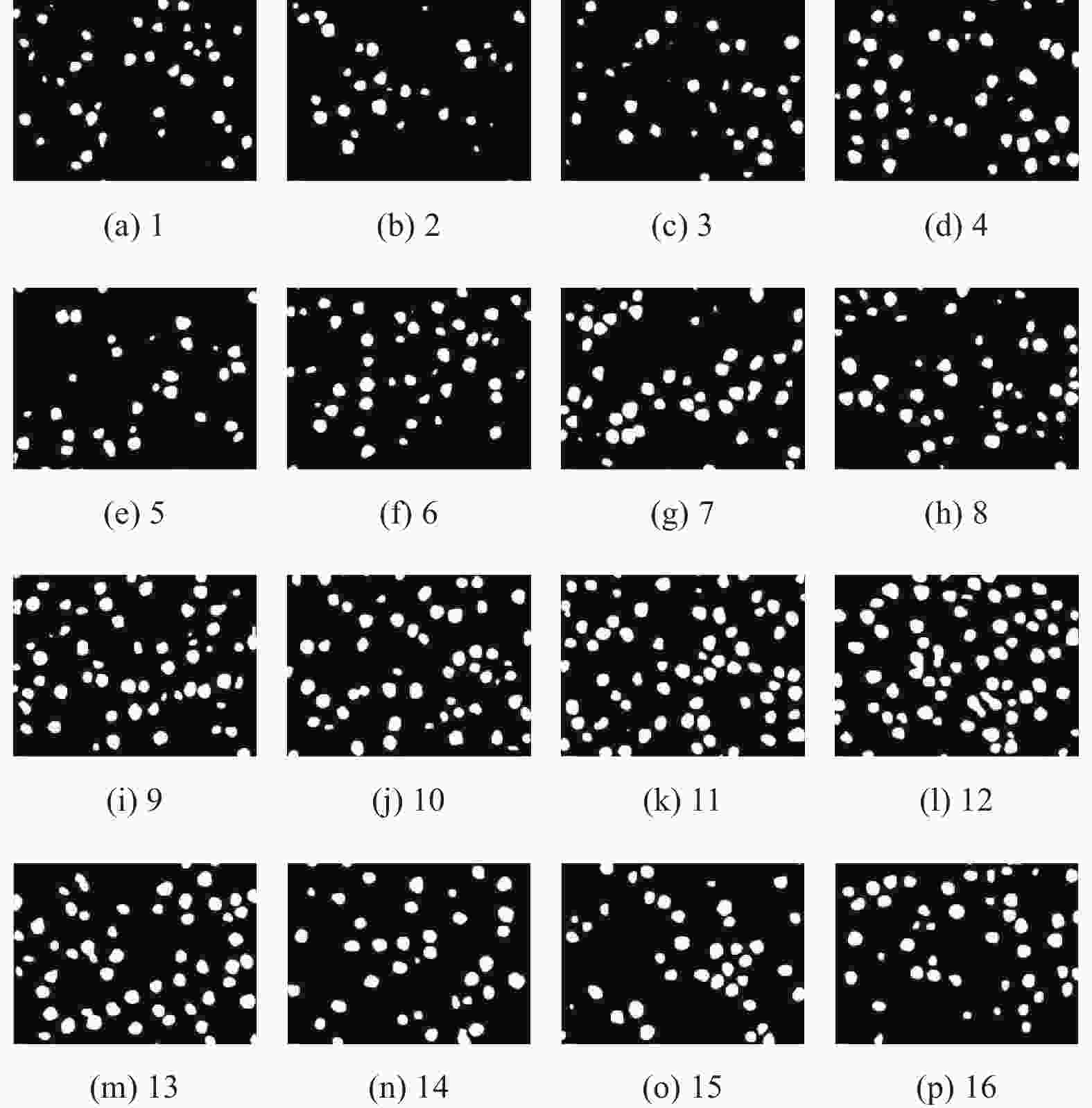
组号 因素水平组合 A B C D 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 3 1 3 3 3 4 1 4 4 4 5 2 1 2 3 6 2 2 1 4 7 2 3 4 1 8 2 4 3 2 9 3 1 3 4 10 3 2 4 3 11 3 3 1 2 12 3 4 2 1 13 4 1 4 2 14 4 2 3 1 15 4 3 2 4 16 4 4 1 3 表 4 各组突出高度得分和最佳高度区间比率
Table 4. Salient height scores and optimal height interval ratio for each group
组名 突出高度得分 S 最佳高度区间比率 γ 1 1.686 37.912[(69/182)×100] 2 1.343 23.810[(50/210)×100] 3 1.478 31.395[(54/172)×100] 4 1.639 32.323[(96/297)×100] 5 1.353 26.786[(60/224)×100] 6 1.557 31.527[(64/203)×100] 7 1.607 31.122[(61/196)×100] 8 1.584 33.992[(86/253)×100] 9 1.892 41.423[(99/239)×100] 10 2.207 50.181[(139/277)×100] 11 2.194 51.339[(115/224)×100] 12 2.619 60.428[(113/187)×100] 13 2.481 57.848[(129/223)×100] 14 2.494 53.846[(70/130)×100] 15 2.199 52.907[(91/172)×100] 16 2.193 48.421[(92/190)×100] 表 5 各因素4水平下突出高度得分的平均响应和效应极差
Table 5. Average response and effect range of salient height scores under four levels of each factor
水平 A B C D k1 1.536 5 1.853 0 1.907 5 2.101 5 k2 1.525 3 1.900 3 1.878 5 1.900 5 k3 2.228 0 1.869 5 1.862 0 1.807 8 k4 2.341 8 2.008 8 1.983 5 1.821 8 R 0.816 5 0.155 8 0.121 5 0.293 7 排序 1 3 4 2 表 6 各因素4水平下最佳高度区间比率的平均响应和效应极差
Table 6. Average response and effect range of optimal height interval ratio under four levels of each factor
水平 A B C D k1 31.360 0 40.992 3 42.299 8 45.827 0 k2 30.856 8 39.841 0 40.982 8 41.747 3 k3 50.842 8 41.690 8 40.164 0 39.195 8 k4 53.255 5 43.791 0 42.868 5 39.545 0 R 22.398 7 3.950 0 2.704 5 6.631 2 排序 1 3 4 2 -
[1] 贾云海, 卢学军, 邓福铭, 等. 金刚石砂轮精密修整工艺研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2009,29(2):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2009.02.008JIA Yunhai, LU Xuejun, DENG Fuming, et al. Study on high accuracy crush dressing of diamond grinding wheel [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2009,29(2):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2009.02.008 [2] SUZUKI K, UEMATSU T, NAKAGAWA T. On-machine trueing/dressing of metal bond grinding wheels by electro-discharge machining [J]. CIRP Annals,1987,36(1):115-118. doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62566-9 [3] 尚振涛, 黄含, 王树启, 等. 粗粒度青铜结合剂金刚石砂轮电火花–机械复合整形试验研究 [J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程,2006,26(6):42-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2006.06.011SHANG Zhentao, HUANG Han, WANG Shuqi, et al. Experimental study on truing of bronze-bonded diamond wheels with coarse abrasive grits using a novel hybrid method [J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2006,26(6):42-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-852X.2006.06.011 [4] CHEN G, CAI S, ZHOU C. On the laser -driven integrated dressing and truing of bronze-bonded grinding wheels [J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2015,60:99-110. [5] CHEN G, MEI L, ZHANG B, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation study on laser truing and dressing of bronze-bonded diamond wheel [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,2010,48:295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.11.006 [6] 蔡颂, 熊彪, 陈根余, 等. 青铜金刚石砂轮的激光整形与修锐 [J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(4):66-75.CAI Song, XIONG Biao, CHEN Genyu, et al. Laser truing and sharpening of bronze-bond diamond grinding wheel [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering,2017,46(4):66-75. [7] 周远航, 张健, 冯爱新, 等. 皮秒绿激光修锐青铜基金刚石砂轮损伤规律与机制 [J]. 中国激光,2021,48(6):197-206.ZHOU Yuanhang, ZHANG Jian, FENG Aixin, et al. Damage law and mechanism of bronze-based diamond grinding wheel sharpening with picosecond green laser [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2021,48(6):197-206. [8] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation [C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(2015). San Juan: IEEE: 3431-3440. [9] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation [C]// MICCIA. International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention(2015). Cham Switzerland: Springer: 234-241. [10] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(12):2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [11] CHEN L, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,40(4):834-848. [12] 李江昀, 杨志方, 郑俊锋, 等. 深度学习技术在钢铁工业中的应用 [J]. 钢铁,2021,56(9):43-49. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210296LI Jiangyun, YANG Zhifang, ZHENG Junfeng, et al. Applications of iron and steel industry with deep learning technologies [J]. Iron & Steel,2021,56(9):43-49. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210296 [13] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M, et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks [C]// CVPR. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(2018). San Juan: IEEE: 4510-4520. [14] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks [C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(2018). San Juan: IEEE: 7132-7141. [15] LIN T, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection [C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision(2017). San Juan: IEEE: 2980-2988. [16] 段念, 王文珊, 于怡青, 等. 不同形状磨粒随机分布磨料表面的三维建模仿真 [J]. 东华大学学报(自然科学版),2016,42(4):500-505.DUAN Nian, WANG Wenshan, YU Yiqing, et al. 3D-parametric modeling and programming of abrasive surface with grains of different shape on random distribution [J]. Journal of Donghua University (Natural Science),2016,42(4):500-505. [17] 赵金坠, 冯克明, 朱建辉, 等. 不同修锐工具对树脂结合剂CBN砂轮修锐效果的影响 [J]. 工具技术,2016,50(12):82-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2016.12.019ZHAO Jinzhui, FENG Keming, ZHU Jianhui, et al. Impact of different dressing tool upon dressing effect of resin bonded CBN grinding wheel [J]. Tool Engineering,2016,50(12):82-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2016.12.019 [18] 苏玲玲, 黄辉, 徐西鹏. 金刚石磨具表面磨粒分布形态的定量评价 [J]. 中国机械工程,2014,25(10):1290-1294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.10.003SU Lingling, HUANG Hui, XU Xipeng. Quantitative measurement of grit distribution of diamond abrasive tools [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2014,25(10):1290-1294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.10.003 [19] 蔡颂, 陈根余, 何杰. 脉冲光纤激光修锐青铜金刚石砂轮相爆炸研究 [J]. 中国激光, 2015(9): 203-210.CAI Song, CHEN Genyu, HE Jie, Studies on the phase explosion of laser dressing bronze-bond diamond grinding wheel by a pulsed fiber laser [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015 (9): 203-210. [20] YOUNG H, CHEN D. Online dressing of profile grinding wheels [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2006,27(9/10):883-888. doi: 10.1007/s00170-004-2271-8 [21] DOMAN D, WARKENTIN A, BAUER R. A survey of recent grinding wheel topography models [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2006,46(3/4):343-352. [22] YAN L, RONG Y, JIANG F, et al. Three-dimension surface characterization of grinding wheel using white light interferometer [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2011,55(1/2/3/4):133-141. -




 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
